|
Return
to Fluchloralin
Index Page
Activity: Herbicide
(dinitroaniline)
Structure:
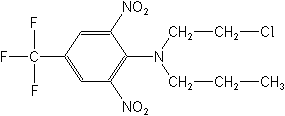
Adverse Effects:
Blood
Brain
CNS
Cytotoxic, genotoxic, and induces apoptosis
Endocrine: Testicular - spermatogenesis
Genotoxic
Liver
Environmental
Degradation products included the following compounds:
- Degradation products were identified by TLC and GLC and
comparison with standard compounds whose structure was confirmed
by IR and MS.
•
N-(2-chloroethyl)-2,6-dinitro-4-trifluoromethylaniline
•
2,6-dinitro-4-trifluoromethylphenol
•
2,6-dinitro-4-trifluoromethylaniline
•
1,2-diamino-6-nitro-4-trifluoromethylbenzene
• 1,2,3-triamino-5-trifluoromethylbenzene
•
2,6-dinitro-N-(2-hydroxypropyl)-N-propyl-4-trifluoromethylaniline
•
2,6-dinitro-N-propyl-4-trifluoromethylaniline
Ref:
Spectrum
Chemical Fact Sheet
|
Blood
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
PubMed Abstract: Basalin,
a herbicide, was administered orally to male rats at doses ranging
from 60 mg to 1.92 g/kg for 13 weeks. Oral LD50 of the compound
was 1.65 g/kg. Toxic effects included hyperexcitability and tremors.
The cumulative lethal dose (CLD50) at the end of week 13 was 135
mg/kg with a cumulative toxicity factor (CTF) of 12.22. At 1.92
g/kg, no animals survived to 13 weeks. At 60 and 120 mg/kg, there
were no significant changes in body weight gain compared with
the controls and a significant decrease
in total leukocyte count (TLC), erythrocyte sedimentation rate
(ESR) and Hb was observed. There was a decrease in
spermatogenesis and infiltration of mononucleated cells
in the liver.
Ref: Toxicol Lett 1983 Aug;18(1-2):13-8.
Subacute toxicity of Basalin in rats. Gupta PK, Singh YP, Parihar
NS.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluchloralin.PubMebAbstract.htm
Brain
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract. Basalin,
a formulation of fluchloralin (N-(2-chloroethyl)-2-6-dinitro-N-propyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)-aniline),
is being very widely used as herbicide in large number of important
crops. But very limited data on its toxicological profile is available.
Its adverse effects on central nervous system and locomotor alterations
in sheep given 5 mg/kg orally have been reported. Preliminary
studies in our laboratory indicated alteration in gait in chicken
given Basalin orally @ 200-500 mg/kg followed by ataxia at higher
doses. Since chicken is a suitable model for neurotoxicity assay,
present studies were conducted on one week old broiler chicks
given Basalin daily for four weeks through feed at different dose
levels of 50 mg/kg (Gr I), 100 mg/kg (Gr II) and 150 mg/kg (Gr
III). Each group contained ten chicks. The control chicks (Gr
C) were given equal amount of normal feed. Activities of brain,
liver and plasma acetylcholinesterase (ACHE), carboxylesterase
(CE) and brain neurotoxicesterase (NTE) were estimated, the tissue
esterases after four weeks treatment and plasma esterases at weekly
intervals. The locomoter activity was determined using inclined
plane at alternate days. Histopathological examinations of brains
and spinal cords of four birds from each group were conducted
after four weeks treatment. The data on
all these experiments indicated inhibition of all tissue and plasma
esterases in a dose dependent manner, which were significant in
chicks of Gr III receiving maximum dose for four weeks.
(Brain NTE 70%, brain and liver ACHE 85.71 and
85.45% respectively and liver CE 85.58% of control activity).
The plasma ACHE and CE activities were significantly inhibited
in this group after two weeks onwards (ACHE90.8-90.3%, CE 84.9-84.5%
of control). Alteration in gait in Gr III chicks was observed
after three weeks treatment and was correlated with NTE inhibition.
Histopathological examinations of brain
and spinal cords of chicks receiving maximum dose revealed increased
number of Schwann cells in brain and small numbers of myelinated
nerve fibers in spinal cord. The studies thus indicated
possibility of neuropathic effects of Basalin on prolonged exposure
or at higher doses.
Ref:
Basalin induced neurotoxic effects in broiler chicks; by Sushma
Rishi and Uma Arora. Toxicology Letters; Volume 95, Supplement
1 , July 1998, Pages 144-145.
