|
Return
to Flumethrin Index Page
Activity: Acaricide,
Insecticide (pyrethroid)
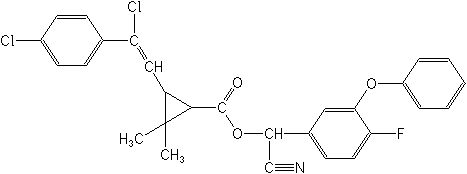
Structure:
Adverse Effects:
Ataxia
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Clastogenic / Genotoxicity
Dermal
Liver
Spleen
Environmental
Flumethrin
is a synethetic pyrethroid ectoparasiticide... applied topically
to cattle, as a pour-on, for
the control of ticks, lice and mites, at a dose rate of
2 mg/kg bw. There are also plastic strips impregnated with
flumethrin which are hung in beehives, for the diagnosis
and treatment of varroa in honey bees.
Flumethrin is not used for crop protection purposes... Flumethrin
is proposed for topical administratin by plunge dipping,
or by pour-on, for the control of ectoparasites such as
ticks, lice, keds and psoroptic, chorioptic and sarcoptic
mites. For the treatment of sheep
scab by plunge dipping, the dip concentrate would be diluted
with water to a concentration of 67 mg flumethrin per liter
of dip wash. The sheep would be immersed for one minute
and the head submerged twice during that period. The dose
used in dipping corresponds to approximately 1.8 mg/kg bw.
Ref:
Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products. Flumethrin
(Extension to sheep). Summary Report (2). April 2000. EMEA/MRL/737/00-FINAL.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flumethrin.eu.sheep.apr2000.pdf
The
acute toxicity of flumethrin was very
variable and depended on the solvent vehicle... the
trans-Z2 isomer was more acutely toxic than
the trans-Z1 isomer. In male Wistar rats, no mortalities
occurred following oral dosing with 5000 mg/kg bw of the
trans-Z1 isomer (in aqueous Cremophor) but 4 out of 5 rats
died following oral dosing with 50 mg/kg bw of the trans-Z2
isomer.
Ref:
Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products. Flumethrin.
Summary Report (1). June 1998. EMEA/MRL/469/98-FINAL. The
European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flumethrin.eu.june.1998.pdf
|
Ataxia
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
-- Groups of 28 mated
female rats received doses of 0, 0.5, 1.0 r 2.0 mg/kg bw per day
orally by gavage from days 6 to 15 of gestation. The test substance
was administered in a vehicle of 2% aqueous Emulphor. Signs of
toxicity (hypoactivity, ptosis, ataxia
and salivation) were observed in the dams given 1.0 and 2.0 mg/bw
day. Body weight and food consumption were
significantllly reduced in the 2.0 mg/kg bw group. The incidence
of foetal delayed ossification was significantly increased in
the 2.0 mg/kg bw group... The NOELs were 0.5 mg/kg bw per day
for maternal toxicity and 1.0 mg/kg bw per day for foetotoxicity.
-- Neurotoxicity
was evaluated in the inclined plane test with flumethrin administered
as a single dose in Cremophor:water (2%) or corn oil/milk emulsions.
The NOELs were 0.3 mg/kg bw and 1.0 mg/kg bw for the Cremophor
and milk formulations respectively. Statisticlaly
significant effects were found following dosing with 5 mg/kg bw
in either vehicle. No positive control group was included and
the sensitivity of the study is uncertain.
Ref: Committee for Veterinary Medicinal
Products. Flumethrin. Summary Report (1). June 1998. EMEA/MRL/469/98-FINAL.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flumethrin.eu.june.1998.pdf
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Groups of 15/sex/dose
Wistar rats were fed diets containing
0, 10, 50 or 250/150 mg/kg feed for 13 weeks. The test substance
was a 50% premix with colloidal SiO2 carrier. Due to severe
weight loss the dose level of 250 mg/kg feed was reduced
to 150 mg/kg feed during week 3. Body weight
gain was significantly reduced in the rats given 150 mg/kg
feed compared with the controls. Skin lesions,
described as ulcerative dermatitis, were observed in the 50 and
150 mg/kg feed groups and were dose-related in severity. The
NOEL was 10 mg/kg feed, equivalent to 0.7/0.8 mg/kg bw per day...
