|
Return
to Fluopicolide Index Page
ACTIVITY:Fungicide
(acylpicolide)
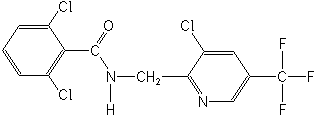
CAS Name:
2,6-dichloro-N-[[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]methyl]benzamide
Structure:
Adverse
Effects:
Boby
weight decrease
Bone
Developmental: Decreased crown-rump length in fetuses
Kidney
Liver
NOTE:
On
3-28-07 US EPA approved tolerances for imported grape and
imported, raisin without US registration
|
Boby
weight decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproductive and developmental
toxicity (page 3)
• In a developmental toxicity study in rats
gavage dosed from gestation days 7 to 20 at levels of 0, 5, 60
or700 mg/kg/day, evidence of maternal and fetal toxicity was observed
at 700 mg/kg/day, the highest dose tested. The
maternal and fetal NOAEL was 60 mg/kg/day based on statistically
lower body weights in dams an fetuses, and
skeletal findings in fetuses that included delayed ossification
of some bones and slight increases in the incidences of various
rib and thoracic vertebrae anomalies.
• In a 2-generation reproductive toxicity
study, fluopicolide was administered to rats at
dietary levels of 0, 100, 500, or 2000 ppm. The NOAEL was 500
ppm (equivalent to 26 and 33 mg/kg/day for males and females respectively)
for developing offspring and for parental/systemic toxicity. The
LOAEL was 2000 ppm based on decreased body
weight and organ weight changes in both F0 anb F1 and F2 pups.
The reproductive NOAEL was 2000 ppm.
Chronic toxicity
(page 4)
i. Lower body weight gain at the
limit dose of 1000 mg/kg/day was the only treatment-related effect
noted in a 52-week dog study performed at 70,
300, and 1000 mg/kg/day by gavage.
iii. The oncogenic potential of fluopicolide was investigated
in C57BL/6 mice at dietary levels of 0, 50, 400,
or 3200 ppm. Significantly lower body weight
gain was seen at 3200 ppm in conjunction with a slight
decrease in food consumption....
Reference: January 1, 2005, submission to
US EPA from Valent U.S.A. Company. Federal Register Docket EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0481-0002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/fluocopicolide.valent.june.2005.pdf
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproductive and developmental
toxicity (page 3)
• In a developmental toxicity study in rats
gavage dosed from gestation days 7 to 20 at levels of 0, 5, 60
or700 mg/kg/day, evidence of maternal and fetal toxicity was observed
at 700 mg/kg/day, the highest dose tested. The
maternal and fetal NOAEL was 60 mg/kg/day based on statistically
lower body weights in dams an fetuses, and skeletal
findings in fetuses that included delayed ossification of some
bones and slight increases in the incidences of various rib and
thoracic vertebrae anomalies.
Reference: January 1, 2005, submission to
US EPA from Valent U.S.A. Company. Federal Register Docket EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0481-0002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/fluocopicolide.valent.june.2005.pdf
• Twenty three mated Sprague-Dawley female rats/group were
dosed orally by gavage with 0, 5, 60 or 700 mg/kg/day from gestation
day 7 through gestation day 20. The mean body weight gain of the
700 mg/kg dams was less than that of the control between days
7 and 21. The mean fetal body weight of the 700 mg/kg offspring
was less than the control value (p<0.05). The
mean crown-rump length of the 700 mg/kg fetuses
was less than the control value (p<0.05). No adverse
effect indicated. Maternal NOEL: 60 mg/kg/day (based on the lower
body weight gain of the 700 mg/kg group); Developmental NOEL:
60 mg/kg/day (based on the lower mean body weight and crown-rump
length of the fetuses in the 1000 mg/kg group).
