|
Return to Index
Page
ACTIVITY:
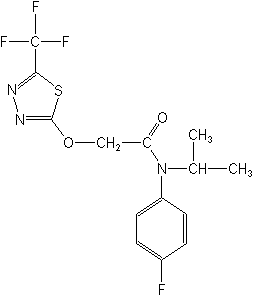
Herbicide (anilide)
CAS Name:
N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]oxy]acetamide
Structure:
| |
| Published
Date |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| May 9, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0965 |
Bayer CropScience.
Pesticide
Tolerance. FINAL RULE.
EPA determined that additional tolerances
are needed in connection with the petitioned-for tolerances
for wheat bran 0.80 ppm, grass forage at 7.0 ppm, and grass
hay at 0.4 ppm, cattle kidney at 0.05 ppm, goat kidney
at 0.05 ppm, hog kidney at 0.05 ppm, horse kidney at 0.05
ppm, and sheep kidney at 0.05 ppm. EPA determined that tolerance
levels are needed that differ from those proposed by the registrant
for sweet corn forage at 0.45 ppm (0.4 ppm proposed) sweet
corn stover at 0.30 ppm, (0.4 ppm proposed) wheat forage at
6.0 ppm (10.0 ppm proposed), wheat grain at 0.60 ppm (1.0
ppm proposed), wheat hay at 1.2 ppm (2.0 ppm proposed), and
wheat straw at 0.35 ppm (0.5 ppm proposed). EPA determined
that tolerances are not necessary for fat, meat, and meat
byproducts of cattle, goat, hog, horse, and sheep. Since permanent
tolerances are being established for wheat
and kidney of cattle, goat, hog, horse, and sheep, emergency
exemption tolerances for these commodities are being deleted.
Prenatal and postnatal sensitivity.
According to EPA: There is no indication of additional susceptibility
of young rats or rabbits following prenatal exposure to flufenacet
in the developmental toxicity studies. There was an indication
of qualitative susceptibility in the 2-generation reproduction
study. Effects seen in the offspring in the reproductive
toxicity studies (including increased
pup death in early lactation and cannibalism) were more severe
than those seen in the parental animals (increased liver weight
and cytomegaly), although there was no difference in
the NOAELs/LOAELS between parental animals and offspring in
that study. Increased susceptibility
(qualitative and quantitative) was seen in the developmental
neurotoxicity study in rats. Decreased
body weight was seen in pups at all dose levels, and additional
effects, including decreased motor activity, delayed developmental
landmarks, and decreases in morphometric measurements were
seen at mid and high doses. Morphometric measurements
were not made at the low dose. A slight decrease in body weight
in mid and high dose dams during early lactation may have
been due to palatability of test substance and was not considered
adverse.
Conclusion. Several factors
weighed in favor of the conclusion that no additional safety
factor is needed to protect the safety of infants and children.
First, there was no evidence of increased susceptibility in
the developmental toxicity studies (rats and rabbits), and
qualitative susceptibility seen in the
rat reproduction study did not raise concerns because the
pup death may be attributable to maternal cannibalism,
and there was a clear NOAEL for the effect. Second, there
are also no additional residual uncertainties with respect
to exposure data:
| General Tolerances
are established for the combined residues of the herbicide
flufenacet, N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,
3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl] oxy]acetamide and its metabolites
containing the 4-fluoro-N-methylethyl benzenamine moiety
in or on the following commodities. |
| Commodity |
Parts per million |
| Cattle, kidney |
0.05 |
| Corn, field, forage |
0.4 |
| Corn, field, grain. |
0.05 |
| Corn, field, stover |
0.4 |
| Corn, sweet, forage |
0.45 |
| Corn, sweet, kernel plus cob with husks
removed |
0.05 |
| Corn, sweet, stover |
0.30 |
| Goat, kidney |
0.05 |
| Hog, kidney |
0.05 |
| Horse, kidney |
0.05 |
| Sheep, kidney |
0.05 |
| Soybean, seed |
0.1 |
| Wheat, bran |
0.80 |
| Wheat, forage |
6.0 |
| Wheat, grain |
0.60 |
| Wheat, hay |
1.2 |
| Wheat, straw |
0.35 |
Tolerances with regional
registrations. Tolerances are established for
combined residues of flufenacet, N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,
3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl]
oxy]acetamide, and its metabolites containing the 4-fluoro-N-
methylethyl benzenamine moiety, with regional registration. |
| Commodity |
Parts per million |
| Grass, forage |
7.0 |
| Grass, hay |
0.4 |
|
| December 20, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0965 |
Bayer CropScience.
