|
Return to
Adverse Effects
Abstracts
NTIS Reports
ACTIVITY: Acaracide,
Insecticide (pyrazole),
Wood Preservative (to
control termites)
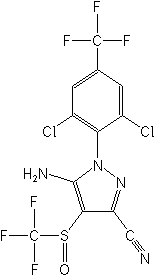
CAS NAME:
5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-[(trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl]-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile
Structure:
Adverse
Effects:
Body
Weight Decrease
Bone
Brain
Cancer: Possible Human Carcinogen - THYROID
Cholesterol
Clastogenicity
CNS
Dermal
Endocrine:
Altered Sex Ratio
Endocrine: Pituitary - (disruption
in the thyroid-pituitary status)
Endocrine: Suspected Endocrine Disruptor
Endocrine: Testicular
Endocrine: Thyroid
Kidney
Liver
Lung
Reproductive/Developmental
Stomach
|
Environmental
Effects:
Contamination
incident:
2001:
Crawfish farmers in Louisiana file Class Action against the
makers of the fipronil insecticide ICON, Rhone-Poulenc/Aventis,
for killing crawfish.
2004: Farmers and landowners in Class Action awarded $45 million.
Environmental
--
Highly toxic to rainbow trout and very highly toxic to bluegill
sunfish
-- The sulfone metabolite is 6.3 times more toxic to rainbow
trout and 3.3 times more toxic than the parent compound to
bluegill sunfish.
-- High toxicity to freshwater aquatic invertebrates. The
sulfone metabolite is 6.6 times more toxic and the desulfinyl
photodegradate 1.9 times more toxic on an acute basis to freshwater
invertebrates than the parent compound.
-- Highly toxic to upland game birds.. The sulfone metabolite
is more toxic than the parent compound to certain bird species.
This metabolite has shown a very high toxicity toward upland
game birds ...
-- Highly toxic to bees, lizards, and gallinaceous birds |
Regulatory
Information
(only comprehensive for the US) |
| US
EPA Registered: |
Yes |
| US
EPA PC Code: |
129121 |
| California
Chemical Code |
3995 |
| US
Tolerances: |
CFR
180.517 |
| FDA
LMS Code: |
A82 |
US
EPA Permit Date
and Registrant: |
2004
- Bayer Crop Science
2003 - Bayer
Environmental Science
1996 - Rhone-Poulenc |
Registered
use in
(includes only a limited list of countries)
|
Australia,
Denmark, Finland, Hungary, India, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand,
Philippines, US
Africa: Burkina
Faso, Cape Verde, Chad, Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, Madagascar, Mali,
Mauritania, Niger, Senegal, South Africa, Tanzania, Uganda
|
| Japan's
Maximum Residue Levels (MRLs) |
Partial
list:
Banana, Broccoli, Button mushroom, Cabbage,
Cauliflower, Corn, Potato, Rice, Sugar Beet, Sugarcane |
US
Maximum Residue Levels permitted
in food commodities
|
Permitted
in or on 18 food commodities, including:
Cattle, Corn, Egg, Goat, Hog, Horse, Milk,
Poultry, Rice, Sheep |
U.K.
|
Proposed
use in compost used for Container-grown ornamentals, outdoors
and under glass (trade name 'Vi-Nil GR' or 'Regent IGR' |
| Other
Information |
| Molecular
Formula: |
C12H4Cl2
F6 N4OS |
| Entry
Year: |
1994 |
| Manufacturers: |
Rhone-Poulenc,
Aventis |
| Other
Names: |
RPA-030,
MB 46030,
264-EUP-95,
264-EUP-100,
264-EUP-101,
264-EUP-104,
264-EUP-105,
264-EUP-117,
264-EUP-119,
PP-7F4832
PP-5F4426
EXP 60818A |
| Manufacture
site: |
FRANCE:
formerly Rhone-Poulenc, Montlucon
FRANCE:
Aventis CropScience SA, AllÕ Chem, Montlucon
FRANCE:
Aventis CropScience SA, Rue de Verdun
F-76410, Saint Aubin-les--Elbeuf |
| Of
special interest: |
| PAN
Data |
•
new - Fipronil:
Material Safety Data Sheets and Labels |
May
28, 2007 - Neonicotinoids,
such as Fipronil, a suspect in
honeybee colony collapse disorder.
