|
Return
to Dichlorotetrafluoroethane
Index Page
Activity: Propellant,
Former EPA List 2 Inert
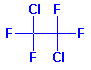
Structure:
Adverse
Effects:
Brain
Carcinogen
CNS
Heart
Lung
Environmental
| Has
not been manufactured in the US since 1995.
Manufacturing/Use
Information: Major Uses:
-- For
1,2-Dichloro-1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethane (USEPA/OPP Pesticide
Code: 326200). Not registered for current use in the U.S.
as of review of database on Sept 8, 2000.
-- Fully
halogenated chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) such as 1,2-dichloro-1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethane
were scheduled for production phase-out in 1987 by the Montreal
Protocol. Although originally scheduled for 50% production
phase-out by the year 2000 in developed countries, the worsening
ozone depletion has forced acceleration of the CFC phase-out.
-- Blowing
agent for cellular polymers.
-- Solvent
and diluent in polymerization of fluoro-olefins, cleaning
and degreasing printed circuit boards,
preparation of explosives and
extraction of volatile substances.
-- Foaming
agent in fire extinguishing and
aerosols ...
-- Inorganic
synthesis in preparation of uranium
tetrafluoride, Freons, and polymer intermediates.
-- In
aerosols with other Freons to lower vapor pressure and produce
non-flammable aerosol propellants ...
-- Refrigerant
in industrial cooling and air conditioning
systems.
-- Used/
in inhibiting of metal erosion in hydraulic fluids; in strengthening
glass bottles; in magnesium refining; and as a reflux
liquid to assist heat removal.
Ref:
1,2-DICHLORO-1,1,2,2-TETRAFLUOROETHANE. CASRN: 76-14-2. TOXNET
profile from Hazardous Substances Data Base. http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/dichlorotetrafluoroe.toxnet.htm |
Brain
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- NEUROLOGIC 0.2.7.1 ACUTE EXPOSURE -Headache, dizziness, and
disorientation are common. Cerebral edema
may be found on autopsy. A syndrome of impaired psychomotor speed,
impaired memory and learning, and emotional lability has been
described in workers with chronic occupational exposure to fluorinated
hydrocarbons.
-- THERE IS A SIGNIFICANT ACCUMULATION OF FLUOROCARBONS IN
BRAIN, LIVER & LUNG COMPARED TO BLOOD LEVELS, SIGNIFYING
A TISSUE DISTRIBUTION OF FLUOROCARBONS SIMILAR TO THAT OF CHLOROFORM.
/FLUOROCARBONS/ [Clayton, G.D., F.E. Clayton (eds.) Patty's Industrial
Hygiene and Toxicology. Volumes 2A, 2B, 2C, 2D, 2E, 2F: Toxicology.
4th ed. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons Inc., 1993-1994. 1203]
-- Aerosol sprays containing fluorocarbon propellants are another
source of solvent intoxication. Prolonged exposure or daily use
may result in damage to several organ systems. Clinical problems
include cardiac arrhythmias, bone marrow depression, cerebral
degeneration, and damage to liver, kidney, & peripheral
nerves. Death occasionally has been attributed to inhalant abuse,
probably via the mechanism of cardiac arrhythmias, especially
accompanying exercise or upper airway obstruction. /fluorocarbon
propellants/ [Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W.
Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological
Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996.
575]
Ref: 1,2-DICHLORO-1,1,2,2-TETRAFLUOROETHANE.
CASRN: 76-14-2. TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances Data
Base.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/dichlorotetrafluoroe.toxnet.htm
Carcinogen
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
PAN
Bad Actor: Carcinogen.
Ref: Pesticide Action Network
http://www.pesticideinfo.org/Detail_Chemical.jsp?Rec_Id=PC35610
/UV-B Radiation is likely to incr by ozone depletion caused by
atmospheric concentrations of chlorofluorocarbons/. Indications
are increasing that UV-B radiation ... plays a role in the induction
and growth of cutaneous melanomas, a ... dangerous
type of skin cancer. ... There are indications that ...
suppression of the immune response by UV-B radiation may occur
in humans. The antigen presenting Langerhans cells in the skin
are damaged and allergic responses are depressed. ... There are
indications that UV-B radiation increases cataract formation,
an important cause of blindness especially in areas with limited
medical facilities. /Chlorofluorocarbons/
[WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 113: Fully Halogenated Chlorofluorocarbons
p.101 (1990)]
Ref: 1,2-DICHLORO-1,1,2,2-TETRAFLUOROETHANE.
