|
Return to
Adverse Effects
Abstracts
ACTIVITY: Insecticide,
Acaricide, Chemosterilant (Benzoylurea)
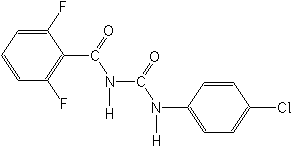
CAS Name: N-[[(4-chlorophenyl)amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide
Structure::
| Adverse
Effects:
Endocrine:
Suspected Disruptor
Endocrine: Testicular
Effects
attributed to PCA (4-Chloroaniline) a metabolite of diflubenzuron:
Bone
Blood
Cancer:
Spleen, Liver due to metabolite 4-chloroaniline
Endocrine: Adrenal
Liver
Spleen
NOTE:
Chloroaniline,
p (or 4-chloroaniline) is
a metabolite of Diflubenzuron. In 2006, USEPA classified chloroaniline,
p as a "Group
B2 -- Probable Human Carcinogen."
"Spleen
(fibrosarcomas,
hemangiosarcomas & osteosarcomas) (M); Adrenal
(pheochromocytomas (M & F);
F344/N rats. Hepatocellular
adenomas/carcinomas (M); Hemangiosarcomas
in spleen and/or liver (M) in
B6C3F1 mice."
Ref: April
26, 2006 . Chemicals
Evaluated for Carcinogenic Potential by the Office of Pesticide
Programs. From: Jess Rowland, Chief Science Information
Management Branch Health Effect Division (7509C) Office of
Pesticide Programs, USEPA. |
| Environmental
Effects:
Acute
aquatic toxicity |
Regulatory
Information
(only comprehensive for the US) |
| US
EPA Registered: |
Yes |
| US
EPA PC Code: |
108201
212200 |
| California
Chemical Code |
1992 |
| US
Tolerances: |
CFR
180.377
CFR 186.2000 |
| FDA
LMS Code: |
651 |
US
EPA Permit Date
and Registrant: |
1976,
Thompson-Haywood |
Registered
use in
(includes only a limited list of countries)
|
Australia,
Canada, Denmark, Finland, Hungary, India, Japan, Netherlands,
New Zealand, Portugal, UK, US
Africa: Burkina Faso, Cape Verde,
Chad, Gambia, Gunina-Bissau, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Niger,
Senegal, South Africa, Tanzania |
| Japan's
Maximum Residue Levels (MRLs) |
Apple,
Artichoke, Barley, Brussel Sprouts, Button mushrooms, Cabbage,
Cotton Seeds, Cucumber, Ginger, Grapefruit, Japanese Plum (inc
prunes), Lemon, Lime, Melons, Onion, Orange, Peach, Pear, Persimon,
Soybeans, Tea, Tomato, Walnut, Watermelon, Wheat
-- Note
very high level - 20 ppm - for Tea (Green, Black, Oolong,
Wulung) |
US
Maximum Residue Levels permitted
in food commodities
|
Permitted
in or on over 400 food commodities, including:
Artichoke, Egg, Grapefruit, Pasture rangeland),
Milk, Mushroom, Pear, Rice, Soybean, Tangerine, Walnut, Cattle,
Goat, Horse, Hog, Poultry, Sheep |
| Other
Information |
| Molecular
Formula: |
C14H9Cl
F2 N2O2 |
| Inventing
Company: |
First
commercialized by.:
Philips-Duphar BV,
The Netherlands
(Solvay Duphar BV) |
| Manufacturers: |
Durphar
BV,
UNIROYAL |
| Other
Names: |
Adept
DFB
Difluron
Dimilin
DU 112307
400-EUP-69
Fleececare
Magnum
PH 60-40
Strike
TH 6040 |
| Manufacture
sites: |
CHINA:
Shijiazhuang Chemical
Factory, Hebei Province
HOLLAND:
Uniroyal, Amsterdam
INDIA:
Gharda Chemicals,
Maharashra |
| Of
special interest: |
| PAN
Data |
| Material
Safety Data Sheets & Labels |
Jan
23, 2006: Conservation
Group Moves for Court Order Restricting Use of 66 Pesticides
in Core Red-Legged Frog Habitat.