Pesticide
Petition PP 0F6095.
-- Corn, sweet, forage at 0.4 parts ppm
-- corn, sweet, kernel plus cob with husks removed at 0.05
ppm
-- corn, sweet, stover at 0.4 ppm
-- wheat, forage at 10.0 ppm
-- wheat, grain at 1.0 ppm
-- wheat, hay at 2.0 ppm
-- wheat, straw at 0.5 ppm
-- seed-grass, forage at 7.0 ppm
-- seed-grass, forage, regrowth at 0.1 ppm
-- seed-grass, hay, regrowth at 0.5 ppm. |
| December 20, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0942 |
Extension
of Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions
EPA has authorized under FIFRA section 18 the use of flufenacet
on winter wheat for control of Italian ryegrass in Idaho,
Oregon, and Washington. This regulation extends time-limited
tolerances for an additional 2-year period in or on the following.
These tolerances will expire and are revoked on December 31,
2009.
-- wheat, grain at 1 ppm;
-- wheat, forage at 10 ppm;
-- wheat, hay at 2 ppm;
-- wheat, straw at 0.50 ppm;
-- meat, kidney at 0.50 ppm;
-- fat of cattle, goat, horse, hog, and sheep at 0.05 ppm;
-- meat byproducts (other than kidney) of cattle, goat, horse,
hog, and sheep at 0.10 ppm for an additional 2-year period.
These tolerances will expire and are revoked on December 31,
2009. |
| June 28, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0084 |
Notice
of Receipt of Requests to Voluntarily Cancel Certain Pesticide
Registrations.
| EPA Registration No. |
Product Name |
Registrant |
000264 WA-01-0039
000264 WA-02-0011 |
Axiom DF Herbicide |
Bayer Cropscience LP
2 T.W. Alexander Drive, Research
Triangle Park, NC 27709. |
|
| Nov
16, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0277 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions.
• Idaho.
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet
on wheat to control Italian ryegrass;
September 23, 2005 to December 31, 2005.
• Oregon. EPA authorized
the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control Italian ryegrass; September 23, 2005 to December
31, 2005.
• Washington. EPA authorized
the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control Italian ryegrass; September 23, 2005 to December
31, 2005. |
| August
3, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0201 |
Cancellation
of Pesticides for Non-payment of Year 2005 Registration Maintenance
Fees.
| Section
24(c) Registrations canceled for non-payment of the
2005
maintenance fee are shown in the following Table 1:
Table
1.--Section 24(c) Registrations Canceled for Non-Payment
of Maintenance Fee |
|
SLN no. |
Product
Name |
| 000264
CO-99-0005 |
Epic
DF Herbicide |
| 000264
OR-02-0001 |
Axiom
DF Herbicide |
|
| March
10, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0057 |
Requests
to Voluntarily Cancel Certain Pesticide Registrations.
Unless a request is withdrawn by September 6, 2005, orders will
be issued canceling these registrations. The Agency will consider
withdrawal requests postmarked no later than September 6, 2005.
| Chemical
Name |
Registration
No. |
Product
Name |
Company
Name and Address |
Flufenacet
(product also contains Atrazine and Metribuzin) |
000264
SD-00-0003 |
Axiom
AT |
Bayer
Cropscience LP, Research
Triangle Pa, NC 27709 |
| 000264-00769 |
Axiom
AT |
|
| Feb
23, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0037 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions.
Idaho Department of Agriculture
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control Italian ryegrass; October 20, 2004 to December 31,
2004.
Oregon Department of Agriculture
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control Italian ryegrass; October 20, 2004 to December
31, 2004. |
| March
17, 2004 |
OPP-2004-0051 |
Pesticide
Emergency
Exemptions.
Georgia
Department
of Agriculture
Specific: EPA authorized the use of
flufenacet on
wheat to control ryegrass; October 27,
2003 to December 31, 2003.