CASRN: 76-14-2. TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances Data
Base.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/dichlorotetrafluoroe.toxnet.htm
CNS
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- SUMMARY TOXICITY
STATEMENT: MILD IRRITANT ... /CNS DEPRESSANT/
IN HIGH CONCN. ASPHYXIANT. [Sax, N.I. Dangerous Properties of
Industrial Materials. 5th ed. New York: Van Nostrand Rheinhold,
1979. 567]
-- Chlorinated hydrocarbons may cause systemic toxicity through
percutaneous absorption. Systemic toxicity includes convulsion,
delirium, and central nervous system depression
/From table/. /Chlorinated hydrocarbons/ [Zenz, C. Occupational
Medicine-Principles and Practical Applications. 2nd ed. St. Louis,
MO: Mosby-Yearbook, Inc, 1988. 160]
Ref:
1,2-DICHLORO-1,1,2,2-TETRAFLUOROETHANE. CASRN: 76-14-2. TOXNET
profile from Hazardous Substances Data Base.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/dichlorotetrafluoroe.toxnet.htm
Heart
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- The American Conference
of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) has assigned dichlorotetrafluoroethane
a threshold limit value (TLV) of 1000 ppm (6990 mg/m(3)) as a
TWA for a normal 8-hour workday and a 40-hour workweek [ACGIH
1994, p. 19].
-- Rationale for Limits: The NIOSH limit is based on the risk
of respiratory irritation, asphyxia at high concentrations [NIOSH
1992]. The ACGIH limit is based on the risk of systemic toxicity
and cardiac sensitization [ACGIH
1991, p. 444].
-- Effects on Animals: dichlorotetrafluoroethane is a cardiac
sensitizer, an asphyxiant, and a weak narcotic at extremely high
concentrations [ACGIH 1991]. Dogs exposed to 200,000 ppm of dichlorotetrafluoroethane
for 16 hours died, but exposures at this level for 8 hours caused
tremor and convulsions [Hathaway
et al. 1991]. Serious arrhythmia
occurred in one of 12 dogs exposed once to 25,000 ppm of dichlorotetrafluoroethane
and given intravenous epinephrine. Dichlorotetrafluoroethane is
reported to reduce pulmonary compliance and act as a bronchoconstrictor
[ACGIH 1991]. Guinea pigs exposed to a dichlorotetrafluoroethane
concentration of 47,000 ppm developed respiratory irritation [Hathaway
et al. 1991]. Repeated exposure to sprayed dichlorotetrafluoroethane
caused localized skin inflammation in rats and irritation of the
eyes of rabbits [ACGIH 1991].
Ref: US OSHA (Occupational Safety &
Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor).
http://www.osha-slc.gov/SLTC/healthguidelines/dichlorotetrafluoroethane/recognition.html
-- In persons with
impaired pulmonary function, especially those with obstructive
airway diseases, the breathing of Refrigerant
114 might cause exacerbation of symptoms due to its irritant
properties. ... In persons with impaired
cardiovascular function, especially those with history of cardiac
arrhythmias, the inhalation of Refrigerant 114 might cause exacerbation
of disorders of the conduction mechanism due to sensitizing effects
on the myocardium. [Mackison, F. W., R. S. Stricoff, and
L. J. Partridge, Jr. (eds.). NIOSH/OSHA - Occupational Health
Guidelines for Chemical Hazards. DHHS(NIOSH) PublicationNo. 81-123
(3 VOLS). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, Jan.
1981. 1]
-- In one study, ten subjects were exposed to CFC-11, CFC-12,
and CFC-114; two mixtures of CFC-11
and CFC-12; & a mixture of CFC-12 and CFC-114 )breathing concn
between 16 & 150 g/cu m [2300 & 21,400 ppm]) for 15, 45, or 60
sec. Significant acute reduction of ventilatory lung capacity
was reported in each case, as well as bradycardia & increased
variability in heart rate & atrioventricular block. It was concluded
that the mixtures exerted stronger respiratory
effects than individual chlorofluorocarbons at the same level
of exposure. [American Conference of Governmental Industrial
Hygienists, Inc. Documentation of the Threshold Limit Values and
Biological Exposure Indices. 6th ed. Volumes I,II, III. Cincinnati,
OH: ACGIH, 1991. 444]
-- 10 PERSONS
WERE EXPOSED TO FREON 114 FOR LENGTHS
OF 15, 45, OR 60 SEC. IT INDUCED BIPHASIC REDN OF VENTILATORY
CAPACITY. MOST PERSONS DEVELOPED VARIATIONS
IN HEART RATE EXCEEDING THOSE NOTED BEFORE EXPOSURE. IN
A FEW THERE WERE INVERSION OF T-WAVE & 1
CASE OF HEART BLOCK. [VALIC ET AL; BR J IND MED 34 (2):
130-6 (1977)]
-- Fluorocarbon propellants are anesthetic and cardiotoxic.
