|
Return
to Index Page
Activity:
Solvent,
US EPA List 2 Inert (Halogenated organic)
Structure:
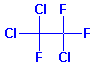
Adverse
Effects:
Brain
CNS
Heart
Liver
Lung
Tremors
Environmental
Fluorocarbon
vapors are 4 to 5 times heavier than air. Thus high concn
tend to accumulate in low-lying areas, resulting in hazard
of inhalation of concentrated vapors, which may be fatal.
/Fluorocarbons/
[Clayton, G.D., F.E. Clayton (eds.) Patty's
Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology. Volumes 2A, 2B, 2C, 2D,
2E, 2F: Toxicology. 4th ed. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons
Inc., 1993-1994. 1195]
Average
Daily Intake: The average daily in take of 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane
in air, (assume 13-31 parts/trillion(1,2)) is 2.0-4.8 ug/day(SRC).
[(1) Fabian P et al; J Geophys Res 90: 13091-3
(1985) (2) Brodzinsky R, Singh HB; pp. 23-184 in Volatile
Organic Chemicals in the Atmosphere: An Assessment of Available
Data Menlo Park, CA: SRI International (1982)]
NIOSH
(NOES Survey 1981-1983) has statistically estimated that
250,773 workers (79,790 of these are female) are potentially
exposed to 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane
in the US(1). Occupational exposure to 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane
may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this
compound at workplaces where it is produced or used. Due
to its long atmospheric residence time, the general population
is exposed to 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane
through inhalation of ambient air. Monitoring data indicate
that the general population may also be exposed to
1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane via ingestion
of contaminated water, and via inhalation and dermal contact
with this compound and other consumer products containing
this compound(SRC).
[(1) NIOSH; National Occupational Exposure Survey (NOES)
(1983)]
Average
Daily Intake: The average daily in take of 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane
in air, (assume 13-31 parts/trillion(1,2)) is 2.0-4.8 ug/day(SRC).
[(1) Fabian P et al; J Geophys Res 90: 13091-3
(1985) (2) Brodzinsky R, Singh HB; pp. 23-184 in Volatile
Organic Chemicals in the Atmosphere: An Assessment of Available
Data Menlo Park, CA: SRI International (1982)]
Ref:
Hazardous Substances Data Bank for 1,1,2-TRICHLORO-1,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANE
CASRN: 76-13-1.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/trichlorotrifluorome.toxnet.htm
|
Accidental
Death:
A
worker died while assisting three workers who were cleaning
out a Freon 113 vapor degreaser
at a chemical fuel plant. During this procedure solvent
was drained off and the residue on the bottom of the degreaser
was cleaned out. The company had written instruction for
cleaning out the degreasing tank. All but about 1 gallon
of the solvent had been drained off. After taking a break
for lunch, the three men returned, picking up the fourth
worker who was experienced in the cleaning operation. Using
removable wooden stairs two men, including the experienced
worker, climbed into the tank. Shortly thereafter both men
had trouble breathing and exited the tank. the experienced
worker collapsed to the floor and died shortly. The other
worker experienced no ill effects. The men were using air
purifying respirators designed for limited use with organic
solvents. The cause of death had not been determined.
[NIOSH; FACE Report: Worker Dies While Cleaning
Freon 13 Degreasing Tank in Virginia, November 21, 1986
Report No. FACE-87-17, 6pp (1986)]
|
Freon
113. Standards for Inhalation Exposure
A. Occupational Exposure Limits (NIOSH, 1997; ACGIH,
1994).
|
1.
Ceiling Limit (C) (not to be exceeded at any time):
|
Not
established.
|
2.
Short-Term Exposure Limit (STEL or ST):
|
1,250
ppm (9,590 mg/m 3 )
|
3.
8-Hour Time Weighted Average (TWA):
|
1,000
ppm (7,670 mg/m 3 )
|
4.
10-Hour Time Weighted Average (TWA):
|
1,000
ppm (7,670 mg/m 3 )
|
5.
Immediately Dangerous to Life & Health (IDLH):
|
2,000
ppm (15,340 mg/m 3 )
|
Freon
113. Acute
Reference Exposure Levels (1-hour exposure)
(OEHHA, 1999)
|
1.
Level protective against mild adverse effects:
|
Not
established
|
2.