San Francisco, Calif. – The Center for Biological Diversity
(CBD) in a legal motion today asked a U.S. District Court to
protect the threatened California red-legged frog (Rana aurora
draytonii) from 66 of the most toxic and persistent pesticides
authorized for use in California, by creating pesticide-free
buffer zones around the frog’s core habitat and by requiring
consumer hazard warnings so that all Californians may learn
how to protect frogs. [Trifluralin was
one of the 66 pesticides.]
In response to a lawsuit filed by CBD against the U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency (EPA) in April of 2002, the District Court
found in September of 2005 that the EPA violated the Endangered
Species Act (ESA) by registering pesticides for use without
considering how they might impact the continued existence of
the red-legged frog. The motion for “injunctive relief”
delivered today asks the court to protect the frog from pesticides
in or adjacent to aquatic frog habitat designated as core recovery
areas, until the EPA completes a formal consultation with the
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) on the impacts of the
pesticides on red-legged frogs, as required under the ESA...
CBD is asking the Court to impose a three-year schedule for
the EPA to determine whether the 66 pesticides may affect the
red-legged frog and to complete formal consultations with USFWS
to ensure the pesticides are not jeopardizing the frog or contributing
to its decline. To minimize harm to frogs during the consultation
process, the motion asks for an injunction on use of the pesticides
around aquatic features and upland habitats within the frog’s
core recovery areas, as designated by USFWS in the agency’s
Recovery Plan for the California Red-legged Frog. This injunction
would also apply buffer areas for terrestrial and aerial pesticide
applications, affecting approximately 7 percent of the current
range of the frog and less than 1 percent of the area of California.
CBD is also requesting that the EPA conduct monitoring for pesticides
in three of the recovery areas to determine whether the buffers
are effectively protecting the frog, inform pesticide users
about the injunction, and post point-of-sale notifications warning
consumers about harmful effects these pesticides may have on
the frog... |
August
2004
- Canada: Re-evaluation
of Diflubenzuron. Proposed Acceptability for Continuing
Registration. No. PACR2004-35. Pest Management Regulatory
Agency.
--The
following statements must be added to the "Precautions"
section of the label:
•
Do not use in residential areas. Residential areas are defined
as sites where bystanders including children may be potentially
exposed during or after spraying. This includes around homes,
on school grounds, in parks, playgrounds, playing fields,
around public buildings or any other areas where the general
public including children could be exposed."
--
A section entitled "Environmental Hazards" must
be added to the label and include the following statements:
•
TOXIC TO AQUATIC ORGANISMS. DO NOT contaminate irrigation
/ drinking water supplies or aquatic habitats by cleaning
of equipment or disposal of wastes.
•
For gypsy moth control, observe buffer zones specified under
Directions for Use.
--
The registrant is required to replace the statement:
•
FOREST INSECT CONTROL: For use only by Plant Protection
Division, Agriculture, Canda
with
the following:
•
FOREST INSECT CONTROL: For use only
by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency
Products
containing DFB registered in Canada as of 31 March 2004:
Dimlin 25% WP Insecticide. Registrant: Crompton Co. Reg. No.:
13816
Diflubenuron Technical Insecticide. Registrant: Crompton Co.
Reg. No. 25451 |
| August
1997 - US
EPA Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) |
| January
28, 1999 - US
EPA Fact Sheet (pdf) |
| 1998
- 1999 - Levels
of residues on Australian wool |
| US
Map of pesticide use based on 1991-1995
data. |
| Insecticide
products - partial
list |
| 2002
-
Review
and synthesis of the environmental impacts of aquaculture.
The Scottish Association for Marine Science
and Napier University. Scottish Executive Central Research Unit. |
| 1998
- US EPA places Diflubenzuron in the category of a "Reduced-Risk
Pesticide" |
| 1996
-
Environmental Health
Criteria Report 184. WHO International
Programme on Chemical Safety. |
| Pesticide
Information Profile - Cornell Management
Education Program |
| Abstracts |
| October
1998 - Structural
Pest Management pesticides. FAN's
compilation of information cited on fluorine and organofluorine
pesticides published in General Pest Management, Category 7A.