-- IN GLP repeated-dose toxicity study, groups of 20/sex/dose
Wistar rats were fed diets containing
0, 10, 40 or 160 mg/kg feed flumethrin for up to 15 weeks. During
mixing of the diets, 1% peanut oil was added to minimise dust
formation. At 160 mg/kg feed, body weight
gain was significantly reduced...
-- Groups of 4/sex/dose Beagle dogs
were fed diets containing 0, 50, 100 or 200 mg/kg feed flumethrin
for 13 weeks. The test substance was a 45.3% premix with colloidal
SiO2 carrier. Skin lesions and emesis
were observed in the groups receiving 50 mg/kg feed and above
and were dose-related in incidence and severity. Over the 13 weeks,
the mean body weight of males given 200
mg/kg feed was decreased and females in this group gained
less weight than the controls...
-- In a 2-generation reproduction study in rats with 2 litters
per generation, flumethrin was administered in the diet at concentrations
of 0, 1, 5 or 50 mg/kg feed. The test substance was a 45.6% premix
with colloidal SiO2 carrier. Food consumption and
body weight gain were reduced in parental animals of the P and
F1 generations... In the 50 mg/kg feed group, pup viability
on days 1 to 4 post-partum and pup body
weights were depressed and signs of pyrethroid-poisoning were
observed in the pubs of the F1a and F 1b litters. The NOEL
was 5 mg/kg feed, equivalent to 0.36 and 0.40 mg/kg bw per day,
in males and females respectively...
-- Groups of 28 mated female rats received doses of 0, 0.5, 1.0
r 2.0 mg/kg bw per day orally by gavage from days 6 to 15 of gestation.
The test substance was administered in a vehicle of 2% aqueous
Emulphor. Signs of toxicity (hypoactivity, ptosis,
ataxia and salivation) were observed in the dams given
1.0 and 2.0 mg/bw day. Body weight and food
consumption were significantllly reduced in the 2.0 mg/kg bw group.
The incidence of foetal delayed ossification
was significantly increased in the 2.0 mg/kg bw group... The NOELs
were 0.5 mg/kg bw per day for maternal toxicity and 1.0 mg/kg
bw per day for foetotoxicity.
Ref: Committee for Veterinary Medicinal
Products. Flumethrin. Summary Report (1). June 1998. EMEA/MRL/469/98-FINAL.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flumethrin.eu.june.1998.pdf
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Studies conducted with
flumethrin in mice showed induction of chromosomal
aberrations in bone marrow cells after a single dermal
application of 5,325 mg/kg to a shaved area or a single intraperitoneal
injection of 2,083 mg/kg, but not after repeated intraperitoneal
injections of 128 mg/kg (Nakano et al. 1996). In contrast, micronuclei
frequency was not significantly elevated after a single dermal
dose of 5,325 mg/kg, but was increased after repeated intraperitoneal
doses of 128 mg/kg (Nakano et al. 1996). (P 61)
Ref: September 2001. Draft
Toxicological Profile for Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids. US Department
of Health and Human Services. Public Health Service Agency for
Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
-- Groups of 28 mated
female rats received doses of 0, 0.5, 1.0 r 2.0 mg/kg bw per day
orally by gavage from days 6 to 15 of gestation. The test substance
was administered in a vehicle of 2% aqueous Emulphor. Signs of
toxicity (hypoactivity, ptosis, ataxia and salivation) were observed
in the dams given 1.0 and 2.0 mg/bw day. Body weight and food
consumption were significantllly reduced in the 2.0 mg/kg bw group.
The incidence of foetal delayed ossification
was significantly increased in the 2.0 mg/kg bw group...
The NOELs were 0.5 mg/kg bw per day for maternal toxicity and
1.0 mg/kg bw per day for foetotoxicity.