Level protective against severe adverse effects:
|
Not
established
|
3.
Level protective against mild adverse effects:
|
Not
established
|
Freon
113. Chronic
Reference Exposure Level (multiple years)
(OEHHA, 2002A)
|
Level
protective of adverse health effects:
|
Not
established.
|
Freon
113. Chronic
Reference Concentration (lifetime exposure)
(IRIS, 2003)
|
Level
protective of adverse health effects:
|
Not
established.
|
Ref:
September
24, 2003 (Revised). Released November 7, 2003)
- FREON [11, 12,
113]. Technical Support Document: Toxicology. Clandestine
Drug Labs/ Methamphetamine. Volume 1, Number 11. California
EPA, Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA),
Department of Toxic Substances Control.
|
Brain
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
.. A single case /was reported/ of sensorimotor neuropathy in
a woman who had worked as a laundress with trichlorotrifluoroethane
(Freon 113) for several years. Weakness,
pain, and paresthesias were most severe distally in the legs.
Electrodiagnostic testing was consistent with axonal
damage. Removal from exposure to trichlorotrifluoroethane
resulted in gradual recovery. [O'Donoghue, J.L. (ed.). Neurotoxicity
of Industrial and Commercial Chemicals. Volume II. Boca Raton,
FL: CRC Press, Inc., 1985. 110]
-- There is a significant accumulation of
fluorocarbons in brain, liver and lung compared to blood
levels, signifying a tissue distribution of fluorocarbons similar
to that of chloroform. [Clayton, G.D., F.E. Clayton (eds.) Patty's
Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology. Volumes 2A, 2B, 2C, 2D, 2E,
2F: Toxicology. 4th ed. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons Inc.,
1993-1994. 1203]
Ref: Hazardous Substances Data Bank for
1,1,2-TRICHLORO-1,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANE CASRN: 76-13-1.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/trichlorotrifluorome.toxnet.htm
CNS
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Human Toxicity Values: TCLO HUMAN INHALATION 4500 PPM; TOXIC
EFFECT: CNS EFFECTS [Sax, N.I. Dangerous
Properties of Industrial Materials. 6th ed. New York, NY: Van
Nostrand Reinhold, 1984. 1458]
-- Animal Toxicity Studies: Non-Human Toxicity Excerpts: THE CHIEF
EFFECTS OF EXPOSURE TO ... /TRICHLOROTRIFLUOROETHANE/
ARE DEPRESSION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
AND IRRITATION OF THE RESPIRATORY TRACT. SUCH EFFECTS OCCUR
IN ANIMALS AT CONCENTRATIONS ABOVE 12000 PPM. MILD LIVER CHANGES
HAVE BEEN NOTICED AT LEVELS SOMEWHAT BELOW THIS. [American Conference
of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Documentation of the Threshold
Limit Values for Substances in Workroom Air. Third Edition, 1971.
Cincinnati, Ohio: American Conference of Governmental Industrial
Hygienists, 1971. (Plus supplements to 1979)267]
-- Psychomotor performance was evaluated using CFC-113
at concentrations of 0.15% (12 g/cu m), 0.25% (19 g/cu m), 0.35%
(27 g/cu m) or 0.45% (35 g/cu m) for 165 min. There was no effect
at the lowest concentration, but there was difficulty
in mental concentration and some decrease in test scores
beginning at 0.35% (27 g/cu m). [WHO; Environmental Health Criteria
113: Fully Halogenated Chlorofluorocarbons p.19 (1990)]
-- GUINEA PIGS EXPOSED ... FOR PERIODS OF 5 MINUTES TO 2 HOURS
SHOWED INCREASING SIGNS OF IRRITATION AND /CNS
DEPRESSION/; NASAL IRRITATION WAS APPARENT IN 5 MINUTES
AT 25000 PPM, AND LOSS OF COORDINATION AT 50000 PPM AFTER 30 MINUTES;
DEATHS OCCURRED AFTER 1 HOUR AT THIS LEVEL. [American Conference
of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Documentation of the Threshold
Limit Values for Substances in Workroom Air. Third Edition, 1971.
