A little information on
Adrenal Glands:
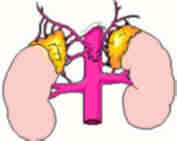
The adrenal glands are orange-colored endocrine glands which
are located on the top of both kidneys. The adrenal glands
are triangular shaped and measure about one-half inch in
height and 3 inches in length. Each gland consists of a
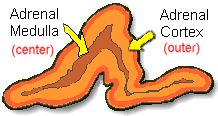
medulla (the center of the gland) which is surrounded by
the cortex. The medulla is responsible for producing epinephrine
and norepinephrine (adrenaline). The adrenal cortex produces
other hormones necessary for fluid and electrolyte (salt)
balance in the body such as cortisone and aldosterone. The
adrenal cortex also makes sex hormones but this only becomes
important if overproduction is present.
Ref: http://www.endocrineweb.com/adrenal.html
|
|
|
The
use of high doses increases the likelihood that potentially
significant toxic effects will be identified. Findings of
adverse effects in any one species do not necessarily indicate
such effects might be generated in humans. From a conservative
risk assessment perspective however, adverse findings in
animal species are assumed to represent potential effects
in humans, unless convincing evidence of species specificity
is available.
--
Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations
|
Note:
This is not an exhaustive list.
When time allows more information will be added.
Chlorodifluoromethane
-
Insecticide, Fungicide, Propellant - CAS No. 75-45-6
Increased kidney, adrenal
and pituitary weights... The female
rats in the 50,000-ppm group exhibited a statistically significant
increase in liver (absolute and relative), kidney (absolute),
adrenal (absolute), and pituitary
(absolute, at interim sacrifice--pituitaries
were not weighed at terminal sacrifice) weights. No nonneoplastic
histopathological changes attributable to exposure to HCFC-22
were observed. The liver weight effect was not considered adverse
because it did not exceed a 10% weight change and there was no
histopathology observed. Based on effects on kidney, adrenal,
and pituitary weight, a NOAEL of
10,000 ppm [NOAEL(HEC) = 5260 mg/cu.m] and a LOAEL of 50,000 ppm
[LOAEL(HEC) = 26,300 mg/cu.m] can be estimated.
Ref: US EPA IRIS for Chlorodifluoromethane.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Chlorodifluoromethane.IRIS.htm
CTFT
Chlorotrifluorotoluene,
4-,Alpha,Alpha,Alpha- Intermediate used
in herbicides - CAS
No. 98-56-6
In 14-day toxicity
studies, 1 of 10 female rats given the top dose of 1000 mg/kg
CTFT in corn oil died on day 8; no deaths of male rats or of mice
of either sex were attributable to the administration of CTFT.
Body weight gains in all groups of rats and mice were similar
with the exception of the top dose (1000 mg/kg) groups of male
and female rats, which lost weight during the first week and resumed
weight gain during the second. CTFT was found to accumulate in
the kidneys of male rats, and there was a linear relationship
between the kidney CTFT concentrations and the kidney levels of
a2u-globulin, as determined by an ELISA assay. Microscopic changes
in male rats included a dose-related toxic nephropathy consistent
with that previously described as "hyaline droplet nephropathy."
Dosed male and female rats also had hepatocyte hypertrophy and
cytoplasmic vacuolization of the adrenal
cortex. Clinical pathology findings suggested a mild anemia
and cholestasis in rats. In contrast to rats, mice did not show
appreciable CTFT concentrations in any tissue evaluated, suggesting
a more rapid elimination of the chemical. However, hepatocellular
hypertrophy, and clinical pathology findings consistent with cholestasis
and mild liver injury, were noted in mice in the 400 and
1000 mg/kg dose groups. These studies demonstrated that oral doses
of CTFT of 400 mg/kg or higher caused liver
hypertrophy in rats and mice and adrenal
changes in rats. Doses of 50 mg/kg or higher caused "hyaline
droplet nephropathy" in male rats. The results were similar with
CTFT administered either in corn oil or in -CD (although absorption
of CTFT was somewhat more rapid with -CD), suggesting that -CD
may be an appropriate vehicle for toxicity studies with other
chemicals.
Ref: National Toxicology Program. July 1992.
Toxicity Studies of p-Chloro-,,Trifluorotoluene (CAS NO: 98-56-6)
Administered in Corn Oil and -Cyclodextrin to F344/N Rats and
B6C3F1 Mice in 14-Day Comparative Gavage Studies.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/CTFT.NTP.ToxicityStudy.1992.htm
Cyfluthrin
-
Insecticide - CAS No. 68359-37-5
-- Subchronic toxicity--
i. 28-Day oral toxicity study in rats. Cyfluthrin was administered
to SPF-Wistar rats via gavage at 0, 5, 20, or 80 (40) mg/kg/day.
The high dose was 80 mg/kg/day during the first and third weeks
and 40 mg/kg/day during the second and fourth weeks. The LOEL
was 80 (40) mg/kg/day in both sexes based on clinical signs of
nerve toxicity, decreases in body weight gain, and changes in
liver and adrenal weights. The NOEL
was 20 mg/kg/day. This study was classified as core minimum.
Ref: Federal Register: November 26, 1997.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Nov.26.1997.htm
-- Rats Four groups
of 30 male and 24 female Mura:SPRA (SPF 68 Han) rats received
14C radiolabelled cyfluthrin as either oral doses of 0.5 or 10
mg/kg bw or intravenous or intraduodenal doses of 0.5 mg/kg bw.
Another group received unlabelled cyfluthrin orally once a day
for 14 consecutive days, followed by a single oral dose of 0.5
mg/kg bw 14C-cyfluthrin... The residues found in the organs and
tissues were influenced by the route of administration, as the
mean relative concentration of cyfluthrin in the bodies of males
and females at sacrifice was lower after oral administration (0.013)
than after intravenous injection (0.06). Female rats had higher
plasma concentrations after oral administration of the single
high or low dose; 48 h after administration, lower concentrations
were detected in the bone and muscle of animals of each sex and
in the testes of males rats. The
sciatic nerve showed a similar relative concentration value, which
may explain the toxic effects observed on the peripheral nervous
system. Higher concentrations were detected in the spleen, adrenal
glands, liver, and plasma of both males and females and
in the ovaries. The renal fatty tissue concentration
was about seven times higher after either oral or intravenous
administration, whereas the mean concentration in brain was significantly
lower ( p = 0.0006-0.006) (Klein et al., 1983).