A Guide for Commercial Applicators. Prepared by: Carolyn Randall,
MSU Pesticide Education Program. Published by
MSU Pesticide Education
(Michigan State University). MSU
manual number: E-2048. |
| Chemical
Profile - Environmental Defense Fund
Scorecard |
| List
of Brand Name Pesticides which use Diflubenzuron -
Environmental Defense Fund Scorecard |
| December
10, 2001 - Australia:
"Current List.
RECORD OF APPROVED ACTIVE CONSTITUENTS FOR CHEMICAL PRODUCTS." |
| August,
2001 -
IR-4 -
New
Products/Transitional Solution List -
This list contains brief descriptions of numerous new pest control
materials that have been introduced over the last several years.
Additionally, it contains information on some "older"
crop protection chemicals that are believed to have room for
new uses. This List includes Diflubenzuron |
Rationale
for US EPA to add Diflubenzuron to the Toxic Release Inventory
In
a 2-year study in which beagle dogs received diflubenzuron
daily in gelatin capsules, the LOAEL for increases in sulfhemoglobin
and methemoglobin was 10 mg/kg/day and the NOAEL was 2 mg/kg/day.
EPA has derived an oral RfD of 0.02 mg/kg/day for this chemical
from this study. Similar effects were noted in two separate
2-year rat feeding studies (the LOAEL was 7.8 to 8 mg/kg/day;
the NOAEL was 2 mg/kg/day), and in a lifetime oral study
in mice (the LOAEL was 12 mg/kg/day; the NOAEL was 2.4 mg/kg/day).
EPA believes that there is sufficient evidence for listing
diflubenzuron on EPCRA section 313 pursuant to EPCRA section
313(d)(2)(B) based on the available hematological toxicity
data. Measured aquatic acute toxicity data for diflubenzuron
include a 48-hour LC 50 of 4.55 ppb for daphnids. EPA
believes that there is sufficient evidence for listing diflubenzuron
on EPCRA section 313 pursuant to EPCRA section 313(d)(2)(C)
based on the environmental toxicity data for this chemical.
Ref:
USEPA/OPPT. Support Document for the Health and Ecological
Toxicity Review of TRI Expansion Chemicals. U. S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC (1993). As
cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV. 40 CFR Part 372.
Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical Release Reporting;
Community Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
|
| June
14, 2001 - Implementation
of the Community Strategy for Endocrine Disruptors - a
range of substances suspected of interfering with the hormone
systems of humans and wildlife. Communication from the Commission
to the Council and the European Parliament. Commission of
the European Communities, Brussels COM (2001) 262 final. (More
information available at: http://europa.eu.int/comm/environment/docum/01262_en.htm
)
This
document presents a "priority list of substances for
further evaluation of their role in endocrine disruption.
During 2000, a candidate list of 553 man-made substances and
9 synthetic/natural hormones has been identified."
Organofluorine
pesticides in this list include: |
| Substances
included on the Endocrine Disruptor Liist |
CAS
No. |
Substances
included on the Endocrine Disruptor Liist |
CAS
No. |
| Bifenthrin |
82657-04-3
|
Flutriafol |
76674-21-0 |
| Cyhalothrin
(@Karate) |
91465-08-6 |
Fluvalinate |
69409-94-5 |
| Diflubenzuron |
35367-38-5 |
Prodiamine |
29091-21-2 |
| Epoxiconazole |
- |
Stannane,
tributylfluoro [Tributyltin fluoride] |
1983-10-4 |
| Fipronil |
- |
Thiazopyr |
- |
| Fluazifop-butyl |
69806-50-4
|
Trifluralin |
- |
| October
2002 - Factsheet. Guidelines
for producing European eco-label and nil residue
wool. Western Australia Department of Agriculture. Also
available at http://www.agric.wa.gov.au/agency/pubns/factsheets/2001/fs02801.pdf |
| No
diflubenzuron or triflumuron to be used, as residue levels are
likely to exceed limits. |
| Eco-label
wool does not mean nil residue wool and the current limits for
pesticide levels can be achieved fairly easily using standard
production systems. The pesticide limits for greasy wool are:
|
| Total
synthetic pyrethroids (SP) |
less
than 0.5 mg/kg |
| Total
organophosphates (OP) |
less than
2 mg/kg |
| Total
insect growth regulators (IGR)* |
less than
2 mg/kg |
| *IGRs
cover diflubenzuron (e.g. Magnum, Strike,
Fleececare etc.) and triflumuron
(e.g. Zapp, etc.). Use of either
of these chemicals is likely to exceed this level,
e.g. expected residues from using triflumuron (e.g. Zapp etc.)
