|
Return to
Index Page
Adverse Effects
Abstracts
ACTIVITY:
Herbicide (unclassified)
CAS Name:
2-[7-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-3-oxo-4-(2-propynyl)-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-6-yl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione
Structure:
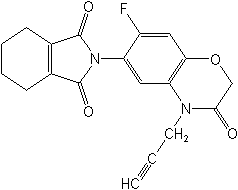
| |
| Published
Date |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| September 28, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0871 |
Valent U.S.A. Corporation. Proposed pesticide tolerance. Pesticide Petition (PP 7F7243) to establish a tolerance for residues of the herbicide flumioxazin in or on the food commodities
-- corn, field grain at 0.02 ppm;
--
corn, field forage at 0.02 ppm
-- corn, field stover at 0.02 ppm.
Practical analytical methods for detecting and measuring levels of flumioxazin have been developed and validated in or on all appropriate agricultural commodities and respective processing fractions. The level of quantitation (LOQ) of flumioxazin in the methods is 0.02 ppm which will allow monitoring of food with residues at the levels proposed for the tolerances. |
| September 28, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0781 |
Valent U.S.A. Corporation. Proposed pesticide tolerance. Pesticide Petition (6F7092) proposes to establish a tolerance for residues of the herbicide in or on the food commodities
-- alfalfa, forage at 1.0 ppm and
--
alfalfa, hay at 2.0 ppm. |
| June 27, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0308 |
IR-4.
Pesticide
Petition. PP 6E7151. Proposal to establish a tolerance
for residues of the herbicide flumioxazin in or on food commodities:
| asparagus |
0.02 ppm |
| aronia berry |
0.02 ppm |
| dry beans |
0.10 ppm |
| buffalo currant |
0.02 ppm |
Bushberry, subgroup
13B
This subgroup includes
5 commodities.
blueberry • currant • elderberry •
gooseberry • huckleberry
|
0.02 ppm |
| Chilean guava |
0.02 ppm |
| European barberry |
0.02 ppm |
| highbush cranberry |
0.02 ppm |
| honeysuckle |
0.02 ppm |
| jostaberry |
0.02 ppm |
| Juneberry |
0.02 ppm |
| lingonberry |
0.02 ppm |
melon, subgroup
9A
This subgroup includes
6 commodities.
cantaloupe • citron melon • melon •
melon, citron • muskmelon • watermelon
|
0.02 ppm |
| Native currant |
0.02 ppm |
nut, tree, crop
group 14
This group includes
16 commodities.
almond • almond, hulls • beechnut •
butternut • cashew • chestnut •
chinquapin • filbert • nut, brazil •
nut, hickory • nut, macadamia • nutmeat,
processed, except peanut • nuts • pecan
• pistachio • walnut
|
0.02 ppm |
| okra |
0.02 ppm |
| salal |
0.02 ppm |
| sea buckthorn |
0.02 ppm |
vegetable, fruiting, crop
group 8
This group includes
17 commodities.
chili, postharvest • eggplant • groundcherry
• pepino • pepper • pepper, bell
• pepper, nonbell • pepper, nonbell, sweet
• tomatillo • tomato • tomato, concentrated
products • tomato, dried pomace • tomato,
paste • tomato, puree • tomato, wet pomace
• vegetable, fruiting • vegetable, fruiting,
group
|
0.02 ppm |
Practical analytical methods for detecting
and measuring levels of flumioxazin have been developed and
validated in/on all appropriate agricultural commodities and
respective processing fractions. The LOQ of flumioxazin in
the methods is 0.02 ppm which will allow monitoring of food
with residues at the levels proposed for the tolerances. |
| June 27, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0308 |
IR-4.
Pesticide
Petition. PP 6E7151. Porposal to amend the tolerances in
40 CFR 180.568 for residues of the herbicide flumioxazin in
or on the food commodity almond, nutmeats be deleted upon establishment
of the crop group tolerance for nut, tree, Crop Group 14. |
| May 3, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2004-0398 |
Valent U.S.A.