-- Groups of
28 male and 28 female Sprague-Dawley rats received diets containing
0, 100, 300, or 1000 mg/kg cyfluthrin (purity, 95%) incorporated
into the powdered diet on a 0.4% maximum clay carrier, daily for
three months... The food consumption and body-weight gains of
females and males at the highest dose were significantly lower
than those of the control group. The body-weight gain depression
in females appeared to recover after cessation of treatment, while
that of the males remained significantly low... The absolute weights
of the liver, heart, and lung were decreased in male rats at the
high dose, and females at this dose had depressed liver, kidney,
adrenal, and ovarian
weights. In both males
and females at the high dose, the relative weight of the submaxillary
gland was increased...
Ref: Cyfluthrin. Toxicological evaluation
of certain veterinary drug residues in food. WHO FOOD ADDITIVES
SERIES 39 Prepared by: The forty-eighth meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO
Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). World Health Organization,
Geneva 1997. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.WHO.Tox.Eval.97.htm
Diflubenzuron
-
Chemosterilant, Insecticide - CAS No. 35367-38-5
Chloroaniline,
p (or 4-chloraniline) is a metabolite of Diflubenzuron.
In 2006, USEPA classified chloroaniline, p as
a "Group B2 -- Probable Human Carcinogen." "Spleen
(fibrosarcomas,
hemangiosarcomas & osteosarcomas) (M); Adrenal
(pheochromocytomas (M & F); F344/N rats. Hepatocellular
adenomas/carcinomas (M); Hemangiosarcomas
in spleen and/or liver (M) in B6C3F1 mice."
Ref: April
26, 2006 . Chemicals Evaluated for Carcinogenic Potential by the
Office of Pesticide Programs. From: Jess Rowland, Chief Science
Information Management Branch Health Effect Division (7509C) Office
of Pesticide Programs, USEPA.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/pesticides.cancer.potential.2006.pdf
--
PCA [p-chloroaniline; a metabolite of Diflubenzuron]
was administered 5 days/week by oral gavage, as a hydrochloride
salt in water, to male and female F344/N rats at doses of 0, 2,
6, or 18 mg/kg/day. Mean body weights of dosed rats were generally
within 5% of those of controls throughout the study. High dose
animals generally showed mild hemolytic anemia and dose-related
methemoglobinemia. Non- neoplastic lesions seen were bone marrow
hyperplasia, hepatic hemosiderosis, and splenic fibrosis, suggesting
treatment-related effects on the hematopoietic system. Adrenal
medullary hyperplasia was
observed in high dose female rats.
The incidence of uncommon sarcomas of the spleen was significantly
increased in high dose male rats. A marginal
increase in pheochromocytomas of the adrenal gland was
seen in high dose male and female rats. It was concluded that,
under the conditions of this 2-year gavage study, there was clear
evidence of carcinogenic activity of PCA hydrochloride for male
F344/N rats and equivocal evidence of carcinogenic activity of
PCA hydrochloride for female F344/N rats.
Ref: Federal Register: December 14, 2001.
(Volume 66, Number 241)] [Notices] [Page 64823-64828]. Notice
of Filing Pesticide Petitions to Establish a Tolerance for a Certain
Pesticide Chemical in or on Food. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Diflubenzuron.FR.Dec14.2001.htm
(p-Chloroaniline: Metabolite of Diflubenzuron): A marginally
increased incidence of pheochromocytomas was also observed in
the adrenal gland of male and female
rats at 18 mg/kg/day. For male rats, the incidence was 13/49,
14/48, 15/48 and 26/49 and for female rats was 2/50, 3/50, 1/50
and 6/50 at dose levels of 0, 2, 6 and 18 mg/kg/day respectively.
Ref: US EPA Reregistration Eligibility Decision
(RED) Diflubenzuron. EPA 738-R-97-008. August 1997.
Dithiopyr
- Herbicide -
CAS No. 97886-45-8
The following results
were presented by a Monsanto scientist.
-- Thirteen-week Feeding Study in Rats.
Dithiopyr was administered via the diet to groups of
12 male and 12 female F-344 rats for 13 weeks at concentrations
of 0, 10, 100, 1000 and 5000 ppm.. Other findings included [no
concentrations listed] multiple organ weight effects,
thyroid follicular hypertrophy, adrenal
cortical hypertrophy, and pulmonary foam cell aggregation.
The subchronic NOEL in rats is considered to be 10 ppm. (The
Institute of Environmental Toxicology, 1988)
-- Four-week Feeding Study in Mice.
Dithiopyr was administered via the diet to groups of 6 male and
6 female CD-1 mice for 4 weeks at concentrations of 0, 300, 1000,
3000, 10,000 and 30,000 ppm... [No concentrations
listed for the following effects:]-- Liver enlargement
and discoloration, adrenal enlargement,
and atrophy of the thymus, spleen, seminal
vesicles, ovaries and uterus were noted on gross post-mortem
examination... (The Institute of Environmental
Toxicology, 1987)
-- Thirteen-week Feeding Study in Mice.
Dithiopyr was administered via the diet to groups of 12 male and
12 female CD-1 mice for 13 weeks at concentrations of 0, 10, 100,
1000 and 5000 ppm... Other findings included [no
concentrations listed]: multiple organ weight effects,
adrenal cortical hypertrophy and
ovarian atrophy. The subchronic NOEL in
mice is considered to be 10 ppm.
(The Institute of Environmental Toxicology, 1989)
-- Eighteen-month Feeding Study in Mice.