... Aerosol propellants produce hallucinogenic effects, and, rarely,
contact dermatitis. /Fluorocarbon propellants/ [Ellenhorn, M.J.
and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment
of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing
Co., Inc. 1988. 528]
-- Clinical pathologists exposed to fluorocarbons in the preparation
of frozen tissue sections have been seen to develop coronary
heart disease. /Fluorocarbons/ [Clayton, G.D., F.E. Clayton
(eds.) Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology. Volumes 2A,
2B, 2C, 2D, 2E, 2F: Toxicology. 4th ed. New York, NY: John Wiley
& Sons Inc., 1993-1994. 1209]
Ref:
1,2-DICHLORO-1,1,2,2-TETRAFLUOROETHANE. CASRN: 76-14-2. TOXNET
profile from Hazardous Substances Data Base.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/dichlorotetrafluoroe.toxnet.htm
Lung
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- The American Conference
of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) has assigned dichlorotetrafluoroethane
a threshold limit value (TLV) of 1000 ppm (6990 mg/m(3)) as a
TWA for a normal 8-hour workday and a 40-hour workweek [ACGIH
1994, p. 19].
-- Rationale for Limits: The NIOSH limit is based on the risk
of respiratory irritation, asphyxia at high concentrations [NIOSH
1992]. The ACGIH limit is based on the risk of systemic toxicity
and cardiac sensitization [ACGIH
1991, p. 444].
-- Effects on Animals: dichlorotetrafluoroethane is a cardiac
sensitizer, an asphyxiant,
and a weak narcotic at extremely high concentrations [ACGIH 1991].
Dogs exposed to 200,000 ppm of dichlorotetrafluoroethane for 16
hours died, but exposures at this level for 8 hours caused
tremor and convulsions [Hathaway et al. 1991]. Serious arrhythmia
occurred in one of 12 dogs exposed once to 25,000 ppm of
dichlorotetrafluoroethane and given intravenous epinephrine. Dichlorotetrafluoroethane
is reported to reduce pulmonary compliance
and act as a bronchoconstrictor [ACGIH
1991]. Guinea pigs exposed to a dichlorotetrafluoroethane concentration
of 47,000 ppm developed respiratory irritation [Hathaway et al.
1991].
Ref: US OSHA (Occupational Safety &
Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor).
http://www.osha-slc.gov/SLTC/healthguidelines/dichlorotetrafluoroethane/recognition.html
|
Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
US EPA:
Class II Ozone-Depleting Substance.
All the class II substances and their isomers are regulated
under the accelerated phaseout.
Ref: http://www.epa.gov/ozone/ods2.html
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons
are known to release chlorine radicals into the stratosphere.
Chlorine radicals act as catalysts to reduce
the net amount of stratospheric ozone.Stratospheric
ozone shields the earth from ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation
(i.e., 290 to 320 nanometers). Decreases in total column
ozone will increase the percentage of UV-B radiation, especially
at its most harmful wavelengths, reaching the earth's surface...Exposure
to UV-B radiation has been implicated by laboratory and
epidemiologic studies as a cause of two types of nonmelanoma
skin cancers: squamous cell cancer and basal cell cancer.
Studies predict that for every 1 percent increase in UV-B
radiation, nonmelanoma skin cancer cases would increase
by about 1 to 3 percent... Because this increased UV-B
radiation can be reasonably anticipated to lead to cancer
and other chronic human health effects and significant adverse
environmental effects, EPA believes there is sufficient
evidence for listing the following HCFCs [Dichlorofluoromethane
was included] that are commercially viable on EPCRA
section 313 pursuant to EPCRA sections 313(d)(2)(B) and
(C). EPA is proposing that the following HCFCs be added
individually to EPCRA section 313:
Ref: USEPA/OPPT. Support Document
for the Health and Ecological Toxicity Review of TRI Expansion
Chemicals. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington,
DC (1993). As cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV. 40 CFR Part 372.
Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical Release Reporting;
Community Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
|
|