Ref: Committee for Veterinary Medicinal
Products. Flumethrin. Summary Report (1). June 1998. EMEA/MRL/469/98-FINAL.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flumethrin.eu.june.1998.pdf
Abstract: The genotoxic
potential of the pyrethroid flumethrin was evaluated by using
the combined protocol of metaphase analysis and micronucleus test
in vivo in mouse bone marrow. The
dermal route was tested in a single treatment and the intraperitoneal
(i.p.) route in a single and a multiple treatment. Flumethrin
showed a cytotoxic effect on both myelopoiesis
and erythropoiesis, as evidenced by a reduction in the
mitotic index and in polychromatic erythrocyte values. An increase
in the frequency of gaps after the dermal exposure and of breaks
only at the highest dose tested in the i.p. treatment indicates
a weak clastogenic potential of the compound.
A significant increase in the frequency of micronucleated polychromatic
erythrocytes was observed after single and multiple i.p. treatments.
In the latter, the induction of micronuclei was highly significant
but not accompanied by an increase in breaks. This may indicate
that the clastogenic effect might
not account by itself for the induction of micronuclei, which
could also have arisen from an aneugenic potential of flumethrin.
Ref: Nakano E et al. (1996).
Evaluation of the Genotoxic Potential of Flumethrin in Mouse
Bone Marrow by Chromosomal Analysis
and Micronucleus Test. Teratogenesis, Carcinogenesis, and Mutagenesis,
Vol. 16, No. 1, pages 37-48.
Clastogenic
/ Genotoxicity (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: The genotoxic
potential of the pyrethroid flumethrin was evaluated by using
the combined protocol of metaphase analysis and micronucleus test
in vivo in mouse bone marrow. The
dermal route was tested in a single treatment and the intraperitoneal
(i.p.) route in a single and a multiple treatment. Flumethrin
showed a cytotoxic effect on both myelopoiesis
and erythropoiesis, as evidenced by a reduction in the
mitotic index and in polychromatic erythrocyte values. An increase
in the frequency of gaps after the dermal exposure and of breaks
only at the highest dose tested in the i.p. treatment indicates
a weak clastogenic potential of the compound.
A significant increase in the frequency of micronucleated polychromatic
erythrocytes was observed after single and multiple i.p. treatments.
In the latter, the induction of micronuclei was highly significant
but not accompanied by an increase in breaks. This may indicate
that the clastogenic effect might
not account by itself for the induction of micronuclei, which
could also have arisen from an aneugenic potential of flumethrin.
Ref: Nakano E et al. (1996).
Evaluation of the Genotoxic Potential of Flumethrin in Mouse
Bone Marrow by Chromosomal Analysis
and Micronucleus Test. Teratogenesis, Carcinogenesis, and Mutagenesis,
Vol. 16, No. 1, pages 37-48.
The
above paper was abstracted in Food and Chemical Toxicology,
Volume 34, Issue 10, October 1996, Page 1021 :
Flumethrin
genotoxicity. Flumethrin,
a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide, tested as the technical
product Bayticol 60%, induced chromosomal damage in the
bone marrow cells when administered to mice by intraperitoneal
injection (Nakano
et al., Teratogenesis, Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
1996, 16, 37). |
Dermal
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
A single case report
was located in which a 47-year-old farmer developed a hypersensitive
response that included a widespread dermal
rash after dipping sheep in a solution, the active component
of which was flumethrin (Box and Lee 1996). The relative contributions
of dermal and inhalation exposure were not indicated in the report.
Ref: DRAFT TOXICOLOGICAL PROFILE FOR PYRETHRINS
AND PYRETHROIDS. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES.
Public Health Service Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease
Registry. September 2001.
http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp155.pdf
-- Groups of 15/sex/dose
Wistar rats were fed diets containing
0, 10, 50 or 250/150 mg/kg feed for 13 weeks. The test substance
was a 50% premix with colloidal SiO2 carrier... Skin
lesions, described as ulcerative dermatitis, were observed
in the 50 and 150 mg/kg feed groups and were dose-related
in severity. The NOEL was 10 mg/kg feed, equivalent to
0.7/0.8 mg/kg bw per day...
-- IN GLP repeated-dose toxicity study, groups of 20/sex/dose
Wistar rats were fed diets containing
0, 10, 40 or 160 mg/kg feed flumethrin for up to 15 weeks. During
mixing of the diets, 1% peanut oil was added to minimise dust
formation. At 160 mg/kg feed, body weight
gain was significantly reduced. Sever
skin lesions were observed in the 160 mg/kg feed group.