Pesticide
tolerance. FINAL
RULE. -- Strawberry
at 0.07 ppm
-- Fruit, pome, group
11 at 0.02 ppm
This group includes 10 commodities.
apple • apple, dried pomace • apple, juice •
apple, wet pomace • crabapple • fruit, pome
• loquat • mayhaw • pear • pear,
oriental • quince
-- Fruit, stone, group
12 at 0.02 ppm
This group includes 14 commodities.
apricot • cherry, sweet • cherry, tart •
fruit, stone • fruit, stone, except plum, prune, dried
• nectarine • peach • plum • plum,
chickasaw • plum, damson • plum, japanese •
plum, prune • plum, prune, dried • plum, prune,
fresh
|
| May
3, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2004-0398 |
Valent.
Pesticide
tolerance. FINAL
RULE.
| Commodity |
PPM |
Fruit,
pome, group 11
This
group includes 10 commodities.
apple • apple, dried pomace • apple, juice
• apple, wet pomace • crabapple •
fruit, pome • loquat • mayhaw •
pear • pear, oriental • quince
|
0.02 |
Fruit,
stone, group 12
This
group includes 14 commodities.
apricot • cherry, sweet • cherry, tart
• fruit, stone • fruit, stone, except
plum, prune, dried • nectarine • peach
• plum • plum, chickasaw • plum,
damson • plum, japanese • plum, prune
• plum, prune, dried • plum, prune, fresh
|
0.02 |
| Strawberry |
0.07 |
|
| August
17, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0222 |
Requests
to Voluntarily Cancel Certain Pesticide Registrations.
|
Registration no. |
Product
Name |
Chemical
Name |
Registrants
Requesting Voluntary Cancellation |
| 059639
SD-02-0001 |
Valor
WDG Herbicide |
Flumioxazin |
Valent
U.S.A. Corp., PO Box
8025, Walnut Cre, CA 94596. |
| 059639
SD-03-0003 |
Gangster
V Herbicide |
Flumioxazin |
Valent
U.S.A. Corp., PO Box
8025, Walnut Cre, CA 94596. |
|
| April
8, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0089 |
IR-4.
Notice of Filing a Pesticide Petition to Establish a Tolerance
in
or on STRAWBERRY at 0.10 ppm.
PP
(Pesticide Petition) 4E6845.
The
toxicological profile for flumioxazin which supports this
petition for tolerances was published in the Federal
Register on March 31, 2004. |
| Dec
8, 2004 |
OPP-2004-0398 |
Valent.
Petition
for pesticide tolerances (PP
4F6829); in
or on the following raw agricultural commodities:
Fruit,
pome (Crop Group 11) at 0.02 ppm
This group includes: |
Fruit,
stone (Crop Group 12) at 0.02 ppm.
This
group includes:
|
•
apple
• apple, dried pomace
• apple, juice
• apple, wet pomace
• crabapple
• fruit, pome
• loquat
• mayhaw
• pear
• pear, oriental
• quince |
•
apricot
• cherry, sweet
• cherry, tart
• fruit, stone
• fruit, stone, except plum, prune, dried
• nectarine
• peach
• plum
• plum, chickasaw
• plum, damson
• plum, japanese
• plum, prune
• plum, prune, dried
• plum, prune, fresh |
-- Note
from FAN: Dried fruits will have
higher levels of pesticide compared to fresh fruits. One would
expect the residues on dried fruits to be several times more
because of the water lost in drying. Dried fruit weighs at
least 2X less and maybe as much as 6X or more times less than
the fresh fruit.
-- The
toxicological profile for flumioxazin which supports this
petition for tolerances was published in the Federal
Register of April 18, 2001 (66 FR 19870) (FRL-6778-5).
-- Note
new language from EPA on Cumulative
Effects
Section
408(b)(2)(D)(v) requires that the Agency must consider
``available information'' concerning the cumulative effects
of a
particular pesticide's residues and ``other substances that
have a
common mechanism of toxicity.'' Available information in
this context
include not only toxicity, chemistry, and exposure data,
but also
scientific policies and methodologies for understanding
common
mechanisms of toxicity and conducting cumulative risk assessments.
