|
Return
to Fluazifop-P-butyl Index Page
Activity:
Herbicide (arylphenoxy
ether ester)
Structure:
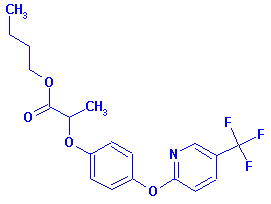
Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body
Weight Decrease
Bone
Endocrine:
Ovary
Endocrine: Pituitary
Endocrine: Prostate
Endocrine:
Testicular
Endocrine: Uterine
Eye
Fetotoxic
Kidney
Liver
Lung
Reproductive
Spleen
Stomach
Teratogenic
Environmental
The
estimate for total domestic use (annual average) is approximately
250,000 lbs. active ingredient. More
than 90% of fluazifop-P-butyl’s total usage is on
soybeans (75%)
and cotton (21%) (page
2).
Ref: October 29, 2003.
Tier 1 Drinking Water Assessment for Fluazifop-P-butyl.
EPA Federal Register Docket No. OPP-2004-0347-0011.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0011.pdf
•
Fluazifop-P-butyl is the resolved isomer ® enantiomer)
of fluazifop-butyl [(R,S)-2-(4((5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl)oxy)phenoxy)propanoic
acid, butyl ester]. The fluazifop-butyl isomers are List
B chemicals. Fluazifop-butyl (PC code 122805) has been canceled
and only fluazifop-P-butyl is being supported for reregistration
(page 5).
• Based on their structures, the Metabolism Assessment
Review Committee (MARC) was unable to conclude that the
major metabolites of fluazifop-P-butyl will be significantly
less toxic than the parent and therefore, recommended that
for risk assessment purposes, the residues
of concern are parent, fluazifop acid (free and conjugated),
5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridone, and 2-(4hydroxyphenoxy) propionic
acid (free and conjugated)... (page 13)
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
•
As of February 16, 2005, Fluazifop-butyl
and Fluazifop-p-butyl,
are both permitted in or on
over 30 food commodities in
the United States - see list at http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/mrls-fluazifop.htm
•
As of January 2005: "Fluazifop-butyl
(PC code 122805) has been canceled and only fluazifop-P-butyl
is being supported for reregistration." - Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
|
Blood
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic/Subcrhonic
Toxicity Studies: Chronic toxicity studies in rodents
have shown liver changes (cellular hypertrophy). The No Effect
Level (LEL) in rats is 10 ppm (0.5 mg/kg/day). Long term feeding
studies in dogs produced a range of potentially serious effects
at high dose rates (red cell, bone marrow and lymphadenopathy
changes and liver and spleen damage) with a No Effect Level of
25 mg/kg/day. Target Organs: Liver,
skin, kidney, eye, bone marrow, blood,
reproductive system.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl). Syngenta. January 21,
2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
411-110 135236 Moxon,
M. E., "Fluazifop-p-butyl: Developmental toxicity study in
the rabbit," Zeneca Central Toxicology Laboratory, Alderley
Park, 3/23/93. Report # CTL/P/3862. Twenty mated NZW rabbits were
dosed by gavage in 1 ml/kg corn oil at 0, 2, or 10 mg/kg/day Fluazifop-p-butyl
technical (90.1% purity) between days 8 and 20 of gestation (natural
mating day was designated “day 1”). There were also 40 mated does
given 50 mg/kg/day of test article, to ensure adequate numbers
of surviving litters. Maternal toxicity was generally low: mean
body weight was unaffected and there were no characteristic clinical
signs. There was one maternal death (killed in extremis) among
the high dose females. Abortion frequencies were 1/18, 2/17, 2/13,
and 4/37 in controls through increasing dose groups, thus not
independently indicative of treatment effects at any dose. Nevertheless,
a combination of marked body weight losses
(average loss of 654 g) and associated signs of “few feces”
or “no feces” among the 4 of the 5 aborted/killed moribund does
is considered treatment-related, setting the maternal NOEL = 10
mg/kg/day..
Ref: May 20, 2002. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA FLUAZIFOP-P-BUTYL. California EPA. Department of Pesticide
Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-butyl.CAepa.02.pdf
Reproductive Effects:
In a 3-generation reproductive study in rats, effects included
reductions in weight gain, fetal weight, ossification, testicular weight,
spleen weight, increased prostate weight and gestational length.
No Effect Level (NEL) was 1 mg/kg/day. Fetotoxic effects seen
in the rabbit, including reduced fetal weight
and reduced ossification at higher doses. No Effect Level (NEL)
was 30 mg/kg/day in rabbits. The NEL for teratogenic effects is
at least 10/mg/day in the rat, with diaphragmatic hernia at higher
doses. Not teratogenic at highest dose tested in rabbits (90 mg/kg/day).