In an oncogenicity study, dithiopyr was administered via the diet
to groups of 70 male and 70 female CD-1 mice for 78 weeks at concentrations
of 0, 3, 30 and 300 ppm... Other findings included [no
concentrations listed]: increased
adrenal weights, adrenal cortical
swelling, spleen enlargement and increased splenic extramedullary
hematopoiesis. The chronic NOEL in mice is considered to be 3
ppm (equivalent to a daily intake of 0.31 mg/kg b.w. in males
and 0.37 mg/kg b.w. in females). (The Institute
of Environmental Toxicology, 1989)
-- REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY
STUDIES 1. Two-generation Reproduction Study in Rats •Dithiopyr
was administered via the diet to groups of 24 male and 24 female
S-D rats over 2 consecutive generations at concentrations of 0,
25, 250 and 2500 ppm... Other findings included [no
concentrations listed]: increased kidney weight, focal
renal tubular atrophy, thyroid follicular
hypertrophy, and adrenal cortical
hypertrophy... (The Institute of
Environmental Toxicology, 1989)
Ref: Summary
of Toxicology Studies With Dithiopyr. Dennis P. WARD. Toxicology
Department, The Agricultural Grop, A Unit of Monsanto
Company (Received February 20, 1993). Also available at
http://wwwsoc.nii.ac.jp/pssj2/tec_info/dithiopy.pdf
Epoxiconazole
-
Fungicide - CAS No. 135319-73-2 (formerly
106325-08-0)
Endocrine disruption.
A series of mechanistic studies were performed to elucidate and
define the aromatase enzyme inhibition properties
of epoxiconazole. The following conclusions can be drawn from
the in vivo data: The effects on the ovaries are assessed to be
the result of the following: Decreasing aromatase enzyme activity
which is responsible for converting both testosterone and adrostendione
(male sex-steroids) into female sex steroids (e.g., estradiol).
This action would result in decreased estradiol (i.e., estrogen)
and increased androgen. As a consequence of reduced estradiol
levels, measured LH and FSH concentrations are slightly altered.
The increased incidences of neoplasms in the ovaries are considered
to be the result of a continuous cell proliferation by these stimulating
[[Page 57342]] hormones of the regulating hormones of the
pituitary-gonadal axis (LH and FSH). The changes adrenals
are assessed to be the result of the following: Decreasing
adrenal-cortical enzyme activity. This action would result
in decreased adrenal hormones such as corticosterone levels. As
a consequence of reduced corticosterone levels, pronounce ACTH
concentrations are found. The increased incidences of neoplasms
in the adrenals are considered to be the result of a continuos
cell proliferation by these stimulating hormones of the pituitary-adrenal
axis ACTH.
Ref: Federal Register: September 22, 2000
[Page 57338-57344]. Notice of Filing Pesticide Petitions to Establish
Tolerances for Certain Pesticide Chemicals in or on Food. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Epoxiconazole.FR.Sept.2000.htm
"Epoxyconazole
106325-08-0 Banned. Low degradability, toxic to water-living organisms
and endocrine effects. 1997."
Definition: "Banned. A substance which for health or environmental
reasons by an authority decision is either no longer approved
for any area of application, or for which an approval or registration
has been denied from the first instance."
Ref: Euopean Commission. Appendix 5. Substances
which may not be included as active ingredients in approved pesticide
products, Chapter 15, Section 2, subsection one.
http://www.kemi.se/lagar_eng/pdf/app5_8.pdf
Etoxazole
- Acaricide - CAS No. 153233-91-1
Subchronic toxicity.
Effects observed at high dose levels consisted primarily of
anemia and histological changes in the adrenal
gland, liver and kidneys.
Ref: August 13, 2003. [Federal Register:
August 13, 2003 (Volume 68, Number 156)] [Notices]. Etoxazole;
Notice of Filing a Pesticide Petition to Establish a Tolerance
for a Certain Pesticide Chemical in or on Food.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/etoxazole.fr.aug.13.2003.htm
Reproduction and fertility
effects (rat). Parental/Systemic
NOAEL = 20 mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 100 mg/kg/ day (M/F), based upon
increased liver weights in the P and F1 males and
increased adrenal weights in the P females Offspring/Systemic
NOAEL = 20 mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 100 mg/kg/ day (M/F), based upon
pup mortality Reproductive NOAEL = 100 mg/kg/day LOAEL = not determined.
Ref:
Federal Register: September 26, 2003. Etoxazole; Pesticide Tolerance.
Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/etoxazole.fr.sept.26.2003.htm
Flonicamid
- Insecticide - CAS No. 158062-67-0
--
In the multi-generation rat reproduction study, the NOAEL was
300 ppm for both parental animals (13.5-32.8 and 16.3-67.0 mg/kg/day,
respectively, for males and females) and their offspring. The
effects at the highest dose of 1,800 ppm included the following:
increased kidney weights and gross and histopathological alterations
in the kidney. Findings noted in the top dose females included
delayed vaginal opening and increased liver, kidney and spleen
weights in the F1 generation and reduced
ovary and adrenal weights in the parental generation and
decreased uterine weights in the F1 female weanlings. There was
an increase in the FSH and LH levels in
F1 females tested for these endpoints. These findings did
not affect the reproductive performance or survival of offspring
in the study.
-- Endocrine
disruption. No special studies investigating potential
estrogenic or other endocrine effects of flonicamid have been
conducted. Some suggestions of possible endocrine effects were
reported at the highest dose tested (1,800 ppm) in the multi-generation
reproduction study which showed increased FSH and LH levels, a
delay in the time to vaginal opening in the F1 generation, and
reduced ovary and adrenal weights
in the parental generation. However, there were no effects on
reproductive performance or survival of the offspring in the study.
At levels that are expected to be found in the environment, flonicamid
will not cause any endocrine-related effects.
