|
Return
to Flusilazole Index Page
Activity: Fungicide
(azole)
Structure:
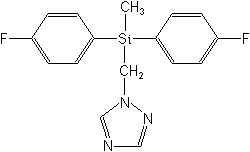
Adverse
Effects:
Bladder
Body Weight Decrease
Bone developmental - Cleft palate
Brain
Conjoined Twins
Developmental
Eye - Microphthalmia and Coloboma
Kidney
Liver
Reproductive
Teratogenic
Tongue
Environmental
Hazard Characterization (Page
13)
1,2,4-triazole (free triazole)
is a metabolite common to a number of triazole-derivative
pesticides, and is found in both mammalian (rat) and plant
metabolism studies. Although for most
pesticides, mammals convert only a small proportion to free
triazole (less than 25%), two
compounds (tetraconazole
and flusilazole) demonstrate relatively high conversion
(68-77%) in rat metabolism studies.
As a plant metabolite, and given the wide use of triazole-derivative
pesticides (used as fungicides on many crops as well as
on turf) free triazole is found in a variety of food commodities,
including animal byproducts. 1,2,4-triazole appears to be
relatively stable in the environment, and may be found in
rotational crops as well as in water...
Source: Human
Health Aggregate Risk Assessment for Triazole-derivative
Fungicide Compounds (1,2,4-Triazole, Triazole Alanine,
Triazole Acetic Acid). US EPA, February 7, 2006.
|
Bladder
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 2-Year Feeding
(oncogenic) - mouse: Systemic NOEL=3.4 mg/kg/day; Systemic LEL=27
mg/kg/day (increased absolute and relative liver
weight and increased hepatocellular fatty change in male
and females); core grade supplementary (E.I. du Pont de Nemours
& Co., Inc., 1985d)
-- 90-Day Feeding - rat: NOEL=125
ppm (6.25 mg/kg/day); LEL=375 ppm (18.75 mg/kg/day) (bladder
hyperplasia, elevated cholesterol);
core grade minimum (E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc.,
1983a)
-- 90-Day Feeding - dog: NOEL=25
ppm (0.625 mg/kg/day); LEL=125 ppm (3.13 mg/kg/day) (bladder
hyperplasia, elevated alanine aminotransferase/serum glutamate
pyruvate transaminase, uric acid, decreased total protein Ca albumen,
cholesterol, increased liver weight); core
grade minimum (E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc., 1983b)
Ref: US EPA IRIS. NuStar CASRN: 85509-19-9.
Available October 6, 2003, at Toxnet.
--The chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity studies in the rat, the
target organs identified were consistent with the sub-chronic
administration studies, i.e., liver and bladder. Flusilazole
was found to be oncogenic at the higher doses, causing bladder
transitional cell neoplasia in both sexes and testicular
Leydig cell adenoma in males. There is evidence
of a proliferative effect of flusilazole in the bladder transitional
epithelium, which is likely the mechanism of tumorigenesis. Therefore,
the urinary bladder tumors are considered to be caused by an epigenetic,
threshold-associated mechanism. Interference of flusilazole
with hypothalmic- pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis is suggested as
a possible mechanism of testicular tumor induction. Evidence in
support of this theory was provided by a comparative study with
the aromatase inhibitor, ketoconazole. Flusilazole did cause a
slight reduction in both serum and testicular - testosterone and
a dose-dependent decrease in serum estradiol, but was far less
potent than ketoconazole. It would avoear reasonable to conclude
that a threshold exists for the induction by flusilazole of testicular
aienomas. The NOEL for neoplasms was 375 ppm (14.8 and 20.5 mg/kg/day
in males and females, respectively). (Page
29)
-- In mouse chronic studies, the target
organs were the liver, kidney, urinary
bladder and urethra. The incidence of hepatocellular adenomas
was increased at L 1000 ppm. Based on the combined results of
two studies, the NOEL for oncogenicity in mice is 200 ppm (36
mgrkglday) in females and 500 ppm (73.1 mg/kg/day) for males.
Since tumors occurred in excess of the MTD, and were preceded
at lower doses by histopathological change consistent with induction-related
hepatotoxicity, it is reasonable to conclude
that the induction of such tumors is related to cytotoxicity,
which demonstrates a clear threshold. (Pages
29-30)
-- Flusilazole was found to exert a clear
systemic toxicity on sub-chronic and chronic administration to
rats, mice and dogs. A similar pattern of effects was apparent
across the three species, with the liver,
urinary system and blood system targeted to varying degrees.
It was found to be oncogenic at high dose levels in both
mice and rats, inducing bladder transitional cell neoplasia in
rats and testicular adenoma in male rats and hepatocellular
adenomas and carcinomas in mice. (Page
30)
Ref: DuPont Punch (Active ingredient: Flusilazole) and DuPont
Charisma (Active ingredients: Flusilazole and Famoxadone): Summary
of data compiled in support of a Section 18 Emergency Exemption
request for control of Asian soybean rust on soybeans. By DuPont
authors: Cosgrove T, Czochor L, Dinter A, Jemberg K, Klemens A,
Marcon A, McInnes B, Mullin L, Russell M, Ryan D, Singles S, Vanderbroeck
V. Revision No. 1: February 2, 2005.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.appendix1.pdf
Blood (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- In a one-year feeding study, dogs were given flusilazole in
the diet at concentrations of 0, 5,20, and 75 pprn (MRID 400421
13). There were treatment-related effects
on hematological parameters at 75 pprn including increased white
blood cell count, ALP activity, and serum cholesterol. Serum total
protein and albumin levels were lower in the male high dose group.
Relative liver weight was increased at 75 ppm. Treatment-related
histopathological changes included liver centrilobular hepatocellular
enlargement and centrilobular inflammation and hyperplasia in
the lymphoid nodules of the gastric mucosa observed in the high
dose. In summary, the effects of feeding flusilazole to dogs for
one year were a dose-related trend towards mild to moderate hepatotoxicity
and a mild leucocytosis (inflammatory) response. The effects were
mainly seen in the high dose group and most pronounced in males.
The liver hypertrophy was considered likely to be an adaptive
response to increased metabolic demand. Based on minimal liver
histology at the mid-dose, 20 ppm (0.7 mgkglday) is considered
a NOAEL. (Pages 18-19)
-- Short-term exposure toxicity of flusilazole was investigated
in rats (gavage and dietary), mice (dietary), dogs (dietary) and
in rabbits (dermal application). The targets
identified were the blood system, liver and urinary bladder.
The dog was found to be the most sensitive species to the hepatotoxicity
and bladder toxicity of flusilazole. Degenerative
liver disorder and evidence of cellular proliferation (hyperplasia)
in the urinary bladder were seen at 125 ppm (4.3 mgikglday) in
the dog. The NOAEL was 0.9 mgkgiday. (Page
29)
Ref: DuPont Punch (Active ingredient: Flusilazole)
and DuPont Charisma (Active ingredients: Flusilazole and Famoxadone):
Summary of data compiled in support of a
Section 18 Emergency Exemption request for control of Asian soybean
rust on soybeans. By DuPont authors: Cosgrove T, Czochor L, Dinter
A, Jemberg K, Klemens A, Marcon A, McInnes B, Mullin L, Russell
M, Ryan D, Singles S, Vanderbroeck V. Revision No. 1: February
2, 2005.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.appendix1.pdf
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 2-Generation Reproduction
- rat: Parental NOEL=3.5 mg/kg/day;
Parental LEL=19 mg/kg/day (decreased body
weight and body weight gain in F1 males during the 90 day
feeding study); Reproductive NOEL and LEL could not be determined;
Developmental NOEL=0.85 mg/kg/day (hydronephrosis
noted at weaning of F2b pups - only trial examined); core grade
supplementary (E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc., 1986b)
-- Teratology - rat: Maternal NOEL=10
mg/kg/day; Maternal LEL=100 mg/kg/day (increased mortality after
day 23 of gestation, prolonged gestation, decreased
food consumption and weight gain,
increased relative and absolute liver weight);
Developmental NOEL (pre and post natal)=2
mg/kg/day; Developmental LEL=10 mg/kg/day (increased incidence
of small renal papilla, distended ureter, dilated renal pelvis,
decreased pup survival); core grade minimum (E.I. du Pont de Nemours
& Co., Inc., 1985b)
-- Teratology - rabbit: Maternal
NOEL=12 mg/kg/day; Maternal LEL=35 mg/kg/day (decreased food consumption
and final body weight were observed at one dose only); Developmental
NOEL=12 mg/kg/day; Developmental LEL=35 mg/kg/day (increased resorptions
and abortions, and decreased fetal weight);
core grade minimum (E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc., 1985c)
Ref: US EPA IRIS. NuStar CASRN: 85509-19-9.
