|
Return to
Adverse Effects
Abstracts
ACTIVITY: Herbicide
(uracil)
CAS Name: 2-[4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-N-(phenylmethyl)butanamide
Structure:
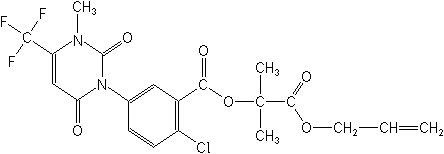
| Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Liver
Spleen |
Regulatory
Information
(only comprehensive for the US) |
| US
EPA Registered: |
Yes
|
| US
EPA PC Code: |
122004 |
| US
Tolerances: |
CFR
180.592 |
Registered
use in
(includes
only a limited list of countries)
|
Australia,
Thailand, US |
US
Maximum Residue Tolerance Levels
|
US:
Kidney & Liver (Cattle, Goats, Hog, Horse, Sheep);
Cotton, gin byproducts
Cotton, undelinted seed |
| Other
Information |
| Molecular
Formula: |
C20H18Cl
F3 N2O6 |
| Manufacturers: |
Syngenta
Novartis |
| Other
Names: |
Inspire
Rebin
CGA-276854
Touchdown B-Power
Logran B-Power
Metabolite: CGA-293731 |
| Manufacture
site: |
SWITZERLAND:
Novartis, Usine de Monthey, Avenue de
lÕIndustrie. |
| Entry
Year: |
1999 |
| Of special interest: |
| PAN
Data |
The
metabolite of butafenacil of concern is CGA-293731:
1-carboxy-1-methylethyl 2-
chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3-methyl-2,6-dioxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1(2H)-pyrimidinyl]
benzoate.
US Tolerances for CGA-293731 are
included for Kidney
& Liver (Cattle, Goats, Hog, Horse, Sheep) |
| Abstracts |
| February
2002 -
Evaluation
of the new active BUTAFENACIL in the products LOGRAN B-POWER
HERBICIDE & TOUCHDOWN B-POWER HERBICIDE. Australia:
National Registration Authority for Agricultural and Veterinary
Chemicals.53545 & 53539. ISSN1443-1335. |
| 2003
- US
EPA 2003 work plan for registration
of 19 conventional pesticides; 6 of the 19 are fluorinated.
They are Butafenacil,
Flonicamid, Flufenpyr-ethyl, Noviflumuron, Quinoxyfen, Trifloxysulfuron |
| Metabolite
or dimer of butafenacil: CGA-293731
(1-carboxy-1-methylethyl 2- chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3-methyl-2,6-dioxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1(2H)-
pyrimidinyl] benzoate) - Ref: US EPA, pesticide tolerance,
Federal Register,
September 19, 2003 |
US
Federal Register
••
Note: Due to length, the following is a partial
list. Click here
to see full list of FR entries
|
| Published
Date |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| November 8, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0084 |
Notice
of Receipt of Requests to Voluntarily Cancel Certain Pesticide Registrations.
| EPA Registration Number |
Product Name |
Registrant |
| 000100-01136 |
Butafenacil Technical |
Syngenta Crop Protection,
Inc.,
Attn: Regulatory Affairs, Po
Box 18300,
Greensboro NC 27419-8300 |
| 000100-01137 |
Inspire EC |
|
| Sept
19, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0282 |
Pesticide
tolerance. FINAL
RULE.
Tolerances
are established for residues of the herbicide butafenacil
in or on the following
| Agricultural
commodities: |
Parts
per million |
| Cotton,
gin byproducts |
10 |
| Cotton,
undelinted seed |
0.50 |
Livestock
commodities:
also includes tolerances for the
residues of the metabolite,
or dimer of butafenacil,
CGA-293731
(1-carboxy-1-methylethyl 2- chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3-methyl-2,6-dioxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1(2H)-
pyrimidinyl] benzoate) |
| Kidney:
Cattle, Goats, Hog, Horse, Sheep |
0.05 |
| Liver:
Cattle, Goats, Hog, Horse, Sheep |
0.50 |
--
food and feed uses. No tolerances have
previously been established for butafenacil.
