|
Return
to Quinoxyfen Index Page
Activity:
Fungicide
(unclassified)
Structure:
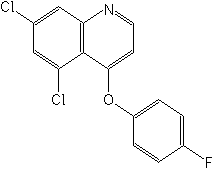
Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Brain
Cholesterol
Endocrine: Pituitary
Endocrine: Testicular
Endocrine: Thymus
Kidney
Liver
Environmental
US:
On
Sept 29, 2003, EPA approved the first-time tolerances to
be established for the residues of quinoxyfen
Cherry (sweet & tart), Grape,
Hop (dried cones)
US.
Time-Limited tolerances to Dec 2007:
Pumpkin
Squash, winter
Vegetable,
cucurbit, subgroup 9A
(includes 19 commodities)
-see
list at bottom of page
|
Blood
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 034 - 181176 "XDE-795:
One Year Chronic Dietary Toxicity Study in Beagle Dogs,"
(Cosse, P.F., Stebbins, K.E., Redmond,
J.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research Laboratory, Health
and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow Chemical
Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-011;
4/21/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Beagle dogs (4/sex/dose) at 0,
5, 20 or 200 mg/kg/day for 1year. NOEL = 20 mg/kg (A male at 200
mg/kg was killed moribund, due to a severe
weight decrease (2 kg), decreased
hemoglobin and RBC counts. Both sexes had significantly
decreased body weights and food consumption
at 200 mg/kg. The report stated it was due to unpalatability of
diet at the high dose, which persisted throughout the majority
of the study. A treatment-related hematological
effect was observed in 1/sex at 200 mg/kg. Alkaline
phosphatase in both sexes at 200 mg/kg was statistically significantly
increased. Liver weights (absolute
& relative) were significantly increased in both sexes at 200
mg/kg. Statistically significantly increased relative organ
weights were observed in both sexes at 200 mg/kg (brain, kidney,
pituitary). Liver histopathology was observed
in 3/sex at 200 mg/kg, primarily in the midzonal region (diffuse,
increased size in hepatocytes, enlarged nuclei and prominent nucleoli).
At 200 mg/kg, 1/sex had increased hepatocyte size, increased bile
in centrilobular canaliculi. Possible adverse effect: At 200 mg/kg,
1/sex showed erythroid proliferation in spleen and liver, due
to treatment-related anemia.) Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/15/01
-- (90-day feeding study) 031; 181173; "XR-795: 13-Week Dietary
Toxicity Study with 4-Week Study in Fischer 344 Rats" (Szabo,
R.A. et al., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas, Lake Jackson
Research Center, The Dow Chemical
Company, Freeport, TX, Laboratory Project Study ID TXT: DR-0325-7474-005,
12/21/92). 821. XR-795 (TSN100010, DECO-104-116, purity
= 99.0%) was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated
diet), 10, 100, or 250 mg/kg/day and fed to 10 Fischer 344 rats
per sex per dose for 13 weeks (an additional 10 rats per sex per
dose at the control and high dose levels were included to test
for recovery for 4 weeks following dosing). No treatment-related
clinical signs were observed. A treatment-related increase in
mean relative liver weight was observed
at 100 and 250 mg/kg/day in animals of both sexes sacrificed after
13 weeks of treatment; in recovery group animals at 250 mg/kg/day,
a treatment-related increase in mean relative liver weight was
observed in males but not females. Microscopic examination revealed
treatment-related hepatocellular hypertrophy with
increased basophilia at 100 and 250 mg/kg/day in animals
of both sexes sacrificed after 13 weeks of treatment persisting
in recovery group males but not in recovery group females. No
adverse effects. NOEL (M/F) = 10 mg/kg/day (based on increased
mean relative liver weights and hepatocellular hypertrophy).
Unacceptable and not upgradeable because no ophthalmological examinations
were conducted. (Corlett, 9/5/01)
Ref: October 4, 2001. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California EPA, Department
of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/quinoxyfen.ca.epa.2001.pdf
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
** 040 - 181140 "XDE-795:
Two-Year Dietary Chronic Toxicity/Oncogenicity Study in Fischer
344 Rats-Final Report," (Redmond, J.M.,
Quast, J.F., Bond, D.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow
Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-007;
6/29/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Fischer 344 rats at 0, 5, 20 or
80 mg/kg/day for 1 Ð 2 years. XDE-795 was administered for 2 years
to 50/sex/dose for chronic/oncogenicity assessment. A satellite
group (15/sex/dose) was sacrificed at 12 months (10/sex/dose for
interim assessment of chronic toxicity; 5/sex/dose to assess neurotoxicity).
NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Females at 80 mg/kg had increased perineal soiling
(satellite & main group). Both sexes had decreased
bodyweights and bodyweight gains at 80 mg/kg throughout
the study...
-- 034 - 181176 ÒXDE-795: One Year Chronic Dietary Toxicity Study
in Beagle Dogs,Ó (Cosse, P.F., Stebbins,
K.E., Redmond, J.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research Laboratory,
Health and Environmental Sciences - The Dow
Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-011;
4/21/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Beagle dogs (4/sex/dose) at 0,
5, 20 or 200 mg/kg/day for 1year. NOEL = 20 mg/kg (A male at 200
mg/kg was killed moribund, due to a severe
weight decrease (2 kg), decreased
hemoglobin and RBC counts. Both sexes had significantly
decreased body weights and food consumption
at 200 mg/kg. The report stated it was due to unpalatability of
diet at the high dose, which persisted throughout the majority
of the study...
-- ** 035 - 181177 "XDE-795: Potential Tumorigenic Effects
in Prolonged Dietary Administration to CD-1 Mice,"(Bellringer,
M.E.; J.R.; Huntingdon Research Centre,
Ltd., Cambridgeshire, UK; HRC Project ID#: DWC/657; 6/5/95).
XR-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline; 97.4% pure)
was fed in diet to Crl:CD-1 (ICR)BR mice (50/sex/dose) at 0, 20,
80 and 250 mg/kg/day for 80 weeks. NOEL = 80 mg/kg (There was
a significantly decreased bodyweight gain
in both sexes at 250 mg/kg (primarily females). The effect was
intermittent in males throughout the study. Relative (to bodyweight)
liver and kidney weights were significantly increased in females
at 250 mg/kg.) There were no histological (neoplastic or
non-neoplastic) effects due to treatment. No adverse effects.
Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/24/01
-- ** 039 Ð 181139 "XDE-795: Two-Generation Dietary Reproduction
Study in Sprague-Dawley Rats," (Liberacki,
A.B., Breslin, W.J., Zwinker, G.M., Johnson, K.A., Freshour, N.L.;
The Toxicology Research Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences,
The Dow Chemical, Midland, MI; Laboratory
ID#'s: DR-0325- 7474-013 [P1, F0, W1, FB, WB, P2, F2 & W4]; 5/23/95).
XDE-795 (97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Sprague-Dawley rats (30/sex/dose)
at 0, 5, 20 and 100 mg/kg/day, 7 days/week for 2 generations.
Systemic NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Kidney pathology
was observed in P1 and P2 females at 100 mg/kg. Males showed liver,
kidney and epididymal histopathology at 100 mg/kg in P1 and P2
adults.) Reproductive NOEL = 100 mg/kg/day (There were no treatment-related
reproductive effects in either sex.) Pup NOEL = 20 mg/kg/ (F1a
& F1b pups showed decreased bodyweights
at 21 days of lactation and this was considered to be due to excessive
dose and decreased food consumption.) No adverse effect. Acceptable.
M. Silva, 8/9/01
-- Rangefinding Study: 037 Ð 181136 "XDE-795: Oral Gavage
Teratology Probe Study in New Zealand White Rabbits,"
(Zablotny, C.L., Yano, B.L., Breslin, W.J.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences, The Dow
Chemical, Midland, MI; Laboratory Project #: DR-0325-7474-014;
11/29/93). XDE-795 (96.2% pure) was administered by oral
gavage to time-mated New Zealand white rabbits (7/dose) at 0 (0.5%
METHOCEL A4M), 100, 300, 600 and 1000 mg/kg/day, days 7-19 of
gestation. Due to extreme maternal toxicity, treatment was discontinued
at 600 and 1000 mg/kg from gestation day 15. Effects included
decreased fecal output, weight loss,
extreme decrease in food consumption. Maternal NOEL = 100 mg/kg
(There were increased clinical observations, as well as decreased
body weight, body weight gain and food consumption at >
300 mg/kg. Liver weights were significantly
increased at 300 mg/kg.) Developmental NOEL > 300 mg/kg (There
were no treatment-related effects at 100 or 300 mg/kg.) No adverse
effect. These data are supplemental. M. Silva, 8/29/01
-- Definitive Study: ** 038 Ð 181138 "XDE-795: Oral Gavage
Teratology Study in New Zealand White Rabbits," (Zablotny,
C.L., Yano, B.L., Breslin, W.J.; The Toxicology Research Laboratory,
Health and Environmental Sciences, The Dow
Chemical, Midland, MI; Laboratory Project #: DR-0325-7474-015;
2/17/94). XDE-795 (96.2% pure) was administered by oral
gavage to time-mated New Zealand white rabbits (18/dose) at 0
(0.5% METHOCEL A4M), 20, 80 and 200 mg/kg/day, days 7-19 of gestation.
Maternal NOEL = 80 mg/kg (There were increased clinical observations
and abortions, as well as decreased body
weight, body weight gain and
food consumption at 200 mg/kg.) Developmental NOEL > 200 mg/kg
(There were no treatment-related effects at any dose.) No adverse
effect. Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/9/01
-- 030; 181170; "XR-795: Four Week Dietary Toxicity Study
in Fischer 344 Rats" (Szabo, J.R. and
Davis, N.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas Lake Jackson
Research Center, The Dow Chemical Company,
Freeport, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID TXT: DR-0325-7474-002,
10/12/92). XR-795 (TSN100003, DECO-36-106, purity = 97.6%)
was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated diet only),
250, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to 5 Fischer
344 rats per sex per dose for 4 weeks. No clinical signs were
observed. A treatment-related decrease in
mean body weight at all dose levels in both sexes was observed.
Treatment-related increases in mean relative
liver (in both sexes at all dose levels) and in mean relative
kidney (in males at all dose levels and in females at 500 and
1000 mg/kg/day) weights and a treatment-related decrease in mean
relative testes weight at 1000 mg/kg/day were observed. Macroscopic
examination revealed bilateral testicular atrophy in 3/5 animals
at 1000 mg/kg/day. Microscopic examination revealed a moderate
to severe decrease in spermatogenesis in 4/5 animals at 1000 mg/kg/day.
Possible adverse effect indicated: testicular atrophy with a decrease
in spermatogenesis. NOEL (M/F) < 250 mg/kg/day (based on
body weight and mean relative organ
weight data). Supplemental (only 5 animals per sex per dose were
used and the animals were only dosed for 4 weeks). (Corlett, 8/27/01)
-- (Corlett, 8/27/01) 030; 181171; "XR-795: Palatability
and Toxicity Probe Study in Beagle Dogs" (Szabo,
J.R. and Rachunek, B.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas
Lake Jackson Research Center, The Dow Chemical
Company, Freeport, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID: DR-0325-7474-001,
2/28/92). XR-795 (TSN100008, Lot # DECO-36-111, purity
= 98.8%) was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated
diet only), 100, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to
1 beagle dog per sex per dose for 30 days. No clinical signs were
observed. A treatment-related decrease in
body weight gain or outright body weight loss at all dose levels
in males and at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day in females was observed.
A treatment-related decrease in feed consumption in males at all
dose levels and in females at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day was observed.
Macroscopic examination revealed a small/atrophic thymus in both
the male and the female at 1000 mg/kg/day and small/atrophic testes
in the male at 1000 mg/kg/day. Microscopic examination revealed
vacuolation of midzonal and centrilobular hepatocytes at 500 and
1000 mg/kg/day in both sexes and thymic lymphoid depletion in
the male and female at 1000 mg/kg/day. No adverse effects. NOEL
(M) < 100 mg/kg/day, NOEL (F) = 100 mg/kg/day (based on
body weight and feed consumption data). Supplemental (only
1 animal per sex per dose was used and the animals were only dosed
for 30 days). (Corlett, 8/28/01)
-- 030; 181172; "XDE-795: Four-Week Dietary Toxicity Study
in Beagle Dogs" (Szabo, J.R. and Davis,
N.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas Lake Jackson Research
Center, The Dow Chemical Company,
Midland, MI, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID: DR-0325-7474-008,
2/19/93). XDE-795 (TSN100010, Lot # DECO-104-116, purity
= 99.0%) was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated
diet only) or 250 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to 2 beagle dogs
per sex per dose for 4 weeks. No clinical signs were observed.