Available October 6, 2003 at Toxnet.
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: This report
describes the first part of a study which was undertaken to examine
the teratogenic potential of triazole compounds used as fungicides
in agriculture. Pregnant Wistar rats were given single oral dosages
of flusilazole or bitertanol on days 9, 10, 11 or 13th of gestation
(positive vaginal smear=day 1) at levels of 1/5, 1/10 and 1/50
LD50. The dosages were calculated from the reported LD50 values
of 1272 mg/kg for flusilazole and
5000 mg/kg for bitertanol. The results of the study demonstrated
that both compounds induce congenital anomalies
when given on days 9, 10 or 11th at levels corresponding to 1/5
and 1/10 LD50. The types of the registered
malformations after flusilazole treatment
were exophthalmus, hypognathia,
macroglossia and cleft palate
and after bitertanol treatment micro- and acaudia and in rare
cases exophthalmus, hypognathia and cleft palate. A clear dose
effect relationship was established for both compounds.
Ref:
Vergieva T (1990). Teratology 1990 Aug;42(2):27A-28A. Triazoles
teratogenicity in rats. Abstract from Toxnet.
•
Definitions:
Exophthalmia (n.) The protrusion
of the eyeball so that the eyelids will not cover it, in consequence
of disease.
Hypognathus - Unequal conjoined
twins in which the rudimentary parasite is attached to the mandible
of the autosite.
Macroglossia
-
Excessively large tongue.
Note
from FAN - not sure if this is appropriate under this category.
PubMed abstract: Triazole-derivatives are antimycotics used in
agriculture as well as in clinical and veterinary therapy. The
aim of the present work is the in vitro comparative study of the
teratogenic activity of triazole (the parental compound), flusilazole
(an agricultural triazole mono-derivative fungicide), and fluconazole
(a clinically used bis-triazole derivative). Rat embryos, 9.5
days old (1 to 3 somites) were exposed in vitro to triazole 500
to 5000 microM, flusilazole 3.125 to 250 microM, or fluconazole
62.5 to 500 microM. After 48 h in culture, the embryos were morphologically
examined and processed for histologic and biochemical analysis.
Flusilazole and fluconazole [antifungal
drug] showed similar teratogenic
effects (abnormalities at the branchial
apparatus level and cell death at the level of the branchial
mesenchyme) at concentration levels of 6.25 microM and higher
for flusilazole and of 125 microM and higher for fluconazole.
By contrast, only slight developmental retardation and blood discoloration
were observed at the highest concentrations of triazole, suggesting
no teratogenic activity for the triazole group.
Ref: Antifungal triazoles induce malformations
in vitro; by Menegola E, Broccia ML, Di Renzo F, Giavini E. Reprod
Toxicol 2001 Jul-Aug;15(4):421-7
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flusilazole.PubMed.Abstrcts.htm
•
Defintion:
branchial apparatus - Of
or pertaining to branchiae or gills. Branchial arches, the
bony or cartilaginous arches which support the gills
on each side of the throat of fishes and amphibians. Branchial
clefts, the openings between the branchial arches through which
water passes. Source: Websters Dictionary
Brain
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: Triazole-derivatives alter the pharyngeal apparatus
morphogenesis of rodent embryos cultured in vitro. The hindbrain
segmentation and the rhombencephalic neural crest cell (NCCs)
migration are altered by Fluconazole exposure in vitro. The aim
of the present work is to identify if a common pathogenic pathway
is detectable also for other molecules of this class of compounds.
9.5 days post coitum (d.p.c.) old rat embryos were exposed in
vitro to the teratogenic concentrations of Flusilazole, Triadimefon
and Triadimenol and cultured for 24, 48 or 60 h. The expression
and localisation of Hox-b1 and Krox-20 proteins (used as markers
for hindbrain segmentation) were evaluated after 24 h of culture.
The localisation and distribution of NCC was evaluated after 24,
30 and 48 h of culture. The morphology of the embryos was analysed
after 48 h, while the branchial nerve structures were evaluated
after 60 h of culture. Hindbrain segmentation and NCC migration
alteration as well as pharyngeal arch and cranial nerve abnormalities
were detected after exposure of the tested molecules. A
common severe teratogenic intrinsic property for the tested molecules
of this chemical class has been found, acting through alteration
of the normal hindbrain developmental pattern.
Reference: Menegola E, Broccia ML, Di Renzo
F, Massa V, Giavini E (2005). Study on the common teratogenic
pathway elicited by the fungicides triazole-derivatives. Toxicol
In Vitro. Sep;19(6):737-48.
Abstract available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=15913947&query_hl=19
1,2,4-triazole targets the nervous
system, both central and peripheral, as
brain lesions (most notably in the cerebellum)
were seen in both rats and mice, and peripheral nerve degeneration
was also seen in the subchronic neurotoxicity study in rats. In
addition, brain weight decreases were
seen in several studies, including in the offspring in the reproductive
toxicity study. In the subchronic/neurotoxicity study, there
is evidence that effects progress over time, with an increase
in incidence of clinical signs (including tremors and muscle fasciculations)
during weeks 8 and 13 that were not seen during earlier evaluations.
Effects were also seen on reproductive organs in both sexes, most
notably ovaries (in rats) and testes (in rats and mice), in both
the reproductive toxicity and subchronic toxicity studies. Hematological
changes, including slightly decreased hemoglobin and/or hematocrit,
have also been seen in multiple studies and species (in rats at
doses of 33 mg/kg/day and above, and in mice at doses of 487 mg/kg/day
and above). Studies depicting the effects of chronic exposure
to free triazole or its conjugates are not currently available.
Ref: Human
Health Aggregate Risk Assessment for Triazole-derivative Fungicide
Compounds (1,2,4-Triazole, Triazole Alanine, Triazole Acetic
Acid). US EPA, February 7, 2006.
abnormalities at the level of the branchial apparatus; disorganisation
and fusions at the level of the cranial nerves; abnormalities
in the migration of NCC, not able to form 3 distinct migration
stripes from the rhomboencephalon to the branchial apparatus;
alteration of the hindbrain segmentation, with reduced and scattered
immunolocalised stripes.
Reference: Massa et al. Mechanisms Involved
In Triazole-Induced Teratogenesis: In Vitro Study. Toxicol Lett
2003 Sep ;144 (Suppl 1 ):S107
Conjoined
Twins
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: This report
describes the first part of a study which was undertaken to examine
the teratogenic potential of triazole compounds used as fungicides
in agriculture. Pregnant Wistar rats were given single oral dosages
of flusilazole or bitertanol on days 9, 10, 11 or 13th of gestation
(positive vaginal smear=day 1) at levels of 1/5, 1/10 and 1/50
LD50. The dosages were calculated from the reported LD50 values
of 1272 mg/kg for flusilazole and
5000 mg/kg for bitertanol. The results of the study demonstrated
that both compounds induce congenital anomalies
when given on days 9, 10 or 11th at levels corresponding to 1/5
and 1/10 LD50. The types of the registered
malformations after flusilazole treatment
were exophthalmus, hypognathia,
macroglossia and cleft
palate and after bitertanol treatment micro- and
acaudia and in rare cases exophthalmus, hypognathia and cleft
palate. A clear dose effect relationship was established for both
compounds.