Cincinnati, Ohio: American Conference of Governmental Industrial
Hygienists, 1971. (Plus supplements to 1979)267]
Ref: Hazardous Substances Data Bank for
1,1,2-TRICHLORO-1,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANE CASRN: 76-13-1.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/trichlorotrifluorome.toxnet.htm
-- Health Hazards - General. ...At
high concentrations, Freon vapor may cause pulmonary edema and
neurological problems such as central nervous
system depression, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, tremors,
seizures, confusion, in-coordination, loss of consciousness, and
paralysis (Hazardtext, 2003B; Dupont, 1996A; OSHA, 1998; NIOSH,
2003C).
-- Predisposing Conditions. Individuals
with pre-existing diseases of the central
nervous or cardiovascular system may have increased susceptibility
to the effects of Freons (Dupont, 1996A; OSHA, 1998; Dupont, 1996B;
Dupont, 1996D). Persons exposed to epinephrine or other sympathomimetic
amines, e.g., bronchodilators and nasal decongestants (e.g., Sudafed
¥), might be at increased risk for the cardiotoxic effects of
Freons (Reprotext, 2003).
-- Special Concerns for Children.
Children may inhale relatively larger doses of Freon because,
relative to their body weight, they have a greater lung surface
area and larger minute volume than adults. Since Freon has a high
vapor density, children could also receive high doses due to their
short stature and the higher levels of Freon vapor that may be
present near the ground when Freon is spilled.
Ref: September
24, 2003 (Revised) - FREON
[11, 12, 113]. Technical Support Document: Toxicology. Clandestine
Drug Labs/ Methamphetamine. Volume 1, Number 11. California EPA,
Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA), Department
of Toxic Substances Control.
Heart
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Interactions: The interaction of Freon
113 and hypoxia on the heart conduction system was investigated
by using the isolated perfused hearts from Wistar rats. The mean
preexposure heart rate was 214.8 beats per minute and the mean
preexposure atrioventricular conduction time (PQ interval was
42.9 milliseconds. Freon 113 alone
elicited significant change to control levels in heart rate
which was enhanced by the coadministration of hypoxia. An enhanced
delayed PQ interval was noted following coadministration of Freon
113 and hypoxia, although significant PQ interval changes were
noted with Freon 113 alone or with
hypoxia alone. In the coadministration
group, a 2:1 atrioventricular block
was elicited in two of four hearts. It was suggested that in occupational
deaths among Freon 113 workers, there
may be complex interactions between hypoxia,
enhanced cardiac sensitivity to circulating epinephrine, and direct
alterations of cardiac muscle cell membrane potentials which result
in arrhythmias following Freon 113 exposures. [Kawakami
T et al; Toxicol Indust Health 6 (3/4): 493-8 (1990)]
-- .. CARDIOTOXIC EFFECTS, MANIFESTED IN
ARRHYTHMIAS ... ARE ASSOCIATED WITH PULMONARY EXPOSURE
TO FLUOROCARBONS, ESPECIALLY ... FLUOROCARBON
113 ... . [Hamilton, A., and H. L. Hardy. Industrial
Toxicology. 3rd ed. Acton, Mass.: Publishing Sciences Group, Inc.,
1974. 293]
-- .. Working with high conc of CFC-113
or other chlorofluorocarbons in confined spaces has the potential
to cause death by cardiac arrhythmia, asphyxiation, or both. ...
