|
Return to Metaflumizone
Index Page
Activity: Insecticide
(unclassified)
Structure
for CAS Name:
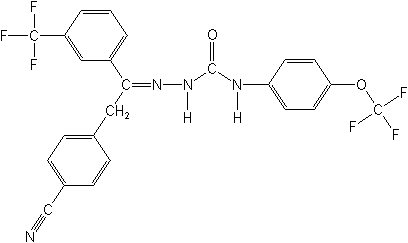
Adverse Effects:
Ataxia
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Clastogenic
Liver
Reproductive
In
October 2004 the pesticide Metaflumizone was first announced
to the public. Soon after, on October 27, US EPA published
a Notice in the Federal
Register with a petition for food tolerances from BASF.
The following are the adverse effects cited by BASF in that
Notice. The
pesticide in this Notice was called BAS 3201 I.
|
Ataxia
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
In a developmental (teratology) toxicity
study in the Himalayan rabbit,
the results indicated that the NOAEL for maternal toxicity was
100 mg/kg b.w./day, based on several clinical symptoms of toxicity
(including ataxia and poor general
state) occurring in 4 of 25 does at 300 mg/kg b.w./day, for which
2 of these 4 does had abortions prior to being sacrificed early,
with a third doe at 300 mg/kg b.w./day being sacrificed moribund.
Similarly, the NOAEL for fetal (prenatal)/ developmental toxicity
was 100 mg/kg b.w./day, based on slightly decreased mean fetal
body weights as well as an increased rate for a certain skeletal
variation, namely incomplete ossification of sternabrae.
Ref: October 27,
2004. Federal Register. Pesticide
tolerance petition.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/metaflumizone.fr.oct.27.04.htm
Blood
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
In the beagle dog, treatment by oral gavage with BAS 320
I for a subchronic duration (90-day
timepoint in the chronic toxicity study) resulted in
reduced body weight gain and/or decreased
food consumption in several dogs at 30 mg/kg b.w./day and slightly
decreased mean cell
hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) at 30 mg/kg b.w./day. Under the
conditions of the study, the NOAEL for oral administration of
BAS 320 I for 90 days was 12 mg/kg b.w./day.
-- In the beagle dog, treatment
via gelatin capsules with BAS 320 I for a 12-month
chronic duration resulted in reduced
body weight gain and/or decreased food consumption in several
dogs at 30 mg/kg b.w./day and slightly
decreased mean MCHC at 30 mg/kg b.w./day. Under the conditions
of the study, the NOAEL for oral administration
of BAS 320 I for 12 months was 12 mg/kg b.w./day.
Ref: October 27,
2004. Federal Register. Pesticide
tolerance petition.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/metaflumizone.fr.oct.27.04.htm
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
Reproductive and developmental
toxicity. ...
a 2-generation reproduction toxicity study in Wistar
rats by oral gavage administration. Originally, the highest
dose tested (HDT) by oral gavage was 75 mg/kg b.w./day, which
induced both excessive maternal toxicity (very high incidences
of poor general health in females during premating, gestation,
and lactation; and statistically decreased
food consumption, body weights, and body weight gain) as
well as excessive developmental toxicity (statistically
impaired pup body weights and body weight gain), which
altogether resulted in high pup mortality. Consequently, a meaningful
assessment of the potential reproductive toxicity of the test
compound at this excessively toxic dose level was not possible.
Thereafter, for the next two successive parental generations of
rats, which were originally derived from the parents treated at
75 mg/kg b.w./day, the HDT was 50 mg/kg b.w./day. Subsequently,
the no observable adverse effect level (NOAEL) for parental toxicity
was 20 mg/kg b.w./day, based on the following effects for females
at 50 mg/kg b.w./day (HDT for two consecutive generations) increased
incidences of poor general health in females during premating,
gestation, and lactation; 3 of 25 dams with complete litter losses;
and statistically significantly reduced
body weights during premating, gestation, and lactation.
The NOAEL for offspring/pup toxicity was 20 mg/kg b.w./day, based
on a slight increased incidence of pup mortality at 50 mg/kg b.w./day.
Whereas the NOAEL for fertility in this study was 50 mg/kg b.w./day
(HDT for two generations), the
NOAEL for reproductive performance was considered to be 20 mg/kg
b.w./day, based on 3 of 25 dams with complete litter losses,
of which 2 of these 3 dams had indications of poor nursing
for their first generation of pups.