Ref:
Vergieva T (1990). Teratology 1990 Aug;42(2):27A-28A. Triazoles
teratogenicity in rats. Abstract from Toxnet.
• Definitions:
Exophthalmia (n.) The protrusion
of the eyeball so that the eyelids will not cover it, in consequence
of disease.
Hypognathus - Unequal conjoined
twins in which the rudimentary parasite is attached to the mandible
of the autosite.
Macroglossia
-
Excessively large tongue.
Much of what is known
about the possible dangers of flusilazole
is considered a trade secret -- unavailable even to state
agents investigating health complaints. What is known about the
fungicide -- which is not approved for use in the United States
-- offers little comfort to those who applied it to Florida farmland
as an undisclosed ingredient in some lots of Benlate 50 DF. According
to a study conducted in Bulgaria, oral doses of flusilazole given
to pregnant rats produced congenital defects such as
protruding eyes,
twins of unequal size joined at the jaw and grossly
enlarged tongues...
Ref: Jan Hollingsworth. Fungicide studies
offer little comfort. Memo: BURIED SECRETS PURSUING A MEDICAL
MYSTERY. December 18, 1995. Tampa Tribune (Florida). page 4.
Developmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Ten developmental toxicity studies were carried out with flusilazole,
six in the rat (one dietary, four gavage, and one dermal) and
four in the rabbit (one dietary and four gavage). In rats, maternal
toxicity included decreased weight gain and food consumption,
increased clinical signs, and increased liver weights. Fetal toxicity
was evidenced by increased incidences of
resorptions, fetal mortality, stunted fetuses, and skeletal variations
(delayed ossifications, supernumerary ribs, and renal pelvis variations)
and decreased fetal weight. Absent
renal papillae occurred at 10 mgkglday and above and cleft palate
occurred at 250 mgkg/day. Taken as
a whole, the NOEL in rats was 0.5 mg/kg/day by the oral route.
By the dermal route 2 mg/kg/day was near a NOAEL based on only
placental, but no fetal effects at this dose. (- In a rabbit dietary
developmental study the NOEL for the dam was 21.2 mg/kg/day and
the developmental NOEL was 2.8 mgkg/day based on decreased litters
and increased resorptions. In the first two rabbit gavage studies,
the maternal and offspring NOELS were both 12 mg/kg/day. In the
second there were increased total resorptions
and one malformation (hydrocephaly) at 35 mg/kg/day. In
the final rabbit gavage study, the maternal NOEL was 7 mgkglday
based on increased clinical signs as 15 mgkglday. The developmental
NOEL was 15 mg/kg/day based on increased resorptions at the high
dose. Taken as a whole, the rabbit maternal NOEL via the gavage
route is 7 mgkg/day and the developmental NOEL is 15 mgikglday.
(Page 30)
-- In the feeding study, dietary concentrations were 0,50, 100,
300 and 900 pprn (MRID 00072999). Maternal food consumption was
reduced at ≥300 pprn during treatment and maternal body
weight gains were reduced at 900 ppm. The number
of resorptions was significantly increased at the two highest
doses and litter size was reduced at the highest dose.
There was a significant dose related increase
in stunted fetuses, significant at ≥300 ppm. There
were no dose-related incidences of malformations. The
incidence of variations (supernumerary and delayed ossifications)
was increased at ≥ 100 ppm. The maternal NOEL was
100 pprn - (9 mgkgiday). EPA considered
the developmental NOAEL to be 100 ppm (9.0 mg/kg/day) and li the
NOEL for malformations to be > 900 pprn (79.2 mg/kg/day) the
highest dose tested. (Page
21)
-- In the first of three rat gavage studies, flusilazole was administered
by gavage (in corn oil) at concentrations of 0, 10,50 and 250
mgikgiday (MRID 00161 169). Maternal morality and clinical signs
occurred at 250 mg/kg/day. Weight gain and food consumption were
decreased and liver weight increased at ≥ 50 mg/kg/day group
during dosing. In the 250 mg/kg/day group mean fetal body weight
was reduced; the incidence of resorptions increased; and the number
of live fetuses per litter were reduced. The number of live fetuses
was also decreased in the intermediate group. There was a significant
increase in malformations (cleft palate and absent renal papillae)
at the maternally toxic dose, 250 mg/kg/day. There was
an unusually high incidence of external
hydrocephaly and distended lateral ventricles in all groups (including
controls). However, this finding did not exhibit a definitive
dose response and was not reproduced in another study over a similar
dose range. Increased fetal variations in
all dosed groups were misaligned sternebra, extra ossifications,
rudimentary and extra ribs and delayed development consisting
of partially ossified sternebra and vertebral arch. The
maternal NOEL was 10 rng/kg/day and no fetal NOEL was established
(< 10 mg/kg/day). (Page
21)
-- In the second gavage study, flusilazole was administered to
rats at doses of 0,0.4,2, 10, 50, and 250 mg/kg/day (MRID 00161170).
Maternal findings at 250 mg/kg/day were reduced feed consumption
and weight gain and increased liver weights. At 50 mg/kg/day,
there was a significant decreased food consumption and weight
for the first two days but not thereafter. Relative liver weight
was increased also at 50 mg/kg/day. A non-statistically
significant increase in stunted fetuses occurred at 2 10 mgkglday.
There was a statistically significant increase
in malformations (cleft palate) in the maternally toxic, high-dose
group. The incidence of total malformations
(mostly absent renal papillae) and fetal variations were significantly
increased at ≥ 10 mg/kg/day. The maternal NOEL 10
mgkg was based on reduced weight gain, liver weight increases
and clinical signs. The developmental NOEL
was 2.0 mgkg, based on increased incidence of skeletal variations.
(Pages 21-22)
-- The third rat developmental gavage study,
was conducted to resolve the biological significance and potential
reversibility of the changes to the urinary system (small or no
papillae, large renal pelvi and dilated ureter) seen in the previous
study (MRID 40640704). Rats were dosed with 0, 0.2,0.4,2, 10,
and 100 mg/kg/day and either sacrificed at gestation day 21 or
22 to examine fetuses (Phase 1) or dams were allowed to deliver
and raise their young to weaning (Phase 2). Maternal toxicity
was evidenced at the high dose in both phases as decreased food
consumption and reduced weight gain, clinical signs (Phase 1 only),
and death (Phase 2). Minimal maternal toxicity (reduction in weight
gain during Phase 2) occurred 10 mg/kg/day. Fetal
effects consisted of increased incidence of resorptions and stunted
fetuses (100 rng/kg/day), increased numbers of fetuses dead at
birth, and lower neonatal survival. In the fetal examinations
there was an increased incidence of small renal papillae, dilated
ureters and subcutaneous hemorrhage at 2 10 mg/lkg/day and bladder
foci at 100 rng/kg/day. There were no apparent treatment-related
malformations. The maternal and reproductive/developmental
was NOAEL 2.0 mg/kg/day. (Page
22)
-- In the fourth rat gavage study (MRID 45042601), rats were dosed
with 0,0.5,2, 10, or 50 mg/kg/day flusilazole on one of the following
three schedules: days 6-15G (gestation) and sacrificed day 16G,
days 6-15G and sacrificed day 21G, or 6-20G and sacrificed on
day 21G. - Results were generally similar between the three designs.
Maternal weight gain was affected at ≥10 mg/kg/day. Red
vaginal discharge was observed at 2 mg/kg/day. Placental weights
were increased at 22 mg/kg/day. Fetal weights were affected
at 50 mg/kg/day only in the group dosed from 6-15G and sacrificed
at 21G. Fetal resorptions were increased at 210 mgkglday.
Fetal variations were increased at ≥2 mg/kg/day.
At 50 mg/kg/day there was one malformation
(naris atresia). The NOEL
for the study was 0.5 mg/kg/day based on minimally increased incidence
of red vaginal discharge, increased placental weight and increased
fetal variations at 2 mg/kg/day. (Page
22)
-- In a rat dermal developmental toxicity study (MRID 44594201),
flusilazole was applied to the skin of pregnant rabbits for six
hourslday on days 6 to 19 of gestation at doses of 0, 2, 10, 50,
and 250 mg/kg/day. Rats were sacrificed on gestation day 20. Mean
maternal weight gains were greatly reduced in the 250 mg/kglday
group. There were no abnormal clinical signs at any concentration.