While fluazifop-p-butyl is fetotoxic when fed to pregnant rats,
human exposure data has concluded that female formulation workers
are not at increased risk of fetotoxic effects when skin protection
measures are applied.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl). Syngenta. January 21,
2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproductive Effects:
In a 3-generation reproductive study in rats, effects included
reductions in weight gain, fetal weight, ossification,
testicular weight, spleen weight, increased prostate weight and
gestational length. No Effect Level (NEL) was 1 mg/kg/day. Fetotoxic
effects seen in the rabbit, including reduced fetal weight and
reduced ossification at higher doses.
No Effect Level (NEL) was 30 mg/kg/day in rabbits. The NEL for
teratogenic effects is at least 10/mg/day in the rat, with diaphragmatic
hernia at higher doses. Not teratogenic at highest dose tested
in rabbits (90 mg/kg/day). While fluazifop-p-butyl is fetotoxic
when fed to pregnant rats, human exposure data has concluded that
female formulation workers are not at increased risk of fetotoxic
effects when skin protection measures are applied.
Chronic/Subcrhonic Toxicity Studies: Chronic toxicity studies
in rodents have shown liver changes (cellular hypertrophy). The
No Effect Level (LEL) in rats is 10 ppm (0.5 mg/kg/day). Long
term feeding studies in dogs produced a range of potentially serious
effects at high dose rates (red cell, bone
marrow and lymphadenopathy changes and liver and spleen
damage) with a No Effect Level of 25 mg/kg/day.
Target Organs: Liver, skin, kidney, eye, bone
marrow, blood, reproductive system.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl). Syngenta. January 21,
2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
-- 411-110 135236 Moxon,
M. E., "Fluazifop-p-butyl: Developmental toxicity study in
the rabbit," Zeneca Central Toxicology Laboratory, Alderley
Park, 3/23/93. Report # CTL/P/3862. Twenty mated NZW rabbits were
dosed by gavage in 1 ml/kg corn oil at 0, 2, or 10 mg/kg/day Fluazifop-p-butyl
technical (90.1% purity) between days 8 and 20 of gestation (natural
mating day was designated “day 1”). There were also 40 mated does
given 50 mg/kg/day of test article, to ensure adequate numbers
of surviving litters... Other maternal and general developmental
toxicity indices did not indicate treatment effects, however modest
ossification delays (2 nd and 5 th
sternebrae) and increased incidence of extra
13 th rib (all at 50 mg/kg/day) placed the developmental
toxicity NOEL = 10 mg/kg/day.
-- 018 994244: Tesh, J. M., Ross, F. W. and Tesh, S. A. "PP009:
Effects of Oral Administration upon Pregnancy in the Rabbit, Final
report". Life Science Research report No. 80/ILK 027/498 [November
28, 1980]. PP009, purity 94.8%, administered via gavage at concentrations
of 10, 30 or 90 mg/kg/day to 20-24 artificially inseminated female
New Zealand rabbits during gestation days 6 through 28. Adverse
effects: increased incidence of cloudy eyes
(12.7%), small fetuses, delayed ossification
and enlarged anterior and posterior fontanelle.
Maternal NOEL = >90 mg/kg/day (no toxicity). UNACCEPTABLE (No
MTD, too few pregnant dams at scheduled sacrifice). (C. Aldous,
8/27/85).
Ref: May 20, 2002. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA FLUAZIFOP-P-BUTYL. California EPA. Department of Pesticide
Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-butyl.CAepa.02.pdf
4.2.3.1 Developmental Toxicity Study Conclusions. The LOAEL is
5.0 mg/kg/day based on decreased fetal weight and increased incidence
of hydroureter in fetuses and litters, and delayed
ossification in a 160 litter/group developmental toxicity study
(MRID# 00088858). This LOAEL is also supported
by a dose related increased fetal incidence in partially ossified
sternebrae and sternebrae bipartite, 5 th (MRID#
46082913, 46082903), and statistically significant increased
incidence of fetuses and litters with interparietals, occipitals
and parietals partially ossified, calcaneum not ossified and increased
manus and pes scores at 5.0 mg/kg/day (MRID#46082903
and 46158401). The NOAEL of 1.0 mg/kg/day in the
160 litter per group study was not selected and a NOAEL of 2.0
mg/kg/day from the Wistar rat studies was selected. Since apparent
effects noted at 0.05 and 1.0 mg/kg/day were either not dose related,
concurrent controls were low, the effects were lower than the
historical control range, or were not statistically significant
in litters, and 2 developmental studies that included a 2 mg/kg/day
dose group failed to elicit a dose dependant response, a NOAEL
of 2.0 mg/kg/day was selected (page 31).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
4.2.3.6 Fluazifop-P-butyl - Wistar Rats. In a developmental toxicity
study (MRID 46158401)[Fluazifop-p-butyl, calculated as 90.1% a.i.;
batch/lot# P12; CTL Ref.# Y02746/021/003] was administered to
[(24 females) Alderly Park strain of Wistar rats] rats/dose by
gavage at dose levels of 0, 0.5, 1.0, 20, or 300 mg a.i./kg bw/day
from days 7 through 16 of gestation. ...