off-shears is 25Ð30 mg/kg... |
| |
| - |
Organo-
phosphates
|
Synthetic
pyrethroids |
Cyromazine |
Dicyclanil |
Diflubenzuron |
Triflumuron |
| 1992-93 |
10.2 |
5.8 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 1993-94 |
9.0 |
6.6 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 1994-95 |
4.3 |
5.7 |
5.2 |
- |
- |
- |
| 1995-96 |
4.4 |
5.5 |
6.3 |
- |
- |
- |
| 1996-97 |
4.5 |
3.8 |
8.7 |
- |
1.2 |
3.5 |
| 1997-98 |
5.8 |
3.3 |
5.8 |
- |
3.6 |
6.1 |
| 1998-99 |
2.4 |
1.6 |
7.4 |
- |
3.5 |
7.6 |
| 1999-00 |
2.2 |
2.0 |
5.1 |
0.1 |
2.9 |
9.0 |
| Source:
Woolmark Company |
US
Federal Register
••
Note: Due to length, not all entries are listed below. Click
here to view all.
|
| Date
Published |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| July 25, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0446 |
Pesticide
tolerance. FINAL RULE. EPA, on its own
initiative, establishes a time-limited
tolerance for diflubenzuron and its metabolites p-chlorophenylurea
and p- chloroaniline in or on lemon at 0.8 ppm.
This action is in response to EPA's granting of an emergency
exemption under section 18 of the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide,
and Rodenticide Act authorizing use of the pesticide on lemon.
This regulation establishes a maximum permissible level for
combined residues of diflubenzuron and its metabolites p-chlorophenylurea
and p-chloroaniline, in this food commodity expressed in terms
of the combined residues of diflubenzuron and its metabolites
CPU and PCA. The tolerance expires and is revoked on December
31, 2010.
Document available with this
final rule:
Diflubenzuron.
Human Health Risk Assessment for the Proposed Establishment
of an Emergency Exemption Tolerance for Use in/on Lemons.
April 16, 2007. Docket ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0446-0002. Excerpt:
(page 6): In subchronic and chronic feeding
studies, the primary endpoint of concern, produced most
likely by PCA, was methemoglobinemia
and/or sulfhemoglobinemia. These effects were evident
in both sexes of mice, rats, and dogs and were produced
by more than one route of administration in rats [i.e.,
oral, dermal and inhalation]. The general consequence of
methemoglobinemia and/or sulfhemoglobinemia is the
impairment of the oxygen transportation capacity of the
blood, which is generally known to be caused by aromatic
amines in both humans and animals.
Cancer.
The Agency has classified diflubenzuron as ``Group E,'' evidence
of non-carcinogenicity for humans, based on lack of evidence
of carcinogenicity in rats and mice. There
are also two metabolites of diflubenzuron; PCA and
CPU. PCA tested positive for splenic tumors in male
rats and hepatocellular adenomas/carcinomas in male mice in
a National Toxicology Program (NTP) study. Therefore, EPA
classified PCA as a ``Group B2'' probable human carcinogen.
The Agency determined for those commodities that contained
PCA and CPU, the Q1* of PCA should be used to calculate the
cancer risk from the sum of these two metabolites.
Based on the submitted metabolism studies, there are two possible
sources for dietary exposure to PCA and CPU: Residues in mushrooms
and residues in milk and liver. Because human exposure to
PCA and CPU will not be affected by the proposed new uses,
and EPA has previously concluded that exposure to these compounds
is safe, therefore, the cancer dietary risk from PCA and CPU
will not be addressed in this document. For a detailed discussion
on the exposure and risks to PCA and CPU, please refer to
the September, 2002 Federal Register document titled Diflubenzuron;
Pesticide Tolerances (September 19, 2002, FR 67 59006). |
| November 29, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0181 |
IR-4.