-- Cancer. Butafenacil showed no evidence of carcinogenicity
in animal tests in two different species, and therefore, a
quantitative cancer risk assessment was not performed.
-- There are currently no registered residential uses of butafenacil.
-- Conditions: As a condition of registration,
the petitioner must submit:
1. A ruminant liver and kidney enforcement method and submit
adequate validation, ILV, and radiovalidation data.
2. Submit confirmatory data on the frozen storage stability
of residues of butafenacil in or on cottonseed, cotton gin
byproduct, cotton hull, cotton meal, and cotton oil.
3. Submit a ruminant feeding study to confirm the Agency's
estimate of maximum residues of butafenacil from the goat
metabolism study.
|
Some excerpts from Table 2.--Subchronic,
Chronic, and Other Toxicity |
Study
type
[Guideline number] |
Results |
90-Day
oral (dietary) toxicity rodents
(rat) - [870.3100] |
NOAEL
= 300 ppm (18.8/20.6 mg/kg/ day M/F). LOAEL = 1,000 ppm
(62.3/69.3 mg/kg/ day M/F) based on decreased
body weight gains, decreased
hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular hemoglobin
(MCH), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), increased red cell
volume, increased bone marrow hypercellularity;
increased bilirubin and urobilinogen; increased alanine
aminotransferase; hepatocyte necrosis; inflammatory
liver cell infiltration |
|
90-Day oral (dietary) toxicity in rodents (mouse)
- [870.3100] |
NOAEL
= 30 ppm (4.11/5.67 mg/kg/day M/F) LOAEL = 100 ppm (13.8/20.1
mg/kg/ day M/F), based on hepatic
histopathology: fatty change, glycogen deposition,
and hypertrophy in both sexes |
| 90-Day
oral (capsule) toxicity in non- rodents (dog)
- [870.3150] |
NOAEL
= 200 mg/kg/ day M/F LOAEL = 1,000 mg/kg/ day M/F, based
on decreases in MCV and MCH in males;
increases in RDW, HDW, platelets and triglycerides in
males; and hemosiderosis in spleen
and liver and extramedullary hematopoiesis the
spleen in males |
|
2-Generation reproduction and fertility effects - [870.3800]
|
Parental/systemic
NOAEL = 30 ppm (2.4/ 2.5 mg/kg/day M/F) Parental/systemic
LOAEL = 300 ppm (23.8/25.2 mg/kg/ day M/F), based on decreased
body weights and food consumption and on increased
incidences of bile duct hyperplasia
and liver necrosis in males and females of both
generations Offspring NOAEL = 300 ppm (23.8/25.2 mg/kg/day
M/F) Offspring LOAEL = 1,000 ppm (79.6/ 83.8 M/F), based
on decreased pup body weight and
body weight gain in both generations Reproductive
NOAEL = 30 ppm (2.4/2.5 mg/ kg/day M/F) Reproductive LOAEL
= 300 ppm (23.8/25.2 mg/kg/day M/F) based
on an increase in the number of days to mating in both
generations |
1-Year chronic oral (capsule) toxicity
(dog) - [870.4100] |
NOAEL = 500 mg/kg/day M/F LOAEL = 1,000 mg/kg/ day M/F,
based on decreased body weight gain
in males, decreased MCV, MCH, and mean corpuscular
hemoglobin concentration
(MCHC); increased thrombocytes and red cell volume distribution
width; hepatic histopathology: glycogen disposition, inclusion
bodies in cytoplasm, and pigment disposition in both sexes,
and focal vaculolation [liver]
in females |
18-Month
carcinogenicity dietary study
(mouse) - [870.4200] |
NOAEL
= 10 ppm (1.17/1.20 mg/kg/day M/F) LOAEL = 60 ppm (6.96/
6.59 mg/kg/day M/ F), based on enlarged
livers with increased weights, and hepatic microscopic
lesions including Kupffer cell hyperplasia, inflammatory
cell infiltration, and single cell necrosis in both sexes
and on deposits of lipofuscin in males No evidence of
carcinogenicity |
Combined
2-Year chronic/ carcinogenicity dietary study
(rat) - [870.4300] |
NOAEL = 100 ppm (3.76/4.43 mg/kg/ day M/F) LOAEL = 300
ppm (11.4/13.0 mg/kg/ day M/F), based on minimal
hepatic abnormalities in the females, including