Ref:
Federal Register: May 23, 2003 (Volume 68, Number 100)] [Notices]
[Page 28218-28222]. Flonicamid; Notice of Filing a Pesticide Petition
to Establish a Tolerance for a Certain Pesticide Chemical in or
on Food.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/Flonicamid.FR.May23.2003.htm
--
90-Day oral toxicity (nonrodents- dogs).
NOAEL is 8 mg/kg/day in males and 20 mg/kg/day for female. LOAEL
is 20 mg/kg/day in males and 50 mg/kg/day in females, based on
acute clinical signs in males and females (vomiting,
first observed on Day 1 and last observed on Day 90), clinical
pathology at 7 weeks (increased total protein
levels in males, lower red blood cells and higher reticulocytes
counts in females), increased adrenal
weights in males, decreased thymus
gland weights in males, and increased
kidney tubular vacuolation in females at study termination.
Ref:
August 31, 2005. Flonicamid; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
Federal Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/flonicamid.fr.aug.31.2005.html
Floransulam
- Herbicide - CAS No. 145701-23-1
Short
term toxicity. Target / critical effect:
Anemia, hepatotoxicity , renal hypertrophy epithelial cells, collecting
ducts, adrenal vacuolation(dog )
Lowest relevant oral NOAEL / NOEL: 1 y & 90 d dog (oral feed)
; 5 mg/kg bw/d;...
Ref: September 18, 2002 - Review report
for the active substance florasulam. European Commission Health
& Consumer Protection Directorate-General.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Florasulam.EU.Sept.2002.pdf
-- The subchronic and
chronic toxicity of florasulam was investigated in the mouse,
rat and dog. A 28-d repeat dose dermal toxicity
study was also carried out in rats. In the subchronic and chronic
studies, treatment-related findings were
observed in the kidney in all species and in the liver
and adrenal glands in dogs. In the
kidney, hypertrophy of the epithelial cells
of the collecting ducts occurred in all species tested.
-- In subchronic and chronic dietary studies, treatment-related
findings were observed in the kidneys in mice, rats and dogs and
in the liver and adrenal glands in the dog.
In the kidney, hypertrophy of the epithelial cells of the collecting
duct was observed in all species tested. In rats, hypertrophy
of the epithelial cells correlated with elevated serum bicarbonate
levels, urinary acidification, decreased urinary specific gravity
and increased kidney weights. In dogs, treatment-related findings
associated with the liver included increased ALP activity, decreased
serum albumin and protein levels, increased liver weights and
increased incidence or severity of hepatic vacuolation.
Dogs also exhibited slight vacuolization of the zona reticularis
and zona fasciculata in the adrenal glands; however, in
the absence of any associated inflammation, necrosis or other
changes, the toxicological significance was uncertain. The most
appropriate NOAEL for subchronic and chronic toxicity end points
is 5.0 mg/kg bw/d in the 90-d and 1-year dietary studies in dogs.
At the LOAEL, 50 mg/kg bw/d, treatment-related findings were observed
in the kidneys and liver in the 90-d and 1-year
dietary studies and in the adrenal glands in the 1-year dietary
study.
Ref: Florasulam EF-1343 Suspension Concentrate
Herbicide. REF2001-12. September 21, 2001. Canadian Pest Management
Regulatory Agency. Health Canada.
http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/pmra-arla/english/pdf/reg/reg2001-12-e.pdf
Fluazifop-butyl
- Herbicide - CAS No. 69806-50-4
**411-083 069476 Virgo,
D. M., “Fluazifop-butyl: 55 week oral toxicity study in beagle
dogs,” Life Science Research, Stock, Essex, England, 10/15/82.
LSR Report No. 81/ILK019/620. Six dogs/sex/group were dosed for
55 weeks with Fluazifop-butyl, 99.6% purity, by gelatin capsules
at dose levels of 0, 5, 25, and 125 mg/kg/day in a chronic study.
Test article within capsules was dissolved in 0.4 ml/kg corn oil
vehicle. NOEL = 5 mg/kg/day. The degree of
adrenal gland cortical fatty degeneration evident in one
mid-dose female was sufficiently greater than that of any of the
control dogs that investigators attributed this finding to treatment.
Cortical fatty degeneration of moderate
to severe degree was observed in one high dose male and in all
high dose females. All other noteworthy findings were limited
to the high dose group, as follows...
Male reproductive toxicity included testicular tubular degeneration
and reduced/absent spermatozoa in epididymides.
Possible adverse effects (many-faceted toxicity, including
mortalities, at 125 mg/kg/day). Acceptable. Aldous, 5/20/02.
Ref: May 20, 2002. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA FLUAZIFOP-P-BUTYL. California EPA. Department of Pesticide
Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-butyl.CAepa.02.pdf
Flufenoxuron
- Acaricide, Insecticide, Herbicide - CAS No. 101463-69-8
Carcinogenicity.
Rat. Groups of 50/sex/group Fischer 344 rats were administered
0, 500, 5000 or 50000 ppm flllufenoxuron in the diet for 24 months...
In
males relative spleen weight was reduced in all treatment groups
(respectively 14, 29 and 32 %)...In
the females there was a significant increase in adrenal weight
in all treatment groups (respectively 9, 7 and 15%).
Ref:
December
1995. Evaluation
of Flufenoxuron use as a public hygiene insecticide. UK: Health
and Safety Executive, Biocides & Pesticides Assessment Unit.
Available at
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
Flumioxazin
- Herbicide - CAS No. 103361-09-7
-- "Three-Month
Subacute Toxicity Study of S-53482 by Dietary Administration in
Rats"; (Haruhiko Adachi; Sumitomo Chemical Co., Environmental
Health Science Laboratory,, Ltd., Osaka, Japan; Study No. 1760;
4/26/91); Sixteen Crj:CD (SD) rats/sex/group were treated in the
diet with 0, 30, 300, 1000 or 3000 ppm of S-53482 (lot no. PYG-89021-M,
purity: 94.8%). Six of these animals/sex/group were treated for
5 weeks. The remaining 10 animals/sex/group were treated
for 13 weeks ((M): 0, 1.94, 19.4, 65.2, 197.3 mg/kg/day, (F) 0,
2.22, 22.4, 72.8, 218.4 mg/kg/day)... Other noted lesions for
the 3000 ppm females were... atrophy of the thymus and the presence
of thymal foam cells (0:0/10 vs. 3000: 3/10), sinus histiocytosis
in the mesenteric lymph node (0:0/10 vs. 3000: 3/10), and
cytoplasmic vacuolation in the adrenal cortex
(0:0/10 vs. 3000: 3/10)...