CNS
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Human
Toxicity Excerpts: SYMPTOMATOLOGY
INDICATES OVERDOSING MAY PRODUCE /CNS DEPRESSION/
AND OTHER GENERAL CNS INVOLVEMENT. [Weed Science Society
of America. Herbicide Handbook. 5th ed. Champaign, Illinois: Weed
Science Society of America, 1983. 238]
Ref: Hazardous Substance Data Bank for FLUCHLORALIN
CASRN: 33245-39-5 from Toxnet.
Abstract.
Male Swiss mice, 25-30 g, were utilized to define some of the
behavioral effects of the herbicides Lasso [alachlor 43%; (A)],
Basalin [fluchloralin 45%; (F)],
Premerge 3 [dinoseb 51%; (D)], and the fungicide Maneb-80 [maneb
80%; (M)]. These compounds were tested for their effects on locomotor
activity and for their ability to establish a conditioned taste
aversion following oral or dermal exposure. Individual and grouped
(N = 5) activity measures were assessed immediately following
the dermal administration of the commercially available pesticide
formulations. Grouped activity measures were also assessed following
the oral administration of the compounds. Total
activity was significantly (p less than 0.05) increased over vehicle
controls in both grouped and individual subjects by A, F, and
D following dermal administration. Grouped activity measures were
also increased by A, F, D, and M following the oral administration
of the compounds...
Ref: The behavioral effects of pesticides in male mice; by Mitchell
JA, Long SF, Wilson MC, Kallman MJ. Neurotoxicol Teratol 1989
Jan-Feb;11(1):45-50.
Abstract.
Basalin, a formulation of fluchloralin (N-(2-chloroethyl)-2-6-dinitro-N-propyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)-aniline),
is being very widely used as herbicide in large number of important
crops. But very limited data on its toxicological profile is available.
Its adverse effects on central nervous system and locomotor alterations
in sheep given 5 mg/kg orally have been reported. Preliminary
studies in our laboratory indicated alteration in gait in chicken
given Basalin orally @ 200-500 mg/kg followed by ataxia at higher
doses. Since chicken is a suitable model for neurotoxicity assay,
present studies were conducted on one week old broiler chicks
given Basalin daily for four weeks through feed at different dose
levels of 50 mg/kg (Gr I), 100 mg/kg (Gr II) and 150 mg/kg (Gr
III). Each group contained ten chicks. The control chicks (Gr
C) were given equal amount of normal feed. Activities of brain,
liver and plasma acetylcholinesterase (ACHE), carboxylesterase
(CE) and brain neurotoxicesterase (NTE) were estimated, the tissue
esterases after four weeks treatment and
plasma esterases at weekly intervals. The locomoter activity was
determined using inclined plane at alternate days. Histopathological
examinations of brains and spinal cords of four birds from each
group were conducted after four weeks treatment. The
data on all these experiments indicated inhibition of all tissue
and plasma esterases in a dose dependent manner, which were significant
in chicks of Gr III receiving maximum dose for four weeks. (Brain
NTE 70%, brain and liver ACHE 85.71 and 85.45% respectively and
liver CE 85.58% of control activity). The plasma ACHE and CE activities
were significantly inhibited in this group after two weeks onwards
(ACHE90.8-90.3%, CE 84.9-84.5% of control). Alteration
in gait in Gr III chicks was observed after three weeks treatment
and was correlated with NTE inhibition. Histopathological
examinations of brain and spinal cords of chicks receiving maximum
dose revealed increased number of Schwann cells in brain and small
numbers of myelinated nerve fibers in spinal cord. The
studies thus indicated possibility of neuropathic effects of Basalin
on prolonged exposure or at higher doses.
Ref: Basalin induced neurotoxic effects
in broiler chicks; by Sushma Rishi and Uma Arora. Toxicology Letters;
Volume 95, Supplement 1 , July 1998, Pages 144-145.
Cytotoxic,
genotoxic, and induces apoptosis
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Pub Med Abstract: Fluchloralin
is cytotoxic and genotoxic and induces apoptosis in mammalian
cells.
The genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of a widely used herbicide,
fluchloralin, were assessed using cultured mammalian cells. Treatment
of cells for 8-12 hr with fluchloralin resulted in a significant
increase in the frequency of metaphase cells with chromosomal
damage. At higher concentrations, the herbicide also induced an
increase in the frequency of sister chromatid exchange. A 50%
loss in viability was observed when cells were exposed to the
herbicide for 72 hr. To understand the mechanism of cell death
caused by fluchloralin, its effect on DNA synthesis and its ability
to induce apoptosis were investigated. Even short (6 hr) treatment
of cells with fluchloralin resulted in a 30-50% inhibition of
DNA synthesis. Agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA from herbicide-treated
cells and cytochemical staining indicate the induction of apoptosis
by fluchloralin.