Pesticide
tolerance. FINAL RULE.
Tolerances are established for combined residues of diflubenzuron,
(N-[[(4-chlorophenyl)amino]carbonyl]-2,6-
difluorobenzamide and its metabolites 4-chlorophenylurea and
4-chloroaniline in or on the raw agricultural commodities
Barley, grain at 0.06 ppm
Barley, hay at 3.0 ppm
Barley, straw at 1.8 ppm
Brassica, leafy greens, subgroup 5B
at 9.0 ppm
This
subgroup includes 10 commodities: broccoli
• broccoli, cavalo • broccoli, chinese •
brussels sprout • cabbage • cabbage, chinese
mustard • cabbage, chinese napa • cauliflower
• cavalo broccolo • kohlrabi
Grain, aspirated fractions at 11 ppm
Oat, forage at 7.0 ppm
Oat, grain at 0.06 ppm
Oat, hay at 6.0 ppm
Oat, straw at 3.5 ppm
Peanut at 0.10 ppm
Peanut, hay at 55 ppm
Peanut, refined oil at 0.20 ppm
Pummelo at 0.50 ppm
Turnip greens at 9.0 ppm
Wheat, forage at 7.0 ppm
Wheat, grain at 0.06 ppm
Wheat, hay at 6.0 ppm
Wheat, straw at 3.5 ppm |
| September 1, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0702 |
Request
for Public Comment on Proposed Stipulated Injunction Involving
66 Pesticides and the California Red-legged Frog.
Center for Biological
Diversity
vs
EPA
|
| April 12, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0181 |
IR-4.
Pesticide
petitions: 5E6965, 5E6966, and 5E6967.
Diflubenzuron and metabolites convertible to p-chloroaniline.
PP 5E6965 proposes to establish tolerances for
-- barley, grain; oat, grain; and wheat, grain at 0.06 ppm
-- barley, forage; oat, forage; and wheat, forage at 5.0 ppm
-- barley, hay; oat, hay; and wheat, hay at 2.0 ppm
-- barley, straw; oat, straw; and wheat, straw at 2.0 ppm
-- barley, aspirated barley fractions at 3.0 ppm
-- oat, aspirated oat fractions at 3.0 ppm
-- wheat, aspirated wheat fractions at 3.0 ppm
-- pummelo at 0.5 ppm.
PP 5E6966
proposes to establish tolerances for
-- brassica, leafy greens subgroup 5B;
turnip at 8.0 ppm
This subgroup includes 8
commodities.
broccoli raab • cabbage, chinese bok choy •
collards • kale • mizuna • mustard greens
• mustard spinach • rape greens
-- eggplant at 1.0 ppm
-- okra at 1.0 ppm.
PP 5E6967
proposes to establish a tolerance for
-- peanut at 0.2 ppm. |
| Dec
21, 2005 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0292 |
Extension
of Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. FINAL
RULE.
EPA has
authorized under FIFRA section 18 the use of diflubenzuron
on wheat and barley for control of grasshoppers in Montana,
Washington, and Idaho. This regulation extends time-limited
tolerances for combined residues of the insecticide diflubenzuron
and its metabolites 4-chlorophenlyurea and 4-chloroaniline
(CPU) and (PCA) in or on wheat
and barley grain at 0.05 ppm, wheat and barley straw at 0.50
ppm, wheat and barley hay at 1.0 ppm, wheat milled byproducts
at 0.10 ppm, and aspirated grain fractions at 30 ppm
for an additional 3-year period. These
tolerances will expire and are revoked on December 31, 2008.
Time-limited tolerances were originally published in the Federal
Register of August 27, 2003. |
| Nov
16, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0277 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions.
• Idaho.
Specific: EPA authorized the use of diflubenzuron on
barley and wheat to control grasshoppers and Mormon crickets;
July 1, 2005 to August 1,
2005.
• Montana. EPA authorized
the use of diflubenzuron on alfalfa
to control grasshoppers and Mormon crickets; August 25, 2005
to September 30, 2005.
• Washington. Specific: EPA
authorized the use of diflubenzuron on barley
and wheat
to control grasshoppers and Mormon crickets; July 1, 2005 to
August 1, 2005. |
| August
31, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0223 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions:
•
Montana.