Microscopic examination of the dams' livers revealed minimal to
mild centrilobular hepatocellular hypertrophy at ≥ 10 mg/kg/day.
There were enlarged placenta observable at ≥ 10 mg/kg/day
and microscopic placental changes at all dose levels. There
were no other maternal effects at 2 mg/kg/day.
Fetuses of dams treated with ≥ 10 mg/kg/day had enlarged
livers and increased variations (rudimentary ribs and unossified
sternebra). The lowest dose (2 rng/kg/day) was considered
to approximate a NOAEL with the only effect being microscopically
observable placental changes. It was not
established whether the effect on placenta represent an adverse
effect. Since placenta contains a large amount of cytochrome P-450
enzymes, the possibility of a metabolic/adaptive role should be
considered. (Page 22)
Ref: DuPont Punch (Active ingredient: Flusilazole)
and DuPont Charisma (Active ingredients: Flusilazole and Famoxadone):
Summary of data compiled in support of a
Section 18 Emergency Exemption request for control of Asian soybean
rust on soybeans. By DuPont authors: Cosgrove T, Czochor L, Dinter
A, Jemberg K, Klemens A, Marcon A, McInnes B, Mullin L, Russell
M, Ryan D, Singles S, Vanderbroeck V. Revision No. 1: February
2, 2005.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.appendix1.pdf
Endocrine
Disruptor
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract:
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) are used as antifungal agents
in agriculture and in medicine, and also for antiestrogen therapy,
e.g., for breast cancer treatment.
Antifungal activity is based on inhibition of fungal CYP51 (lanosterol
14alpha-demethylase), and estrogen biosynthesis reduction is due
to azole inhibition of CYP19 (aromatase).
Inhibition of aromatase by antifungal agents is usually
an unwanted side effect and may cause endocrine disruption. A
fluorimetric assay based on human recombinant CYP19 enzyme with
dibenzylfluorescein as a substrate was used to compare the inhibitory
potency of 22 azole compounds. Dose responses were established
and duplicate datasets were analyzed with a nonlinear mixed-effects
model with cumulative normal distribution for the logarithm of
concentration. IC50 values (50% inhibitory concentration) of 13
fungicides used in agriculture ranged more than 700-fold, starting
from 0.047 microM. The potency of seven human drugs spanned more
than 7000-fold, starting from 0.019 microM. Most
potent fungicides included prochloraz, flusilazole,
and imazalil, and most potent medicinal antifungals were bifonazole,
miconazole, and clotrimazole. These in vitro data indicate that
the top-ranking azoles used as antifungal agents or drugs are
as potent inhibitors of aromatase as are antiestrogen therapeutics
used to treat breast cancer. These putative
effects of azole agents and drugs on steroid biosynthesis and
sex hormone balance should be considered when used in human subjects
and also in wildlife exposed to azole fungicides used in agriculture.
Ref:
Comparative assessment of the inhibition of recombinant human
CYP19 (aromatase) by azoles used in agriculture and as drugs for
humans. Trosken
ER, Scholz K, Lutz RW, Volkel W, Zarn JA, Lutz WK. Endocr Res.
2004 Aug;30(3):387-94.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=15554355
•
Definition of aromatase inhibition:
Prevention of the formation of estradiol, a female hormone,
by interfering with an aromatase enzyme. Aromatase inhibition
is a type of hormone therapy used in postmenopausal women who
have hormone-dependent breast cancer.
Endocrine:
Testicular (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- A second, two-year chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity flusilazole
feeding study was carried out in the rat to achieve an MTD (MRID
42613202). Rats were fed diets containing 0, 125, 375, and 750
pprn flusilazole for two years. Toxicologically significant effects
of treatment with flusilazole were seen at every dose level in
this study. The following were also observed: mortality (5) and
induced hepatocellular hypertrophy, fatty change and mixed cell
foci, testicular interstitial cell hyperplasia
and interstitial cell adenomas in males; decreased mean
final body weight and hepatocellular centrilobular hypertrophy
in females; and increased mean absolute and relative liver weights,
hepatocellular lamellar bodies, urinary bladder mucosal hyperplasia,
and --. transitional cell neoplasms in both sexes. There was no
NOEL for non-neoplastic lesions in either sex. The NOEL for neoplasms
was 375 pprn (14.8 and 20.5 mgikglday in males and females, respectively).
- (Page 18)
-- In the rat, target organs were consistent with the subchronic
administration studies, i.e., liver and bladder. Flusilazole was
oncogenic at the higher doses, causing bladder transitional cell
neoplasia in both sexes and testicular Leydig
cell adenomas in males... Based on subsequent mechanistic
work (see mechanistic section that follows) interference
of flusilazole with hypothalmic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis is
a possible mechanism of testicular tumor induction. Therefore,
it is reasonable to conclude that a threshold exists for the induction
by flusilazole of testicular adenomas. The NOEL for neoplasms
was 375 pprn (14.8 and 20.5 mglkglday in males and females, respectively).
(Page 19)
SUPPLEMENTARY MECHANISTIC STUDIES
---- A 90-day study (MRID 42613204) was conducted to investigate
mechanisms of toxicity (hepatotoxicity) and oncogenicity (urinary
bladder transitional cell tumors and testicular
Leydig cell adenomas) of flusilazole in the rat. Since
genotoxicity tests were negative, a non-genotoxic mechanisms of
tumor induction were investigated i.e., increased cellular proliferation
rates due to irritation or chronic toxicity, and peroxisome proliferation-mediated
events. Flusilazole was administered to rats in the diet at concentrations
of 0, 10, 125, 375 and 750 ppm. Rats were sacrificed after 1 or
2 weeks or 1.5 or 3 months. Liver weight increases correlated
well with the observed cytochrome P-450 induction. It was concluded
from these results that the liver toxicity seen in this study
and therefore the long-term studies also was due to the observed
induction of cytochrome P-450 causing proliferation of the SER
and hepatocellular hypertrophy. In the urinary bladder, there
was a clear proliferative response following treatment with flusilazole.
Serum hormone levels were not significantly altered in this study.
It was suggested that the mechanism may lie in the ability to
inhibit cytochrome P-450 activity thereby inhibiting steroidogenesis.
An additional study was carried out to further investigate the
possible mechanism of testicular adenoma induction. The results
of this study support the proposal that the toxicity of flusilazole
results from effects on cytochrome P-450, and direct toxic effects
on the bladder. (Page 28)
---- In the final two-year feeding study in the rat, flusilazole
was found to induce testicular adenomas in males. A possible
non-genotoxic mechanism for such tumor induction was investigated
(HLR 410-93). Flusilazole has been shown
to inhibit cytochrome P-450 by the same mechanism as ketoconazole
(an anti-tumor agent used in the treatment of human testicular
carcinoma). In an in vivo experiment, rats were treated
twice daily with either 0, 10,25, 75 or 125 mg/kg/day of flusilazole
or 0, 10, 25,50 or 100 mg/kg/day of ketoconazole for 14 days.
In an in vitro experiment, Leydig cells were isolated
from rats and cultured with ketoconazole or flusilazole and the
concentrations of steroids were measured. In the in vivo
study, relative accessory sex gland weights were reduced with
ketoconazole, but not flusilazole. It was concluded that either
the flusilazole was less potent than ketoconazole or operated
by another mechanism. Ketoconazole produced a decrease in serum
testosterone and related steroids. Flusilazole
caused reduction in both serum and testicular testosterone and
estradiol, but was far less potent than ketoconazole. It
was proposed that this data supported the theory that flusilazole
could induce Leydig cell tumors by decreasing testosterone and
estradiol synthesis thus disrupting the HPT axis. (Page
28)
-- The chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity
studies in the rat, the target organs identified were consistent
with the sub-chronic administration studies, i.e., liver and bladder.