Treatment-related decreases in mean body
weight and in mean feed consumption
were observed in both males and females. Microscopic examination
revealed treatment-related vacuolation of midzonal and centrilobular
hepatocytes in both males and females. No adverse effects.
NOEL (M/F) < 250 mg/kg/day (based on body
weight and feed consumption data and microscopic findings).
Supplemental (only 2 animals per sex per dose were used, only
1 treatment level was used, and the animals were only dosed for
4 weeks). (Corlett, 8/29/01)
Ref: October 4, 2001. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California EPA, Department
of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/quinoxyfen.ca.epa.2001.pdf
Brain
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 040 - 181140 "XDE-795:
Two-Year Dietary Chronic Toxicity/Oncogenicity Study in Fischer
344 Rats-Final Report," (Redmond, J.M.,
Quast, J.F., Bond, D.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow
Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-007;
6/29/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Fischer 344 rats at 0, 5, 20 or
80 mg/kg/day for 1 Ð 2 years. XDE-795 was administered for 2 years
to 50/sex/dose for chronic/oncogenicity assessment. A satellite
group (15/sex/dose) was sacrificed at 12 months (10/sex/dose for
interim assessment of chronic toxicity; 5/sex/dose to assess neurotoxicity).
NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Females at 80 mg/kg had increased perineal soiling
(satellite & main group). Both sexes had decreased bodyweights
and bodyweight gains at 80 mg/kg throughout the study. Urea nitrogen
was increased in males at 80 mg/kg at 18 and 24 months. Alanine
amino transferase (80 mg/kg) was decreased in males at 24 months.
Females had cholesterol levels that were statistically significantly
increased at 80 mg/kg at 18 and 24 months. Liver and kidney weights
(absolute & relative) were statistically significantly increased
in both sexes at 80 mg/kg at 12 months. Relative
brain weights in both sexes were increased at 80 mg/kg
by 24 months. Males had increased absolute and relative testes
weights at 80 mg/kg and females had decreased relative heart and
increased relative kidney weights at 80 mg/kg at 24 months. There
was an increased incidence in chronic progressive glomerulonephropathy
in males at 80 mg/kgÑ37 versus 19 in control, p < 0.05.) No adverse
effects. Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/21/01
-- ** 034 - 181176 "XDE-795: One Year Chronic Dietary Toxicity
Study in Beagle Dogs," (Cosse, P.F., Stebbins, K.E., Redmond,
J.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research Laboratory, Health
and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow Chemical Company, Midland,
MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-011; 4/21/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Beagle dogs (4/sex/dose) at 0,
5, 20 or 200 mg/kg/day for 1year. NOEL = 20 mg/kg (A male at 200
mg/kg was killed moribund, due to a severe weight decrease (2
kg), decreased hemoglobin and RBC counts. Both sexes had significantly
decreased body weights and food consumption at 200 mg/kg. The
report stated it was due to unpalatability of diet at the high
dose, which persisted throughout the majority of the study. A
treatment-related hematological effect was observed in 1/sex at
200 mg/kg. Alkaline phosphatase in both sexes at 200 mg/kg was
statistically significantly increased. Liver weights (absolute
& relative) were significantly increased in both sexes at 200
mg/kg. Statistically significantly increased
relative organ weights were observed in both sexes at 200
mg/kg (brain, kidney, pituitary).
Liver histopathology was observed in 3/sex at 200 mg/kg, primarily
in the midzonal region (diffuse, increased size in hepatocytes,
enlarged nuclei and prominent nucleoli). At 200 mg/kg, 1/sex had
increased hepatocyte size, increased bile in centrilobular canaliculi.
Possible adverse effect: At 200 mg/kg, 1/sex showed erythroid
proliferation in spleen and liver, due to treatment-related anemia.)
Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/15/01
Ref: October 4, 2001 - SUMMARY
OF TOXICOLOGY DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California
EPA, Department of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
Cholesterol
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
** 040 - 181140 "XDE-795:
Two-Year Dietary Chronic Toxicity/Oncogenicity Study in Fischer
344 Rats-Final Report," (Redmond, J.M.,
Quast, J.F., Bond, D.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow
Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-007;
6/29/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Fischer 344 rats at 0, 5, 20 or
80 mg/kg/day for 1 Ð 2 years. XDE-795 was administered for 2 years
to 50/sex/dose for chronic/oncogenicity assessment. A satellite
group (15/sex/dose) was sacrificed at 12 months (10/sex/dose for
interim assessment of chronic toxicity; 5/sex/dose to assess neurotoxicity).
NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Females at 80 mg/kg had increased perineal soiling
(satellite & main group). Both sexes had decreased
bodyweights and bodyweight gains at 80 mg/kg throughout the study.
Urea nitrogen was increased in males at 80 mg/kg at 18
and 24 months. Alanine amino transferase (80 mg/kg) was decreased
in males at 24 months. Females had cholesterol
levels that were statistically significantly increased
at 80 mg/kg at 18 and 24 months. Liver and
kidney weights (absolute & relative) were statistically significantly
increased in both sexes at 80 mg/kg at 12 months. Relative brain
weights in both sexes were increased at 80 mg/kg by 24 months.
Males had increased absolute and relative testes weights at 80
mg/kg and females had decreased relative heart and increased relative
kidney weights at 80 mg/kg at 24 months. There was an increased
incidence in chronic progressive glomerulonephropathy in males
at 80 mg/kgÑ37 versus 19 in control, p < 0.05.) No adverse
effects. Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/21/01
Ref: October 4, 2001. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California EPA, Department
of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/quinoxyfen.ca.epa.2001.pdf
Endocrine-
Pituitary (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 034 - 181176 "XDE-795:
One Year Chronic Dietary Toxicity Study in Beagle Dogs,"
(Cosse, P.F., Stebbins, K.E., Redmond, J.M.,
Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research Laboratory, Health and Environmental
Sciences Ð The Dow Chemical Company,
Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-011; 4/21/95).
XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline; 97.4% pure)
was fed in diet to Beagle dogs (4/sex/dose) at 0, 5, 20 or 200
mg/kg/day for 1year. NOEL = 20 mg/kg (A male at 200 mg/kg was
killed moribund, due to a severe weight decrease (2 kg), decreased
hemoglobin and RBC counts. Both sexes had significantly decreased
body weights and food consumption at 200 mg/kg. The report stated
it was due to unpalatability of diet at the high dose, which persisted
throughout the majority of the study. A treatment-related hematological
effect was observed in 1/sex at 200 mg/kg. Alkaline phosphatase
in both sexes at 200 mg/kg was statistically significantly increased.
Liver weights (absolute & relative) were significantly increased
in both sexes at 200 mg/kg. Statistically
significantly increased relative organ weights were observed
in both sexes at 200 mg/kg (brain, kidney,
pituitary). Liver histopathology was observed in 3/sex
at 200 mg/kg, primarily in the midzonal region (diffuse, increased
size in hepatocytes, enlarged nuclei and prominent nucleoli).
At 200 mg/kg, 1/sex had increased hepatocyte size, increased bile
in centrilobular canaliculi. Possible adverse effect: At 200 mg/kg,
1/sex showed erythroid proliferation in spleen and liver, due
to treatment-related anemia.) Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/15/01
Ref: October 4, 2001 - SUMMARY
OF TOXICOLOGY DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California
EPA, Department of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch
Endocrine:
Testicular
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- ** 039 Ð 181139
"XDE-795: Two-Generation Dietary Reproduction Study in Sprague-Dawley
Rats," (Liberacki, A.B., Breslin, W.J.,
Zwinker, G.M., Johnson, K.A., Freshour, N.L.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences, The Dow
Chemical, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#'s: DR-0325- 7474-013
[P1, F0, W1, FB, WB, P2, F2 & W4]; 5/23/95). XDE-795 (97.4%
pure) was fed in diet to Sprague-Dawley
rats (30/sex/dose) at 0, 5, 20 and 100 mg/kg/day, 7 days/week
for 2 generations. Systemic NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Kidney pathology
was observed in P1 and P2 females at 100 mg/kg. Males showed liver,
kidney and epididymal histopathology
at 100 mg/kg in P1 and P2 adults.) Reproductive NOEL = 100 mg/kg/day
(There were no treatment-related reproductive effects in either
sex.) Pup NOEL = 20 mg/kg/ (F1a & F1b pups showed decreased bodyweights
at 21 days of lactation and this was considered to be due to excessive
dose and decreased food consumption.) No adverse effect.
Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/9/01
-- 030; 181170; "XR-795: Four Week Dietary Toxicity Study
in Fischer 344 Rats" (Szabo, J.R. and
Davis, N.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas Lake Jackson
Research Center, The Dow Chemical Company,
Freeport, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID TXT: DR-0325-7474-002,
10/12/92). XR-795 (TSN100003, DECO-36-106, purity = 97.6%)
was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated diet only),
250, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to 5 Fischer
344 rats per sex per dose for 4 weeks. No clinical signs were
observed. A treatment-related decrease in
mean body weight at all dose levels in both sexes was observed.
Treatment-related increases in mean relative liver (in both sexes
at all dose levels) and in mean relative kidney (in males at all
dose levels and in females at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day) weights
and a treatment-related decrease in mean relative testes weight
at 1000 mg/kg/day were observed. Macroscopic examination revealed
bilateral testicular atrophy in 3/5 animals
at 1000 mg/kg/day. Microscopic examination revealed a
moderate to severe decrease in spermatogenesis in 4/5 animals
at 1000 mg/kg/day. Possible adverse effect indicated:
testicular atrophy with a decrease in spermatogenesis. NOEL
(M/F) < 250 mg/kg/day (based on body weight
and mean relative organ weight data). Supplemental (only
5 animals per sex per dose were used and the animals were only
dosed for 4 weeks). (Corlett, 8/27/01)
-- (Corlett, 8/27/01) 030; 181171; "XR-795: Palatability
and Toxicity Probe Study in Beagle Dogs" (Szabo,
J.R. and Rachunek, B.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas
Lake Jackson Research Center, The Dow Chemical
Company, Freeport, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID: DR-0325-7474-001,
2/28/92). XR-795 (TSN100008, Lot # DECO-36-111, purity
= 98.8%) was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated
diet only), 100, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to
1 beagle dog per sex per dose for 30 days. No clinical signs were
observed. A treatment-related decrease in
body weight gain or outright body weight loss at all dose levels
in males and at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day in females was observed.
A treatment-related decrease in feed consumption in males at all
dose levels and in females at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day was observed.
Macroscopic examination revealed a small/atrophic
thymus in both the male and the female at 1000 mg/kg/day
and small/atrophic testes in the
male at 1000 mg/kg/day. Microscopic examination revealed vacuolation
of midzonal and centrilobular hepatocytes at 500 and 1000
mg/kg/day in both sexes and thymic lymphoid
depletion in the male and female at 1000 mg/kg/day. No
adverse effects. NOEL (M) < 100 mg/kg/day, NOEL (F) = 100 mg/kg/day
(based on body weight
and feed consumption data). Supplemental (only 1 animal per sex
per dose was used and the animals were only dosed for 30 days).
(Corlett, 8/28/01)
Ref: October 4, 2001. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California EPA, Department
of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/quinoxyfen.ca.epa.2001.pdf
Endocrine:
Thymus (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- (Corlett, 8/27/01)
030; 181171; "XR-795: Palatability and Toxicity Probe Study
in Beagle Dogs" (Szabo, J.R. and Rachunek,
B.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas Lake Jackson Research
Center, The Dow Chemical Company,
Freeport, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID: DR-0325-7474-001,
2/28/92). XR-795 (TSN100008, Lot # DECO-36-111, purity
= 98.8%) was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated
diet only), 100, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to
1 beagle dog per sex per dose for 30 days. No clinical signs were
observed. A treatment-related decrease in
body weight gain or outright body weight loss at all dose levels
in males and at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day in females was observed.