Ref:
January 32, 2003 (revised) -
Summary of Toxicological
Data. California EPA, Department of
Pesticides Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
Fluometuron
- Herbicide - CAS No. 2164-17-2
-- CHRONIC TOXICITY.
Rats were fed 7.5, 75, or 750 mg/kg/day
for 90 days. At the 750 mg/kg dose, decreased body weight and
congestion in the spleen,
adrenals, liver, and kidneys
were evident. The NOAEL for this study was 7.5 mg/kg/day (100
ppm). When doses of 1.5, 15 or 150 mg/kg/day were fed to puppies
for 90 days, congestion of the liver, kidneys and spleen occurred
at the 150 mg/kg dose. No effects were seen at 15 mg/kg/day (400
ppm) (20).
Ref: Flumeturon. EXTOXNET. Pesticide Information
Profile. March 1994.
http://pmep.cce.cornell.edu/profiles/extoxnet/dienochlor-glyphosate/fluometuron-ext.html
Fluoxastrobin
- Fungicide - CAS No. 193740-76-0
•
90-Day oral toxicity-rats. reduced
body weight gain and
food intake, vacuolation in the zona fasciculate of the
adrenal cortex, calculi in the urethra and
kidney, and histological lesions in kidney, urinary bladder, and
urethra;
Ref: Federal Register. September 16, 2005.
Fluoxastrobin; Pesticide Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/fluoxastrobin.fr.sept16.05.html
Fluroxypyr
- Herbicide - CAS No. 69377-81-7
-- Chronic toxicity.
EPA has established the RfD for fluroxypyr at 0.5 mg/kg/day. This
RfD is based on histopathological lesions in the kidneys, decreased
testes weights, and increased adrenal
weights in both sexes observed in a 4-week range-finding
feeding study in the dog with a NOAEL of 50 mg/kg/day. An uncertainty
factor of 100 was used in calculating the RfD to account for both
inter- and intra-species variations.
-- A 90-day feeding study in Wistar rats (10/sex/group) administered
fluroxypyr (98.5% a.i.) in the diet at 0, 80, 750, 1,000 or 1,500
milligrams/kilogram/day (mg/kg/day) for 13 weeks. Significant
nephrotoxicity and deaths were observed at 1,000 and 1,500 mg/kg/day
in both sexes, and in males at 750 mg/kg/day. Death was due to
renal papillary necrosis. Also observed were signs of ill health,
emaciation, decreased food intake, increased kidney weight, histopathological
lesions and decreased renal function. Histological changes were
observed in the adrenals in both
sexes at 1,000 and 1,500 mg/kg/day. In males the NOAEL for this
study is 80 mg/kg/day, and the LOEL is 750 mg/ kg/day based on
kidney effects and death. In females the NOAEL is 750 mg/kg/day,
with the LOEL at 1,000 mg/kg/day based on kidney effects and death.
-- A 28-day feeding study in Beagle dogs administered Fluroxypyr
98.0% a.i. in the diet at levels of 0, 50, 150 or 450 mg/kg/day
for 28 days. Dogs at 500 mg/kg/day exhibited ataxia and hind limb
weakness as well as decreases in body weight and food consumption
and were sacrificed on days 16/17 of the study. Histopathology
showed moderate acute tubular nephrosis and a slight to moderate
acute gastroenteritis. Some early signs of acute tubular nephrosis
were also seen in both sexes of dogs at 150 mg/kg/day. The NOAEL
for the study was 50 mg/kg/ day, the LOEL was 150 mg/kg/day based
on histopathological lesions in the kidneys,
decreased testes weights, and increased
adrenal weights in both sexes.
Ref: Federal Register: September 30, 1998.
Fluroxypyr; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluroxypyr.FR.Sept.30.1998.htm
Fluroxypyr
1-methylheptyl ester -
Herbicide - CAS No. 81406-37-3
Reproductive toxicity
study. In the 2-generation reproductive toxicity study in rats,
the maternal (systemic) NOAEL was 100 mg/kg/ day, based on
increased kidney weights and kidney histopathology at the LOAEL
of 500 mg/kg/day. The developmental (pup) NOAEL was 500 mg/kg/
day, based on decreased body weight at the LOAEL of 1,000 mg/kg/day.
The reproductive NOAEL was 1,000 mg/kg/day (HDT).... Chronic dietary
all populations: 28-day dog range- finding feeding study LOAEL
= 150 mg/kg/day based on histopathological lesions in the kidneys,
decreased testes weights, and increased
adrenal weights in both sexes...
Ref: Federal Register. September 17, 2001.
Fluroxypyr 1-Methylheptyl Ester; Pesticide Tolerances for Emergency
Exemptions. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluroxypyr.FR.Sept.17.2001.htm
Flurprimidol
- Plant Growth Regulator - CAS No. 56425-91-3
-- A l-year dog study
treated with flurprimidol at doses of 0, 0.5, 1.5, 7.0 and 30.0
mg/kg/day, the NOEl was 7.0 mg/kg/day and the LEL was 30.0 mg/kg/day
Highest Dose Tested (HDT) based on adrenal
changes including decreased plasma cortisol response to ACTH stimulation
(males and degenerative changes of the adrenal
cortex (males and females). The histopathology was limited
to the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex
and was characterized by eosinophilic degeneration, vacuolation
and cortical atrophy. There was a slight increase in hepatic p-nitroanisole
0-demethylase activity (males).
Ref: EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet for Flurprimidol.