Some mild skin lesions were also
observed in the 40 mg/kg feed group. Decreased red cell values
and increased leucocyte counts in the 160 mg/kg feed group were
probably associated with the skin lesions. At termination, histopathological
examination revealed ulcerative skin lesions
in all rats given 160 mg/kg feed and some rats from the 40 mg/kg
feed group. Increased extramedullary
haematopoiesis and reduced haemosiderin storage in the spleen
were also observed in the 160 mg/kg feed group. The NOEL
was 10 mg/kg feed, equivalent to 0.7/0.8 mg/kg bw per day in males/females
respectively.
-- Groups of 4/sex/dose Beagle dogs
were fed diets containing 0, 50, 100 or 200 mg/kg feed flumethrin
for 13 weeks. The test substance was a 45.3% premix with colloidal
SiO2 carrier. Skin lesions and emesis
were observed in the groups receiving 50 mg/kg feed and above
and were dose-related in incidence and severity. Over the 13 weeks,
the mean body weight of males given 200 mg/kg feed was decreased
and females in this group gained less weight than the controls...
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) concentrations were significantly
increased in dogs given 200 mg/kg feed and slightly increased
in dogs given 100 mg/kg feed. At termination,
treatment-related skin lesions were observed in all treated groups;
the epithelial layer of the epidermis was
thickened and covered with hyperkeratotic material in places.
In 2 dogs given 200 mg/kg feed, the epidermis was ulcerated. No
NOEL was established in this study.
Ref: Committee for Veterinary Medicinal
Products. Flumethrin. Summary Report (1). June 1998. EMEA/MRL/469/98-FINAL.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flumethrin.eu.june.1998.pdf
Liver
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
Abstract: The effects
of repeated exposure to the pyrethroid insecticide flumethrin
(40 mg/kg intraperitoneally once a day for 6 days) on the activity
of cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenases and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
as well as on antipyrine disposition were investigated in male
Wistar rats. Pretreatment with flumethrin decreased the activities
of NADPH-cytochrome c reductase (38%), aniline hydroxylase (53%),
aminopyrine N-demethylase (54%), and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
(34%), and the content of cytochrome P450 (36%) in hepatic microsomes.
Total plasma clearance of antipyrine was decreased by flumethrin
pretreatment (54%), while the elimination half-life at beta phase
and the mean residence time of antipyrine were increased (96 and
88%, respectively). Urinary excretion of norantipyrine, 4-hydroxyantipyrine,
and 3-hydroxymethylantipyrine was decreased by 60, 38, and 33%,
respectively, in the 96 hr after flumethrin treatment. In addition,
the rate constants for formation of each of these metabolites
were decreased by an average of approximately 74%. These
findings provide evidence that flumethrin exposure diminishes
hepatic enzyme levels and catalytic activities of monooxygenase
systems as well as oxidative metabolism of antipyrine.
Ref: Effects
of flumethrin on hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes and antipyrine
disposition in rats; by A Anadon et al. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol
1995 May;132(1):14-8.
Spleen
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- IN GLP repeated-dose
toxicity study, groups of 20/sex/dose Wistar rats were fed diets
containing 0, 10, 40 or 160 mg/kg feed flumethrin for up to 15
weeks. During mixing of the diets, 1% peanut oil was added to
minimise dust formation. At 160 mg/kg feed,
body weight gain was significantly reduced. Sever skin lesions
were observed in the 160 mg/kg feed group. Some mild skin lesions
were also observed in the 40 mg/kg feed group. Decreased red cell
values and increased leucocyte counts in the 160 mg/kg feed group
were probably associated with the skin lesions. At termination,
histopathological examination revealed ulcerative skin lesions
in all rats given 160 mg/kg feed and some rats from the 40 mg/kg
feed group. Increased extramedullary
haematopoiesis and reduced haemosiderin storage in the spleen
were also observed in the 160 mg/kg feed group. The NOEL was 10
mg/kg feed, equivalent to 0.7/0.8 mg/kg bw per day in males/females
respectively..
Ref: Committee for Veterinary Medicinal
Products. Flumethrin. Summary Report (1). June 1998. EMEA/MRL/469/98-FINAL.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flumethrin.eu.june.1998.pdf
|