Developmental effects were shown by delayed ossification in many
parameters at ≥20 mg/kg/day. The incidence of parietals
partially ossified were statistically significant and dose related
in fetuses and litters at 20 mg/kg/day. The statistically significant
increase in interparietals partially ossified in fetuses at 20
mg/kg/day exceeded historical controls and support the delayed
ossification of the parietal bones. Cervical vertebral arches
4 and 5 partially ossified and centrum (4 th not ossified) at
20 mg/kg/day showed statistically significantly increased incidence
in fetuses and litters. Manus Scores were statistically significantly
increased at 1.0, 20, and 300 mg/kg/day. Pes score were
statistically significantly increased at 20 and 300 mg/kg/day.
... For developmental toxicity, the NOAEL
is 1.0 mg/kg/day and the LOAEL is 20 mg/kg/day based on dose related
delayed ossification in skull bones [parietal], delayed ossification
of the cervical arches and centrum (not ossified) in fetuses and
litters and delayed ossification of the manus and pes.
(Page 36-37).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
Endocrine:
Ovary (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
ONCOGENICITY, MOUSE
[OR HAMSTER] 411-125 180756 Rattray, N. J., "Fluazifop-p-butyl:
80 week carcinogenicity study in hamsters," Central Toxicology
Laboratory (CTL), Alderley Park Macclesfield, 2/1/01. Lab Study
ID: Syngenta No.1606-01. Golden Syrian hamsters, 51/sex/group,
were dosed in diet with 0, 0, 200, 750, or 3000 ppm fluazifop-p-butyl
(91.6%) for 81-83 weeks. The dual control groups were treated
identically. An additional 12/sex/group (same doses) were allocated
for 1-yr sacrifice (for hematology only). Estimated achieved doses
were 12.5, 47, and 194 mg/kg/day (M) and 12.1, 46, and 181 mg/kg/day
(F). No NOEL was established... Findings at the higher two dose
levels only included decreased testes weights,
reduced spermatozoa counts in epididymides
and increased cataract development in males.
Stromal cell/sex cord hyperplasia was elevated
in high dose females. Benign stromal cell/sex cord tumors
were slightly but significantly elevated in 3000 ppm females (incidences
of 1, 1, 3, 4, and 5 in controls through high dose groups, respectively).
Study is not acceptable, but presumed upgradeable (there is a
need to explain why this species was selected for this study,
and individual data for hamsters should be provided). The ovarian
tumor findings, in addition to the several noted histopathology
findings without NOEL's, are possible adverse effects. Contemporary
historical control data are needed if the registrant desires to
re-visit DPR conclusions about findings of this study. The DPR
review briefly discusses some ramifications of ovarian and testicular
findings. Aldous, 5/20/02.
Ref: May 20, 2002. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA FLUAZIFOP-P-BUTYL. California EPA. Department of Pesticide
Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-butyl.CAepa.02.pdf
Target
Organs: Liver, skin, kidney, eye, bone marrow, blood, reproductive
system.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl).
Syngenta. January 21, 2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
Endocrine:
Pituitary
The chronic dietary (all populations), intermediate-term dermal
and inhalation, and intermediateterm incidental oral endpoints
were selected from the 2-generation reproduction study in rats
based on decreased spleen, testes
and epididymal weights in males, and decreased
uterine and
pituitary weights in females (page 5) ... Reproduction
and fertility effects (rats). Reproductive NOAEL = M/F 0.74/0.88mg/kg/day
LOAEL = M/F 5.8/7.1 mg/kg/day based on decreased abs. & rel
testes & epididymal weight and in females decreased pituitary
& uterine weights (age 23) ...
F1 adult females showed an absolute (28%) and relative (18%) statistically
significant increase in ovarian weight at 250 ppm. In F1 adult
females, absolute pituitary weights (13%20%)
and uterine weights (18%-25%) were statistically
significantly reduced at 80-250 ppm. Relative pituitary
weights (18%-27%) and uterine weights (19%-29%) were reduced in
F1 adult females at 80-250 ppm.
• Comments about Study/Endpoint/Uncertainty Factor: The
study/dose/endpoint is appropriate for the route (oral) and duration
(chronic) of concern. Although the endpoint of concern in based
on male reproductive effects, decreases
in pituitary and uterine weights were seen in females at a comparable
NOAEL (0.88 mg/kg/day) and LOAEL (7.1 mg/kg/day) (page
45).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
Endocrine:
Prostate (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproductive Effects:
In a 3-generation reproductive study in rats, effects included
reductions in weight gain, fetal weight, ossification,
testicular weight, spleen weight, increased prostate
weight and gestational length. No Effect Level (NEL) was 1 mg/kg/day.