Flusilazole was found to be oncogenic
at the higher doses, causing bladder transitional cell neoplasia
in both sexes and testicular Leydig cell adenoma in males. There
is evidence of a proliferative effect of flusilazole in the bladder
transitional epithelium, which is likely the mechanism of tumorigenesis.
Therefore, the urinary bladder tumors are considered to be caused
by an epigenetic, threshold-associated mechanism. Interference
of flusilazole with hypothalmic- pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis
is suggested as a possible mechanism of testicular tumor induction.
Evidence in support of this theory was provided by a comparative
study with the aromatase inhibitor, ketoconazole. Flusilazole
did cause a slight reduction in both serum and testicular - testosterone
and a dose-dependent decrease in serum estradiol, but was far
less potent than ketoconazole. It would
appear reasonable to conclude that a threshold exists for the
induction by flusilazole of testicular aienomas. The NOEL
for neoplasms was 375 ppm (14.8 and 20.5 mglkgiday in males and
females, respectively). (Page 29)
Ref: DuPont Punch (Active ingredient: Flusilazole)
and DuPont Charisma (Active ingredients: Flusilazole and Famoxadone):
Summary of data compiled in support of a
Section 18 Emergency Exemption request for control of Asian soybean
rust on soybeans. By DuPont authors: Cosgrove T, Czochor L, Dinter
A, Jemberg K, Klemens A, Marcon A, McInnes B, Mullin L, Russell
M, Ryan D, Singles S, Vanderbroeck V. Revision No. 1: February
2, 2005.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.appendix1.pdf
Eye
- Microphthalmia
and Coloboma (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Parents
believe that exposure to Flusilazol during pregnacy resulted in
severe eye deformities such as microphthalmia
(small eyes) and coloboma,
a defect in the structure of the eyes.
Ref: Scottish Daily Record & Sunday
Mail Ltd. - Sunday Mail. October 15, 2000
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flusilazole.Scot.EYE.2000.htm
• Definitions:
Coloboma - A defect of the iris
caused by a failure of the eyeball to fuse properly during fetal
development. These are developmental anomalies and do not worsen
as the child grows older.
Microphthalmia - An unnatural
smallness of the eyes, occurring as the result of disease or
of imperfect development.
Abstract: This report
describes the first part of a study which was undertaken to examine
the teratogenic potential of triazole compounds used as fungicides
in agriculture. Pregnant Wistar rats were given single oral dosages
of flusilazole or bitertanol on days 9, 10, 11 or 13th of gestation
(positive vaginal smear=day 1) at levels of 1/5, 1/10 and 1/50
LD50. The dosages were calculated from the reported LD50 values
of 1272 mg/kg for flusilazole and
5000 mg/kg for bitertanol. The results of the study demonstrated
that both compounds induce congenital anomalies
when given on days 9, 10 or 11th at levels corresponding to 1/5
and 1/10 LD50. The types of the registered
malformations after flusilazole treatment
were exophthalmus, hypognathia,
macroglossia and cleft
palate and after bitertanol treatment micro- and
acaudia and in rare cases exophthalmus, hypognathia and cleft
palate. A clear dose effect relationship was established for both
compounds.
Ref: Vergieva T (1990). Teratology 1990
Aug;42(2):27A-28A. Triazoles teratogenicity in rats. Abstract
from Toxnet.
•
Definitions:
Exophthalmia (n.) The protrusion
of the eyeball so that the eyelids will not cover it, in consequence
of disease.
Hypognathus - Unequal conjoined
twins in which the rudimentary parasite is attached to the mandible
of the autosite.
Macroglossia
-
Excessively large tongue.
Much of what is known
about the possible dangers of flusilazole
is considered a trade secret -- unavailable even to state
agents investigating health complaints. What is known about the
fungicide -- which is not approved for use in the United States
-- offers little comfort to those who applied it to Florida farmland
as an undisclosed ingredient in some lots of Benlate 50 DF. According
to a study conducted in Bulgaria, oral doses of flusilazole given
to pregnant rats produced congenital
defects such as protruding
eyes, twins of unequal size joined at the jaw and
grossly enlarged tongues...
Ref: Jan Hollingsworth. Fungicide studies
offer little comfort. Memo: BURIED SECRETS PURSUING A MEDICAL
MYSTERY. December 18, 1995. Tampa Tribune (Florida). page 4
Kidney
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 2-Generation Reproduction
- rat: Parental NOEL=3.5 mg/kg/day;
Parental LEL=19 mg/kg/day (decreased body
weight and body weight gain in F1 males during the 90 day feeding
study); Reproductive NOEL and LEL could not be determined;
Developmental NOEL=0.85 mg/kg/day (hydronephrosis
noted at weaning of F2b pups - only trial examined); core grade
supplementary (E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc., 1986b)
-- Teratology - rat: Maternal NOEL=10
mg/kg/day; Maternal LEL=100 mg/kg/day (increased mortality after
day 23 of gestation, prolonged gestation,
decreased food consumption and weight gain, increased relative
and absolute liver weight); Developmental NOEL (pre and
post natal)=2 mg/kg/day; Developmental LEL=10 mg/kg/day (increased
incidence of small renal papilla, distended
ureter, dilated renal pelvis,
decreased pup survival); core grade minimum (E.I. du Pont de Nemours
& Co., Inc., 1985b)
Ref:
US EPA IRIS. NuStar CASRN: 85509-19-9. Available October 6, 2003,
at Toxnet.
•
Definitions:
-- Hydronephrosis: Pathological
chronic enlargement of the collecting channels of a kidney,
leading to compression and eventual destruction of kidney tissue,
and diminishing kidney functionning.
-- renal papilla
- Renal
Papillary Necrosis Alternate Names : Necrosis - Renal Papillae,
Renal Medullary Necrosis Definition A disorder of the kidney
involving death of some or all of the renal papillae.
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Oral RfD Summary:
Critical Effect Experimental Doses. Liver
cell enlargement. 1-Year Dog Feeding Study. du Pont, 1985.
NOEL: 5 ppm (0.2 mg/kg/day) LEL: 20 ppm (0.7 mg/kg/day).
-- Nustar was administered in the diet at 0, 5, 20, or 75 ppm
(0, 0.2, 0.7, or 2.5 mg/kg bw/day) to 5 dogs/sex/dose for 1 year.
Hypertrophy of the centrilobular hepatocytes
was noted in both sexes at the mid- and high-dose levels. Changes
observed only at the high dose were consistent with hepatotoxicity
and inflammation. In males these included: increased WBC counts
due to increased neutrophils, monocytes and eosinophils; increased
alkaline phosphatase and decreased cholesterol and total protein;
and hepatocytic vacuolation. Increased liver weight and centrilobular
inflammation of the liver occurred in both males and females.
Thus, the NOEL and LEL for systemic toxicity are 5 ppm (0.2 mg/kg/day)
and 20 ppm (0.7 mg/kg/day), respectively. [E.I. du Pont de Nemours
and Company. 1985. MRID No. 40042113. Available from EPA. Write
to FOI, EPA, Washington, DC 20460.]
-- 2-Year Feeding (oncogenic) - rat: No increase in neoplastic
lesions at any dose; Systemic NOEL=0.46 mg/kg/day; Systemic LEL=2.3
mg/kg/day (hepatic changes in females at
1 year, including increased relative liver weight and hepatocellular
hypertrophy); core grade minimum (E.I. du Pont de Nemours
& Co., Inc., 1986a)
-- Teratology - rat: Maternal NOEL=10
mg/kg/day; Maternal LEL=100 mg/kg/day (increased mortality after
day 23 of gestation, prolonged gestation, decreased
food consumption and weight gain, increased relative and absolute
liver weight); Developmental NOEL (pre and post natal)=2
mg/kg/day; Developmental LEL=10 mg/kg/day (increased incidence
of small renal papilla, distended ureter, dilated renal pelvis,
decreased pup survival); core grade minimum (E.I. du Pont
de Nemours & Co., Inc., 1985b)
-- 2-Year Feeding (oncogenic) - mouse: Systemic NOEL=3.4 mg/kg/day;
Systemic LEL=27 mg/kg/day (increased absolute and relative liver
weight and increased hepatocellular fatty change in male
and females); core grade supplementary (E.I. du Pont de Nemours
& Co., Inc., 1985d)
-- 90-Day Feeding - dog: NOEL=25
ppm (0.625 mg/kg/day); LEL=125 ppm (3.13 mg/kg/day) (bladder
hyperplasia, elevated alanine aminotransferase/serum glutamate
pyruvate transaminase, uric acid, decreased total protein Ca albumen,
cholesterol, increased liver weight);
core grade minimum (E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc., 1983b)
Ref: US EPA IRIS. NuStar CASRN: 85509-19-9.