"... In
sublethal doses, however, research has shown that imidacloprid
and other neonicotinoids, such as fipronil, can impair honeybees'
memory and learning, as well as their motor activity and
navigation. When foraging for food and collecting
nectar, honeybees memorize the smells of flowers and create
a kind of olfactory map for subsequent trips... The possibility
that neonicotinoids are at the heart of the bee die-off
implies a far more complex problem because of the widespread
use of pesticides. Every year these chemicals are applied
to hundreds of millions of acres of agricultural lands,
gardens, golf courses and public and private lawns across
the United States. Their use on major crops nearly tripled
between 1964 and 1982, from 233 million pounds to 612 million
pounds of active ingredients. And since then, their use
has exploded. By 1999, the U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency reported 5 billion pounds of pesticides used on U.S.
crops, forests, lawns, flowers, homes and buildings..".
The Star-Ledger (Newark, N.J.)
|
May
18, 2005
- Tick
box plan kicked out of Nahanton.
By Karla Hailer-Fidelman. Newton TAB (MA)
|
| May
6, 2005 - Australia: The Northern Territory Government is considering
fipronil as an alternative to the use of Mirex, which is being
phased out. Fipronil is approved for citrus and amenity trees
and "it's already been introduced to the grape farmers
at Ti-Tree last year. There are plans to extend the use to mangoes,
cashews and rambutans as well." Ref: ABC
News Online. |
| April
15 2005 - Ask
Dr. D., The Bolton Common (MA) and FAN's response. |
| 2004-2006
- US EPA CHEERS study in Jacksonville, Duval County, Florida.
This 2-year study of children's exposure to selected pesticides
and chemicals has ignited enormous controversy. Fipronil
was one of 16 pesticides selected to be monitored in children
(ages 0-3 years). See FAN's
updates on this study. |
2004.
SPECIAL: Louisiana
crawfish farmers and landowners who suffered severe losses
due to Icon contamination receive $45 million in a Class Action
settlement. See:
• A
little background on the geneology and events of the insecticide
Icon
• Index
to some documents and reports pertaining to the Class Action
•
News
Items related to the settlement |
| April
2004 - Evaluation
on: Fipronil (Horticultural Uses). UK Dept. for Environment,
Food & Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate. Note:
while the UK "evaluation reports" contain a lot of
data, their availability online are the model for user unfriendly:
after you have waited for the long download time, you can neither
search nor copy the document. |
| September
2003 - The
Reconsideration of Approvals and Registrations Relating to FIPRONIL.
REVIEW SCOPE DOCUMENT. Australian
Pesticides & Veterinary Medicines Authority Canberra Australia. |
| 2001
- 2002 -
Class Action suit charges
Aventis for pesticide damaged crawfish farms. The
crawfish farmers allege that the pesticide ICON (Fipronil) devastated
Louisiana's 2000 and 2001 crawfish crop after its introduction
on the rice seed in 1999. In 2000, Louisiana's crawfish production
dropped from 41 million pounds to 16 million pounds. |
2002
- Aventis Environmental Science has agreed to acquire the Maxforce
product line from Clorox for an undisclosed sum. The
Maxforce line, based on firponil or hydramethylnon, consists
of a range of products to control ants and cockroaches, and
is sold to the professional pest control markets in over 100
countries. Clorox will continue to sell its consumer insecticies,
including the "Combat" and "Black Flag"
branded products, into the consumer markets. Aventis already
has the exclusive rights to market the Maxforce line in Europe,
whilst also selling it in South America.
Under the new agreement, Aventis will now have global rights
to sell Maxforce to the professional pest control markets.
Ref: February 2002. Agrochemical
Service. PhytoPhile. |
December
2001 - ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
OF FIPRONIL by Pete Connelly. Environmental Monitoring
Branch, Department of Pesticide Regulation, California Environmental
Protection Agency. |
| November
2000 -
Health and Environmental Effects of Fipronil. By
C.C.D. Tingle, J.A. Rother, C.F. Dewhurst, S. Lauer & W.J. King.
Pesticide Action Network UK. |
2000
-
"P" is for Poison.
Update on Pesticide Use in California Schools, by
TM Olle. A report by Californians for Pesticide Reform. Also
available at: http://www.calpirg.org/healthyschools/PDFs/healthyschools.pdf
The fluorinated pesticides cited in this
report are: Benefin
(Benfluralin), Bifenthrin,
Bromethalin, Cyfluthrin, Fipronil,
Fluazifop-butyl, Hydramethylnon, Lambda-cyhalothrin, Sulfuryl
fluoride (Vikane), Trifluralin |
| Abstracts |
| Reports
available from The National Technical Information Service |
| May
1996 -
New Pesticide Fact Sheet. US EPA |
| Insecticide
Products - partial list |
| June
2002. Animal Residue Data Sheet.
Australia National Regulatory Authority
(NRA) for Agricultual & Veterinary Chemicals. |
| August
10, 2004 |
August
10, 2004: a North Carolina hockey team (the Hurricanes) accepts
sponsorship deal with BASF-Termidor. Termidor
is a termite insecticide with fipronil its active ingredient. |
| May
9, 2003 |
US
EPA grants public health exemption to New York State Bureau
of Pesticides to control vectors for Lyme Disease.