Although, the Agency has some information in its files that
may turn
out to be helpful in eventually determining whether a pesticide
shares
a common mechanism of toxicity with any other substances,
EPA does not
at this time have the methodologies to resolve the complex
scientific
issues concerning common mechanism of toxicity in a meaningful
way for
most registered pesticides.
--
Note EPA's retention of a Safety
Factor
The
FQPA safety factor (as required by the Food Quality Protection
Act
of August 3, 1996) has been retained at 10x in assessing
the risk posed
by flumioxazin. The
reasons for retaining the 10x safety factor are as
follows. First, there is evidence
of increased susceptibility of rat
fetuses to in utero exposure to flumioxazin by the oral
and dermal
route in the prenatal developmental toxicity studies in
rats. In
addition, there is evidence of increased susceptibility
of young
animals exposed to flumioxazin in the 2-generation reproduction
toxicity study in rats. Finally, there is concern for the
severity of
the effects observed in fetuses and young animals when compared
to
those observed in the maternal and parental animals.
|
| Nov
10, 2004 |
OPP-2004-0232 |
Three
Pesticide Emergency Exemptions.
• Louisiana
--- Crisis:
On May 7, 2004, for the use of flumioxazin
on sweet potatoes to control
annual broadleaf weeds. This program ended on July 15, 2004.
Contact: (Libby Pemberton)
--- Specific: EPA authorized the use of flumioxazin
on sweet potatoes to control
annual broadleaf weeds; May 13, 2004 to July 31, 2004.
Contact: (Libby Pemberton)
• Mississippi - EPA authorized
the use of flumioxazin on sweet
potatoes to control annual broadleaf weeds; May 13,
2004 to July 31, 2004. Contact: (Libby Pemberton) |
| August
25, 2004 |
OPP-2004-0212 |
Valent.
Pesticide Tolerances.
FINAL
RULE. The
nature of the toxic effects caused by flumioxazin are discussed
in a March 31,
2004 Federal Register document
| Tolerances
for Commodity |
PPM |
| Almond
(hulls) |
0.70 |
| Almond
(nutmeat) |
0.02 |
| Garlic
(bulb) |
0.02 |
| Grape |
0.02 |
| Onion
(dry bulb) |
0.02 |
| Peppermint
(tops) |
0.04 |
| Pistachio. |
0.02 |
| Shallot
(bulb) |
0.02 |
| Spearmint
(tops) |
0.04 |
| Sugarcane
(cane) |
0.20 |
| Tuberous/corm
vegetables (Subgroup 1C) • |
0.02 |
| •
Subgroup
1C includes:
arracacha
• arrowroot • artichoke, chinese • artichoke,
jerusalem • canna, edible • cassava •
chayote root • chufa • dasheen • ginger
• leren • potato • potato culls •
potato granules flakes • potato peel, wet •
potato processed potato waste • potato, specialty
• sweet potato • tanier • turmeric •
yam bean • yam, true |
| Excerpts
from Table 2.--Summary of Toxicological Dose and Endpoints
for Flumioxazin for Use in Human Risk Assessment |
|
Exposure Scenario |
Dose
Used in Risk
Assessment, Interspecies and Intraspecies and any Traditional
UF |
Special
FQPA SF and Level of Concern for Risk Assessment |
Study
and Toxicological Effects |
Acute
dietary (females 13-49 years of
age) |
NOAEL
= 3 mg/kg/day
Acute RfD = 0.03 mg/kg day. |
Special
FQPA SF = 1
aPAD = acute RfD/FQPA
SF = 0.03 mg/kg/day. |
Oral
developmental and supplemental prenatal studies (rat)
LOAEL = 10 mg/kg/day
based on cardiovascular effects (especially
ventricular septal defects in fetuses) |
| Chronic
dietary (all populations) |
NOAEL = 2 mg/kg/day
UF = 100
Chronic RfD = 0.02 mg/kg/day. |
Special
FQPA SF = 1
cPAD = chronic RfD/FQPA
SF = 0.02 mg/kg/day. |
2-Year
chronic/ carcinogenicity study (rat)
LOAEL = 18 mg/kg/day based on increased
chronic nephropathy in males and decreased hematological
parameters in females
(Hgb, MCV, MCH and MCHC) |
--
EPA determined that the special 10X SF to protect infants
and children should be removed.