• Four mated female SpragueDawley rats/group
were dosed orally by gavage with 500 or 1000 mg/kg/day from day
7 through day 20 of gestation. The vehicle was aqueous 1% (w/v)
methyl cellulose. The number of live fetuses/litter was inversely
affected with 13.0 for the 500 mg/kg group and 9.3 for the 1000
mg/kg group. The mean fetal weight and crown-rump
length for the 1000 mg/kg offspring were 2.78 g and 32.6
cm as compared to 3.12 g and 34.1 cm for the 500 mg/kg group.
There was an apparent treatment-related effect upon both
the dams and the development of the fetuses in the 1000 mg/kg
group.
• Rabbit Oral Developmental Toxicity (Teratogenicity) Study
(Including Addendum). Twenty three mated female Himalayan rabbits/group
were dosed orally by gavage with 0, 5, 20 or 60 mg/kg/day from
day 6 through day 28 of gestation. Three does in the 60 mg/kg
group died during the study. Fifteen does in the 60 mg/kg group
and 1 doe in the 20 mg/kg group delivered their offspring prematurely.
The mean food consumption of the 5 does in the 60 mg/kg group
which delivered live fetuses was less than that of the control
during the last 6 days of the treatment (p<0.05). The
mean body weight and crown-rump length of the
fetuses in the 60 mg/kg group were less than the respective control
values (p<0.05). Developmental NOEL: 20 mg/kg/day (based
upon the lower mean body weight and the crownrump length of the
fetuses in the 60 mg/kg/day group).
Ref: Fluopicolide: summary of toxicology
data. California EPA, Department of Pesticide Regulation, Medical
Toxicology Branch. May 2, 2007.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/fluopicolide.ca.epa.2007.pdf
Developmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• Twenty three mated Sprague-Dawley female rats/group were
dosed orally by gavage with 0, 5, 60 or 700 mg/kg/day from gestation
day 7 through gestation day 20. The mean body weight gain of the
700 mg/kg dams was less than that of the control between days
7 and 21. The mean fetal body weight of the 700 mg/kg offspring
was less than the control value (p<0.05). The
mean crown-rump length of the 700 mg/kg fetuses
was less than the control value (p<0.05). No adverse
effect indicated. Maternal NOEL: 60 mg/kg/day (based on the lower
body weight gain of the 700 mg/kg group); Developmental NOEL:
60 mg/kg/day (based on the lower mean body weight and crown-rump
length of the fetuses in the 1000 mg/kg group).
• Four mated female SpragueDawley rats/group
were dosed orally by gavage with 500 or 1000 mg/kg/day from day
7 through day 20 of gestation. The vehicle was aqueous 1% (w/v)
methyl cellulose. The number of live fetuses/litter was inversely
affected with 13.0 for the 500 mg/kg group and 9.3 for the 1000
mg/kg group. The mean fetal weight and crown-rump
length for the 1000 mg/kg offspring were 2.78 g and 32.6
cm as compared to 3.12 g and 34.1 cm for the 500 mg/kg group.
There was an apparent treatment-related effect upon both
the dams and the development of the fetuses in the 1000 mg/kg
group.
• Rabbit Oral Developmental Toxicity (Teratogenicity) Study
(Including Addendum). Twenty three mated female Himalayan rabbits/group
were dosed orally by gavage with 0, 5, 20 or 60 mg/kg/day from
day 6 through day 28 of gestation. Three does in the 60 mg/kg
group died during the study. Fifteen does in the 60 mg/kg group
and 1 doe in the 20 mg/kg group delivered their offspring prematurely.
The mean food consumption of the 5 does in the 60 mg/kg group
which delivered live fetuses was less than that of the control
during the last 6 days of the treatment (p<0.05). The
mean body weight and crown-rump length of the
fetuses in the 60 mg/kg group were less than the respective control
values (p<0.05). Developmental NOEL: 20 mg/kg/day (based
upon the lower mean body weight and the crownrump length of the
fetuses in the 60 mg/kg/day group).