Available October 6, 2003, at Toxnet.
-- Short-term exposure toxicity of flusilazole was investigated
in rats (gavage and dietary), mice (dietary), dogs (dietary) and
in rabbits (dermal application). The targets identified were the
blood system, liver and urinary bladder. The dog was found to
be the most sensitive species to the hepatotoxicity and bladder
toxicity of flusilazole. Degenerative liver
disorder and evidence of cellular proliferation (hyperplasia)
in the urinary bladder were seen at 125 ppm (4.3 mgikglday) in
the dog. The NOAEL was 0.9 mgkgiday. (Page
29)
Ref: DuPont Punch (Active ingredient: Flusilazole)
and DuPont Charisma (Active ingredients: Flusilazole and Famoxadone):
Summary of data compiled in support of a
Section 18 Emergency Exemption request for control of Asian soybean
rust on soybeans. By DuPont authors: Cosgrove T, Czochor L, Dinter
A, Jemberg K, Klemens A, Marcon A, McInnes B, Mullin L, Russell
M, Ryan D, Singles S, Vanderbroeck V. Revision No. 1: February
2, 2005.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.appendix1.pdf
Reproductive
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
the effects of flusilazole on reproductive parameters were investigated
in one single-generation and two multigeneration studies. In the
single-generation study, there were effects on pup viability and
weights. In the first multigeneration study, there was no parental
toxicity demonstrated at doses up to 250 ppm. Offspring findings,
mostly at the high dose level included reduced number of live
pups at birth and reduced viability during lactation. The NOEL
r- for this study was 50 ppm based on perinatal effects. The same
dose levels were used in the second study. Minimal signs of treatment-related
effects seen in the 50 (not significant) and 250 pprn parental
animals consisted of body weight effects in parental females.
A significant increase in gestation length
and periparturient deaths occurred in the high dose group. This
finding was consistent with reduced viability of pups at birth.
In addition, pups did not thrive and reduced weight gain and survival
was recorded for litters of dams fed 250 pprn in all matings.
The NOEL for reproductive/offspring effects was 50 ppm. (Pages
20-21)
Ref: DuPont Punch
(Active ingredient: Flusilazole) and DuPont Charisma (Active ingredients:
Flusilazole and Famoxadone): Summary of
data compiled in support of a Section 18 Emergency Exemption request
for control of Asian soybean rust on soybeans. By DuPont authors:
Cosgrove T, Czochor L, Dinter A, Jemberg K, Klemens A, Marcon
A, McInnes B, Mullin L, Russell M, Ryan D, Singles S, Vanderbroeck
V. Revision No. 1: February 2, 2005.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.appendix1.pdf
-- Although
fish early life-stage tests provide useful information on sensitive
life stages of fish, for flusilazole
in particular the risk assessment has explicitly identified fish
and other aquatic species to be at risk from agricultural use
of this a.s., and there is evidence that flusilazole may
have specific effects on the reproductive process. Therefore
the SCP cannot conclude that a NOEC based on a fish early life-stage
test for a single species is necessarily adequate in this particular
case to ensure sufficient protection of fish populations from
adverse effects on reproduction.
-- The monograph (volume 3, pp. 230-233) identified aquatic species,
and fish in particular, as possibly at risk from flusilazole.
In addition, a dose-dependent decrease in
serum estradiol levels by flusilazole, considered to be indicative
of aromatase inhibition, was observed in
studies with rats (volume 3, p. 73). Aromatase
inhibition is significant for reproduction since aromatization
of testosterone is the process by which oestrogen is formed in
vertebrates (Trant et al. 1997). This reaction is mediated
by the cytochrome P450 aromatase. It has been shown that oestrogen
(i.e., oestradiol) plays a major role in the reproductive physilogy
of all vertebrates, including gamete development and maturation,
and induces the hepatic synthesis of the yolk precursor, vitellogenin.
Studies in which fish have been exposed to aromatase inhibitors
suggest that aromatase activity, specificity or expression levels
vary with maturation stage and among species (Bl‡zquez et al.
2001, Zerulla et al. 2002).
-- ... Neither of the above tests was designed to investigate
possible effects on reproductive output or mating behaviour of
adult fish. Given that there is evidence that flusilazole is an
aromatase inhibitor, there are specific concerns that reproduction
could be adversely affected by this substance. Therefore potential
effects on mating behaviour, time to sexual maturity, reproductive
output and timing, fertilisation success, and sex ratio of offspring
are also of concern and should be explicitly addressed by a test
designed for this purpose.
Ref: July 2002 - Opinion of the
Scientific Committee on Plants on specific questions from the
Commission concerning the evaluation of flusilazole in the Council
Directive 91/414/EEC. European Commission. Health & Consumer Protection
Directorate-General.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.eu.july.2002.pdf
1,2,4-triazole -
Effects were also seen on reproductive organs in both sexes, most
notably ovaries (in rats) and testes (in rats and mice),
in both the reproductive toxicity and subchronic toxicity studies....
Ref: Human
Health Aggregate Risk Assessment for Triazole-derivative Fungicide
Compounds (1,2,4-Triazole, Triazole Alanine, Triazole Acetic
Acid). US EPA, February 7, 2006.
Teratogenic
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: Triazole-derivatives alter the pharyngeal apparatus
morphogenesis of rodent embryos cultured in vitro. The hindbrain
segmentation and the rhombencephalic neural crest cell (NCCs)
migration are altered by Fluconazole exposure in vitro. The aim
of the present work is to identify if a common pathogenic pathway
is detectable also for other molecules of this class of compounds.
9.5 days post coitum (d.p.c.) old rat embryos were exposed in
vitro to the teratogenic concentrations of Flusilazole, Triadimefon
and Triadimenol and cultured for 24, 48 or 60 h. The expression
and localisation of Hox-b1 and Krox-20 proteins (used as markers
for hindbrain segmentation) were evaluated after 24 h of culture.
The localisation and distribution of NCC was evaluated after 24,
30 and 48 h of culture. The morphology of the embryos was analysed
after 48 h, while the branchial nerve structures were evaluated
after 60 h of culture. Hindbrain segmentation and NCC migration
alteration as well as pharyngeal arch and cranial nerve abnormalities
were detected after exposure of the tested molecules. A
common severe teratogenic intrinsic property for the tested molecules
of this chemical class has been found, acting through alteration
of the normal hindbrain developmental pattern.
Reference: Menegola E, Broccia ML, Di Renzo
F, Massa V, Giavini E (2005). Study on the common teratogenic
pathway elicited by the fungicides triazole-derivatives. Toxicol
In Vitro. Sep;19(6):737-48.
Abstract available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=15913947&query_hl=19
abnormalities at the level of the branchial apparatus; disorganisation
and fusions at the level of the cranial nerves; abnormalities
in the migration of NCC, not able to form 3 distinct migration
stripes from the rhomboencephalon to the branchial apparatus;
alteration of the hindbrain segmentation, with reduced and scattered
immunolocalised stripes.