-- In a developmental (teratology) toxicity
study in the Wistar rat, the
results indicated that the NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 40
mg/kg b.w./day, based on statistically decreased
food consumption and body weight gains at 120 mg/kg b.w./day
(HDT). The NOAEL for fetal (prenatal) /developmental toxicity
was 120 mg/kg b.w./day (HDT).
-- Chronic toxicity. In the Sprague-Dawley
rat, treatment by oral gavage with
BAS 320 I for a 2-year chronic duration resulted in dose-related
increased incidences of hepatocellular centrilobular hypertrophy
in the livers of males and females at 60
mg/kg b.w./day and at 300/200 mg/kg b.w./day and hepatocellular
basophilic alteration in males at 60 and 300 mg/kg b.w./day.
(Note: Beginning the first day of Week 3, the dose level of the
high-dose females was lowered from 300 to 200 mg/kg b.w./day,
due to an adverse effect of -71%
decreased body weight gain as compared to controls.)
-- In the beagle dog, treatment via
gelatin capsules with BAS 320 I for a 12-month chronic duration
resulted in reduced body weight gain
and/or decreased food consumption in several dogs at 30 mg/kg
b.w./day and slightly decreased mean MCHC at 30 mg/kg b.w./day
... For BAS 320 I, the lowest NOAEL for chronic toxic effects
is 12 mg/kg b.w./day from the 12-month dog study.
-- Subchronic toxicity study with Z-Isomer.
In the Sprague-Dawley rat, treatment by oral gavage with the Z-isomer
of BAS 320 I for a subchronic (90-day) duration resulted in impaired
body weight gain only in females at the mid-dose (300 mg/kg
b.w./day) and the high-dose (1,000 mg/kg b.w./day), as compared
to controls. Several microscopic changes were observed in female
animals at these two dose levels, but all morphologic changes
were regarded to be indirect effects of the impaired
body weight gain.
Ref: October 27,
2004. Federal Register. Pesticide
tolerance petition.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/metaflumizone.fr.oct.27.04.htm
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
In a developmental (teratology) toxicity
study in the Himalayan rabbit,
the results indicated that the NOAEL for maternal toxicity was
100 mg/kg b.w./day, based on several clinical symptoms of toxicity
(including ataxia and poor general state) occurring in 4 of 25
does at 300 mg/kg b.w./day, for which 2 of these 4 does had abortions
prior to being sacrificed early, with a third doe at 300 mg/kg
b.w./day being sacrificed moribund. Similarly, the NOAEL for fetal
(prenatal)/ developmental toxicity was 100 mg/kg b.w./day, based
on slightly decreased mean fetal body weights as well as an increased
rate for a certain skeletal variation, namely incomplete ossification
of sternabrae.
Ref: October 27,
2004. Federal Register. Pesticide
tolerance petition.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/metaflumizone.fr.oct.27.04.htm
Clastogenic
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Genotoxicty.
In a battery of three in vitro and two in vivo mutagenicity assays
consisting of all required end-points (point mutation, chromosomal
damage, and DNA damage and repair), the weight of the evidence
for BAS 320 I indicates a lack of potential genotoxicity.
Specifically, for the battery of three in vitro mutagenicity assays
with BAS 320 I, no positive responses were observed for increased
revertant frequencies with and without metabolic activation bacterial
reverse mutation assay or for increased mutant frequencies with
and without metabolic activation Hypoxanthine guanine phophoribosyl
transferase (HGPRT) locus assay. Although
there was a positive result for a statistically increased number
of structurally aberrant metaphases in the chromosomes, which
indicates clastogenic potential under in vitro conditions, this
result was only observed without metabolic activation cytogenicity
study with V79 cells.
Importantly, the potential biological significance of this
apparent chromosome damage observed in vitro only without metabolic
activation, was evaluated in vivo using the mouse micronucleus
assay. Testing in the in vivo micronucleus study with NMRI mice
was conducted at a high dose level (2,000 mg/kg b.w.) that demonstrated
clinical symptoms of toxicity, including piloerection and poor
general state, in 5 of 5 animals. No significant or dose-related
increases in chromosomal damage were observed in this in vivo
test, indicating that BAS 320 I does not cause chromosomal aberrations
in intact animals.
