|
Return to
Index Page
Adverse Effects
Abstracts
ACTIVITY:
Herbicide (dinitroaniline)
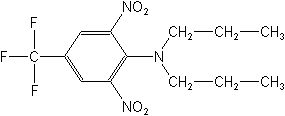
CAS Name:
2,6-dinitro-N,N-dipropyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzenamine
Structure:
Reports
available from
The National Technical Information Service (NTIS)
Order from NTIS by: phone at 1-800-553-NTIS (U.S. customers);
(703)605-6000 (other countries); fax at (703)605-6900; and
email at orders@ntis.gov. NTIS is located at 5285 Port Royal
Road, Springfield, VA, 22161, USA. |
| Order
No. |
Date/Title |
Keywords
/ Abstract |
NTIS/03490070
71 pages
|
2003
-
Evaluation of Diazinon and Chlorpyrifos Concentrations and
Loads, and Other Pesticide Concentrations, at Selected Sites
in the San Joaquin Valley, California, April to August,
2001.
Authors:
Domagalski JL, Munday C
Geological
Survey, Sacramento, CA. Water Resources Div.
California Dept. of Pesticide Regulation, Riverside. |
Water-resources
investigations.
This document is color dependent and/or in landscape layout.
It is currently available on CD-ROM and paper only. CD-ROM
contains 71 page document. Prepared in cooperation with
California Dept. of Pesticide Regulation, Riverside.
Twelve sites in the San Joaquin Valley of California were
monitored weekly during the growing and irrigation season
of 2001 for a total of 51 pesticides and pesticide degradation
products, with primary interest on the concentration, load,
and basin yield of organophosphorus insecticides, especially
diazinon and chlorpyrifos. Diazinon was detected frequently,
up to 100 percent of the time, at many of the sampling sites,
but with generally low concentrations. Other
pesticides that were frequently detected during this study
included herbicides such as metolachlor, simazine,
and trifluralin, and insecticides
such as carbaryl, carbofuran, and propargite. At Orestimba
Creek, DDE, a degradation product of DDT, was detected at
a frequency of 95 percent. |
NTIS/OTS0509656
EPA/OTS;
Doc #40-8376146 |
2000
(?)
- TELEPHONE COMMUNICATION: FROM MONTEDISON
USA INC TO USEPA |
Keywords:
U S EPA
ANILINES
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
PRODUCTION AND PROCESS
CAS
Registry Numbers:
1582-09-8 |
NTIS/PB96-188735
244p
This
report is available online |
1996
- Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED): Trifluralin.
(Includes RED Facts: Trifluralin Fact Sheet).
Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC. Office of Prevention,
Pesticides and Toxic Substances.
Eligibility Decision. |
This
document presents the Agency's decision regarding the reregistration
eligibility of the registered uses of trifluralin. Section
I is the introduction. Section II describes trifluralin, its
uses, data requirements and regulatory history. Section III
discusses the human health and enviroinmental assessment based
on the data available to the Agency. Section IV presents the
reregistration decision for trifluralin. Section V discusses
the reregistration requirements for trifluralin. Finally,
Section VI is the Appendices which support this Reregistration
|
NTIS/PB96-106950
40p |
1995
- Chemical Protective Gloves for Seven Commercial Herbicides.
Authors:
Berardinelli SP, Sanderson WT, Hall RC
National
Inst. for Occupational Safety and Health, Morgantown, WV.
Div. of Safety Research. |
The
breakthrough times of seven commonly used herbicides through
various commercially available protective gloves were determined.
Glove samples were challenged with the concentrated herbicide
formulations using ASTM Test Method F-739. Based solely
on chemical resistance data, the specialty laminate (Silver
Shield, 4H) afforded workers the most protection, the longest
breakthrough time, against all seven herbicides tested.