Ref: Fluopicolide: summary of toxicology
data. California EPA, Department of Pesticide Regulation, Medical
Toxicology Branch. May 2, 2007.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/fluopicolide.ca.epa.2007.pdf
Kidney
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic
toxicity (page 4)
ii. Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity was assessed in rats
at dietary levels of 50, 200, 750 and 2500 ppm. The NOAEL was
200 ppm (8.4 mg/kg/day in males and 10.8 mg/kg/day in females)
based on microscopic changes in the liver
and kidneys similar to those observed in the 90-day rat study.
No evidence of carcinogenicity was observed in rats up to 2500
ppm.
Subchronic
toxicity (pages 3-4)
Ninety-day feeding studies were conducted
in dogs, mice and rats.
iii. In a 90-day rat study with dietary
levels of 100, 1400 and 20,000 ppm, the maximum tolerated dose
(MTD) was exceeded at 20,000 ppm based on body weight gain of
30 to 40% below control. The target
organs identified in rats were the liver
(centrilobular hypertrophy) in both sexes and the kidneys
in males (accumulation of hyaline droplets, single cell death
at the proximal tubule epithelium, slight foci of basophilic tubules
and granular casts)
at 1400 ppm and 20,000 ppm. The NOAEL
was 100 ppm, equivalent to 7.4 and 8.4 mg/kg/day, in males and
females, respectively.
Reference: January
1, 2005, submission to US EPA from Valent U.S.A. Company. Federal
Register Docket EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0481-0002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/fluocopicolide.valent.june.2005.pdf
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic
toxicity (page 4)
ii. Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity was assessed in rats
at dietary levels of 50, 200, 750 and 2500 ppm. The NOAEL was
200 ppm (8.4 mg/kg/day in males and 10.8 mg/kg/day in females)
based on microscopic changes in the liver
and kidneys similar to those observed in the 90-day rat study.
No evidence of carcinogenicity was observed in rats up to 2500
ppm.
iii. The oncogenic potential of fluopicolide was investigated
in C57BL/6 mice at dietary levels of 0, 50, 400,
or 3200 ppm. Significantly lower body weight
gain was seen at 3200 ppm in conjunction with a slight
decrease in food consumption. Increased
liver weight and centrilobular hepatocellular hypertrophy
were observed at 400 and 3200 ppm in both sexes. In addition at
3200 ppm, an increased incidence of hepatocellular
adenomas was noted in both sexes, but the incidence of
hepatocellular carcinomas was not affected. The NOAEL was 50 ppm
(equivalent to 7.9 and 11.5 mg/kg/day in males and females, respectively).
Subsequent mechanistic work demonstrated a marked transient hepatocellular
profileration, whch returned to control levels after 28 days of
treatment. This was accompanied by a clear induction of total
cytochrome P-450 and related enzymes. These results parallel findings
with Phenobarbital, which has a well understood threshold-based
mechanism of roden tumor formation commonly known to be of no
relevance to humans.
Subchronic toxicity (pages 3-4)
Ninety-day feeding studies were conducted in dogs, mice and rats.
ii. In 90-day feeding studies in both CD-1 and C57BL/6 mice,
liver was the only target organ identified
with hepatocellular hypertrophy seen at dietary levels
of 320 ppm and higher. The NOAEL in C57BL/6 mice was 200 ppm (equivalent
to 37.8 and 52.8 mg/kg/day in males and females, respectively.)
iii. In a 90-day rat study with dietary levels of 100, 1400 and
20,000 ppm, the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was exceeded at 20,000
ppm based on body weight gain of 30 to 40% below control. The
target organs identified in rats were the liver (centrilobular
hypertrophy) in both sexes and the kidneys
in males (accumulation of hyaline droplets, single cell death
at the proximal tubule epithelium, slight foci of basophilic tubules
and granular casts) at 1400
ppm and 20,000 ppm. The NOAEL was 100 ppm, equivalent to
7.4 and 8.4 mg/kg/day, in males and females, respectively.
Reference: January
1, 2005, submission to US EPA from Valent U.S.A. Company. Federal
Register Docket EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0481-0002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/fluocopicolide.valent.june.2005.pdf
|