MAXFORCE Tick Management System,
an unregistered end-use product, containing 0.70% fipronil,
manufactured by Bayer Environmental
Science, may be used. Applications may be made until
December 31, 2003. |
| June 2002 |
In
Australia when Fipronil is used for "Control
of Argentine ants in vineyards - As a soil injection for control
of termites in immature, non-bearing citrus and mango orchards"
no maximum
residue levels are required. Ref: June
2002. Table 5. Uses of substances where maximum residue limits
are not necessary. Australian National Registration Authority
for Agricultural Veterinary Chemicals. The MRL Standard. Maximum
residue limits in food and animal feedstuff.
http://www.nra.gov.au/residues/mrl5.pdf
|
| April
17, 2002 |
Bayer's
acquistion of Aventis. Discussion of Acrinathrin, Beta-Cyfluthrin,
Cyfluthrin, Ethiprole, Fipronil,
Fluquinconazole. European Commission press release. |
| Dec 10,
2001 |
Australia:
"Current List.
RECORD OF APPROVED ACTIVE CONSTITUENTS FOR CHEMICAL PRODUCTS." |
| June 2000 |
Article
in Pesticide News, No. 48. |
| Oct 2001
|
Glossary
of Pesticide Chemicals. A listing of pesticides subject
to analysis of residues in foods and feeds by the US Food and
Drug Administration. |
| April
2000 |
Food
and Drug Administration Pesticide Residue Monitoring. -
Table 3. Pesticides detectable by methods used in 1999 regulatory
monitoring. |
| 2000 |
Pilot
program to test insecticide on fire ants at military bases in
South Carolina. |
| Oct 1998
|
Structural
Pest Management pesticides. FAN's
compilation of information cited on fluorine and organofluorine
pesticides published in General Pest Management, Category 7A.
A Guide for Commercial Applicators. Prepared by: Carolyn Randall,
MSU Pesticide Education Program. Published by MSU
Pesticide Education (Michigan State University). MSU
manual number: E-2048. |
| |
Current
Uses in Pets |
| Aug 2001 |
-
IR-4: New
Products/Transitional Solution List - This
list contains brief descriptions of numerous new pest control
materials that have been introduced over the last several years.
Additionally, it contains information on some "older"
crop protection chemicals that are believed to have room for
new uses. This List includes Fipronil |
| June
14, 2001 - Implementation
of the Community Strategy for Endocrine Disruptors - a
range of substances suspected of interfering with the hormone
systems of humans and wildlife. Communication from the Commission
to the Council and the European Parliament. Commission of
the European Communities, Brussels COM (2001) 262 final. (More
information available at: http://europa.eu.int/comm/environment/docum/01262_en.htm
)
This
document presents a "priority list of substances for
further evaluation of their role in endocrine disruption.
During 2000, a candidate list of 553 man-made substances and
9 synthetic/natural hormones has been identified." Organofluorine
pesticides in this list include: |
| Substances
included on the Endocrine Disruptor Liist |
CAS
No. |
Substances
included on the Endocrine Disruptor Liist |
CAS
No. |
| Bifenthrin |
82657-04-3
|
Flutriafol |
76674-21-0 |
| Cyhalothrin
(@Karate) |
91465-08-6 |
Fluvalinate |
69409-94-5 |
| Diflubenzuron |
35367-38-5 |
Prodiamine |
29091-21-2 |
| Epoxiconazole |
- |
Stannane,
tributylfluoro [Tributyltin fluoride] |
1983-10-4 |
| Fipronil |
120068-37-3 |
Thiazopyr |
- |
| Fluazifop-butyl |
69806-50-4
|
Trifluralin |
- |
US
Federal Register
••
Note: Due to length, the following is a partial
list. Click here
to see full list of FR entries.
|
| Date
Published |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| August 25, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0659 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions; Agency Decisions and State and Federal
Agency Crisis Declarations
• Oregon: On May 10, 2006, for the use of fipronil on
rutabaga and turnip to control
cabbage maggots. This program is expected to end on September
30, 2006. |
| August
24, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0206 |
BASF
& IR-4:
Pesticide tolerance
petitions.