Reason for Issuance: New Chemical Registration. Date Issued: FEB
22 1989. Fact Sheet Number: 202.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flurprimidol.EPA.Facts.1989.htm
Hydramethylnon
- Insecticide - CAS No. 67485-29-4
- On May 28, 1998,
the Agency’s Cancer Peer Review Committee concluded that the dose
levels of 100 ppm in males, and 50 ppm in females were adequate
to assess the carcinogenic potential of hydramethylnon in rats....
The statistically significant increases
in tumors observed in the uterus
(adenomatous polyps) and adrenals
(medullary adenomas) were not considered
to be biologically significant since they were seen at excessive
doses (i.e., at 200 ppm). Under the conditions of this
study, the NOAEL was 50 ppm (2.4 mg/kg/day in males, 3.0 mg/kg/day
in females), and the LOAEL was 100 ppm (4.9 mg/kg/day in males,
6.2 mg/kg/day in females) based on small,
soft testes, decreased testicular weights, and testicular atrophy
in males; and decreased body weight gain in females. This
study is classified as acceptable and satisfies guideline requirement
83-5 for a chronic feeding/carcinogenicity study in rodents.
Ref: US EPA. Reregistration Eligibility
Decision (RED) Hydramethylnon. EPA 738-R-98-023. December 1998.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Hydramethylnon.RED.1998.pdf
Lactofen
- Herbicide - CAS No. 77501-63-4
Dog chronic toxicity LOAEL = 3.96 mg/kg/day based
on increased incidence of
proteinaceous casts in the kidneys,
and statistically significant increases
in the absolute weights of the thyroid and adrenal glands in males.
Ref:
Sept 24, 2004. Lactofen. Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal
Register.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/lactofen.fr.sept.24.2004.htm
-- Subchronic feeding--
Mice-- 3-month. Groups of Male and female mice were fed diets
containing Lactofen Technical at concentrations of 0, 40, 200,
1,000, 5,000, and 10,000 for 13-weeks. At week 5, the dosage of
the 40 ppm groups was increased to 2,000 ppm. Treatment related
mortality occurred at dosages above 1,000 ppm. The LOEL was 200
ppm based on: increased WBC; decreased hematocrit, hemoglobin
and RBC; increased alkaline phosphatase, SGOT, SGPT, cholesterol
and total serum protein levels; increased weights or enlargement
of the spleen, liver, adrenals, heart
and kidney; histopathological changes of the liver, kidney,
thymus, spleen, ovaries and testes. In general, effects were slight
in the 200 ppm groups, and moderate to severe in the 1,000 ppm
groups.
Ref: Federal Register: February 25,
1998 [Page 9532-9540]. Notice of Filing of Pesticide Petition.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Lactofen.FR.Feb.1998.htm
Novaluron
- Insecticide - CAS No. 116714-46-6
Chloroaniline,
p (or 4-chloraniline)
is a metabolite of Novaluron. In 2006, USEPA classified chloroaniline,
p as a "Group
B2 -- Probable Human Carcinogen."
"Spleen
(fibrosarcomas,
hemangiosarcomas & osteosarcomas) (M); Adrenal
(pheochromocytomas (M & F); F344/N
rats. Hepatocellular adenomas/carcinomas
(M); Hemangiosarcomas in spleen and/or
liver (M) in B6C3F1 mice."
Ref: April
26, 2006 . Chemicals Evaluated for Carcinogenic Potential by the
Office of Pesticide Programs. From: Jess Rowland, Chief Science
Information Management Branch Health Effect Division (7509C) Office
of Pesticide Programs, USEPA.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/pesticides.cancer.potential.2006.pdf
Noviflumuron
- Insecticide - CAS No. 121451-02-3
-- “XDE-007: One-Year Dietary Toxicity
Study in Beagle Dogs,” (Stebbins, K.E., Day, S.J.,
Thomas, J.; Toxicology & Environmental Research and Consulting,
The Dow Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory Project Study
ID #: 142640; 3/5/04). XDE-007 (97.9% pure) was fed in diet to
Beagle dogs (4/sex/dose) for 1 year at 0, 0.003, 0.03 or 0.225%
(equivalent to 0, 0.74, 9.3 and 69 mg/kg/day - Males and 0, 0.94,
8.7 and 70 mg/kg/day - females)... There
was a statistically significant increase in absolute adrenal weights
(analyzed across both sexes) at 0.225% without histological findings.
-- “XDE-007: One-Generation Dietary
Reproduction Toxicity Study With CrossFostering in CD Rats,”
(Marty, M.S., Zablotny, C.L., Liberacki, A.B., Yano, B.L.;Toxicology
& Environmental Research and Consulting, The Dow Chemical
Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory Project Study ID: 011221; 3/23/04).
XDE -007 (97.9% pure) was fed in diet to Crl:CD (SD) IGS BR rats
(30/sex/dose) at 0, 0.5, 5 and 100 mg/kg/day continuously from
pre-mating (10 weeks) of parental generation, through breeding
(2 weeks), gestation (3 weeks) and lactation through weaning of
F1 offspring. Although designed as a 2 generation
reproduction study, it was terminated after 1 generation due to
excessive F1 pup mortality at 100 mg/kg/day. Subsequently
a Cross-fostering Study was performed to determine whether the
decreased survival in pups from XDE-007 treated P1 rats resulted
from in utero or lactational exposure. Parental Systemic NOEL
= 0.5 mg/kg/day (Tonoclonic convulsions were observed in 2/30
males and 1/24 females at 100 mg/kg/day. Males had statistically
significantly decreased food consumption from day 8 until termination
at 100 mg/kg. Females had statistically significantly decreased
food consumption during lactation. Male
P1 premating body weights were statistically significantly decreased
at 100 mg/kg/day. Mean gestational body
weight gain in females was statistically significantly decreased
GD 0 - 7 (but not GD 0 - 21) and lactation days 7 - 13 at 100
mg/kg/day.) Reproduction and Fertility NOEL = 0.5 mg/kg/day (P1
female gestation survival was decreased and gestation length was
increased at 100 mg/kg. Pup NOEL = 0.5 mg/kg (F1
survival was drastically decreased throughout lactation at 100
mg/kg. Clinical effects were increased in pups at 100 mg/kg,
primarily tonoclonic convulsions, no milk in stomach, entire litter
loss and death. Pup weights were statistically
significantly decreased at 100 mg/kg. Cross-fostering data
indicate the proximate toxicant (either XDE-007 and/or its metabolites)
led to decreased pup survival through the maternal milk and not
through exposure in utero. Possible adverse effect indicated:
excessive neonatal/pup mortality and increased
tonoclonic convulsions in pups (17/24 litters) at 100 mg/kg.