A treatment-related decrease in feed consumption in males at all
dose levels and in females at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day was observed.
Macroscopic examination revealed a small/atrophic
thymus in both the male and the female at 1000 mg/kg/day
and small/atrophic testes in the male at
1000 mg/kg/day. Microscopic examination revealed vacuolation of
midzonal and centrilobular hepatocytes at 500 and 1000
mg/kg/day in both sexes and thymic lymphoid
depletion in the male and female at 1000 mg/kg/day. No
adverse effects. NOEL (M) < 100 mg/kg/day, NOEL (F) = 100 mg/kg/day
(based on body weight and feed consumption data). Supplemental
(only 1 animal per sex per dose was used and the animals were
only dosed for 30 days). (Corlett, 8/28/01)
Ref: October 4, 2001 - SUMMARY
OF TOXICOLOGY DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California
EPA, Department of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch
Kidney
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
** 040 - 181140 "XDE-795:
Two-Year Dietary Chronic Toxicity/Oncogenicity Study in Fischer
344 Rats-Final Report," (Redmond, J.M.,
Quast, J.F., Bond, D.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow
Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-007;
6/29/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Fischer 344 rats at 0, 5, 20 or
80 mg/kg/day for 1 - 2 years. XDE-795 was administered for 2 years
to 50/sex/dose for chronic/oncogenicity assessment. A satellite
group (15/sex/dose) was sacrificed at 12 months (10/sex/dose for
interim assessment of chronic toxicity; 5/sex/dose to assess neurotoxicity).
NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Females at 80 mg/kg had increased perineal soiling
(satellite & main group). Both sexes had decreased bodyweights
and bodyweight gains at 80 mg/kg throughout the study. Urea nitrogen
was increased in males at 80 mg/kg at 18 and 24 months. Alanine
amino transferase (80 mg/kg) was decreased in males at 24 months.
Females had cholesterol levels that were statistically significantly
increased at 80 mg/kg at 18 and 24 months.
Liver and kidney
weights (absolute & relative) were statistically significantly
increased in both sexes at 80 mg/kg at 12 months.
Relative brain weights in both sexes were increased at 80 mg/kg
by 24 months. Males had increased absolute and relative testes
weights at 80 mg/kg and females had decreased relative heart and
increased relative kidney weights at 80 mg/kg at 24 months. There
was an increased incidence in chronic progressive
glomerulonephropathy in males at 80 mg/kgÑ37 versus 19
in control, p < 0.05.) No adverse effects. Acceptable. M. Silva,
8/21/01
-- 034 - 181176 "XDE-795: One Year Chronic Dietary Toxicity
Study in Beagle Dogs," (Cosse, P.F.,
Stebbins, K.E., Redmond, J.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow
Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-011;
4/21/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Beagle dogs (4/sex/dose) at 0,
5, 20 or 200 mg/kg/day for 1year. NOEL = 20 mg/kg (A male at 200
mg/kg was killed moribund, due to a severe
weight decrease (2 kg), decreased hemoglobin and RBC counts. Both
sexes had significantly decreased body weights and food consumption
at 200 mg/kg. The report stated it was due to unpalatability of
diet at the high dose, which persisted throughout the majority
of the study. A treatment-related hematological effect was observed
in 1/sex at 200 mg/kg. Alkaline phosphatase in both sexes at 200
mg/kg was statistically significantly increased. Liver weights
(absolute & relative) were significantly increased in both sexes
at 200 mg/kg. Statistically significantly
increased relative organ weights
were observed in both sexes at 200 mg/kg (brain, kidney,
pituitary). Liver histopathology
was observed in 3/sex at 200 mg/kg, primarily in the midzonal
region (diffuse, increased size in hepatocytes, enlarged nuclei
and prominent nucleoli). At 200 mg/kg, 1/sex had increased hepatocyte
size, increased bile in centrilobular canaliculi. Possible adverse
effect: At 200 mg/kg, 1/sex showed erythroid
proliferation in spleen and liver, due to treatment-related anemia.)
Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/15/01
-- ** 035 - 181177 "XDE-795: Potential Tumorigenic Effects
in Prolonged Dietary Administration to CD-1 Mice," (Bellringer,
M.E.; J.R.; Huntingdon Research Centre,
Ltd., Cambridgeshire, UK; HRC Project ID#: DWC/657; 6/5/95).
XR-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Crl:CD-1 (ICR)BR mice (50/sex/dose)
at 0, 20, 80 and 250 mg/kg/day for 80 weeks. NOEL = 80 mg/kg (There
was a significantly decreased bodyweight gain in both sexes
at 250 mg/kg (primarily females). The effect was intermittent
in males throughout the study. Relative (to bodyweight)
liver and kidney weights were significantly
increased in females at 250 mg/kg.) There were no histological
(neoplastic or non-neoplastic) effects due to treatment. No adverse
effects. Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/24/01
-- ** 039 Ð 181139 "XDE-795: Two-Generation Dietary Reproduction
Study in Sprague-Dawley Rats," (Liberacki,
A.B., Breslin, W.J., Zwinker, G.M., Johnson, K.A., Freshour, N.L.;
The Toxicology Research Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences,
The Dow Chemical, Midland, MI; Laboratory
ID#'s: DR-0325- 7474-013 [P1, F0, W1, FB, WB, P2, F2 & W4]; 5/23/95).
XDE-795 (97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Sprague-Dawley rats (30/sex/dose)
at 0, 5, 20 and 100 mg/kg/day, 7 days/week for 2 generations.