Reference: Massa et al. Mechanisms Involved
In Triazole-Induced Teratogenesis: In Vitro Study. Toxicol Lett
2003 Sep ;144 (Suppl 1 ):S107
Abstract: This report
describes the first part of a study which was undertaken to examine
the teratogenic potential of triazole compounds used as fungicides
in agriculture. Pregnant Wistar rats
were given single oral dosages of flusilazole or bitertanol on
days 9, 10, 11 or 13th of gestation (positive vaginal smear=day
1) at levels of 1/5, 1/10 and 1/50 LD50. The dosages were calculated
from the reported LD50 values of 1272 mg/kg for
flusilazole and 5000 mg/kg for bitertanol. The results
of the study demonstrated that both compounds
induce congenital anomalies when given on days 9, 10 or 11th at
levels corresponding to 1/5 and 1/10 LD50. The types of
the registered malformations after flusilazole
treatment were exophthalmus, hypognathia,
macroglossia and cleft
palate and after bitertanol treatment micro- and
acaudia and in rare cases exophthalmus, hypognathia and cleft
palate. A clear dose effect relationship was established for both
compounds.
Ref:
Vergieva T (1990). Teratology 1990 Aug;42(2):27A-28A. Triazoles
teratogenicity in rats. Abstract from Toxnet.
•
Definitions:
Exophthalmia (n.) The protrusion
of the eyeball so that the eyelids will not cover it, in consequence
of disease.
Hypognathus - Unequal conjoined
twins in which the rudimentary parasite is attached to the mandible
of the autosite.
Macroglossia
-
Excessively large tongue.
PubMed abstract: Triazole-derivatives
are antimycotics used in agriculture as well as in clinical and
veterinary therapy. The aim of the present work is the in vitro
comparative study of the teratogenic activity of triazole (the
parental compound), flusilazole (an agricultural triazole mono-derivative
fungicide), and fluconazole (a clinically used bis-triazole derivative).
Rat embryos, 9.5 days old (1 to 3 somites) were exposed in vitro
to triazole 500 to 5000 microM, flusilazole 3.125 to 250 microM,
or fluconazole 62.5 to 500 microM. After 48 h in culture, the
embryos were morphologically examined and processed for histologic
and biochemical analysis. Flusilazole
and fluconazole [antifungal drug] showed similar teratogenic
effects (abnormalities at the branchial
apparatus level and cell death at the level of the branchial
mesenchyme) at concentration levels of 6.25 microM and higher
for flusilazole and of 125 microM and higher for fluconazole.
By contrast, only slight developmental retardation and blood discoloration
were observed at the highest concentrations of triazole, suggesting
no teratogenic activity for the triazole group.
Ref: Antifungal triazoles induce malformations
in vitro; by Menegola E, Broccia ML, Di Renzo F, Giavini E. Reprod
Toxicol 2001 Jul-Aug;15(4):421-7
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flusilazole.PubMed.Abstrcts.htm
Much of what is known
about the possible dangers of flusilazole
is considered a trade secret -- unavailable even to state
agents investigating health complaints. What is known about the
fungicide -- which is not approved for use in the United States
-- offers little comfort to those who applied it to Florida farmland
as an undisclosed ingredient in some lots of Benlate 50 DF. According
to a study conducted in Bulgaria, oral doses of flusilazole given
to pregnant rats produced
congenital defects such as protruding
eyes, twins of unequal size joined at the jaw and
grossly enlarged tongues...
Ref: Jan Hollingsworth. Fungicide studies
offer little comfort. Memo: BURIED SECRETS PURSUING A MEDICAL
MYSTERY. December 18, 1995. Tampa Tribune (Florida). page 4.
Parents
believe that exposure to Flusilazol during pregnacy resulted in
severe eye deformities such as microphthalmia
(small eyes) and coloboma,
a defect in the structure of the eyes.
Ref: Scottish Daily Record & Sunday
Mail Ltd. - Sunday Mail. October 15, 2000
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flusilazole.Scot.EYE.2000.htm
•
Definitions:
Coloboma - A defect of the iris
caused by a failure of the eyeball to fuse properly during fetal
development. These are developmental anomalies and do not worsen
as the child grows older.
Microphthalmia - An unnatural
smallness of the eyes, occurring as the result of disease or
of imperfect development.
Abstract.
Silane,[Bis(4-Flouorophenyl)] (Methyl)(1H,1,2,4-Triazol-1-ymethyl-INH-6573
(CAS# 85509-19-9) was evaluated to
determine its embryo-fetal toxicity and teratogenic potential
when administered by oral gavage to twenty-five rats (Charles
River CD strain) per treatment group on days 7 through 16 of gestation
at doses of 0, 10, 50, and 250 mg/kg body weight. At 250 mg/kg
maternal deaths occurred and overt toxicity
expressed as decreased body weight gain and feed consumption and
by a significant increase of chromodacryorrhea, chromorhinorrhea,
wet and stained underbodies, and alopecia. Slight maternal toxicity
at 50 mg/kg was expressed as a significant decrease in feed consumption.
The mean relative liver weight was significantly increased in
the 250 and 50 mg/kg treatment groups. No maternal toxicity was
noted at 10 mg/kg and below. Embryo-fetal
toxicity was noted at all treatment levels. At 250 mg/kg
a decrease in fetal body weight and an increase in fetal deaths
were reported. The incidence of skeletal
variations were increased significantly above controls at all
treatment levels. An
increase in fetal head malformations were reported in all groups,
including controls.
Male to female sex ratios of litters were not reported.
Due to the incidence of fetal head malformations across all groups,
no NOEL was reported in this study.
Ref: 1992 - INITIAL SUBMISSION: EMBRYO-FETAL
TOXICITY AND TERATOGENICITY STUDY OF INH-6573-39 BY GAVAGE IN
THE RAT (FINAL REPORT) WITH ATTACHMENTS AND COVER LETTER DATED
03-27-92. HASKELL LAB [E I DUPONT DE NEMOURS & CO]. Report
No. NTIS/OTS0535920 from The National Technical Information Service.
Tongue
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: This report
describes the first part of a study which was undertaken to examine
the teratogenic potential of triazole compounds used as fungicides
in agriculture. Pregnant Wistar rats
were given single oral dosages of flusilazole or bitertanol on
days 9, 10, 11 or 13th of gestation (positive vaginal smear=day
1) at levels of 1/5, 1/10 and 1/50 LD50. The dosages were calculated
from the reported LD50 values of 1272 mg/kg for
flusilazole and 5000 mg/kg for bitertanol. The results
of the study demonstrated that both compounds
induce congenital anomalies when given on days 9, 10 or 11th at
levels corresponding to 1/5 and 1/10 LD50. The types of
the registered malformations after flusilazole
treatment were exophthalmus, hypognathia,
macroglossia and cleft
palate and after bitertanol treatment micro- and
acaudia and in rare cases exophthalmus, hypognathia and cleft
palate. A clear dose effect relationship was established for both
compounds.
Ref:
Vergieva T (1990). Teratology 1990 Aug;42(2):27A-28A. Triazoles
teratogenicity in rats. Abstract from Toxnet.
•
Definitions:
Exophthalmia (n.) The protrusion
of the eyeball so that the eyelids will not cover it, in consequence
of disease.
Hypognathus - Unequal conjoined
twins in which the rudimentary parasite is attached to the mandible
of the autosite.
Macroglossia
-
Excessively large tongue.
Much of what is known
about the possible dangers of flusilazole
is considered a trade secret -- unavailable even to state
agents investigating health complaints. What is known about the
fungicide -- which is not approved for use in the United States
-- offers little comfort to those who applied it to Florida farmland
as an undisclosed ingredient in some lots of Benlate 50 DF. According
to a study conducted in Bulgaria, oral doses of flusilazole given
to pregnant rats produced congenital defects such as
protruding eyes, twins of unequal size joined
at the jaw and grossly enlarged
tongues...
Ref: Jan Hollingsworth. Fungicide studies
offer little comfort. Memo: BURIED SECRETS PURSUING A MEDICAL
MYSTERY. December 18, 1995. Tampa Tribune (Florida). page 4.
| Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproductive
process -- Although fish early life-stage tests
provide useful information on sensitive life stages of fish,
for flusilazole
in particular the risk assessment has explicitly identified
fish and other aquatic species to be at risk from agricultural
use of this a.s., and there is evidence that flusilazole
may have specific effects on the reproductive process. Therefore
the SCP cannot conclude that a NOEC based on a fish early
life-stage test for a single species is necessarily adequate
in this particular case to ensure sufficient protection
of fish populations from adverse effects on reproduction.