Moreover,
it has also been recognized by EPA that more weight should be
placed on in vivo systems than in vitro systems as expressed in
the Agency's weight of evidence for genotoxic evaluation of a
chemical
included in the ``Guidelines for Mutagenicity Risk
Assessment'' (Federal Register, September 24, 1986, Vol. 51: 34006-34012).
Thus, the negative in vivo results (non-clastogenicity for chromosomal
aberrations) observed in the mouse micronucleus assay and the
rat hepatocytes assay, should override the
positive results obtained in the in vitro assay only without
metabolic activation. Furthermore, it has been noted that in vitro
systems may simulate abnormal physiological conditions from prolonged
exposure to a chemical in the absence of S-9 metabolic activation
(Brusick, D.J. (editor) 1987. Genotoxicity Produced in Cultured
Mammalian Cell Assay by Treatment Conditions. Mutation Research,
Vol. 189, No.1: 1-69 and Sofuni, T. 1993. Japanese Guidelines
for Mutagenicity Testing. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis,
Vol. 21, No.1: 2-7). Consequently, based
on the weight of the evidence presented above, BAS 320 I does
not pose a genotoxic concern.
Ref: October 27, 2004. Federal Register.
Pesticide
tolerance petition.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/metaflumizone.fr.oct.27.04.htm
Definitions:
In vivo
= In a living cell or organism.
In
vitro
= In an experimental situation outside the organism.
Biological or chemical work done in the test tube (in
vitro is Latin for "in glass") rather than in
living systems.
|
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
Chronic toxicity. In the Sprague-Dawley
rat, treatment by oral gavage with
BAS 320 I for a 2-year chronic duration resulted in dose-related
increased incidences of hepatocellular centrilobular
hypertrophy in the livers of males and females at 60 mg/kg
b.w./day and at 300/200 mg/kg b.w./day and hepatocellular
basophilic alteration in males at 60 and 300 mg/kg b.w./day.
(Note: Beginning the first day of Week 3, the dose level of the
high-dose females was lowered from 300 to 200 mg/kg b.w./day,
due to an adverse effect of -71% decreased
body weight gain as compared to controls.)
Ref: October 27,
2004. Federal Register. Pesticide
tolerance petition.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/metaflumizone.fr.oct.27.04.htm
Reproductive
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
Reproductive and developmental
toxicity. ...
a 2-generation reproduction toxicity study in Wistar
rats by oral gavage administration. Originally, the highest
dose tested (HDT) by oral gavage was 75 mg/kg b.w./day, which
induced both excessive maternal toxicity
(very high incidences of poor general health in females during
premating, gestation, and lactation; and statistically decreased
food consumption, body weights, and body weight gain) as well
as excessive developmental toxicity (statistically
impaired pup body weights and body weight gain), which altogether
resulted in high pup mortality. Consequently, a meaningful
assessment of the potential reproductive toxicity of the test
compound at this excessively toxic dose level was not possible.
Thereafter, for the next two successive parental generations of
rats, which were originally derived from the parents treated at
75 mg/kg b.w./day, the HDT was 50 mg/kg b.w./day. Subsequently,
the no observable adverse effect level (NOAEL) for parental toxicity
was 20 mg/kg b.w./day, based on the following effects for females
at 50 mg/kg b.w./day (HDT for two consecutive generations) increased
incidences of poor general health in females during premating,
gestation, and lactation; 3 of 25 dams with complete litter losses;
and statistically significantly reduced
body weights during premating, gestation, and lactation.
The NOAEL for offspring/pup toxicity was 20 mg/kg b.w./day, based
on a slight increased incidence of pup mortality at 50 mg/kg b.w./day.
Whereas the NOAEL for fertility in this study was 50 mg/kg b.w./day
(HDT for two generations), the NOAEL for
reproductive performance was considered to be 20 mg/kg b.w./day,
based on 3 of 25 dams with complete litter losses, of which
2 of these 3 dams had indications of poor nursing for their first
generation of pups.
Ref: October 27,
2004. Federal Register. Pesticide
tolerance petition.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/metaflumizone.fr.oct.27.04.htm
|