These data are supplemental. M. Silva, 7/20/04
-- “XDE-007: Two-Generation Dietary
Reproduction Toxicity Study in CD Rats,” (Carney,
E.W., Zablotny, C.L., Liberacki, A.B., Yano, B.L.;Toxicology &
Environmental Research and Consulting, The Dow Chemical Company,
Midland, MI; 3/22/04). XDE -007 (97.9% pure) was fed in diet to
Crl:CD (SD) IGS BR rats (30/sex/dose/generation) at 0, 0.5, 5
or 25 mg/kg/day continuously from pre-mating of parental generation
1 (P1) through weaning of offspring through 2 generations (2 matings
for P2 generation) to F2b weaning. Parental Systemic NOEL = 5.0
mg/kg/day (There were increased absolute
and relative liver weights in both sexes of P1 and P2 adults at
25 mg/kg and in P1 female liver weights at 5.0 mg/kg. P1
male relative kidney weights, P2 female absolute kidney weights,
P2 male relative spleen and thyroid weights and P2 female absolute
and relative adrenal weights were increased at 25 mg/kg.) ...
Ref:
August 2005 - Summary of toxicological data. California EPA, Department
of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/noviflumuron.ca.epa.2005.pdf
Oxyfluorfen
- Herbicide - CAS No. 42874-03-3
Absolute and relative
thymus weights were decreased in mid-dose males (-14%/-10%)and
high-dose males (-32%/- 18%)...Vacuolation of the
adrenal cortex was present in high-dose
females. Thymic atrophy occurred
in high-dose males and females.... Fine
vacuolation of adrenal glands (slight) and cortical atrophy
of the thymus (slight) were increased in
high-dose males... Absolute and/or relative organ weights in the
high-dose groups that showed statistically significant
changes relative to control weights (thyroid gland in both sexes
and kidney in females at 12 months and brain, pituitary, and spleen
in females sacrificed at 24 months) had no microscopic
correlates and are not considered toxicologically significant.
Ref: US EPA. Toxicology Chapter for RED.
August 8, 2001.
http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/reregistration/oxyfluorfen/oxytoxchapter.pdf
Picolinafen
- Herbicide - CAS No. 137641-05-5
In the 78-week dietary
study, there was no evidence to indicate that picolinafen was
oncogenic in the mouse. In the rat 2-year dietary study, there
was a non-statistically significant, increased
incidence of benign neoplasms (benign pheochromocytomas) in the
adrenal gland medullary region for males at 500 ppm (highest dose
tested). The incidence was within recent historical control
data for benign medullary neoplasms. In addition, there was no
decrease in the time-to-appearance of the induced tumour and no
dose-response relationship in proliferative changes usually associated
with neoplasms, benign or malignant, in the adrenal medulla. Published
literature indicates that proliferative lesions of the adrenal
medulla in male rats occurs at relatively high incidences and
can be spontaneous (age-related) in nature. Based on these findings,
the slight increased incidence of benign neoplasms in the adrenal
gland medullary region noted for males at 500 ppm, was most likely
spontaneous in nature and not treatment-related. The weight of
evidence suggests that picolinafen is not likely to be oncogenic
in humans.
Ref:
February 17, 2003 - Canada. Picolinafen. Regulatory Note REG2003-02.
Alternative Strategies and Regulatory Affairs Division, Pest Management
Regulatory Agency.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/picolinafen.canada.feb.2003.pdf
PFOS - PFOA
- Insecticide, US EPA List 3 Inert
Adverse signs of toxicity
observed in Rhesus monkey studies included anorexia, emesis, diarrhea,
hypoactivity, prostration, convulsions, atrophy
of the salivary glands and the pancreas, marked decreases
in serum cholesterol, and lipid depletion
in the adrenals. The dose range for these effects was reported
between 1.5-300 mg/kg/day. No monkeys survived
beyond 3 weeks into treatment at 10 mg/kg/day or beyond 7 weeks
into treatment at doses as low as 4.5 mg/kg/day.
Ref:
November 21, 2002 report: Hazard Assessment of Perfluorooctane
sulfonate (PFOS) and its salts.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. ENV/JM/RD(2002)17/FINAL.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/pfos.final.report.nov.2002.pdf
In
the second study, Goldenthal et al. (1978a) administered rhesus
monkeys, 2/sex/group,
doses of 0, 0.5, 1.5 or 4.5 rng/kg/day PFOS (FC-95) in distilled
water by gavage for 90 days... All monkeys in the 4.5 mg/kg/day
group died or were sacrificed in extremis between week 5 and 7
of the study. Beginning on the first or second day of the study,
these monkeys exhibited signs of gastrointestinal tract toxicity
including anorexia, emesis, black stool and dehydration. All of
the monkeys had decreased activity and just prior to death showed
marked to severe rigidity, convulsions, generalized body trembling
and prostration. The mean body weight decreased from 3.44 kg at
the beginning of the study to 2.7 kg at week 5 . After 30 days
of treatment, there was a significant reduction in serum cholesterol
and a 50% reduction in serum alkaline phosphatase activity. At
necropsy, mean organ weights were comparable among the control
and treated monkeys. Histologic examination showed several treatment
related lesions. All the male and females
had marked diffuse lipid depletion in the adrenals. One
male and two females had moderate diffuse atrophy of the pancreatic
exocrine cells with decreased cell size and loss of zymogen granules.