North Carolina Department
of Agriculture
Specific: EPA authorized the use of
flufenacet on
wheat to control ryegrass; October 14,
2003 to December 31, 2003.
South Carolina Clemson
University
Specific: EPA authorized the use of
flufenacet on wheat to
control ryegrass; November 20, 2003 to January 31, 2004.
Virginia Department
of Agriculture and Consumer Services
Specific: EPA authorized the use of
flufenacet on wheat to
control ryegrass; October 16, 2003 to March 31, 2004.
|
| Nov
26, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0358 |
6
Pesticide Emergency Exemptions.
-- Idaho Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on
wheat to control grass weeds; September
1, 2003 to June 30, 2004.
--
Idaho Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet
on triticale to control grass weeds;
September 1, 2003 to June 30, 2004.
-- Oregon Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on
wheat to control grass weeds; September
1, 2003 to June 30, 2004.
--
Oregon Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet
on triticale to control grass weeds;
September 1, 2003 to June 30, 2004.
-- Washington Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on
wheat to control grass weeds; September 1, 2003 to June
30, 2004.
--
Washington Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet
on triticale to control grass weeds;
September 1, 2003 to June 30, 2004. |
| June
25, 2002 |
OPP-2003-0181 |
Pesticide
tolerances. FINAL RULE.
The
following studies are required as a condition of registration.
1. A special comparative sensitivity study on thyroid hormone
levels in neonatal and adult rats.
2. 28-day inhalation toxicity study in rats.
-- Developmental
Neurotoxicity study in rats:
--- LOAEL = 1.7 mg/kg/day day. based on
decreased body weight/body weight gain, and missing morphometric
measurements in caudate/putamen, in pups.
-- 90-Day oral toxicity rodents - rat:
LOAEL = 6.0(m) mg/kg/day based on decreased T4; 28.8
mg/kg/day (f) and on hematology and clinical chemistry findings
-- 90-day feeding - mouse: LOAEL (mg/kg/day)=64.2
(m), 91.3(f) based on systemic toxicity and histopathology
of the liver, spleen, and thyroid.
-- 90-Day oral toxicity in nonrodents:
LOAEL (mg/kg/day)= 7.20 (m); 6.90 (f) based on increases
in LDH, globulin, and spleen pigment in females, decreased
T4 and ALT values in both sexes, decreased albumin in males,
and decreased serum glucose in females
-- 21/28-Day dermal toxicity: LOAEL(mg/kg/day)=
150(m);1,000(f) based on decreased T4 and FT4 levels
in both sexes and histopathological findings in females
-- Prenatal developmental toxicity in
rodents (rat): LOAEL = 125 mg/kg/day based on decreased
fetal body weight, delayed ossificaition in skull, vertebrae,
sternebrae, and appendages, and increased extra ribs.
-- Prenatal developmental toxicity in
in nonrodents (rabbits):
Developmental NOAEL = 25 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 125 mg/kg/day based
on
increased skeletal variations.
-- Reproduction and fertility effects - rat: LOAEL = 7.4 (m),
(8.2 (f) mg/kg/day based
on increased liver weight in F1 females and hepatocytomegaly
in F1 males Reproductive NOAEL = 1.3
mg/kg/day LOAEL = 6.9 mg/kg/day based on increased
pup death in early lactation (including cannibalism) for F1
liters and the same effects in F1 and F2 pups at 36 mg/kg/day.
-- Chronic toxicity dogs: NOAEL = 1.29(m), 1.14(f) mg/kg/day
LOAEL = 27.75 (m), 26.82(f) mg/kg/day
based on
increased alkaline phosphatase, kidney, and liver weight in
both sexes, increased cholesterol in males, decreased T3,
T4, and ALT values in both sexes, and increased incidences
of microscopic lesions in the brain, eye, kidney, spinal cord,
sciatic nerve, and liver.
-- Chronic toxicity/ oncogenicity in rodents (rat): LOAEL
= 19.3 (m), 24.4(f) mg/kg/day based
on methemoglobinemia
and multi-organ effects in blood, kidney, spleen, heart, brain,
eye, liver and uterus. No evidence of carcinogenicity
-- Carcinogenicity mice: NOAEL = <7.4
((m), 9.4 (f) mg/kg/day LOAEL = 7.4 (m), 38.4 (f) mg/kg/day
based on increased incidence and severity of cataracts.