4 reports of 12 fatalities resulting from occupational exposure
to CFC-113 under conditions typical
of situations in which CFC-113 can
cause death. In most of the reports, the conc of CFC-113
was not specified. However, in one of the deaths from cardiac
arrhythmia, the exposure was for 1 min & the CFC-113
concn measured 24 hr after exposure was 7600 ppm. In a death from
asphyxiation, the CFC-113 conc was
estimated to be 300,000 ppm, but the duration of exposure was
not stated; however from the description of the incident, the
exposure was relatively brief. [American Conference of Governmental
Industrial Hygienists, Inc. Documentation of the Threshold Limit
Values and Biological Exposure Indices. 6th ed. Volumes I, II,
III. Cincinnati, OH: ACGIH, 1991.1633]
-- IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS VARIABLE DEGREES OF TACHYCARDIA,
MYOCARDIAL DEPRESSION, AND HYPOTENSION
HAVE BEEN DESCRIBED. [Hamilton, A., and H. L. Hardy. Industrial
Toxicology. 3rd ed. Acton, Mass.: Publishing Sciences Group, Inc.,
1974. 293]
-- TRICHLOROTRIFLUOROETHANE CAUSED
TACHYCARDIA, HYPOTENSION IN ANESTHETIZED
RHESUS MONKEYS WHEN INHALED @ 2.5-5%. [AVIADO DM, SMITH DG; TOXICOL
3 (2): 241-52 (1975)]
-- TRICHLOROTRIFLUOROETHANE @ 2.5
& 5% DEPRESSED VENTRICULAR FUNCTION IN HEART-LUNG
PREPN FROM DOG. [AVIADO DM, BELEJ M; TOXICOLOGY 3 (1): 78-86 (1975)]
-- Various animal studies (non-human primates and dogs) have indicated
that acute exposure to high concn of CFC-113
(as low as 2,000 ppm or 15,400 mg/cu m in a 6 hr exposure
period) followed by a large injected dose of epinephrine resulted
in cardiac arrhythmias. [USEPA; Health
Assessment Document for 1,1,2-Trichloro-1,2,2-Trifluoroethane
p.2 (1983) EPA-600/58-82-002F]
Ref: Hazardous Substances Data Bank for
1,1,2-TRICHLORO-1,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANE CASRN: 76-13-1.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/trichlorotrifluorome.toxnet.htm
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Studies of 4 to 6-weeks duration, conducted at concn <25,000
ppm, reported variable findings. After 19 seven-hr exposures at
5000 ppm, some rats developed slight, diffuse, degenerative fatty
infiltration; no such changes or other pathological findings were
observed in three subsequent similar studies. No clinical, biochemical,
or pathologic changes developed after twenty 3.5 hr daily exposures
of rats & guinea pigs, or rats & dogs after 20 six-hr exposures
at 5100 ppm or in rats after 30 seven-hr exposures at 2520 ppm;
however, after inhaling 5000 ppm, 7 hr/day for 30 days, body-weight
gain was depressed in the rat. After 14 days of continuous exposure
of monkeys, dogs, mice, and rats at 2000 ppm, no adverse effects
could be detected. The only morphologic & biochemical changes
noted in male Wistar rats inhaling 1000 or 2000 ppm CFC-113,
6 hr/day, 5 days/week were proliferation of
hepatic smooth endoplasmic reticulum & induction of hepatic microsomal
enzymes. [American Conference of Governmental Industrial
Hygienists, Inc. Documentation of the Threshold Limit Values and
Biological Exposure Indices. 6th ed. Volumes I, II, III. Cincinnati,
OH: ACGIH, 1991.1632]
-- Animal Toxicity Studies: Non-Human Toxicity Excerpts: THE CHIEF
EFFECTS OF EXPOSURE TO ... /TRICHLOROTRIFLUOROETHANE/
ARE DEPRESSION OF THE CENTRAL
NERVOUS SYSTEM AND IRRITATION OF THE RESPIRATORY
TRACT. SUCH EFFECTS OCCUR IN ANIMALS AT CONCENTRATIONS
ABOVE 12000 PPM. MILD LIVER CHANGES HAVE
BEEN NOTICED AT LEVELS SOMEWHAT BELOW THIS. [American Conference
of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Documentation of the Threshold
Limit Values for Substances in Workroom Air. Third Edition, 1971.
Cincinnati, Ohio: American Conference of Governmental Industrial
Hygienists, 1971. (Plus supplements to 1979)267]
Ref: Hazardous Substances Data Bank for
1,1,2-TRICHLORO-1,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANE CASRN: 76-13-1.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/trichlorotrifluorome.toxnet.htm
Lung
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Animal Toxicity Studies: Non-Human Toxicity Excerpts: THE
CHIEF EFFECTS OF EXPOSURE TO ... /TRICHLOROTRIFLUOROETHANE/
ARE DEPRESSION OF THE CENTRAL
NERVOUS SYSTEM AND IRRITATION OF THE RESPIRATORY
TRACT. SUCH EFFECTS OCCUR IN ANIMALS AT CONCENTRATIONS
ABOVE 12000 PPM. MILD LIVER CHANGES HAVE BEEN NOTICED AT LEVELS
SOMEWHAT BELOW THIS. [American Conference of Governmental Industrial
Hygienists. Documentation of the Threshold Limit Values for Substances
in Workroom Air. Third Edition, 1971. Cincinnati, Ohio: American
Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists, 1971. (Plus
supplements to 1979)267]
-- ... ACUTE INHALATION STUDIES OF RATS TO THE VAPOR FOR 6 HOURS
SHOWED PULMONARY CHANGES AROUND LEVELS
OF 30000 PPM, BUT NO MORTALITY UNTIL LEVELS AROUND 87000 PPM.
