|
Return
to Profluralin Index Page
Activity:
Herbicide
(2,6-Dinitroaniline)
Structure:
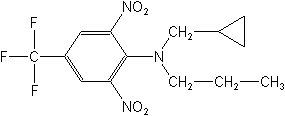
Adverse
Effects:
Cancer
Liver
Environmental
•
Very little toxicological data accessible.
•
WHO: believed obsolete or discontinued
|
Cancer
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract:
TD3: The Health and Environmental Effects Profile for profluralin
was prepared by the Office of Health and Environmental Assessment,
Environmental Criteria and Assessment Office, Cincinnati, OH for
the Office of Solid Waste to support listings of hazardous constituents
of a wide range of waste streams under Section 3001 of the Resource
Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). Both published literature
and information obtained from Agency program office files were
evaluated as the authors pertained to potential human health,
aquatic life and environmental effects of hazardous waste constituents.
Quantitative estimates have been presented provided sufficient
data are available. Profluralin has been evaluated as a carcinogen.
The
human carcinogen potency factor (q(l)*) for profluralin is .028
(mg/kg bw/day)-1 for oral exposure.
Ref: Health and Environmental Effects Profile for Profluralin.
US EPA. 1988. NTIS/PB88-162334, 26p
Liver
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
(FAN
NOTE: Very little Tox data available)
-- Lifetime feeding studies with high dose levels of profluralin
technical have produced an increased incidence of hepatic
tumors in mice.
Ref: March 1985. Profile of Herbicide (Tolban).
Pesticide Management Education Program at Cornell Univeristy.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Profluralin.Tolban.1985.fct.htm
-- IN RAT-LIVER MICROSOMES...PROFLURALIN
WAS METABOLIZED ANALOGOUSLY /TO TRIFLURALIN,
BY HYDROXYLATION OF THE PROPYL RESIDUE AND/OR N-DEALKYLATION/...
THE BENZIMIDAZOLE WAS A METABOLITE.
[The Chemical Society. Foreign
Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 5: A Review of the Literature
Published during 1976 and 1977. London: The Chemical Society,
1979. 487]
-- Profluralin was extensively metabolized in vitro by normal
and phenobarbital-induced rat liver microsomes. Metabolites produced
indicated that profluralin metabolism involved N-dealkylation,
aliphatic hydroxylation, nitro reduction and cyclization. Analyses
... indicated the formation of 2,6-dinitro-N-(n-propan-3-ol)-alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-p-toluidine
and the corresponding N-(n-propan-2-ol) analog. N-dealkylation
of profluralin gave the des-n-propyl and di-dealkylated analogs
and 2-ethyl-7-nitro-5-trifluoromethyl benzimidazole ...
[Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides-Update
III. Special Scientific Report- Wildlife No. 232. Washington,
DC: U.S.Department of the Interior, Fish and
Wildlife Service, 1980. 254]
Ref. Hazardous Substances Data Bank for
PROFLURALIN CASRN: 26399-36-0.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/profluralin.toxnet.hsdb.htm
|
Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--Toxic
to Honey Bees
-- Very High Bioconcentration in Aquatic
Organisms
-- Environmental Bioconcentration: An estimated BCF value
of 10,200 was calculated for profluralin(SRC), using an
experimental log Kow of 5.58(1) and a recommended regression-derived
equation(2). According to a classification scheme, this
BCF value suggests that bioconcentration in aquatic organisms
will be very high(3). [(1) Ellgehausen H et al; Pestic
Sci 12: 219-27 (1981)(2) Lyman WJ et al; Handbook of Chemical
Property Estimation Methods. Washington DC: Amer Chem Soc
pp. 5-4, 5-10 (1990) (3) Franke C et al; Chemosphere 29:
1501-14 (1994)]
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous
Substances Data Bank.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Profluralin.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
Abstract:
HEEP COPYRIGHT: BIOL ABS. The persistence and phytotoxicity
of dinitramine (n4,N4-diethyl-alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-3,5-dinitrotoluene-2,4-diamine),
fluchloralin (N-(2-chloroethyl)-2, 6-dinitro- N-propyl-4-
(trifluoromethyl)aniline), profluralin (N-(cyclopropylmethyl)alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-2,
6-dinitro-N-propyl-p-toluidine) and trifluralin (alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-N-N-dipropyl-p-toluidine)
were compared in 3 Manitoba soils: sandy loam, clay loam
and clay. The phytotoxicities of all chemicals decreased
with increased organic matter. The phytotoxicities of the
dinitroanilines were: dinitramine > trifluralin > profluralin
= fluchloralin. Increased organic matter increased the persistence
of trifluralin and fluchloralin. Profluralin
and dinitramine persistence increased with increased clay
and organic matter content. Profluralin
was the most persistent chemical over all soil types. Under
environmental conditions that retard dinitroaniline loss
from Manitoba soils, residues of some of these herbicides
may cause crop injury the year after application.
Ref: PRITCHARD MK et al. (1980). Persistence
and phytotoxicity of dinitroaniline herbicides in Manitoba,
Canada, soils. CAN J PLANT SCI; 60 (1). 1980. 5-12.
|
|