EPA authorized the use of diflubenzuron
on barley and wheat to control
grasshoppers; June 22, 2005 to July 15, 2005. Contact: (Libby
Pemberton).
• Nevada. EPA authorized
the use of diflubenzuron on alfalfa
to control Mormon cricket and grasshopper; June 3,
2005 to October 31, 2005. Contact: (Libby Pemberton).
• Utah. Specific: EPA authorized
the use of diflubenzuron on alfalfa
to control Mormon cricket and grasshopper; June 8, 2005 to
October 31, 2005. Contact: (Libby Pemberton).
• Wyoming. Specific: EPA
authorized the use of diflubenzuron
on alfalfa to control Mormon cricket and grasshoppers; June
23, 2005 to October 31, 2005. Contact: (Libby Pemberton). |
| August
3, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0201 |
Cancellation
of Pesticides for Non-payment of Year 2005 Registration Maintenance
Fees.
| Section
24(c) Registrations canceled for non-payment of the
2005
maintenance fee are shown in the following Table 1:
Table
1.--Section 24(c) Registrations Canceled for Non-Payment
of Maintenance Fee |
|
SLN no. |
Product
Name |
| 000400
OR-00-0021 |
Dimilin
2l |
| 000400
OR-02-0009 |
Dimilin
2l |
|
| Dec 22,
2004 |
OPP-2004-0350 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions.
•
Idaho
-- Specific: EPA authorized the use of diflubenzuron
on alfalfa to control Mormon crickets
and grasshoppers; September 7, 2004 to October 31, 2004. Contact:
(Libby Pemberton)
• Montana
-- Specific: EPA authorized the use of diflubenzuron
on alfalfa to control Mormon crickets
and grasshoppers; September 7, 2004 to October 31, 2004. Contact:
(Libby Pemberton) |
| Nov 10,
2004 |
OPP-2004-0232 |
Seven
Pesticide Emergency Exemptions.
• Idaho
--- Crisis: On May 3, 2004, for the use of diflubenzuron
on alfalfa to control Mormon
cricket and grasshoppers. This program is expected to end
on October 31, 2004. Contact: (Libby Pemberton)
--- On June 8, 2004, for the use of diflubenzuron on
barley and wheat to control Mormon
cricket and grasshoppers. This program ended on July 14, 2004.
Contact: (Libby Pemberton)
• Montana
--- Crisis: On May 20, 2004, for the use of diflubenzuron
on alfalfa to control grasshoppers.
This program is expected to end on September 30, 2004. Contact:
(Libby Pemberton)
--- EPA authorized the use of diflubenzuron on wheat
and barley to control grasshoppers and Morom crickets;
April 16, 2004 to July 15, 2004. Contact: (Barbara Madden)
• Nevada - Specific: EPA
authorized the use of diflubenzuron
on alfalfa to control grasshoppers
and Mormon crickets; April 16, 2004 to October 31, 2004. Contact:
(Barbara Madden)
• North Dakota - EPA authorized
the use of diflubenzuron on wheat
and barley to control various grasshopper species;
June 30, 2004 to July 15, 2004. Contact: (Libby Pemberton)
• Washington - Crisis:
On June 3, 2004, for the use of diflubenzuron
on barley and wheat to control
Mormon cricket and grasshoppers. This program ended on July
14, 2004. Contact: (Libby Pemberton)
|
| Oct 27,
2004 |
OPP-2004-0338 |
Cancellation
of Pesticides for Non-payment of Year 2004 Registration Maintenance
Fees.
Table
1.--Section 24(c) Registrations Canceled for Non-Payment
of
Maintenance Fee |
| Name
of Pesticide |
Product
Name |
Registrant |
SLN
No. |
| Diflubenzuron |
Dimilin
25 W for Cotton/Soybean |
Crompton
Manufacturing Company, Inc. |
000400
CA-94-0004 |
| Diflubenzuron |
Dimilin
25W for Cotton/soybean |
Crompton
Manufacturing Company, Inc. |
000400
OR-88-0013 |
|
••
Note: Due to length, not all entries are listed above. Click
here to view all.
|
|