The FQPA factor is removed because developmental toxicity
and offspring toxicity NOAELs/LOAELs are well characterized;
there is a well-defined dose-response curve for the cardiovascular
effects and the
endpoints of concern are used for overall risk assessments
are
appropriate for the route of exposure and population subgroups.
|
| Aug
18, 2004 |
OPP-2004-0054 |
Notice
of Receipt of Requests To Voluntarily Cancel Certain Pesticide
Registrations.
| Registration
No. |
Product
Name |
EPA
Company No. |
Company
Name and Address |
| 059639
WA-03-0003 |
Valor
Herbicide |
059639
|
Valent
U.S.A. Corp.,
1600
Riviera Ave. Suite 200, Walnut
Cre, CA 94596 |
|
| March
31, 2004 |
OPP-2004-0089 |
Valent.
Pesticide Tolerance.
FINAL
RULE.
| Commodity |
PPM |
| Cotton,
gin byproducts |
0.60 |
| Cottonseed
|
0.02 |
|
| March
17, 2004 |
OPP-2004-0047 |
IR-4;
Valent. Pesticide
tolerance petition.
1.
PP 3E6777 proposes tolerances for peppermint,
tops; peppermint,
oil; spearmint, tops; and spearmint, oil at 0.04 ppm.
2.
PP 3E6788 proposes tolerances for onion,
dry bulb; garlic, bulb;
and shallot, bulb at 0.02 ppm.
3. PP 3E6779 proposes tolerances for vegetable,
tuberous and corm
subgroup 1C at 0.02 ppm.
[This
group includes: arracacha; arrowroot; artichoke,
chinese; artichoke, jerusalem; canna, edible; cassava; chayote
root; chufa; dasheen; ginger; leren; potato; potato culls;
potato granules flakes; potato peel, wet; potato processed
potato waste; potato, specialty; sweet potato; tanier; turmeric;
yam bean; yam, true.]
The toxicological
profile for flumioxazin which supports thesepetitions for tolerances was previously published in the Federal
Register of April 18, 2001
•
Infants and children-- Safety
factor for infants and children.The FQPA safety factor has been retained at 10X in assessing
the risk posed by flumioxazin. The reasons
for retaining the 10X safety factorare as follows. First, there is evidence
of increased susceptibility of rat fetuses to in utero exposure to flumioxazin by the oral
and dermal route in the prenatal developmental toxicity studies in rats.
In addition, there is evidence of increased susceptibility of
young
animals exposed to flumioxazin in the 2-generation reproduction toxicity study in rats. Finally, there is concern for the
severity of the effects observed in fetuses and young animals when compared
to those observed in the maternal and parental animals.
Since the additional 10X safety factor has been retained to
account for the apparent increased susceptibility from prenatal or
postnatal exposures to flumioxazin, it would be appropriate to apply
the extra 10X safety factor to only selected subpopulations, e.g. infants
and children <6 years old and females >13 years old. For
these assessments, however, the 10X safety factor has been
applied to all population subgroups for all exposure durations
(acute and chronic), thus making these assessments additionally
conservative. |
| Nov
26, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0358 |
Requests
for Pesticide Emergency Exemptions.
1 Approval:
-- Louisiana Department of Agriculture
and Forestry. Crisis. On June 19, 2003, for the use of flumioxazin
on sweet potatoes to control weeds.
This program ended on July 15, 2003. A ``crisis exemption''
is initiated by a State or Federal agency (and is confirmed
by EPA) when there is insufficient time to request and obtain
EPA permission for use of a pesticide in an emergency.
3 Denials:
-- Arkansas State Plant Board.
Denial. On August 26, 2003 EPA
denied the use of flumioxazin on cotton to control broad
leaf weeds. This request was denied because the criteria for
an emergency situation were not met.
--
Louisiana Department of Agriculture
and Forestry. Denial.
On August 26, 2003 EPA denied the use
of flumioxazin on cotton to control broad leaf weeds.
This request was denied because the criteria for an emergency
situation were not met.