No evidence of carcinogenicity
The
Agency considered the lack of comparative data for thyroid
hormone levels in adult and neonatal animals. Available data
support the possibility of decreases in thyroid hormones in
adult animals (decreases were observed in several studies
conducted in rats, mice, rabbits, and dogs) at dose levels
similar to those used in the submitted DNT study. Because
of the above concern, a special comparative
study on thyroid hormone levels in neonatal and adult rats
is being requested by the Agency as a condition of registration.
| (a)
General. Tolerances are established for the combined residues
of the herbicide and its metabolites containing the 4-fluoro-N-methylethyl
benzenamine moiety in or on the following raw agricultural
commodities: |
| Corn,
field, forage |
0.4
ppm |
| Corn,
field, grain |
0.05
ppm |
| Corn,
field, stove |
0.4
ppm |
| Soybean,
seed |
0.1
ppm |
| Indirect
or inadvertent residues. Tolerances are established for
indirect or inadvertent residues of the herbicide and
its metabolites containing the 4- fluoro-N-methylethyl
benzenamine moiety in or on the raw agricultural commodities
listed in paragraph (a) of this section. |
| Commodity |
Final
Rule |
Proposed
by Bayer |
| Alfalfa,
forage |
0.1
ppm |
0.1
ppm |
| Alfalfa,
hay |
0.1
ppm |
0.1
ppm |
| Alfalfa,
seed |
0.1
ppm |
0.1
ppm |
| Clover,
forage |
0.1
ppm |
0.1
ppm |
| Clover,
hay |
0.1
ppm |
0.1
ppm |
| Grain,
cereal, group 15, except rice |
0.1
ppm |
0.4
ppm |
| Grain,
cereal, forage, fodder, and straw, group 0.1 16, except
rice |
0.1
ppm |
10.0
ppm |
| Grass,
forage, fodder, and hay, group 17 |
0.1
ppm |
0.1
ppm |
|
| Feb
24, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0033 |
Pesticide
Emergency Excemptions:
-- Georgia. Specific: EPA authorized
the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control ryegrass; October 10, 2002 to December 31,
2002.
-- Idaho.
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
and triticale to control ryegrass; October 10, 2002
to June 30, 2003.
-- North
Carolina.
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on
wheat to control ryegrass; October 10, 2002 to December
31, 2002.
-- Oregon.
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
and triticale to control ryegrass; October 10, 2002
to June 30, 2003.
-- South
Carolina.
Clemson University. Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet
on wheat to control annual ryegrass;
November 20, 2002 to December 31, 2002.
-- Virginia.
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control ryegrass; October 10, 2002 to December 31,
2002.
-- Washington.
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on
wheat and triticale to control
ryegrass; October 10, 2002 to June 30, 2003. |
| Jan
16, 2003 |
OPP-2002-0336
|
Extension of Tolerances
for Emergency Exemptions. EPA has authorized under FIFRA
section 18 the use of N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[[5-
(trifluoromethyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]oxy]acetamide
on wheat and triticale for control of ryegrass in Idaho, Oregon,
and Washington. This regulation extends a time-limited
tolerance for combined residues of the herbicide N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[[5-
(trifluoromethyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]oxy]acetamide and
its metabolites containing the 4-fluoro-N-methylethyl benzenamine
moiety in or on wheat grain at 1 ppm,
wheat forage at 10 ppm, wheat hay at 2 ppm, wheat straw at
0.5 ppm, meat and fat of cattle, goats, horses, hogs, and
sheep at 0.05 ppm, meat byproducts (other than kidney) of
cattle, goats, horses, hogs, and sheep at 0.10 ppm and kidney
of cattle, goats, horses, hogs, and sheep at 0.50 ppm for
an additional 1-year, 11 months. These tolerances will
expire and are revoked on June 30, 2005. Time-limited tolerances
were originally published in the Federal Register of August
6, 1999 (64 FR 42839) (FRL-6091-9). |
| Feb
13, 2002 |
OPP-181085 |
- Emergency
Exemptions:
- Idaho:
EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat and triticale
to control annual ryegrass; October 3, 2001 to June 30,
2002.