Pesticide
petition 5F6948 from BASF
for residues of mixture comprising
fipronil, and its metabolites
5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-[(trifluoromethyl)
sulfonyl]-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile
and
5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-[(trifluoromethyl)thio]-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile
and its photodegradate 5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-[(1R,S)-(trifluoromethyl)]-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile
in or on the raw agricultural commodities |
| corm
vegetables (crop group 1-C) |
0.04 ppm |
|
and indirect and inadvertent residues on |
| wheat,
grain |
0.005
ppm |
| wheat,
forage |
0.02 ppm |
| wheat,
hay and straw |
0.03
ppm |
Pesticide
petition 2E6490 from the Interregional Research Project
No. 4 (IR-4),
for residues of
mixture comprising fipronil, and its metabolites
5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-[(trifluoromethyl)
sulfonyl]-1H-pyrazole-3-
carbonitrile
and
5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-[(trifluoromethyl)thio]-H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile
and its photodegradate
5-amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-[(1R,S)-(trifluoromethyl)]-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile
in or on the raw agricultural commodities: |
| onion
(dry bulb) |
0.02
ppm |
| garlic |
0.02
ppm |
| shallot
(dry bulb) |
0.02
ppm |
•
Fipronil and its sulfone and amide constitute
greater than 75% of the identified residues in all studies.
•
Reproductive and developmental toxicity. The
developmental toxicity NOELs in the rat
and rabbit were 20 mg/kg/day (HDT) and 1 mg/kg/day
(HDT), respectively.
Maternal toxicity was observed in the rat at the HDT as evidenced
by decreased body weight gain
and food efficiency. In
the rabbit, the maternal
toxicity NOAEL was less than 0.1 mg/kg/day, based
on reduced body weight gain and food efficiency at
all dose levels tested. In a two-generation
rat study, the NOEL for parental
(systemic) toxicity was 3 ppm (0.26 mg/kg/day for both sexes
combined), based on increased weight of the thyroid
glands and liver in males and females,
decreased weight of the pituitary
gland in females, and an increased incidence
of follicular epithelial hypertrophy in females at
30 ppm. The NOEL for reproductive toxicity was 30 ppm
(2.64 mg/kg/day for both sexes combined), based on clinical
signs of toxicity in pups, decreased litter size, decreased
pup body weights, decreased mating, decreased fertility index,
reduced pre- and postnatal survival, and delays in physical
development at 300 ppm (26.03 and 28.40 mg/kg/day for
males and females, respectively).
• In
a developmental neurotoxicity study in the rat,
the NOAEL for maternal toxicity was
10 ppm (0.91 mg/kg/day), based on decreased body weights
and body weight gain at 200 ppm (HDT;
15 mg/kg/day). Considerable maternal toxicity at the
HDT prevented adequate neurotoxicity evaluation of pups at
this dose level. There was no evidence of neurotoxicity
at 10 ppm (0.91 mg/kg/day), which was the NOAEL for developmental
neurotoxicity. The NOAEL for general
developmental toxicity was 0.5 ppm (0.05 mg/kg/day), based
on systemic effects consisting of decreases
in pup weights during lactation and increases in time of preputial
separation in males at 10 ppm.
• Subchronic
toxicity. The
NOAEL for systemic toxicity in
rat was 5 ppm (0.35 mg/kg/day
for both sexes combined), based on alterations in serum
protein values and increased weight of the liver and thyroid
at 30 ppm (1.93 and 2.28 mg/kg/day for males and females,
respectively). The
NOAELs in the dog
were 2 and 0.5 mg/kg/day for male and
female, respectively, based on clinical signs of toxicity
in males at 10 mg/kg/day and clinical signs of toxicity and
decreased body weight gain in females at 2 mg/kg/day.
The NOAEL for mice was 10 ppm
(1.27 and 1.72 mg/kg/day for males and females, respectively),
based on a possible decreased body weight gain at 25 ppm (3.2
and 4.53 mg/kg/day for males and females, respectively). A
repeated dose dermal study in the rabbit
had a systemic NOAEL of 5 mg/kg/day, based on decreased
body weight gain and food consumption at 10 mg/kg/day,
and a dermal irritation NOEL of 10.0 mg/kg/day (HDT).
• Subchronic
neurotoxicity study in
rats,
the NOEL was 5 ppm (0.301 and 0.351 mg/kg/day for males and
females, respectively), based on results of the
functional observational battery (FOB) at 150 ppm (8.89
and 10.8 mg/kg/day for males and females, respectively).