[American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Documentation
of the Threshold Limit Values for Substances in Workroom Air.
Third Edition, 1971. Cincinnati, Ohio: American Conference of
Governmental Industrial Hygienists, 1971. (Plus supplements to
1979)267]
Ref: Hazardous Substances Data Bank for
1,1,2-TRICHLORO-1,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANE CASRN: 76-13-1.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/trichlorotrifluorome.toxnet.htm
Tremors
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
HIGH VAPOR CONCN (EG, 20%) MAY CAUSE CONFUSION, PULMONARY IRRITATION,
TREMORS & RARELY COMA ... BUT ...
THESE EFFECTS WERE GENERALLY TRANSIENT & WITHOUT LATE SEQUELAE.
/FLUOROCARBON REFRIGERANTS & PROPELLANTS/ [Gosselin, R.E., R.P.
Smith, H.C. Hodge. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products.
5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1984.,p. II-159]
Ref: Hazardous Substances Data Bank for
1,1,2-TRICHLORO-1,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANE CASRN: 76-13-1.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/trichlorotrifluorome.toxnet.htm
|
Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
US
EPA: Class 1 Ozone Depleting Substance. Lifetime
of Global Warming Potential: 85 years
Ref:
http://www.epa.gov/ozone/ods.html
The
stratospheric lifetime of this compound ranges between 63
and 122 years(5).
As a result of this persistence in the atmosphere(5), this
vapor-phase compound can be transported long distances and
therefore, its concn should be fairly uniform throughout
the globe away from known sources(SRC).
[(1) Bidleman TF; Environ Sci Technol 22: 361-367 (1988)
(2) Boublik T et al; The Vapour Pressures of Pure Substances.
2nd Rev Ed, Amsterdam: Elsevier p. 74 (1984) (3) Horvath
AL et al; J Phys Chem Ref Data 28: 395-507 (1999) (4) Dilling
WL; pp. 154-97 in Environmental Risk Analysis for Chemicals.
Conway RA, ed. NY, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co (1982) (5)
Chou CC et al; J Phys Chem 82: 1-7 (1978)]
Ref:
Hazardous Substances Data Bank for 1,1,2-TRICHLORO-1,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANE
CASRN: 76-13-1.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/trichlorotrifluorome.toxnet.htm
Environmental
Contamination Concerns
A. Surface Water. Bioconcentration
in organisms is low to moderate; BCF
(Bioconcentration factor: the ratio of the chemical concentration
in the organism to that in surrounding water) is from 11-86.
B. Groundwater.
In general, Freons that are spilled onto soil have the potential
to leach into groundwater, because they do not bind
well to soil (Hazardtext, 2003B; HSDB, 2001A; HSDB, 2001B).
Fully halogenated hydrocarbons such as Freons 11, 12, and
113 are very resistant to chemical
and biological degradation and are likely to be persistent
contaminants if they reach groundwater.
D. Soil. If
Freon is spilled onto soil, a portion may evaporate from
the surface and the remainder will leach downward into the
soil. Mobility through the soil is expected to be moderate
based on estimated Koc values. Freon
does not bind well to soil, and leaching to groundwater
is possible (Hazardtext, 2003B; HSDB, 2001B).
E. Air. Once released to air,
Freon exists solely as a gas. In the atmosphere, fully halogenated
Freons diffuse to the troposphere, where they are very stable
and can be transported great distances. Wet deposition may
result in some loss, but re-volatilization into the atmosphere
is likely. The only degradation process is diffusion to
the stratosphere, where photolytic destruction of Freons
results in depletion of stratospheric ozone, thereby increasing
the amount of ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation reaching the
earthÕs surface (Hazardtext, 2003B; HSDB, 2001A; HSDB, 2001B).
Ref:
September
24, 2003 (Revised). Released November 7, 2003)
- FREON [11, 12,
113]. Technical Support Document: Toxicology. Clandestine
Drug Labs/ Methamphetamine. Volume 1, Number 11. California
EPA, Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA),
Department of Toxic Substances Control.
|
|