Target Organs: Liver, skin, kidney,
eye, bone marrow, blood, reproductive system.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl).
Syngenta. January 21, 2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
Endocrine:
Testicular (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
4.1.3 Dose-response. A statistically significant, but marginally
adequate dose-response was shown in the
testes weight, and epididymal weight, decrement in the parental
and F1 generation in the adult rat,
potentially due to reduced sperm content. The
cancer study in hamsters showed a
good dose response in testes weight decrement. Since the
statistically significant effects were seen in the male P0 and
F1 parents and in the hamster study, the effects were considered
treatment related. The testicular endpoint from the reproduction
study was selected for the chronic RfD, intermediate-term oral
incidental exposure, intermediate and long-term dermal and inhalation
exposure. Other studies showed testes weight decrement and epididymal
effects at higher dose levels, but there were only equivocal histological
effects shown. Although extensive short-term studies on the testes
weight decrement and epididymal effects were conducted, all
failed to show that the effect was incidental or find an explanation
for the effect. However, the more sensitive studies on
sperm count were not among the extra studies conducted. An acceptable
negative study of sufficient duration on sperm parameters would
add confidence to the possibility that the testes and epididymal
weight decrement seen in the rat reproduction study were incidental
and not reproducible. The uterine weight decrement seen in the
reproduction study showed a good dose-response and was supported
by a dose-response in the pituitary weight decrement at the same
doses. In addition, in the hamster, hyperplasia in the ovary was
seen at high dose levels. One of the subchronic
studies in the rat with fluazifop-P-butyl
showed testicular weight decrement, while the other one
with fluazifop-butyl did not at approximately the same doses as
in the reproduction study; at the highest dose tested in the subchronic
study with fluazifop-butyl absolute testes weights were increased
30%. The reason is unknown, but may be due to animal variation
or other unknown factors such as edema. The
testes and epididymal weight decrement and uterine and ovarian
effects suggest possible endocrine related effects. However,
negative in vitro studies suggest estrogen and androgen hormones
were not involved. Agonistic and antagonistic studies with fluazifop-butyl,
fluazifop-P-butyl and the fluazifop acid metabolite were conducted
in yeast cells containing human estrogen and androgen receptors.
No receptor activity was found with any of the test materials
over a sufficiently wide concentration range (page 18-19).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
ONCOGENICITY, MOUSE
[OR HAMSTER] 411-125 180756 Rattray, N. J., "Fluazifop-p-butyl:
80 week carcinogenicity study in hamsters," Central Toxicology
Laboratory (CTL), Alderley Park Macclesfield, 2/1/01. Lab Study
ID: Syngenta No.1606-01. Golden Syrian hamsters, 51/sex/group,
were dosed in diet with 0, 0, 200, 750, or 3000 ppm fluazifop-p-butyl
(91.6%) for 81-83 weeks. The dual control groups were treated
identically. An additional 12/sex/group (same doses) were allocated
for 1-yr sacrifice (for hematology only). Estimated achieved doses
were 12.5, 47, and 194 mg/kg/day (M) and 12.1, 46, and 181 mg/kg/day
(F). No NOEL was established... Findings at the higher two dose
levels only included decreased testes weights,
reduced spermatozoa counts in epididymides and
increased cataract development in males.
Stromal cell/sex cord hyperplasia was elevated
in high dose females... Aldous, 5/20/02.
Ref: May 20, 2002. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA FLUAZIFOP-P-BUTYL. California EPA. Department of Pesticide
Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-butyl.CAepa.02.pdf
--
Reproductive Effects: In a 3-generation reproductive study in
rats, effects included reductions in weight gain, fetal weight,
ossification, testicular weight,
spleen weight, increased prostate
weight and gestational length. No Effect Level (NEL) was 1 mg/kg/day.
Target Organs: Liver, skin, kidney,
eye, bone marrow, blood, reproductive system.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl).
Syngenta. January 21, 2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
The chronic dietary (all populations), intermediate-term dermal
and inhalation, and intermediateterm incidental oral endpoints
were selected from the 2-generation reproduction study in rats
based on decreased spleen, testes
and epididymal weights in males, and decreased uterine
and pituitary weights in females (page 5).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
Endocrine:
Uterine
The chronic dietary (all populations), intermediate-term dermal
and inhalation, and intermediateterm incidental oral endpoints
were selected from the 2-generation reproduction study in rats
based on decreased spleen, testes
and epididymal weights in males, and decreased
uterine and pituitary weights in females (page 5). ...
