|
Return to
Adverse Effects
Abstracts
ACTIVITY:
Herbicide (sulfonylurea)
CAS Name:
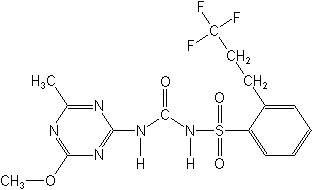
N-[[(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]carbonyl]-2-(3,3,3-trifluoropropyl)benzenesulfonamide
Structure:
| Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Endocrine: Breast
Endocrine: Testicular
Endocrine:
Uterus
Heart
Liver |
| Environmental
Effects:
EU:
Particular attention should be given to the potential for
groundwater contamination, when the active substance is applied
in regions with vulnerable soil and/or climate conditions. |
Regulatory
Information
(only comprehensive for the US) |
| US
EPA Registered: |
Yes |
| US
EPA PC Code: |
129031 |
| California
Chemical Code |
5115
|
| US
Tolerances: |
CFR
180.481 |
Registered
use in
(includes only a limited list of countries)
|
Canada,
Germany, Hungary, Portugal, South Africa, UK, US |
| Other
Information |
| Molecular
Formula: |
C15H16
F3 N5O4S |
| Entry
Year: |
1992 |
| Inventing
Company: |
Ciba
Geigy |
| Manufacturers: |
Novartis |
| Other
Names: |
CGA
152005
Exceed
Peak |
| Of
special interest: |
| PAN
Data |
| Material
Safety Data Sheets & Labels |
| May
9, 2005 - U.S. Congressman John Coble (R-NC) introduced
a bill "To suspend temporarily the duty on formulations
of Prosulfuron" up to December 31, 2008. The bill was referred
to the House Committee on Ways and Means. |
| July
2, 2002 - Review
report for the active substance prosulfuron. European
Commission Health & Consumer Protection Directorate-General. |
February
18, 2002 - European
Commission decision to extend provisional authorisation
granted for new active substances: carfentrazone-ethyl,
cinidon-ethyl, cyhalofop-butyl,
ethoxysulfuron, famoxadone, flazasulfuron,
flufenacet, flumioxazine,
flurtamone,
fosthiazate, isoxaflutole, metalaxyl-M,
prosulfuron, Pseudomonas
chlororaphis, quinoxyfen, Spodoptera
exigua nuclear polyhedrosis virus and sulfosulfuron.
-- Organofluorine pesticides highlighted
in red. |
| Abstracts |
| Up
to December 31, 1999 -
U.S. Residue limits for pesticides in meat, poultry and egg
products. USDA. |
| August
2001
- IR-4:
New Products/Transitional
Solution List - This
list contains brief descriptions of numerous new pest control
materials that have been introduced over the last several years.
Additionally, it contains information on some "older"
crop protection chemicals that are believed to have room for
new uses. This List includes:
Prosulfuron |
| October
2001 - Glossary
of Pesticide Chemicals. A listing
of pesticides subject to analysis of residues in foods and feeds
by the US Food and Drug Administration. |
US
Federal Register
••
Note: Due to length, the following is a partial
list. Click here
to see full list of FR entries.
|
| Date
Published |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| Dec
31, 2002 |
OPP-2002-0343 |
SYNGENTA
- Pesticide Tolerance
Petition; for residues in or on the raw agricultural commodities
| Commodity |
PPM |
| cereal
grains group (except rice and wild rice) grain |
0.10
|
| cereal
grains group (except rice and wild rice) fodder |
0.10
|
| cereal
grains group (except rice and wild rice) straw |
0.02 |
| cereal
grains group (except rice and wild rice) hay |
0.20
|
| milk |
0.01
|
| meat,
fat, kidney, liver, and meat by-products of cattle, goats,
hogs, horses, and sheep |
0.05
|
--
Acute toxicity. EPA has set an acute reference dose of 0.1
milligram/kilogram/day (mg/kg/day) based upon a no observed
adverse effect level (NOAEL) of 10 mg/kg/day from the rat
acute neurotoxicity study (lowest observed adverse
effect level (LOAEL) of 250 mg/kg/day due to reduced motor
activity and body temperature in males and impaired righting
reflex in females) and a 100-fold uncertainty factor (UF).
-- In a rat teratology study, evidence of maternal toxicity
(decreased body weight gain and
reduced food consumption) and developmental toxicity (increased
incidence of skeletal variations that was not significantly
different from the historical control) was found at the maximum
tolerated dose of 400 mg/kg.
-- Chronic toxicity. In the 1-year dog
chronic dosing study, the NOAEL was 1.84 mg/kg/day
based on hematologic and clinical
chemistry effects and incidence of lipofuscin
accumulation in the liver at 18.6 mg/kg/day.
-- In the 18-month mouse carcinogenicity study, there was
no evidence of carcinogenic effects up to the highest dose
tested (HDT) of 1,062 mg/kg/day. The NOAEL was 1.71 mg/kg/day
in males, and 100 mg/kg/ day in females based on increased
incidence/severity of centrilobular
hepatocellular hypertrophy.
-- A 2-year chronic feeding/carcinogenicity study in rats
indicated systemic NOAEL of 7.9 mg/kg/day was based on decreased
body weight and body weight gain, hematopoietic
effects (males), and possibly increased serum GGT and
decreased liver, kidney, and adrenal
weights (females) at 79.9 mg/kg/ day. There was uncertain
evidence of carcinogenicity with slight increases in the incidence
of mammary gland adenocarcinomas in
females at 95.7 and 205.8 mg/kg/day, slight increase
in incidence of benign testicular interstitial
cell tumors at 79.9 and 160.9 mg/kg/day (significant
trend only). Considering the weight of the evidence,
the EPA Reference Dose Committee previously concluded that
the chemical should be classified as a
Group D carcinogen (inadequate evidence), not classifiable
as to human carcinogenicity. The HIARC (meeting December 2,
1999) accepted the previous conclusions and updated
the cancer classification to the new classification: ``data
are inadeqate,'' with no new studies required. EPA
has set a chronic reference dose of 0.02 mg/kg based on a
NOAEL of 1.84 mg/kg in a dog feeding study and a 100-fold
UF. |
|