Nitrile and butyl gloves, based on chemical permeation and
chemical degradation, were protective against AATrex-4L
(1912249), Dual-8E (51218452), Lasso Micro-Tech (15972608),
Sencor-DF (21087649), and Gramoxone-Extra (4685147). However,
they were not protective against Judge
(15972608) or Treflan-MTF (1582-09-8). Nitrile
and butyl glove materials were wrinkled and distorted after
1 hour exposures to Treflan MTF or Judge. The authors
note that wrinkled or distorted gloves should be taken as
an indicator of a chemical incompatibility between the herbicide
and the glove material. |
NTIS/01280182
19p |
1994
-
Atmospheric transfer of agrochemicals: Final report.
Authors:
Pattey E
Center
for Land & Biological Resources Research (Canada), Ottawa
(Ontario). |
CLBRR
contribution no. 94-107.
On cover: Great Lakes Water Quality Initiatives.
The relaxed eddy-accumulation (REA) technique is a relatively
new method to measure trace gas fluxes. This report describes
a study whose objectives were: To develop methods based
on the REA technique to quantify the emission & surface
deposition rates of agrochemicals and other toxic substances;
to measure the atmosphere/surface exchange of agrochemicals
in the Great Lakes region using two tower-based REA systems
having different trapping devices; and to measure the atmosphere/surface
exchange of agrochemicals in the Great Lakes region using
an aircraft-based REA system. Findings
are presented from studies of vapor fluxes of triallate,
trifluralin, metolachlor, and
metribuzin at field sites; and from estimates of atmosphere/surface
exchange of atrazine and metolachlor. The suitability of
the instrumentation developed is discussed along with the
implications of the findings for the Great Lakes ecosystem. |
NTIS/PB95-138434
68p |
1994
- Use of Landfarming to Remediate Soil Contaminated by Pesticide
Waste.
Authors:
Felsot AS. Mitchell JK, Dzantor EK
Illinois
Natural History Survey, Champaign.
Washington State Univ., Richland. Food and Environmental
Quality Lab.
Illinois Univ. at Urbana-Champaign. Dept. of Agricultural
Engineering.
Tennessee Valley Authority, Muscle Shoals, AL.
Supporting
Agency: Illinois Dept. of Energy and Natural Resources,
Champaign. Hazardous Waste Research and Information Center. |
This
project tested the effectiveness and environmental safety
of landfarming by using 30 m2 plots outfitted for collection
of runoff and leachate. Degradation and phytotoxicity of
herbicides following landfarming of waste-contaminated soil
(=landfarmed plots) was compared to degradation and phytotoxicity
of the same compounds following spraying (=sprayed plots).
The landfarmed soil and contained alachlor, trifluralin,
atrazine, and metolachlor. Three rates of application, were
made based on a nominal 1X, 5X, and 10X rate of alachlor
application, which was the most prevalent herbicide contaminant.
Herbicide residues in landfarmed plots degraded at a similar
rate to residues in sprayed plots within the first 100 days
after application, but degradation slowed appreciably thereafter.
Final rept. Jul 90-Jun 93. See also PB95-138426. Prepared
in cooperation with Washington State Univ., Richland. Food
and Environmental Quality Lab., Illinois Univ. at Urbana-Champaign.
Dept. of Agricultural Engineeri [abstract truncated] |
NTIS/MIC-93-01683
98p |
1992
- Canadian water quality guidelines for trifluralin.
Authors:
Kent RA
Ecosystem
Sciences and Evaluation Directorate. Eco-health Branch,
Ottawa (Ontario). |
Trifluralin
is an orange crystalline solid compound with a molecular
formula of C13H16F3N3O4 and trade names Treflan, Friflurex,
Co-op Garden Weed Preventer, Heritage Selective Granular
Herbicide, Rival and Fortress. It is used to control a wide
range of annual grasses and broadleaf weeds in bean, canola,
and vegetable crops. This document summarizes the information
on its uses, fate, and effects on raw water for drinking
water supply, freshwater aquatic life, agricultural uses,
recreational water quality and aesthetics and industrial
water supplies. From this information, water quality guidelines
for protection of specific water uses are recommended. Scientific
series no. 190. Bilingual 93-01682/2. |
| NTIS/01290276 |
1992
-
Trifluralin.