- Oregon-
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
and triticale to control annual ryegrass; October 3, 2001
to June 30, 2002.
- South
Carolina
- Crisis: On November 16, 2001, for the use of flufenacet
on wheat to control annual ryegrass. This program ended
December 31, 2001.
- South
Carolina-
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control annual ryegrass; November 29, 2001 to December
31, 2001.
- Virginia
-
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control annual ryegrass; October 1, 2001 to December
31, 2001.
- Washington
-
Specific: EPA authorized the use of flufenacet on wheat
and triticale to control annual ryegrass; October 3, 2001
to June 30, 2002.
|
| Dec
20, 2000 |
OPP-181078 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions. US EPA authorized the following: In
Idaho, the use of flufenacet on wheat to control annual ryegrass;
10/5/00 to 6/30/01. In Oregon, the use of flufenacet on wheat
to control annual ryegrass; 10/5/00 to 6/30/01. In Virginia,
the use of flufenacet on wheat to control annual ryegrass; 10/18/00
to 12/31/00. In Washington, the use of flufenacet on wheat to
control annual ryegrass; 10/5/00 to 6/30/01. |
| Oct
27, 2000 |
OPP-301073 |
Extension
of Tolerance for Emergency Exemptions. - FINAL RULE.
This regulation extends time-limited tolerances for combined
residues of the herbicide and its metabolites containing the
4-fluoro-N-methylethyl benzenamine moiety in or on wheat grain
at 1 ppm, wheat forage at 10 ppm, wheat hay at 2 ppm, wheat
straw at 0.5 ppm, meat, kidney and fat of cattle, goats, horses,
hogs, and sheep at 0.05 ppm and meat by-products (other than
kidney) of cattle, goats, horses, hogs, and sheep at 0.1 ppm
for an additional two-year period. These tolerances will expire
and are revoked on July 31, 2003. |
| March
29, 2000 |
PF-925 |
Petition
for Pesticide tolerances for
flufenacet and
metabolites
containing the 4-fluoro-N-methylethyl benzenamine moiety in
or on the raw agricultural commodities (RAC) wheat grain at
0.5 ppm; wheat forage at 9.0 ppm; , wheat hay at 1.0 ppm; wheat
bran at 1.0 ppm; wheat germ at 0.5 ppm; wheat straw, seed- grass
forage at 0.5 ppm; seed-grass forage from re-growth at 18.0
ppm; seed-grass hay from re- growth at 0.1 ppm; seed-grass straw
at 0.5 ppm; sweet corn kernel plus cob with husks removed at
0.05 ppm.
-- Acute Toxicity: The acute oral LD50 was 1,617
milligrams/kilograms (mg/kg) for males and
589 mg/kg for
females.
-- According to EPA: flufenacet should
be considered as a candidate for evaluation as an endocrine
disrupter when the criteria are established.
-- Reproductive and developmental toxicity:
---- A 2-generation rat reproduction study with a parental systemic
no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) of 20 ppm (1.4 mg/kg/day
in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females) and a reproductive NOAEL
of 20 ppm (1.3 mg/kg/day) and a parental systemic lowest observed
adverse effect level (LOAEL) of 100 ppm (7.4 mg/kg/day in males
and 8.2 mg/kg/day in females), based on increased
liver weight in F1 females and
hepatocytomegaly in F1 males, and a
reproductive LOAEL of 100 ppm (6.9 mg/kg/ day) based on increased
pup death in early lactation (including cannibalism) for F1
litters and the same effects in both F1 and F2
pups at the high dose level of 500 ppm (37.2 mg/kg/day in males
and 41.5 mg/kg/day in females), respectively.
---- A rat developmental study with a maternal NOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day
and with a maternal LOAEL of 125 mg/kg/day based on decreased
body weight gain initially and a developmental NOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day
and a developmental LOAEL of 125 mg/kg/day based on decreased
fetal body weight, delayed development
mainly delays in ossification in the skull, vertebrae, sternebrae,
and appendages, and an increase in the incidence of extra ribs.
---- A rabbit developmental study with a maternal NOAEL of 5
mg/kg/ day and a maternal LOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day based on
histopathological finds in the liver and a developmental
NOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day and a developmental LOAEL of 125 mg/kg/day
based on increased skeletal variations.