Systemic NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Kidney pathology
was observed in P1 and P2 females at 100 mg/kg. Males showed
liver, kidney and
epididymal histopathology at 100 mg/kg in P1 and
P2 adults.) Reproductive NOEL = 100 mg/kg/day (There were no treatment-related
reproductive effects in either sex.) Pup
NOEL = 20 mg/kg/ (F1a & F1b pups showed decreased bodyweights
at 21 days of lactation and this was considered to be due
to excessive dose and decreased food consumption.) No adverse
effect. Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/9/01
-- 030; 181170; "XR-795: Four Week Dietary Toxicity Study
in Fischer 344 Rats" (Szabo, J.R. and
Davis, N.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas Lake Jackson
Research Center, The Dow Chemical Company,
Freeport, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID TXT: DR-0325-7474-002,
10/12/92). XR-795 (TSN100003, DECO-36-106, purity = 97.6%)
was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated diet only),
250, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to 5 Fischer
344 rats per sex per dose for 4 weeks. No clinical signs were
observed. A treatment-related decrease in
mean body weight at all dose levels in both sexes was observed.
Treatment-related increases in mean relative liver (in
both sexes at all dose levels) and in mean
relative kidney (in males at all dose levels and in females
at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day) weights and a treatment-related decrease
in mean relative testes weight at 1000 mg/kg/day
were observed. Macroscopic examination revealed bilateral testicular
atrophy in 3/5 animals at 1000 mg/kg/day. Microscopic examination
revealed a moderate to severe decrease in spermatogenesis in 4/5
animals at 1000 mg/kg/day. Possible adverse effect indicated:
testicular atrophy with a decrease in spermatogenesis. NOEL (M/F)
< 250 mg/kg/day (based on body weight and mean relative
organ weight data). Supplemental (only 5 animals per sex per dose
were used and the animals were only dosed for 4 weeks). (Corlett,
8/27/01)
Ref: October 4, 2001. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California EPA, Department
of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/quinoxyfen.ca.epa.2001.pdf
Liver
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
** 040 - 181140 "XDE-795:
Two-Year Dietary Chronic Toxicity/Oncogenicity Study in Fischer
344 Rats-Final Report," (Redmond, J.M.,
Quast, J.F., Bond, D.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow
Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-007;
6/29/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Fischer 344 rats at 0, 5, 20 or
80 mg/kg/day for 1 Ð 2 years. XDE-795 was administered for 2 years
to 50/sex/dose for chronic/oncogenicity assessment. A satellite
group (15/sex/dose) was sacrificed at 12 months (10/sex/dose for
interim assessment of chronic toxicity; 5/sex/dose to assess neurotoxicity).
NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Females at 80 mg/kg had increased perineal soiling
(satellite & main group). Both sexes had decreased
bodyweights and bodyweight gains
at 80 mg/kg throughout the study. Urea nitrogen was increased
in males at 80 mg/kg at 18 and 24 months. Alanine amino transferase
(80 mg/kg) was decreased in males at 24 months. Females had cholesterol
levels that were statistically significantly increased at 80 mg/kg
at 18 and 24 months. Liver and kidney
weights (absolute & relative) were statistically significantly
increased in both sexes at 80 mg/kg at 12 months. Relative
brain weights in both sexes were increased at 80 mg/kg by 24 months.
Males had increased absolute and relative testes weights at 80
mg/kg and females had decreased relative heart and increased relative
kidney weights at 80 mg/kg at 24 months. There was an
increased incidence in chronic progressive glomerulonephropathy
in males at 80 mg/kgÑ37 versus 19 in control, p < 0.05.)
No adverse effects. Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/21/01
-- 034 - 181176 "XDE-795: One Year Chronic Dietary Toxicity
Study in Beagle Dogs," (Cosse, P.F.,
Stebbins, K.E., Redmond, J.M., Ormand, J.R.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences Ð The Dow
Chemical Company, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-011;
4/21/95). XDE-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline;
97.4% pure) was fed in diet to Beagle dogs (4/sex/dose) at 0,
5, 20 or 200 mg/kg/day for 1year. NOEL = 20 mg/kg (A male at 200
mg/kg was killed moribund, due to a severe
weight decrease (2 kg), decreased hemoglobin and RBC counts. Both
sexes had significantly decreased body weights and food consumption
at 200 mg/kg. The report stated it was due to unpalatability of
diet at the high dose, which persisted throughout the majority
of the study. A treatment-related hematological effect was observed
in 1/sex at 200 mg/kg. Alkaline phosphatase in both sexes at 200
mg/kg was statistically significantly increased. Liver
weights (absolute & relative) were significantly increased in
both sexes at 200 mg/kg. Statistically significantly increased
relative organ weights were observed in both sexes at 200 mg/kg
(brain, kidney, pituitary). Liver
histopathology was observed in 3/sex at 200 mg/kg, primarily in
the midzonal region (diffuse, increased size in hepatocytes, enlarged
nuclei and prominent nucleoli). At 200 mg/kg, 1/sex had increased
hepatocyte size, increased bile in centrilobular canaliculi. Possible
adverse effect: At 200 mg/kg, 1/sex showed erythroid
proliferation in spleen and liver, due to treatment-related
anemia.) Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/15/01
-- Subchronic Study: 029 - 181169 "XR-795: 13-Week Dietary
Toxicity Study in CD-1 Mice," (Grandjean,
M., Szabo, J.R.; Health and Environmental Sciences - Texas, Lake
Jackson Research Center, The Dow Chemical,
Freeport, TX; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-003; 10/12/92).
XR-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline; 98.7% pure)
was fed in diet to CD-1 mice (10/sex/dose) at 0, 10, 50, 100 or
500 mg/kg/day for 13 weeks. NOEL = 100 mg/kg (Relative
liver weights were significantly increased in both sexes
at 500 mg/kg. All animals (both sexes) had
hepatocellular hypertrophy (centrilobular & midzonal-diffuse)
at 500 mg/kg only. Hepatic inflammation (1/10-M) and hepatocellular
necrosis (3/10-M, 4/10-F) occurred only at 500 mg/kg.) No adverse
effects. Not acceptable but possibly upgradeable with submission
of results of ophthalmological examination. M. Silva, 8/15/01
-- ** 035 - 181177 "XDE-795: Potential Tumorigenic Effects
in Prolonged Dietary Administration to CD-1 Mice," (Bellringer,
M.E.; J.R.; Huntingdon Research Centre,
Ltd., Cambridgeshire, UK; HRC Project ID#: DWC/657; 6/5/95).