The uterine weight decrement seen in the
reproduction study showed a good dose-response and was
supported by a dose-response in the pituitary weight decrement
at the same doses. In addition, in the hamster, hyperplasia in
the ovary was seen at high dose levels. One of the subchronic
studies in the rat with fluazifop-P-butyl showed testicular weight
decrement, while the other one with fluazifop-butyl did not at
approximately the same doses as in the reproduction study; at
the highest dose tested in the subchronic study with fluazifop-butyl
absolute testes weights were increased 30%. The reason is unknown,
but may be due to animal variation or other unknown factors such
as edema. The testes and epididymal weight decrement and uterine
and ovarian effects suggest possible endocrine
related effects. However, negative in vitro studies suggest
estrogen and androgen hormones were not involved. Agonistic and
antagonistic studies with fluazifop-butyl, fluazifop-P-butyl and
the fluazifop acid metabolite were conducted in yeast cells containing
human estrogen and androgen receptors. No receptor activity was
found with any of the test materials over a sufficiently wide
concentration range (page 19).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
Eye
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 018 994244: Tesh,
J. M., Ross, F. W. and Tesh, S. A. "PP009: Effects of Oral Administration
upon Pregnancy in the Rabbit, Final report". Life Science Research
report No. 80/ILK 027/498 [November 28, 1980]. PP009, purity 94.8%,
administered via gavage at concentrations of 10, 30 or 90 mg/kg/day
to 20-24 artificially inseminated female New Zealand rabbits during
gestation days 6 through 28. Adverse effects: increased incidence
of cloudy eyes (12.7%), small
fetuses, delayed ossification and enlarged anterior and posterior
fontanelle. Maternal NOEL = >90 mg/kg/day (no toxicity).
UNACCEPTABLE (No MTD, too few pregnant dams at scheduled sacrifice).
(C. Aldous, 8/27/85).
-- ONCOGENICITY, MOUSE [OR HAMSTER] 411-125 180756 Rattray, N.
J., “Fluazifop-p-butyl: 80 week carcinogenicity study in hamsters,”
Central Toxicology Laboratory (CTL), Alderley Park Macclesfield,
2/1/01. Lab Study ID: Syngenta No.1606-01. Golden Syrian hamsters,
51/sex/group, were dosed in diet with 0, 0, 200, 750, or 3000
ppm fluazifop-p-butyl (91.6%) for 81-83 weeks. The dual control
groups were treated identically. An additional 12/sex/group (same
doses) were allocated for 1-yr sacrifice (for hematology only).
Estimated achieved doses were 12.5, 47, and 194 mg/kg/day (M)
and 12.1, 46, and 181 mg/kg/day (F). No NOEL was established...
Findings at the higher two dose levels only included decreased
testes weights, reduced spermatozoa counts in epididymides and
increased
cataract development in males...
Ref: May 20, 2002. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA FLUAZIFOP-P-BUTYL. California EPA. Department of Pesticide
Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-butyl.CAepa.02.pdf
4.2.3.8 Fluazifop-P-butyl - Rabbit In a developmental toxicity
study [MRID 46082904] [fluazifop-p-butyl (90.1% a.i., batch/lot
# P12)] was administered to [(20 females) New Zealand White] rabbits/group
by gavage in corn oil vehicle [1 ml/kg] at dose levels of 0, 2,
10 or 50 mg a.i./kg bw/day from days 8 through 20 of gestation.
Day sperm was found was designated as day 1. On day 30 of gestation,
dams were killed and the uterine contents examined for live and
dead fetuses. Fetuses were weighed, examined for external and
visceral abnormalities, sexed, eviscerated and stained for skeletal
examination. ... Treatment related effects on development were
seen in the 50 mg/kg/day group only. Statistically significant
extra 13 th rib and delayed ossification was seen in sternebrae
2 and 5. An increase in partially ossified 5 sternebrae was seen
at 10 mg/kg/day, but the litter incidence was not increased. A
nominal increase in malformations were seen at 50 mg/kg/day, such
as acephaly [1 fetus/1 litter], cebocephaly
[1 fetus/1 litter], cleft palate [1 fetus/1 litter], microphthalmia
[1 fetus/1 litter], gastroschisis [1 fetus/1
litter], and multiple anomalies in 1 fetus/1 litter. None
were duplicated and all could have occurred 1 to 3 times in the
same litter, with 0 in control. Since individual
animal data was not submitted, this incidence in litters could
not be verified. For developmental toxicity, the
NOAEL is 10 mg/kg/day and the LOAEL is 50 mg/kg/day based on increased
13 th rib and increased incidence of delayed ossification of sternebrae
2 and 5. (page 39).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
Definitions:
Acephaly:
literally means absence of the head. The acephalic fetus is
a parasitic twin attached to an otherwise intact fetus. The
acephalic fetus has a body but lacks a head and a heart; the
fetus’s neck is attached to the normal twin. The blood
circulation of the acephalic fetus is provided by the heart
of the twin. The acephalic fetus can not exist independently
of the fetus to which it is attached.
Ref:
http://www.icomm.ca/geneinfo/acep.htm
Cebocephaly:
A facial anomaly, characterized by a small, flattened nose with
a single nostril situated below incomplete
or underdeveloped closely set eyes.