---- Subchronic toxicity--i. A 84-day rat feeding study with
a NOAEL less than 100 ppm (6.0 mg/kg/day) for males and a NOAEL
of 100 ppm (7.2 mg/kg/day) for females and with a LOAEL of 100
ppm (6.8 mg/kg/day) for males based on suppression
of thyroxine (T4) level, and a LOAEL of 400 ppm (28.8
mg/kg/day) for females based on hematology, and clinical chemistry
findings.
---- A 13-week mouse feeding study with a NOAEL of 100 ppm (18.2
mg/ kg/day for males and 24.5 mg/kg/day for females), and a
LOAEL of 400 ppm (64.2 mg/kg/day for males and 91.3 mg/kg/day
for females) based on histopathology of
the liver, spleen and thyroid.
--- A 13-week dog dietary study with a NOAEL of 50 ppm (1.70
mg/ kg/day for males and 1.67 mg/kg/day for females), and a
LOAEL of 200 ppm (6.90 mg/kg/day for males and 7.20 mg/kg/day
for females), based on evidence that the
bio-transformation capacity of the liver has been exceeded (as
indicated by increase in LDH, liver weight, ALK and hepatomegaly),
globulin and spleen pigment in females, decreased T4
and ALT values in both sexes, decreased albumin in males, and
decreased serum glucose in females.
---- A 21-day rabbit dermal study with the dermal irritation
NOAEL of 1,000 mg/kg/day for males and females, and a systemic
NOAEL of 20 mg/kg/day for males and 150 mg/kg/day for females,
and a systemic LOAEL of 150 mg/kg/day for males and 1,000 mg/kg/day
for females based on clinical chemistry data (decreased T4
and FT4 levels in both sexes) and centrilobular
hepatocytomegaly in females.
---- Chronic toxicity. A 1-year dog chronic feeding study with
a NOAEL was 40 ppm (1.29 mg/kg/day in males and 1.14 mg/kg/day
in females), and a LOAEL of 800 ppm (27.75 mg/kg/day in males
and 26.82 mg/kg/day in females) based on
increased alkaline phosphatase, kidney, and liver weight in
both sexes, increased cholesterol in males, decreased T2,
T4 and ALT values in both sexes, and increased incidences
of microscopic lesions in the brain, eye, kidney, spinal
cord, sciatic nerve, and liver.
---- A rat chronic feeding/carcinogenicity study with a NOAEL
less than 25 ppm (1.2 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in
females), and a LOAEL of 25 ppm (1.2 mg/kg/day in males and
1.5 mg/kg/day in females) based on methemoglobinemia,
and multi-organ effects in blood, kidney, spleen, heart, and
uterus. Under experimental conditions the treatment did
not alter the spontaneous tumor profile.
---- In a mouse carcinogenicity study the NOAEL was less than
50 ppm (7.4 mg/kg/day) for males and the NOAEL was 50 ppm (9.4
mg/kg/day) for females. The LOAEL was 50 ppm (7.4 mg/kg/day)
for males and the LOAEL was 200 ppm (38.4 mg/kg/day)
for females based on cataract incidence
and severity.
---- Metabolite toxicology. A 55-day dog study with subcutaneous
administration of thiadone flufenacet metabolite supports the
hypothesis that limitations in glutathione
interdependent pathways and antioxidant stress result
in metabolic lesions in the brain and heart following
flufenacet exposure.
-- Other studies.
---- An acute rat neurotoxicity study with a NOAEL less than
75 mg/kg/day and a LOAEL of 75 mg/kg/day based on decreased
motor activity in males.
---- A rat subchronic neurotoxicity study with a NOAEL of 120
ppm (7.3 mg/kg/day in males and 8.4 mg/kg/day in females),
and a LOAEL of 600 ppm (38.1 mg/kg/day in males and 42.6 mg/kg/day
in females) based on microscopic lesions
in the cerebellum/medulla and spinal cords.
Pesticide Petition No. 0F6095 |
| Aug
6, 1999 |
OPP-300897 |
Pesticide
Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions.. - FINAL RULE.