-- Mississippi Department of Agriculture
and Commerce. Denial. On August
26, 2003 EPA denied the use of flumioxazin
on cotton to control broad leaf
weeds. This request was denied because the criteria for an emergency
situation were not met. |
| Aug
27, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0253 |
Pesticide
tolerance for Emergency Exemption. This
regulation establishes a time-limited tolerance for residues
of flumioxazin in or on sweet potato,
roots at 0.02 ppm in connection with a crisis exemption
declared by the State of Louisiana. This regulation
establishes a maximum permissible level for residues of flumioxazin
in this food commodity. The tolerance will expire and is revoked
on June 30, 2006.
-- parent
flumioxazin and the metabolites 482-HA and APF are the residues
of concern in drinking water.
-- Acute Dietary. NOAEL = 3.0. Cardiac
effects (interventricular
septal
defects)
were seen
in the oral developmental
and supplemental
prenatal
studies in rats.
-- Chronic Dietary. NOAEL = 2. Kidney
effects were seen in males and anemia
was seen in females in the 2-year toxicity study in
rats.
-- FQPA Safety Factor. A 10x Safety factor was retained because
(1) there
was evidence of increased
susceptibility
of fetuses exposed to flumioxazin by both the oral and dermal
route in the prenatal developmental toxicity studies in rats,
(2) there was evidence of increased susceptibility of young
animals exposed to flumioxazin in the 2-generation reproduction
toxicity in rats, and
(3) there is concern for the severity of the effects in fetuses
and young animals when compared to the maternal or parental
animals. |
| Dec
31, 2002 |
OPP-2002-0349 |
Valent.
Pesticide tolerance
petitions. EPA has received pesticide petitions (PP
1F6296, 0F6171) from Valent U.S.A. Corporation, 1333
North California Boulevard, Suite 600,
Walnut Creek, California 94596-8025 proposing to amend 40 CFR
part 180 by establishing a tolerance for residues of the herbicide
chemical flumioxazin
| In
or on the raw agricultural commodities: |
PPM |
| Cotton,
gin byproducts |
0.60 |
| Cotton
|
0.02 |
| Grape |
0.02 |
| Almonds |
0.02 |
| Almond,
hulls |
0.70 |
| Sugarcane |
0.20 |
Mechanistic studies. A series of scientific studies were conducted
to examine the mechanism and species differences in the production
of developmental toxicity by flumioxazin. This research demonstrates
clear species differences between rats, rabbits, mice, and (in
vitro) humans and indicates a high degree
of correlation between the interruption of heme synthesis and
the production of developmental toxicity in rats. The
data support that the rat is a conservative model for use in
the risk assessment for humans. Specifically the studies demonstrate
that:
• Flumioxazin interferes with normal
heme biosynthesis resulting in sidroblastic anemia and porphyria
in adult rats.
• 14C-Flumioxazin administered to pregnant rats on
day 12 of gestation crosses the placenta and reaches the rat
fetus at maximum levels of radiocarbon (and flumioxazin),
4 hours later.
• No clear pattern of adsorption, distribution, metabolism,
or excretion was evident which could account for the species-specific
development toxicity in rats.
• The critical period of sensitivity
to the developmental effects of flumioxazin in rats is day 12
of gestation. This correlates with the peak
period of protoporphyrin IX (PPIX) accumulation in maternal
rat liver and the rat fetus.
• A histological examination of rat fetus indicated signs
of fetal anemia within 6 hours after
dosing, but no histological changes in
the fetal rat heart were observed until 36 or 48 hour after
treatment. No effects were observed in rabbit fetus treated
in the same manner as the rats.
• Other observations in the pathogenesis of the developmental
effects of flumioxazin in rat fetuses included: enlarged
heart, edema, anemia (decreased red blood cell count and hemoglobin),
delayed closure of the interventricular foramen, reduced serum
protein and incomplete/delayed ossification of the ribs.
• The observation of enlarged heart, edema and anemia
preceding the occurrence of fetal mortality suggest these effects
may be instrumental in the cause of fetal
deaths.
• The occurrence of an enlarged heart preceding the failure
of interventricular foramen closure could be related to the
pathogenesis rather than a direct toxic effect of flumioxazin
on cardiac tissue.