a fatty change and increased mitotic activity No evidence
of carcinogenicity |
|
In vitro mammalian cells in culture - [870.5300] |
Evidence
of borderline induction of mutant colonies in
presence of S9 in a mammalian cell gene mutation assay
at the hypoxanthine guanine phophoribosyl transferase
(HGPRT) locus of Chinese hamster V79 cells |
|
Mechanistic studies - [870.7485] |
Effects
on enzymes of cultured mouse, rat, and/or human hepatocytes
involved with heme biosynthesis |
|
Mechanistic studies - [870.7485] |
Effects
on liver microsomal and plasma
protox activity and its metabolic conversion |
|
Mechanistic studies - [870.7485] |
Effects on porphyrin profile in rats; treatment induced
porphyria, consisting of accumulation of selected porphyrins
in the liver, spleen,
and plasma and increased excretion in urine and
feces |
|
Mechanistic studies - [870.7485] |
Test
substance interferes with heme
biosynthesis in rats, as evidenced by dose- dependent,
pronounced porphyria in the liver,
spleen, and plasma; increased
porphyrin excretion, and decreased activity of various
isoenzymes of the hepatic microsomal cytochrome P450 system |
Some
excerpts from Table 3.--Toxicological Dose and Endpoints
for Butafenacil
- a summary of the toxicological endpoints used for human
risk assessment |
-- Exposure Scenario
-- Dose Used in Risk Assessment,
UF
-- Special FQPA SF* and Level of
Concern for Risk Assessment |
Study
and Toxicological Effects |
--
Chronic dietary (All populations)
-- NOAEL= 1.2 mg/kg/day UF = 100
-- Chronic RfD = 0.012 mg/ kg/day.
-- Special FQPA SF = 1 cPAD = chronic
RfD
-- Special FQPA SF = 0.012 mg/kg/day. |
Mouse
oncogenicity study.
The LOAEL is 6.96 mg/kg/. day, based on enlarged
livers with increased
weights, and hepatic microscopic lesions including Kupffer
cell hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltration, and
single cell necrosis in both sexes and on deposits of
lipofuscin in males |
--
Short-term inhalation (1 to 30 days)
-- Oral NOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/ day
-- Residential LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = 100 |
90-day
rat feeding study.
The LOAEL for this study is 62.3 mg/kg/ day based on decreased
hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean
corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular volume, increased
red cell volume distribution width, and increased
incidence of bone marrow hypercellularity |
--
Short-term incidental oral (1 to 30 days)
-- Intermediate-term incidental oral (1- 6 months)
-- LOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/day
-- Residential LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = NA |
90-day
rat feeding study.
The LOAEL for this study is 62.3 mg/kg/ day, based on
decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit,
mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular volume,
increased red cell volume distribution width, and increased
incidence of bone marrow hypercellularity |
--
Short-term inhalation (1 to 30 days)
-- Intermediate-term inhalation (1 to 6 months)
-- Oral NOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/day
-- Residential
LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = 100 |
Same
as above |
--
Long-term inhalation (>6 months)
-- Oral NOAEL = 1.2 mg/kg/day
-- Residential
LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = 100 |
Mouse
oncogenicity study.
The LOAEL is 6.96 mg/kg/ day, based on enlarged livers
with increased weights, and hepatic microscopic lesions
including Kupffer cell hyperplasia, inflammatory cell
infiltration, and single cell necrosis in both sexes and
on deposits of lipofuscin in males |
|
| ••
Note: Due to length, the above is a partial list. Click
here to see full list of FR entries. |
|