-- The monograph (volume 3, pp. 230-233) identified aquatic
species, and fish in particular, as possibly at risk from
flusilazole. In addition, a dose-dependent
decrease in serum estradiol levels by flusilazole, considered
to be indicative of aromatase inhibition, was
observed in studies with rats (volume 3, p.
73). Aromatase inhibition is significant
for reproduction since aromatization of testosterone is
the process by which oestrogen is formed in vertebrates
(Trant et al. 1997). This reaction is mediated by the cytochrome
P450 aromatase. It has been shown that oestrogen (i.e.,
oestradiol) plays a major role in the reproductive physilogy
of all vertebrates, including gamete development and maturation,
and induces the hepatic synthesis of the yolk precursor,
vitellogenin. Studies in which fish have been exposed to
aromatase inhibitors suggest that aromatase activity, specificity
or expression levels vary with maturation stage and among
species (Bl‡zquez et al. 2001, Zerulla et al. 2002).
-- ... Neither of the above tests was designed to investigate
possible effects on reproductive output or mating behaviour
of adult fish. Given that there is evidence that flusilazole
is an aromatase inhibitor, there are specific concerns that
reproduction could be adversely affected by this substance.
Therefore potential effects on mating behaviour, time to
sexual maturity, reproductive output and timing, fertilisation
success, and sex ratio of offspring are also of concern
and should be explicitly addressed by a test designed for
this purpose.
Ref: July 2002 - Opinion
of the Scientific Committee on Plants on specific questions
from the Commission concerning the evaluation of flusilazole
in the Council Directive 91/414/EEC. European Commission.
Health & Consumer Protection Directorate-General.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.eu.july.2002.pdf
-- For
flusilazole, no data are available to assess the impact
on organic matter decomposition. Except earthworms and soil
microflora, no soil-dwelling organisms have been tested.
Given the persistence of flusilazole
in soil and the environmental and agronomical importance
of the organic matter breakdown for soil fertility, the
Committee considers a risk assessment based solely on the
existing data as not adequate.
-- Although fish early life-stage tests provide useful information
on sensitive life stages of fish, for flusilazole
in particular the risk assessment has explicitly identified
fish and other aquatic species to be at risk from agricultural
use of this a.s., and there is evidence that flusilazole
may have specific effects on the reproductive process. Therefore
the SCP cannot conclude that a NOEC based on a fish early
life-stage test for a single species is necessarily adequate
in this particular case to ensure sufficient protection
of fish populations from adverse effects on reproduction.
-- The monograph (volume 3, pp. 230-233) identified aquatic
species, and fish in particular, as possibly at risk from
flusilazole. In addition, a dose-dependent
decrease in serum estradiol levels by flusilazole, considered
to be indicative of aromatase inhibition, was observed in
studies with rats (volume 3, p. 73). Aromatase
inhibition is significant for reproduction since aromatization
of testosterone is the process by which oestrogen is formed
in vertebrates (Trant et al. 1997). This reaction
is mediated by the cytochrome P450 aromatase. It has been
shown that oestrogen (i.e., oestradiol) plays a major role
in the reproductive physilogy of all vertebrates, including
gamete development and maturation, and induces the hepatic
synthesis of the yolk precursor, vitellogenin. Studies in
which fish have been exposed to aromatase inhibitors suggest
that aromatase activity, specificity or expression levels
vary with maturation stage and among species (Bl‡zquez et
al. 2001, Zerulla et al. 2002).
-- ... Neither of the above tests was designed to investigate
possible effects on reproductive output or mating behaviour
of adult fish. Given that there is evidence that flusilazole
is an aromatase inhibitor, there are specific concerns that
reproduction could be adversely affected by this substance.
Therefore potential effects on mating behaviour, time to
sexual maturity, reproductive output and timing, fertilisation
success, and sex ratio of offspring are also of concern
and should be explicitly addressed by a test designed for
this purpose.
Ref: July 2002 - Opinion
of the Scientific Committee on Plants on specific questions
from the Commission concerning the evaluation of flusilazole
in the Council Directive 91/414/EEC. European Commission.
Health & Consumer Protection Directorate-General.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.eu.july.2002.pdf
Ecotoxicology
(page 11)
• Acute toxicity to oysters - shell deposition
• Acute toxicity to mysid shrimp
• Acute toxicity to sheepshead minnow
• Chronic toxicity to mysid shrimp
• Chronic toxicity to sheepshead minnow
•• A waiver will be requested for the cbironomid
sediment toxicity test with Chironomus tentans (a Chironomus
riparius study will be submitted in support of the waiver)
.Algal toxicity (Anabaena, Navicula, Skeletonema)
• Aquatic plant toxicity - Lemna
Ref: DuPont
Punch (Active ingredient: Flusilazole) and DuPont Charisma
(Active ingredients: Flusilazole and Famoxadone): Summary
of data compiled in support of a Section 18 Emergency Exemption
request for control of Asian soybean rust on soybeans. By
DuPont authors: Cosgrove T, Czochor L, Dinter A, Jemberg
K, Klemens A, Marcon A, McInnes B, Mullin L, Russell M,
Ryan D, Singles S, Vanderbroeck V. Revision No. 1: February
2, 2005.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/flusilazole.appendix1.pdf
Persistent
in soil
"Flusilazole
85509-19-9 Withdrawn. Low degradability. 1994."
Definition: "Withdrawn.
A substance which the manufacturer has either withdrawn
from the market, or for which he has withdrawn his application
for registration, approval, or renewed approval and when
it is clear that these measures were undertaken due to the
health or environmental properties of the substance."
Ref: Euopean Commission.
Appendix 5. Substances which may not be included as active
ingredients in approved pesticide products, Chapter 15,
Section 2, subsection one.
http://www.kemi.se/lagar_eng/pdf/app5_8.pdf
Soil
dissipation. The Meeting reviewed the final report of
a 3-year soil dissipation study (4 applications per year)
for which an interim report was reviewed by the 1989 JMPR.
It confirms the 1989 observations that over 92% of the radioactivity
is confined to the top 8 cm of soil over the test period,
and that the predominant residues in this segment are flusilazole
and its silanol metabolite IN-F7321. The author cites statistical
evaluation of the data to support the view that residues
will reach a steady level at 57% of yearly application levels
after repeated application levels under worst-case conditions.
The
report cites the steady-state conclusion, the strong adsorption
to the top layers of soil, the lack of residues exceeding
0.01 mg/kg in the 24-36 cm soil depths and the weak leaching
potential indicated in other studies as evidence that residues
in ground water were unlikely. While the data indicate that
over 92% of the radioactivity remains in the top 8 cm of
the silt loam soil investigated, and indeed that residue
levels are extremely low in the 24-36 cm depths, it also
shows an increasing penetration by low levels of radioactivity
over the test period in this soil type. The identity of
these residues in the deeper soil segments was not indicated.
While
the adsorption of this persistent pesticide to soil is strong,
the 1989 JMPR had noted that uptake of low residue levels
can occur in rotational crops and that the leaching potential
would be less for silt loams (as in this study) than for
more sandy soils. Because the silt loam study was under
worst-case conditions (bare ground, repeated applications)
and was consistent with reassuring findings of a number
of other relevant studies, the Meeting accepted that ground
water residues from silt loam soils were unlikely.
Ref: 1993
FAO/WHO JOINT MEETING ON PESTICIDE RESIDUES Geneva, 20-29
September 1993. PESTICIDE
RESIDUES IN FOOD. REPORT OF THE 1993 JOINT FAO/WHO MEETING
OF EXPERTS. 4.24 FLUSILAZOLE (165). RESIDUE AND ANALYTICAL
ASPECTS.
|
|