Two males and one female had moderate diffuse atrophy of the serous
alveolar cells characterized by decreased cell size and loss of
cytoplasmic granules.
Ref:
Sulfornated Perfluorochemicals
in the Environment: Sources, Dispersion, Fate and Effects.
Prepared by 3M. March 1,2000.
3.5 Reproductive Toxicity
Studies in Animals
York (2002) conducted an oral two-generation reproductive toxicity
study of APFO, which is summarized below. Although this preliminary
risk assessment focuses on developmental toxicity, the summary
below of the two generation reproductive toxicity study includes
all endpoints. Five groups of 30 Sprague-Dawley rats per sex per
dose group were administered APFO by gavage at doses of 0,1,3,10,
and 30 mg/kg/day six weeks prior to and during mating. Treatment
of the F0 male rats continued until mating was confirmed,and treatment
of the F0 female rats continued throughout gestation, parturition,
and lactation....
Parental Males (F0)... No treatment-related
effects were seen at necropsy or upon microscopic examination
of the reproductive organs, with the exception of increased thickness
and prominence of the zona glomerulosa and
vacuolation of the cells of the adrenal cortex in the 10
and 30 mg/kg/day dosegroups.
F1 Males ... The absolute weight
of the prostate, brain and left adrenal
gland were significantly decreased
in the 30 mg/kg/day dosage group.
The ratios of the weights of the seminal vesicles, with and without
fluid, liver and left and right kidneys to the terminal body weights
were significantly increased in all treated groups... Histopathologic
examination of the reproductive organs was unremarkable; however,
treatment-related microscopic changes were observed in the adrenal
glands of high-dose animals (cytoplasmic hypertrophy and vacuolation
of the cells of the adrenal cortex) and in the liver of
animals treated with 3,10,and 30 mg/kg/day (hepatocellular hypertrophy).
No other treatment- related effects were reported.
Ref: April
10, 2003: Preliminary
Risk Assessment of the Developmental Toxicity associated with
Exposure to Perfluorooctanoic Acid and its Salts. US
EPA Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics. 63 pages.
Pyridalyl
- Insecticide - CAS No. 179101-81-6
Subchronic toxicity.
-- Pyridalyl technical was tested in rats
in a 3-month feeding study. Effects included decreased body weight
gain, altered blood biochemistry, increased relative liver weight
and histopathological changes in
the liver, ovary, adrenal and
lung. The NOAEL is 100 ppm (5.56 mg/kg/day in males and 6.45 mg/kg/day
in females).
-- A 13-week
feeding study in mice was
conducted. Effects included decreased
body weight gain, hematological and blood biochemical effects,increased
liver weight, decreased kidney and ovary weights and histopathological
changes in liver, kidney, ovary and adrenal.
The NOAEL is 70 ppm
in males (8.169 mg/kg/day) and 700 ppm in females (86.78
mg/kg/day).
--
A 13-week oral (capsule) toxicity study
was conducted in
dogs. Effects included
decreased body weight gain, clinical signs indicative of respiratory
distress, hematological and blood biochemistry effects, increased
liver, lung and kidney weights and histopathological
alterations of the lung, kidney, adrenal
and liver. The NOAEL was 10 mg/kg/day.
Ref: Federal Register: December 5, 2003.
Pyridalyl; Notice of Filing a Pesticide Petition.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/pyridalyl.fr.dec.5.2003.htm
Sulfuryl
fluoride - Fumigant insecticide -
CAS No. 2699-79-8
- (870.4100) Chronic
toxicity--rodents. NOAEL = 3.5 for M and 16 for F mg/kg/
day
LOAEL = 20 ppm or 14 for M and 80 ppm or 62 for F mg/kg/day based
on dental fluorosis* in males and for females greatly increased
mortality (due mostly to severe kidney toxicity which led to kidney
failure); and histopathology in brain (vacuolation in cerebrum
and thalmus/ hypothalmus), adrenal cortex,
eyes, liver, nasal tissue and respiratory
tract; and, dental fluorosis*.
- (870.4300) 2-Year combined chronic/carcinogenicity--rat.
NOAEL = 3.5 for M and 16 for F mg/kg/day. LOAEL = 20 ppm or 14
for M and 80 ppm or 62 for F mg/kg/day based on dental fluorosis*
in males and for females greatly increased mortality (due mostly
to severe kidney toxicity which led to kidney failure); and histopathology
in brain (vacuolation in cerebrum and thalmus/hypothalmus), adrenal
cortex, eyes, liver, nasal
tissue and respiratory tract; and, dental fluorosis*.
Ref: January
23, 2004. Sulfuryl Fluoride; Pesticide Tolerance.
40 CFR Part 180 [OPP-2003-0373; FRL-7342-1]. Final Rule. Federal
Register
Transfluthrin
- Insecticide - CAS
No. 118712-89-3
3.2.4 Carcinogenicity
Studies. ... In a combined chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity
study, groups of 60 Wistar rats (strain
Bor:WISW (SPF Cpb) of both sexes were administered transfluthrin
(94.5-95% pure) in the diet at concentrations of 0, 20, 200 or
2000 ppm for 109 weeks. In addition, groups
of 10 male and 10 female rats were treated identically for full
interim necropsy at 52 weeks... Benign
adrenal tumours seen in males are within the control ranges
for Wistar rats...
Ref: Evaluation on: Transfluthrin Use as
a Public Hygiene Insecticide. September 1997. Prepared by: the
UK Health and Safety Executive, Biocides & Pesticides Assessment
Unit, Magdalen House, Stanley Precinct, Bootle, Merseyside L20
3QZ. Available from: Department for Environment, Food and Rural
Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate, Mallard House, Kings Pool,
3 Peasholme Green, York YO1 7PX. UK.
Also at
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
• Note: This was transcribed
from the copy available on the web. While one can easily read
this report on the web, the report is inaccessible, or locked,
to any attempt to copy it. Any errors are mine. EC.
|