This regulation establishes time-limited tolerances for combined
residues of N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[[5- (trifluoromethyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]oxy]acetamide
and its metabolites containing the 4-fluoro-N-methylethyl benzenamine
moiety in or on wheat grain, wheat forage, wheat hay, wheat
straw, and meat, fat, meat byproducts, and kidney of cattle,
goats, horses, hogs, and sheep. These tolerances will expire
and are revoked on July 31, 2001. |
|
Sept 23, 1998 |
OPP-300712 |
BAYER
- request:
Time-Limited Pesticide Tolerances.- FINAL RULE.
This regulation establishes a time-limited tolerance for indirect
or inadvertent residues in or on certain raw agricultural
commodities when present therein as a result of the application
of flufenacet to field corn and soybeans as a herbicide.These
tolerances expire April 30, 2003. |
|
June 23, 1998 |
PF-813 |
BAYER
- Pesticide
Tolerance Petition for residues and metabolites containing
the 4-fluoro-N- methylethyl benzenamine moiety in or on
the raw agricultural commodities of Crop Group 15 (cereal
grains), Crop Group 16 (forage, stover and hay of cereal grains),
Crop Group 17 (grass forage, and grass hay), alfalfa forage,
alfalfa hay, alfalfa seed, clover forage, and clover hay at
0.1 ppm when present therein as a result of the application
of flufenacet to field corn and soybeans as a herbicide. |
| May
29, 1998 |
na |
- BAYER
- Conditional
approval of 3 new herbicide product registrations:
- FOE
5043 Technical Herbicide for use only in the manufacturing
of herbicides. EPA Reg. No. 3125-486
- FOE
5043 DF Herbicide for control of certain grass and broadleaf
weeds in corn and soybeans. EPA File Reg. No. 3125-487
- Axiom
DF Herbicide for control of certain grass and broadleaf
weeds in corn and soybeans. EPA Reg. No. 3125-488. The product
Axiom DF also contains 13.6% of the active ingredient metribuzin
1-amino-6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3- (methylthio)-1,2,4-triazin-5(4H)-one.
|
| May
13, 1998 |
na |
BAYER
- Correction
to Time-Limited Pesticide Tolerance. - FINAL RULE..
For residues in or on: CORN, FIELD: forage (0.4 ppm); grain
(0.05 ppm); stover (0.4 ppm); Soybean seed (0.1 ppm). This
tolerance expires April 30, 2003. |
|
April 10, 1998 |
OPP-300636 |
BAYER
- Time-Limited
Pesticide Tolerance. - FINAL RULE. For residues
in or on: CORN, FIELD: forage (0.05 ppm); grain (0.4 ppm),
stover (0.4 ppm); Soybean seed (0.1 ppm). |
| April
2, 1997 |
PF-723 |
BAYER
- Pesticide
Tolerance Petition; for residues of the herbicide FOE 5043
in or on the raw agricultural commodities, field corn grain
at 0.05 ppm, field corn forage at 0.4 ppm, field corn stover
(fodder) at 0.4 ppm, soybean seed at 0.1 ppm, milk at 0.01
ppm, meat at 0.05 ppm, and meat byproducts at 0.05 ppm. |
| June
12, 1996 |
PF-646 |
BAYER
- Petition
for Pesticide Tolerances for the herbicide FOE 5043 in or
on the raw agricultural commodities field corn grain at 0.05
ppm, field corn forage at 0.4 ppm, field corn stover (fodder)
at 0.4 ppm, soybeans at 0.1 ppm, milk at 0.01 ppm, meat at
0.05 ppm, and meat by products at 0.05 ppm. |
| May
1, 1996 |
OPP-30409 |
- BAYER
- Application
to Register three herbicide products:
- FOE
5043, for use only in the manufacturing of herbicides. Active
ingredient at 95 %. EPA File Symbol: 3125-UIA.
- FOE
5043 DF, for control of certain grass and broadleaf weeds
in corn and soybeans. Active ingredient at 60 %. EPA File
Symbol: 3125-UIT
- Axiom
DF, for control of certain grass and broadleaf weeds in
corn and soybeans. Active ingredients flufenacet and Metribuzin
4-amino-6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-(methylthio)-1,2,4- triazin-5(4H)-one
at 54.4 and 13.6 % respectively. EPA File Symbol: 3125-UII.
|
|