• A strong correlation exists between PPIX accumulation,
an indicator of disrupted heme synthesis, and developmental
toxicity. Evidence of this correlation exists on the basis of
species differences between rats and rabbits; the
critical period of sensitivity in the rat; and compound-specific
differences with two chemicals structurally
related to flumioxazin, one which produces developmental
effects in rats and one which does not. |
| Nov
27, 2002 |
OPP-2002-0313. |
EPA
denied 2 Emergency Exemption requests for the use of flumioxazin:
-- Louisiana:
Denial: On July 18, 2002, EPA denied
the use of flumioxazin on cotton to control weeds.
This request was denied because it did not meet the criteria
of an urgent, non-routine situation based on the availability
of registered alternatives.
-- Mississippi:
Denial: On July 18, 2002 EPA denied
the use of flumioxazin on cotton to control weeds.
This request was denied because it did not meet the criteria
of an urgent, non-routine situation based on the availability
of registered alternatives. |
| Nov
14, 2001 |
OPP-181082 |
- Requests
for Pesticide Emergency Exemptions.
- Louisiana:
On
August 3, 2001, EPA denied the use of flumioxazin on sugarcane
to control red morning glory species. This request was denied
based on the fact that it was not demonstrated that an urgent
and non-routine situation exists due to the presence of
red morning glory species. Additionally, the economic data
were not sufficient to demonstrate that significant economic
losses could be expected.
- Louisiana:
On
August 9, 2001, EPA denied the use of flumioxazin on cotton
to control pigweed and other weeds. This request was denied
based on the fact that it was not demonstrated that an urgent
and non-routine situation exists due to the presence of
pigweed and other weeds in cotton.
- Mississippi:
On August 9, 2001, EPA denied the use of flumioxazin on
cotton to control pigweed and
other weeds. This request was denied based on the fact that
it was not demonstrated that an urgent and non-routine situation
exists due to the presence of pigweed and other weeds in
cotton.
|
| April
18, 2001 |
OPP-301116 |
VALENT
- Pesticide
Tolerances for residues in or on soybean seed and peanut nutmeat
at 0.02 ppm. - FINAL RULE. |
| Feb
14, 2001 |
PF-996 |
VALENT
- Petition
to Establish Tolerances; for residues in or on the raw
agricultural commodities soybean seed and peanut nutmeat at
0.01 ppm, and on sugar cane at 0.2 ppm. |
| Sept
6, 2000 |
PF-966 |
VALENT
- Petition
to Establish Tolerances. Pesticide Petitions PP
7F4841 and PP 0F6171 for
residues in or on the raw agricultural commodities soybean
seed and peanut
nutmeat at 0.01 ppm and on sugarcane cane at 0.2 ppm.
Children
...
Developmental toxicity was observed
by both oral and dermal routes in rats. Therefore,
reliable data support use of the standard 100-fold
uncertainty factor and an additional uncertainty factor of
10X for flumioxazin to be further protective of infants and
children.
Developmental
toxicity studies. Flumioxazin
shows developmental toxicity in the absence of maternal toxicity
in rats. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that the effect is
specifically related to the inhibition of heme synthesis,
that the effect shows considerable species specificity, and
that the rat is a conservative surrogate species for the potential
for developmental toxicity in man. No developmental toxicity
was observed in rabbits. Developmental toxicity to the pups
was seen in the rat reproduction study at doses that were
not toxic to the parental animals.
Reproductive
toxicity study.
In the 2-generation reproduction study in the rat dietary
levels of 0, 50, 100, 200 and 300 ppm established a systemic
NOAEL of 200 ppm based on increased clinical signs (both sexes
and generations); mortality, gross and histopathology
findings in the liver (F1 females); decreased body weight/
weight gain (F0 and F1 females during gestation, F1 males
during premating) and decreased food consumption (F0 and F1
females during lactation). The reproductive NOAEL of 100 ppm
was mainly based on developmental toxicity at 200 ppm. Observed
at 200 ppm were a decreased number of
liveborn pups and reduced pup body weights. At
300 ppm the following effects were observed: decreased pup
body weight (both generations); decreased
number of live pups/litter and viability index (both generations);
increased incidence of abnormalities of the reproductive organs
(predominately atrophied or hypoplastic testes and/or epididymides
in F1 males); decreased gestation index (F0 females); decreased
mating and fertility indices (F1 males) and increased clinical
signs (F1 pups).