Federal-Provincial
Subcommittee on Drinking Water (Canada), Ottawa (Ontario).
|
Guidelines
for Canadian drinking water quality - supporting document.
Text in English and French (Bilingual). French ed. (La Trifluraline)
on the same fiche.
Trifluralin (or treflan) is a dinitroaniline-based herbicide
widely used for pre-emergence control of weeds in crops. This
report describes the physical/chemical characteristics of
trifluralin, its use & sources in the environment, environmental
concentrations detected in water & food, analytical methods
& water treatment technology, and health effects. It then
presents a guideline for the maximum acceptable concentration
of trifluralin in drinking water, along with the rationale
for the guideline. |
NTIS/OTS0544613
EPA/OTS;
Doc #88-920005956 |
1992
- INITIAL SUBMISSION: ACUTE RAT INHALATION STUDY WITH FLURIDONE
AND TRIFLURALIN WITH COVER LETTER DATED
08-03-92 |
ELI
LILLY & CO
FLURIDONE AND TRIFLURALIN
HEALTH EFFECTS
ACUTE TOXICITY
MAMMALS
RATS
INHALATION |
NTIS/OTS0543386
EPA/OTS;
Doc #88-920005923 |
1992
- INITIAL SUBMISSION: LETTER FROM ELI LILLY & CO TO USEPA
SUBMITTING RESULTS ON AN ACUTE INHALATION STUDY WITH FLURIDONE
AND TRIFLURALIN IN RATS WITH ATTACHMENTS |
Keywords:
ELI LILLY & CO
FLURIDONE
HEALTH EFFECTS
ACUTE TOXICITY
MAMMALS
RATS
INHALATION
CAS
Registry Numbers:
1582-09-8
59756-60-4 |
NTIS/PB92-156611
71p |
1991
- Observed and Simulated Distribution of Selected Herbicides
in Silty Loam, Sandy Loam, and Clay Soil Profiles Near
Topeka, Kansas, 1986-88.
Authors:
Perry CA
Geological
Survey, Lawrence, KS. Water Resources Div. |
The
report describes the distribution of selected herbicides
in the unsaturated zone and the use of data collected from
1986-88 to evaluate simulations of leaching by PRZM and
LEACH. The scope of the report includes determination of
the traveltime of five herbicides (atrazine, alachlor, metolachlor,
trifluralin, and 2,4-D) through the unsaturated zones
of three soil types (silty loam, sandy loam, and clay) under
varying rainfall amounts and irrigation practices. The main
objectives of the study were to: (1) document observed movement
of herbicides through the unsaturated zone of three soil
types and (2) compare the observed movement to simulated
movement using the Pesticide Root Zone Model (PRZM) and
the 'Leaching Evaluation of Agricultural Chemicals Handbook'
(LEACH). Water resources investigation. Sponsored by Kansas
Dept. of Health and |
NTIS/DE92002913
12p |
1991
- Contaminated soil stabilization demonstration.
Authors:
Kemp CJ, Sackschewsky MR, Sampson AE, Phillips SJ
Westinghouse
Hanford Co., Richland, WA.
Supporting
Agency: Department of Energy, Washington, DC. |
Long-term
herbicide control along with a shotcrete cover was constructed
at the Hanford Site in May 1991. The cover system allows
for maintenance-free containment of contaminants by preventing
wind and water transport of contaminants from the soil surface,
preventing plant uptake of contaminants, and minimizing
water infiltration through the soil column. The
cover is composed of two parts: a commercial nonwoven geotextile
material impregnated with trifluralin, and a >5-centimeter
top cover of shotcrete containing polyethylene fibers. The
herbicide-impregnated geotextile functions to prevent plant
root growth into contaminated soil if any holes or cracks
develop in the shotcrete layer. The
herbicide component, trifluralin, is mixed into polymer
nodules that degrade slowly over many years, thus releasing
trifluralin slowly over time. The shotcrete topcover
was sprayed using a sludge pump and air compressor to form
a hard, impenetrable surface that prevents wind erosion
and reduces water infiltr [abstract truncated] |
NTIS/PB93-118305
21p |
1991
- Baseline Characteristics of the Organic Constituents of
the Big Sioux Aquifer, Eastern South
Dakota.