Ref: http://www.icomm.ca/geneinfo/cephaly.htm
Gastroschisis: is an abdominal
wall defect located to the side of the umbilical cord (umbilicus).
The infant is born with intestines protruding through this defect
and no protective sac is present.
Ref: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002924.htm
Microphthalmia - small eye syndrome.
Microphthalmia is a disorder in which one or both eyes are abnormally
small.
Fetotoxic
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
Reproductive Effects: In a 3-generation reproductive study in
rats, effects included reductions in weight gain, fetal weight,
ossification, testicular weight, spleen weight, increased prostate
weight and gestational length. No Effect Level (NEL) was 1 mg/kg/day.
Fetotoxic effects seen in the rabbit, including reduced fetal
weight and reduced ossification at higher doses. No Effect Level
(NEL)
was 30 mg/kg/day in rabbits. The NEL for teratogenic
effects is at least 10/mg/day in the rat, with diaphragmatic
hernia at higher doses. Not teratogenic at highest dose
tested in rabbits (90 mg/kg/day). While
fluazifop-p-butyl is fetotoxic
when fed to
pregnant rats, human exposure data has concluded
that female formulation workers are not at increased risk of fetotoxic
effects when skin protection measures are applied.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for
Fusilade DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl). Syngenta. January
21, 2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
Kidney
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
... Subchronic and chronic toxicity studies with fluazifop-butyl
or fluazifop-P-butyl show that the rat is more sensitive to toxic
effects than the dog, rabbit or hamster, possibly due to longer
retention time of the major metabolite (fluazifop acid) in the
rat. The kidney and liver
are the target organs and the toxicity is expressed as exacerbation
of age related kidney toxicity and liver toxicity in the presence
of peroxasome proliferation (page 5).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
ONCOGENICITY, MOUSE
[OR HAMSTER] 411-125 180756 Rattray, N. J., "Fluazifop-p-butyl:
80 week carcinogenicity study in hamsters," Central Toxicology
Laboratory (CTL), Alderley Park Macclesfield, 2/1/01. Lab Study
ID: Syngenta No.1606-01. Golden Syrian hamsters, 51/sex/group,
were dosed in diet with 0, 0, 200, 750, or 3000 ppm fluazifop-p-butyl
(91.6%) for 81-83 weeks. The dual control groups were treated
identically. An additional 12/sex/group (same doses) were allocated
for 1-yr sacrifice (for hematology only). Estimated achieved doses
were 12.5, 47, and 194 mg/kg/day (M) and 12.1, 46, and 181 mg/kg/day
(F). No NOEL was established. Changes seen at all dose levels
included chronic progressive nephropathy,
factoring both incidence and degree, in kidneys of both sexes;
gall stone formation at all dose levels
in males; testicular tubular degeneration,
factoring both incidence and degree, dose-related in all treated
male groups; and elevated liver weights in all female groups.,,
Ref: May 20, 2002. SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY
DATA FLUAZIFOP-P-BUTYL. California EPA. Department of Pesticide
Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-butyl.CAepa.02.pdf
4.2.3.1 Developmental Toxicity Study Conclusions. The LOAEL is
5.0 mg/kg/day based on decreased fetal weight and increased
incidence of hydroureter in fetuses and litters, and delayed
ossification in a 160 litter/group developmental toxicity study
(MRID# 00088858). (page 31).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
Liver
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
... Subchronic and chronic toxicity studies with fluazifop-butyl
or fluazifop-P-butyl show that the rat is more sensitive to toxic
effects than the dog, rabbit or hamster, possibly due to longer
retention time of the major metabolite (fluazifop acid) in the
rat. The kidney and liver are the target
organs and the toxicity is expressed as exacerbation of age related
kidney toxicity and liver toxicity in the presence of peroxasome
proliferation (page 5).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
Chronic/Subcrhonic
Toxicity Studies: Chronic toxicity studies in rodents have shown
liver changes (cellular hypertrophy). The No Effect Level
(LEL) in rats is 10 ppm (0.5 mg/kg/day). Long term feeding studies
in dogs produced a range of potentially serious effects at high
dose rates (red cell, bone marrow and lymphadenopathy changes
and liver and spleen damage) with
a No Effect Level of 25 mg/kg/day. Target Organs:
Liver, skin, kidney, eye, bone marrow, blood, reproductive
system.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl). Syngenta. January 21,
2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
Lung
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
*Acute
Toxicity:...
Breathing small amounts of the product Fusilade 2000 may cause
vomiting and severe lung congestion;
larger amounts may ultimately lead to labored
breathing, coma, and death [37].