Ref:
Environ Mol Mutagen 1998;31(3):257-62. Fluchloralin
is cytotoxic and genotoxic and induces apoptosis in mammalian
cells.
Sinha S, Panneerselvam N, Shanmugam G.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=9585264&dopt=Abstract
Abstract:
The genotoxic effect of fluchloralin (33245-39-5) in cultured
human blood lymphocytes was investigated. Venous blood samples
were obtained from healthy donors and lymphocyte cultures were
established. Cell cultures were treated with 2.5, 5.0, or 10 micrograms/milliliter
(microg/ml) fluchloralin for 24 or 48 hours. Following treatment,
slides were prepared and cells were scored for chromatid aberrations.
In a micronuclei (MN) test, cell were exposed up to 50microg/ml
fluchloralin for up to 48 hours. Cell microslides were prepared
and scored for MN frequency. Treatment of the lymphocytes for
24 to 48 hours resulted in a significant dose dependent increase
in the total number of chromatid type aberrations. The frequency
of chromatid aberrations was high compared to isochromatid breaks
at all dose levels. The increase in the frequency of isochromatid
breaks was notable after 48 hours of treatment. Gap formation
was high at all concentrations. Multiple aberrated cells showed
a dose dependent increase at both time points. The frequency of
occurrence of MN in cultured human blood lymphocytes following
fluchloralin treatment was noted. The induction of MN formation
was similar and significant at 24 and 48 hours of treatment at
2.5 to 10microg/ml. At the higher concentrations
there was a statistically dose related increase in the frequency
of micronucleated binucleate cells. The
authors conclude that fluchloralin at higher concentrations have
the ability to damage the human genome.
Ref: Genotoxicity
of the herbicide fluchloralin on human lymphocytes in vitro: chromosomal
aberration and micronucleus tests; by Panneerselvam N, Sinha S,
Shanmugam G. Mutat Res
1995 Aug;344(1-2):69-72
Endocrine:
Testicular
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract.
Subacute and acute toxicity of the herbicide N-propyl-N-(2-chloroethyl)-2,6-dinitro-4-trifluromethyl-aniline
(33245-39-5) (Basalin) was investigated. Some male albino-rats
received graded doses from 0.5 to 4 grams per kilogram (g/kg)
of the compound, orally administered as a single dose. Median
lethal doses (LD50) were calculated. Other rats received 60, 120,
240, 480, or 960 milligrams (mg)/kg or 1.92g/kg Basalin, orally
administered 6 days a week for 13 weeks, and cumulative LD50 were
determined. Animals receiving 60 and 120mg/kg Basalin were killed;
liver, kidney, heart, spleen, brain, lung, testes, and adrenal
glands were weighed, sectioned, and examined
for structural changes. Blood total leukocyte count, erythrocyte
sedimentation rate, packed cell volume, and blood glucose were
measured. The oral LD50 for Basalin in male rats was 1.65g/kg.
No animals receiving Basalin at a dose of 1.92g/kg or more daily
for 1 week survived. Animals developed hyperexcitability and tremors;
these were followed by convulsions and death. The cumulative LD50
after 13 weeks was 135mg/kg. Basalin had a slow and steady cumulative
effect, reaching a maximum after 10 weeks. In animals receiving
60 or 120mg/kg of the herbicide for 13 weeks, liver weight was
significantly increased whereas that of spleen, heart,
testes, and adrenal glands was significantly decreased. Total
leukocytes, hemoglobin, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were
increased in a dose dependent manner. Blood glucose showed a 10
percent decrease at 120mg/kg Basalin. The 60mg/kg dose did not
produce significant pathological change in the organs examined.
However, 120mg/kg provoked infiltration of mononuclear cells in
liver tissue. Spermatids in seminiferous
tubules were reduced at this dose; a few tubules were coalescing
and filled with binucleate spermatogonial cells. The authors
conclude that oral administration of Basalin as a single dose
or with repeated administration produces a dose dependent toxicity.
Ref: Toxicol Lett 1983 Aug;18(1-2):13-8.
Subacute toxicity of Basalin in rats. Gupta PK, Singh YP, Parihar
NS.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluchloralin.PubMebAbstract.htm
Genotoxic
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Pub Med Abstract: Fluchloralin
is cytotoxic and genotoxic and induces apoptosis in mammalian
cells.
The genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of a widely used herbicide,
fluchloralin, were assessed using cultured mammalian cells. Treatment
of cells for 8-12 hr with fluchloralin resulted in a significant
increase in the frequency of metaphase cells with chromosomal
damage. At higher concentrations, the herbicide also induced an
increase in the frequency of sister chromatid exchange. A 50%
loss in viability was observed when cells were exposed to the
herbicide for 72 hr. To understand the mechanism of cell death
caused by fluchloralin, its effect on DNA synthesis and its ability
to induce apoptosis were investigated. Even short (6 hr) treatment
of cells with fluchloralin resulted in a 30-50% inhibition of
DNA synthesis. Agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA from herbicide-treated
cells and cytochemical staining indicate the induction
of apoptosis by fluchloralin.
Ref: Environ Mol Mutagen 1998;31(3):257-62.
Fluchloralin
is cytotoxic and genotoxic and induces apoptosis in mammalian
cells. Sinha S, Panneerselvam
N, Shanmugam G.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=9585264&dopt=Abstract
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
PubMed Abstract: Basalin
[Fluchloralin], a herbicide, was administered orally to male rats
at doses ranging from 60 mg to 1.92 g/kg for 13 weeks. Oral LD50
of the compound was 1.65 g/kg. Toxic effects included hyperexcitability
and tremors. The cumulative lethal dose (CLD50) at the end of
week 13 was 135 mg/kg with a cumulative toxicity factor (CTF)
of 12.22. At 1.92 g/kg, no animals survived to 13 weeks. At 60
and 120 mg/kg, there were no significant changes in body weight
gain compared with the controls and a significant decrease in
total leukocyte count (TLC), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
and Hb was observed. There was a decrease in spermatogenesis
and infiltration of mononucleated
cells in the liver.
Ref: Toxicol Lett 1983 Aug;18(1-2):13-8.
Subacute toxicity of Basalin in rats by Gupta PK, Singh YP, and
Parihar NS.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluchloralin.PubMebAbstract.htm
|
Environmental
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
Persistence
in soil: Abstract:
The persistence, binding, and metabolism of six dinitroaniline
herbicides, including trifluralin, profluralin, dinitramine,
butralin, fluchloralin, and chlornidine, added to Matapeake
silt loam were determined after 3, 5, and 7 months. Dinitramine
was rapidly degraded during the first 5 months,
while butralin and chlornidine were less persistent than
fluchloralin, profluralin, and trifluralin after 7 months.
The latter three herbicides were similar in persistence
and binding properties. The parent herbicide was the major
extractable product detected in soil at each sampling time.
Degradation products were identified by cochromatography
on thin-layer plates, retention times on gas-liquid and
high-pressure liquid chromatography, and mass spectral analysis.
Dealkylated and cyclic derivatives of the parent herbicide
were detected as metabolites. The cyclic products included
benzimidazole derivatives of dinitramine, trifluralin, and
fluchloralin; a morpholine derivative of chlornidine; and
a quinoxaline derivative of fluchloralin. A unique metabolite
of butralin was derived from the parent material by the
loss of one nitro substituent.
Ref: Persistence and metabolism of dinitroaniline herbicides
in soils; by P. C. Kearney et al. Pesticide Biochemistry
and Physiology; 6:3; 229-238 June 1976.
Environmental
Bioconcentration:
Based upon a measured Koc value of 3600, the BCF of fluchloralin
has been estimated to be 250(1); using fluchloralin's reported
water solubility of <1 ppm(1), the BCF can be estimated
to be >618(1). These estimated BCF
values suggest that bioconcentration in aquatic organisms
may have some environmental importance(SRC). [(1)
Kenaga EE; Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 4: 26-38 (1980)]
Ref: Hazardous Substance Data Bank
for FLUCHLORALIN CASRN: 33245-39-5 from Toxnet.
Ref:
Data from Pesticide Action Network:
http://www.pesticideinfo.org/PCW/List_AquireAcuteSum.jsp?CAS_No=33245-39-5&Rec_Id=PC33166 |
| Common
Name |
Scientific
Name |
Avg
Species LC50 (ug/L) |
LC50
Std Dev |
Number
of Studies |
Avg
Species Rating |
| FISH |
| Channel
catfish |
Ictalurus punctatus |
255.0
|
135.0 |
2 |
Highly
Toxic |
| Bluegill
|
Lepomis
macrochirus |
25,218
|
34,683 |
5 |
Slightly
Toxic |
| Rainbow
trout,donaldson trout |
Oncorhynchus
mykiss |
6,001
|
7,408 |
7 |
Moderately
Toxic |
| INSECTS |
| Midge
|
Chironomus
plumosus |
31.1
|
25.5
|
2 |
Very
Highly Toxic |
| MOLLUSCS |
| Snail |
Bellamya bengalensis |
202.5 |
24.5 |
2 |
Highly Toxic |
| ZOOPLANKTON |
| Scud |
Gammarus pseudolimnaeus |
56.0 |
|
1 |
Very
Highly Toxic |
|
|