Rats.
In
the definitive rat oral developmental toxicity study, pregnant
rats were administered oral doses of 0, 1, 3, 10 or 30 mg/kg/
day of flumioxazin technical on days 6 through 15 of gestation.
No maternal deaths were observed at any dosage and no treatment-related
effects on clinical signs or food consumption were noted.
A decrease in maternal body weight gain was found at 30 mg/kg/day.
The number of live fetuses and fetal body weights were decreased
in the 30 mg/kg/day group and the incidence of embryo mortality
tended to be higher but was not statistically significant
...
The incidence of fetuses with cardiovascular abnormalities,
primarily VSD, was increased in the 30 mg/kg/day group. Other
developmental effects observed at 30 mg/kg/day included an
increase in the incidence of wavy ribs and curvature of the
scapula, and a decrease in the number of ossified sacrococcygeal
vertebral bodies. Based on these findings,
a maternal NOAEL of 30 mg/kg/day and a developmental NOAEL
of 3 mg/kg/day are proposed.
Mechanistic
Studies.
A series of scientific studies were conducted to examine the
mechanism and species differences in the production of developmental
toxicity by flumioxazin ... Specifically
the studies demonstrate that: Flumioxazin interferes with
normal heme biosynthesis
resulting in sidroblastic anemia and porphyria in adult rats.
\14\C-Flumioxazin administered to pregnant rats on day 12
of gestation crosses the placenta and reaches the rat fetus
at maximum levels of radiocarbon (and flumioxazin), 4 hours
later ... The critical period of sensitivity to the developmental
effects of flumioxazin in rats is day 12 of gestation. This
correlates with the peak period of protoporphyrin IX (PPIX)
accumulation in maternal rat liver and the rat fetus.
A
histological examination of rat fetus indicated signs of fetal
anemia within 6 hours after
dosing, but no histological
changes in the fetal rat heart were observed until 36 or 48
hour after treatment ...
Other
observations
in the pathogenesis of the developmental effects of flumioxazin
in rat fetuses included: enlarged heart, edema, anemia
(decreased red blood cell count and hemoglobin), delayed closure
of the interventricular foramen, reduced serum protein and
incomplete/delayed ossification of the ribs. The observation
of enlarged heart, edema and anemia preceding
the occurrence of fetal mortality suggest these effects may
be instrumental in the cause of fetal deaths. The
occurrence of an enlarged heart preceding the failure of interventricular
foramen closure could be related to the pathogenesis rather
than a direct toxic effect of flumioxazin on cardiac tissue.
A strong correlation exists between PPIX accumulation, an
indicator of disrupted heme synthesis, and developmental toxicity.
Evidence of this correlation exists on the basis of species
differences between rats and rabbits; the critical period
of sensitivity in the rat; and compound-specific differences
with two chemicals structurally related to flumioxazin, one
which produces developmental effects in rats and one which
does not.
There
are other pesticidal compounds that are structurally related
to flumioxazin and have similar effects on animals ... Valent
will submit information for EPA to consider concerning
potential
cumulative effects of flumioxazin consistent with the schedule
established
by EPA in
the Federal Register (August 4, 1997) (62 FR 42020) (FRL-5734-4)
and other subsequent EPA publications pursuant to the Food
Quality Protection Act (FQPA) |
| Nov
13, 1996 |
na |
- VALENT
- Issuance
of Experimental Use Permit:
- 59639-EUP-118;
allows the use of 91.78 pounds (45.89 each year) of the
herbicide on 480 acres of soybeans to evaluate the control
of various broadleaf weeds. The program is authorized only
in the States of Arkansas, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas,
Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi,
Missouri, Nebraska, North Carolina, Ohio, Tennessee, and
Virginia. The experimental use permit is effective from
August 1, 1996 to August 1, 1998.
|
|