XR-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline; 97.4% pure)
was fed in diet to Crl:CD-1 (ICR)BR mice (50/sex/dose) at 0, 20,
80 and 250 mg/kg/day for 80 weeks. NOEL = 80 mg/kg (There was
a significantly decreased bodyweight gain
in both sexes at 250 mg/kg (primarily females). The effect
was intermittent in males throughout the study. Relative (to bodyweight)
liver and kidney weights were significantly
increased in females at 250 mg/kg.) There were no histological
(neoplastic or non-neoplastic) effects due to treatment. No adverse
effects. Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/24/01
-- ** 039 Ð 181139 "XDE-795: Two-Generation Dietary Reproduction
Study in Sprague-Dawley Rats," (Liberacki,
A.B., Breslin, W.J., Zwinker, G.M., Johnson, K.A., Freshour, N.L.;
The Toxicology Research Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences,
The Dow Chemical, Midland, MI; Laboratory ID#'s: DR-0325- 7474-013
[P1, F0, W1, FB, WB, P2, F2 & W4]; 5/23/95). XDE-795 (97.4%
pure) was fed in diet to Sprague-Dawley rats (30/sex/dose) at
0, 5, 20 and 100 mg/kg/day, 7 days/week for 2 generations. Systemic
NOEL = 20 mg/kg (Kidney pathology was observed
in P1 and P2 females at 100 mg/kg. Males showed liver,
kidney and epididymal histopathology at 100 mg/kg in P1
and P2 adults.) Reproductive NOEL = 100 mg/kg/day (There were
no treatment-related reproductive effects in either sex.) Pup
NOEL = 20 mg/kg/ (F1a & F1b pups showed
decreased bodyweights at 21 days of lactation and this
was considered to be due to excessive dose and decreased food
consumption.) No adverse effect. Acceptable. M. Silva, 8/9/01
-- Rangefinding Study: 037 Ð 181136 "XDE-795: Oral Gavage
Teratology Probe Study in New Zealand White Rabbits,"
(Zablotny, C.L., Yano, B.L., Breslin, W.J.; The Toxicology Research
Laboratory, Health and Environmental Sciences, The Dow
Chemical, Midland, MI; Laboratory Project #: DR-0325-7474-014;
11/29/93). XDE-795 (96.2% pure) was administered by oral
gavage to time-mated New Zealand white rabbits (7/dose) at 0 (0.5%
METHOCEL A4M), 100, 300, 600 and 1000 mg/kg/day, days 7-19 of
gestation. Due to extreme maternal toxicity, treatment was discontinued
at 600 and 1000 mg/kg from gestation day 15. Effects included
decreased fecal output, weight loss,
extreme decrease in food consumption. Maternal NOEL = 100 mg/kg
(There were increased clinical observations, as well as decreased
body weight, body weight gain and food consumption at >
300 mg/kg. Liver weights were significantly
increased at 300 mg/kg.) Developmental NOEL > 300 mg/kg
(There were no treatment-related effects at 100 or 300 mg/kg.)
No adverse effect. These data are supplemental. M. Silva, 8/29/01
-- (90-day feeding study) 031; 181173; "XR-795: 13-Week Dietary
Toxicity Study with 4-Week Study in Fischer 344 Rats" (Szabo,
R.A. et al., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas, Lake Jackson
Research Center, The Dow Chemical
Company, Freeport, TX, Laboratory Project Study ID TXT: DR-0325-7474-005,
12/21/92). 821. XR-795 (TSN100010, DECO-104-116, purity
= 99.0%) was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated
diet), 10, 100, or 250 mg/kg/day and fed to 10 Fischer 344 rats
per sex per dose for 13 weeks (an additional 10 rats per sex per
dose at the control and high dose levels were included to test
for recovery for 4 weeks following dosing). No treatment-related
clinical signs were observed. A treatment-related increase in
mean relative liver weight was observed
at 100 and 250 mg/kg/day in animals of both sexes sacrificed after
13 weeks of treatment; in recovery group animals at 250 mg/kg/day,
a treatment-related increase in mean relative liver weight was
observed in males but not females. Microscopic examination revealed
treatment-related hepatocellular hypertrophy
with increased basophilia
at 100 and 250 mg/kg/day in animals of both sexes sacrificed
after 13 weeks of treatment persisting in recovery group males
but not in recovery group females. No adverse effects. NOEL (M/F)
= 10 mg/kg/day (based on increased mean
relative liver weights and hepatocellular hypertrophy).
Unacceptable and not upgradeable because no ophthalmological examinations
were conducted. (Corlett, 9/5/01)
-- 030; 181170; "XR-795: Four Week Dietary Toxicity Study
in Fischer 344 Rats" (Szabo, J.R. and
Davis, N.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas Lake Jackson
Research Center, The Dow Chemical Company,
Freeport, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID TXT: DR-0325-7474-002,
10/12/92). XR-795 (TSN100003, DECO-36-106, purity = 97.6%)
was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated diet only),
250, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to 5 Fischer
344 rats per sex per dose for 4 weeks. No clinical signs were
observed. A treatment-related decrease in
mean body weight at all dose levels in both sexes was observed.
Treatment-related increases in mean
relative liver (in both sexes at all dose levels) and in
mean relative kidney (in males at all dose levels and in
females at 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day) weights and a treatment-related
decrease in mean relative testes weight at 1000 mg/kg/day were
observed. Macroscopic examination revealed
bilateral testicular atrophy in 3/5 animals at 1000 mg/kg/day.
Microscopic examination revealed a moderate to severe decrease
in spermatogenesis in 4/5 animals at 1000 mg/kg/day. Possible
adverse effect indicated: testicular atrophy with a decrease in
spermatogenesis. NOEL (M/F) < 250 mg/kg/day (based on body weight
and mean relative organ weight data). Supplemental (only
5 animals per sex per dose were used and the animals were only
dosed for 4 weeks). (Corlett, 8/27/01)
-- 030; 181172; "XDE-795: Four-Week Dietary Toxicity Study
in Beagle Dogs" (Szabo, J.R. and Davis,
N.L., Health and Environmental Sciences-Texas Lake Jackson Research
Center, The Dow Chemical Company,
Midland, MI, Texas, Laboratory Project Study ID: DR-0325-7474-008,
2/19/93). XDE-795 (TSN100010, Lot # DECO-104-116, purity
= 99.0%) was admixed to the diet at dose levels of 0 (untreated
diet only) or 250 mg/kg/day and fed continuously to 2 beagle dogs
per sex per dose for 4 weeks. No clinical signs were observed.