•
Chronic toxicity. The
NOAEL for systemic toxicity in a 1-year feeding study in the
dog was 0.3 mg/kg/day in females and 1 mg/kg/day in
males, based on clinical signs of neurotoxicity at 1 and 2
mg/kg/day in females and males, respectively.
The NOAEL for systemic toxicity in mice
was 0.5 ppm (0.06 mg/kg/day) based on
decreased body weight gain, decreased food conversion efficiency
in males, increased liver weights, and liver histopathology
at 10 ppm (1.3 mg/kg/day). Fipronil was not
carcinogenic when administrated to mice
at dose levels up to 60 ppm. The NOAEL
in a 2-year dietary study in
the rat
was 0.5 ppm (0.019 and 0.025 mg/kg/day
for males and females, respectively) based on
clinical signs of toxicity and alterations in clinical chemistry
and thyroid parameters at 1.5 ppm (0.059
and 0.078 mg/kg/day for males and females, respectively).
• Cancer. The EPA's Health Effects
Division Carcinogenicity Peer Review Committee classified
fipronil in Group C - Possible
Human Carcinogen, based on thyroid tumors observed in rats
at 300 ppm (HDT). Mechanistic data indicate that these tumors
are related to a disruption in the thyroid-pituitary status
and are specific to the rat. In
addition, there was no apparent concern for mutagenic activity.
Thus, it was recommended that RfD methodology, i.e. non-linear
or threshold, be used for the estimation of human risk.
• Acute neurotoxicity. The
NOEL was 2 mg/kg, based on decreases in body weight gain and
food consumption
in males and females during the week following treatment,
decreases in locomotor activity, hind-limb
splay and rectal temperature
6-hour post dosing in males and females, and decreases
in the proportion of males with an immediate righting reflex
on days 7 and 14, at 12 mg/kg/day. In
a rat developmental
toxicity study, the NOEL was 1 mg/kg/day, based
on the slight increase in fetal and litter incidence
of reduced ossification of several bones at 2.5 mg/kg/day.
•
Subchronic toxicity. The
NOAEL in the rat was 3 ppm (0.18
and 0.21 mg/kg/day in males and females, respectively), based
on clinical signs of toxicity in both sexes and decreased
body weight and body weight gain in males at 10 ppm.
The NOEL for the mouse was 0.5
ppm (0.08
mg/kg/day), based on the aggressive
and irritable behavior with increased motor activity in males
at 2 ppm. The
NOEL for the dog was 9.5 ppm
(0.29 mg/kg/day), based on behavioral
changes in females at 35 ppm (1.05 mg/kg/day).
• The rat chronic/carcinogenicity
study was negative for carcinogenicity. The LOAEL for
females was 0.5 ppm (0.032 mg/kg/day), based on clinical signs
of toxicity. There was no NOEL established. For males, the
NOAEL was 2 ppm (0.098 mg/kg/day), based on clinical signs
of toxicity, and stomach and lung histopathology at 10 ppm
(0.497 mg/kg/day).
• Endocrine
disruption.
Data from the reproduction/ developmental toxicity and short-
and long-term repeated dose toxicity studies with fipronil
in the rat, rabbit, mouse, or dog, do not suggest any endocrine
disruption activity. This information is based on the absence
of any treatment-related effects from the histopathological
examination of reproductive organs as well as the absence
of possible effects on fertility, reproductive performance,
or any other aspect of reproductive function, or on growth
and development of the offspring. Evidence of offspring toxicity
was observed only in the presence of significant parental
toxicity. Fipronil disrupts the thyroid-pituitary
axis. However,
mechanistic studies have demonstrated that fipronil decreases
thyroid hormone levels in long-term studies via increased
clearance, rather than a direct effect on the thyroid. Concerns
related
to long-term exposure of fipronil are addressed in human risk
estimates, as the chronic RfD (0.0002 mg/kg/day) is based
on endpoints that include thyroid hormone related effects
in rats.
• Drinking Water. A
drinking water monitoring study for fipronil and relevant
metabolites in surface water from the corn growing regions
has been conducted (MRID 45526101).
The ground water values model by the EPA when the cotton use
was examined will also be used for comparison. The samples
were collected on regular intervals between April and August.
The water samples wereanalyzed for firponil and metabolites:
MB45950, MB46136, and MB46513.
• Post-application
exposure of children can occur from three scenarios:
(1) Incidental ingestion of fipronil pellets or granules;
(2) incidental ingestion of soil (hand to mouth) from fipronil
treated residential areas; and
(3) incidental ingestion (hand to mouth) of fipronil from
treated pets.
|
••
Note: Due to length, the above is a partial list.
Click here
to see full list of FR entries.
|
|