Ref: EXTOXNET. Pesticide Information Profile
for Fluazifop-p-butyl. Cornell University.
http://ace.ace.orst.edu/info/extoxnet/pips/fluazifo.htm
Reproductive
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic/Subcrhonic
Toxicity Studies: Chronic toxicity studies in rodents
have shown liver changes (cellular hypertrophy). The No Effect
Level (LEL) in rats is 10 ppm (0.5 mg/kg/day). Long term feeding
studies in dogs produced a range of potentially serious effects
at high dose rates (red cell, bone marrow and lymphadenopathy
changes and liver and spleen damage) with a No Effect Level of
25 mg/kg/day. Target Organs: Liver,
skin, kidney, eye, bone marrow, blood, reproductive
system.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl). Syngenta. January 21,
2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
"Fluazifop-P-butyl
79241-46-6 Withdrawn. Teratogenic and
suspected reproductive effects in experimental animals.
1991."
Definition: "Withdrawn. A substance
which the manufacturer has either withdrawn from the market, or
for which he has withdrawn his application for registration, approval,
or renewed approval and when it is clear that these measures were
undertaken due to the health or environmental properties of the
substance."
Ref:
Euopean Commission. Appendix 5. Substances which may not be included
as active ingredients in approved pesticide products, Chapter
15, Section 2, subsection one.
http://www.kemi.se/lagar_eng/pdf/app5_8.pdf
Spleen
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproductive Effects:
In a 3-generation reproductive study in rats, effects included
reductions in weight gain, fetal weight, ossification, testicular
weight, spleen weight, increased
prostate weight and gestational length. No Effect Level (NEL)
was 1 mg/kg/day...
Chronic/Subcrhonic Toxicity Studies: Chronic toxicity studies
in rodents have shown liver changes (cellular hypertrophy). The
No Effect Level (LEL) in rats is 10 ppm (0.5 mg/kg/day). Long
term feeding studies in dogs produced a range of potentially serious
effects at high dose rates (red cell, bone marrow and lymphadenopathy
changes and liver and spleen damage)
with a No Effect Level of 25 mg/kg/day., Target Organs: Liver,
skin, kidney, eye, bone marrow, blood, reproductive system.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Fusilade
DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl). Syngenta. January 21,
2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
The chronic dietary (all populations), intermediate-term dermal
and inhalation, and intermediateterm incidental oral endpoints
were selected from the 2-generation reproduction study in rats
based on decreased spleen, testes
and epididymal weights in males, and decreased uterine and pituitary
weights in females (page 5).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
Stomach
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Acute
Toxicity... A
single dose of the formulated compound (Fusilade 2000) can cause
severe stomach and intestine disturbance.
Ref: EXTOXNET. Pesticide Information Profile
for Fluazifop-p-butyl. Cornell University.
http://ace.ace.orst.edu/info/extoxnet/pips/fluazifo.htm
Teratogenic
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
--
Reproductive Effects: In a 3-generation reproductive study in
rats, effects included reductions in weight gain, fetal weight,
ossification, testicular weight, spleen weight, increased prostate
weight and gestational length. No Effect Level (NEL) was 1 mg/kg/day.
Fetotoxic effects seen in the rabbit, including reduced fetal
weight and reduced ossification at higher doses. No Effect Level
(NEL)
was 30 mg/kg/day in rabbits. The NEL for teratogenic
effects is at least 10/mg/day in the rat, with diaphragmatic
hernia at higher doses. Not teratogenic at highest dose
tested in rabbits (90 mg/kg/day). While
fluazifop-p-butyl is fetotoxic
when fed to
pregnant rats, human exposure data has concluded that female formulation
workers are not at increased risk of fetotoxic effects when skin
protection measures are applied.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for
Fusilade DX (active indredient Fluazifop-P-Butyl). Syngenta. January
21, 2002.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluazifop-P-Butyl.MSDS.pdf
"Fluazifop-P-butyl
79241-46-6 Withdrawn. Teratogenic and
suspected reproductive effects in experimental animals. 1991."
Definition: "Withdrawn. A substance which the manufacturer
has either withdrawn from the market, or for which he has withdrawn
his application for registration, approval, or renewed approval
and when it is clear that these measures were undertaken due to
the health or environmental properties of the substance."
Ref:
Euopean Commission. Appendix 5. Substances which may not be included
as active ingredients in approved pesticide products, Chapter
15, Section 2, subsection one.
http://www.kemi.se/lagar_eng/pdf/app5_8.pdf
4.2.3.8 Fluazifop-P-butyl - Rabbit In a developmental toxicity
study [MRID 46082904] [fluazifop-p-butyl (90.1% a.i., batch/lot
# P12)] was administered to [(20 females) New Zealand White] rabbits/group
by gavage in corn oil vehicle [1 ml/kg] at dose levels of 0, 2,
10 or 50 mg a.i./kg bw/day from days 8 through 20 of gestation.