Treatment-related decreases in mean body
weight and in mean feed consumption were observed in both
males and females. Microscopic examination revealed treatment-related
vacuolation of midzonal and centrilobular
hepatocytes in both males and females. No adverse effects.
NOEL (M/F) < 250 mg/kg/day (based on body
weight and feed consumption data and microscopic findings).
Supplemental (only 2 animals per sex per dose were used, only
1 treatment level was used, and the animals were only dosed for
4 weeks). (Corlett, 8/29/01)
-- 029 - 181169 "XR-795: 13-Week Dietary Toxicity Study in
CD-1 Mice," (Grandjean, M., Szabo,
J.R.; Health and Environmental Sciences - Texas, Lake Jackson
Research Center, The Dow Chemical,
Freeport, TX; Laboratory ID#: DR-0325-7474-003; 10/12/92).
XR-795 (5,7-dichloro-4-[4-flurophenoxy]quinoline; 98.7% pure)
was fed in diet to CD-1 mice (10/sex/dose) at 0, 10, 50, 100 or
500 mg/kg/day for 13 weeks. NOEL = 100 mg/kg (Relative liver
weights were significantly increased in both sexes at 500
mg/kg. All animals (both sexes) had hepatocellular
hypertrophy (centrilobular & midzonal-diffuse) at 500 mg/kg
only. Hepatic inflammation (1/10-M)
and hepatocellular necrosis (3/10-M,
4/10-F) occurred only at 500 mg/kg.) No adverse effects. Not acceptable
but possibly upgradeable with submission of results of ophthalmological
examination. M. Silva, 8/15/01
Ref: October 4, 2001. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California EPA, Department
of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/quinoxyfen.ca.epa.2001.pdf
| Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Examination
and possible vote on a draft Commission Decision making
it possible for Member States to extend provisional authorisations
granted for the new active substances carfentrazone, cinidon-ethyl,
cyhalofop-butyl, ethoxysulfuron, famoxadone, flazasulfuron,
flufenacet, flumioxazine, flurtamone, fosthiazate, isoxaflutole,
metalaxyl-M, Pseudomonas chlororaphis, quinoxyfen,
Spodoptera exigua nuclear polyhedrosis virus and sulfosulfuron
(SANCO/3963/2001 rev 6).
...
Sweden supports a decision of non-inclusion of quinoxyfen
in Annex I to Directive 91/414/EEC. The possible environmental
impact of quinoxyfen cannot be shown to be acceptable with
sufficient security. This is due to the
high persistence, high potential for bioaccumulation and
indicated potential for long-range transport. Substances
like quinoxyfen may accumulate in various environmental
compartments, including biota, and the effects of such accumulation
are unpredictable. The Swedish opinion is that whatever
the final results of the additional, ongoing study on organic
matter breakdown may be, those results cannot be sufficient
to demonstrate an acceptable impact.
Ref: SHORT REPORT OF THE MEETING OF
THE STANDING COMMITTEE ON PLANT HEALTH HELD ON 7 DECEMBER
2001 IN BRUXELLES. SCPH 5/01. European Commission.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/quinoxyfen.eu.dec.7.2001.pdf
|
A
February
16, 2005,
check at the Code
of Federal Regulations for Quinoxyfen: this fungicide
is permitted in or on 25
food commodities in the United
States. The
following list identifies these crops for which EPA has set
pesticide tolerances.
Note:
On September 29, 2003, US EPA approved the first-time tolerances
to be established for the residues of quinoxyfen - see Final
Rule in Federal Register.
|
| [Code
of Federal Regulations]
[Title 40, Volume 22]
[Revised as of July 1, 2004]
From the U.S. Government Printing Office via GPO Access
[CITE: 40CFR180.588]
[Page 515]
TITLE 40--PROTECTION OF ENVIRONMENT
CHAPTER I--ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY (CONTINUED)
PART 180_TOLERANCES AND EXEMPTIONS FROM TOLERANCES FOR PESTICIDE
CHEMICALS
IN FOOD--Table of Contents
Subpart C_Specific Tolerances
Sec. 180.588 Quinoxyfen; tolerances
for residues.
(a) General. Tolerances are established for residues of the
fungicide quinoxyfen, 5,7-dichloro-4-(4-fluorophenoxy)quinoline
in or on
the following raw agricultural commodities: |
| Commodity |
Parts
per million |
CFR |
| Cherry,
sweet |
0.30 |
180.588
|
| Cherry,
tart |
0.30 |
180.588
|
| Hop, dried
cones |
0.30 |
180.588
|
| Grape |
0.60 |
180.588
|
(b)
Section 18 emergency exemptions. Time-limited tolerances
are
established for residues of the fungicide quinoxyfen, 5,7-dichloro-4-
(4-fluorophenoxy)quinoline in connection with use of the
pesticide
under section 18 emergency exemptions granted by EPA. The
time-limited
tolerances will expire and are revoked on the date specified
in the
following table:
Note:
The following tolerances were published in the Federal
Register, January 28, 2005.
|
| Commodity |
Parts
per million |
Expiration/
Revocation Date |
| Pumpkin |
0.30 |
12/31/07 |
| Squash,
winter |
0.30 |
12/31/07 |
Vegetable,
cucurbit, subgroup 9A
This
group includes 19 commodities - see Ref. 1 below.
|
0.30 |
12/31/07 |
| (b)
Section 18 emergency exemptions. [Reserved]
(c) Tolerances with regional registrations. [Reserved]
(d) Indirect or inadvertent residues. [Reserved] |
(Ref
1) Vegetable, cucurbit,
group 09.
This group includes 19 commodities.
balsam
apple • balsam pear • cantaloupe • chayote,
fruit • cucumber • cucumber, chinese •
cucurbits • gherkin, west indian • gourd, edible
• melon • melon, citron • muskmelon •
pumpkin • squash • squash, summer • squash,
winter • vegetable, cucurbit, group • watermelon
• waxgourd, chinese
|
|