Day sperm was found was designated as day 1. On day 30 of gestation,
dams were killed and the uterine contents examined for live and
dead fetuses. Fetuses were weighed, examined for external and
visceral abnormalities, sexed, eviscerated and stained for skeletal
examination. ... Treatment related effects on development were
seen in the 50 mg/kg/day group only. Statistically significant
extra 13 th rib and delayed ossification was seen in sternebrae
2 and 5. An increase in partially ossified 5 sternebrae was seen
at 10 mg/kg/day, but the litter incidence was not increased. A
nominal increase in malformations were seen at 50 mg/kg/day, such
as acephaly [1 fetus/1 litter], cebocephaly
[1 fetus/1 litter], cleft palate [1
fetus/1 litter], microphthalmia [1
fetus/1 litter], gastroschisis [1
fetus/1 litter], and multiple anomalies
in 1 fetus/1 litter. None were duplicated and all could
have occurred 1 to 3 times in the same litter, with 0 in control.
Since individual animal data was not submitted,
this incidence in litters could not be verified.
For developmental toxicity, the NOAEL is 10 mg/kg/day and the
LOAEL is 50 mg/kg/day based on increased 13 th rib and increased
incidence of delayed ossification of sternebrae 2 and 5. (page
39).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
Definitions:
Acephaly:
literally means absence of the head. The acephalic fetus is
a parasitic twin attached to an otherwise intact fetus. The
acephalic fetus has a body but lacks a head and a heart; the
fetus’s neck is attached to the normal twin. The blood
circulation of the acephalic fetus is provided by the heart
of the twin. The acephalic fetus can not exist independently
of the fetus to which it is attached.
Ref:
http://www.icomm.ca/geneinfo/acep.htm
Cebocephaly:
A facial anomaly, characterized by a small, flattened nose with
a single nostril situated below incomplete
or underdeveloped closely set eyes.
Ref: http://www.icomm.ca/geneinfo/cephaly.htm
Gastroschisis: is an abdominal
wall defect located to the side of the umbilical cord (umbilicus).
The infant is born with intestines protruding through this defect
and no protective sac is present.
Ref: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002924.htm
Microphthalmia - small eye syndrome.
Microphthalmia is a disorder in which one or both eyes are abnormally
small.
An acute dietary endpoint for females 13-49 years of age was
selected from a developmental toxicity study in rats, based on
diaphragmatic hernia. ... The overall rat studies showed a NOAEL/LOAEL
of 2.0/5.0 mg/kg/day. The NOAEL/LOAEL was chosen from among MRID#
0008858, 46082903, 46082913 and 46518401. For a single dose effect,
the NOAEL/LOAELs are 50/200 mg/kg/day based on the diaphragmatic
hernia malformations (Page 31).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
|
Environmental
(click on for all
fluorinated pesticides)
3.3
Environmental Degradation. Environmental fate studies indicate
that fluazifop-P-butyl is not mobile and not persistent.
The predominant environmental fate process appears to be
microbially-assisted hydrolysis to fluazifop acid and 5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridone
[major metabolites], which are considered to be mobile and
therefore, can potentially reach surface and ground waters.
Aerobic soil metabolism studies showed that the half-life
of the parent ester is on the order of a few hours. The
properties of fluazifop acid, namely high mobility and long
persistence in water (78-day hydrolysis half-life at pH
7) and anaerobic soil (half-life 1 to 3 years, MRID# 92067033)
indicate that it might persist from year to year in the
subsurface, and move with flowing ground water. The
degradate 5 trifluoromethyl-2-pyridone does not sorb to
soil, indicating very high mobility. A minor degradate is
2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-trifluromethylpyridine. There are
no data on its mobility, but it is expected to be similar
to that of fluazifop acid. ... Water softening, in which
the alkalinity is raised to pH 10 or 11 by the addition
of lime or soda ash, will rapidly degrade the parent fluazifop-P-butyl
to fluazifop acid (page 11-12).
Ref:
December 10, 2004. US
EPA> Fluazifop-P-butyl: Revised HED Chapter of the Tolerance
Reassessment Eligibility Decision (TRED) Document. EPA Docket
number: OPP-2004-0347-0003
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0003.pdf
-- see also: http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/f-p-b.opp-2004-0347-0011.pdf
Effects
on aquatic organisms: Fluazifop-p-butyl
may be highly to moderately toxic
to fish, but only slightly
toxic to other aquatic species, such as invertebrates.
The reported 96-hour LC50 values for the technical product
in fish species are 0.53 mg/L in bluegill
sunfish and 1.37 mg/L in rainbow trout [5], indicating very
high to high toxicity. The 48-hour LC50 in Daphnia
magna (an aquatic invertebrate) is reported as greater than
10 mg/L [5], indicating only slight toxicity.
Ref: Fluazifop-p-butyl.
E X T O X N E T Pesticide Information Profiles. Revised
June 1996.
http://ace.ace.orst.edu/info/extoxnet/pips/fluazifo.htm
|
|