Authors:
Rice JA
South
Dakota State Univ., Brookings. Water Resources Research
Inst.
South Dakota State Univ., Brookings. Dept. of Chemistry.
Supporting
Agency: Geological Survey, Reston, VA. Water Resources Div. |
A
geochemical baseline study has been completed which describes
the regional variation of the pH, DOC, Ca, Mg, Na, and K
concentrations, and the concentrations of the herbicides
atrazine, 2,4-dichlorophyenoxy acetic acid and treflan.
Under baseline sampling conditions there were very few detections
of any of these three herbicides in any of the samples and
all of the samples which contained one or more of these
compounds had concentrations that were below the 50 ng (parts-per-trillion)
level. The other six parameters show variation throughout
the study area but the apparent heterogeneity of the groundwater's
dissolved constituents prevented the assignment of statistical
significance to any of the observed trends. Final rept.
1 May 89-30 Apr 91. Prepared in cooperation with South Dakota
State Univ., Brookings. Dept. of Chemistry. Sponsored by
Geological Survey, Reston, VA. Water Resources Div.
|
| NTIS/PB91-201459
154p |
1990
- Pesticide Monitoring: Illinois EPA's Summary of Results,
1985-1989.
Authors:
Moyer L, Cross J
Illinois
State Environmental Protection Agency, Springfield. Div.
of Water Pollution Control. |
In
October 1985, the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency
(IEPA) expanded pesticide monitoring in surface waters to
include herbicides and organophosphate insecticides commonly
used in agricultural practices. Pesticides selected include
seven herbicides (alachlor, atrazine, butylate, cyanazine,
metolachlor, metribuzin, trifluralin),
seven organophosphate insecticides (chloropyrifos, diazinon,
fonofos, malathion, methyl parathion, phorate, terbufos)
and one fungicide (captan). Monitoring efforts included
the establishment of the Pesticide Monitoring Subnetwork
within IEPA's existing Ambient Water Quality Monitoring
Network (AWQMN) as well as intensive monitoring related
to storm event runoff. The pesticide subnetwork consists
of 30 stations within the 208 station AWQMN, and are located
in predominately agricultural watersheds in Illinois.
Intensive monitoring related to storm event runoff was conducted
at two stations; Macoupin Creek in Macoupin County and Spring
Creek in Sangamon County. The [absract truncated] |
NTIS/PB88-858212
61p |
1988
-
Herbicide Residues: Methods for the Detection and Monitoring.
January 1970-February 1988 (Citations from Pollution Abstracts).
National
Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA. |
This
bibliography contains citations concerning techniques and
processes for the detection of herbicide residues. Specific
detection and monitoring methods for individual herbicides
such as trifluralin, D 2-4 herbicide, and the trazines are
discussed. Performance evaluations are included. (This updated
bibliography contains 162 citations, 11 of which are new
entries to the previous edition.) Rept. for Jan 70-Feb 88.
Supersedes PB87-851846. Prepared in cooperation with Cambridge
Scientific Abstracts, Washington, DC. |
NTIS/PB89-237218
18p |
1988
-
Biological and Abiotic Degradation of Xenobiotic Compounds
in Vitro Estaurine Water and Sedimentater Systems.
Authors:
Walker WW, Cripe CR, Pritchard PH, Bourquin AW
Battelle
Columbus Labs., OH.
Gulf Coast Research Lab., Ocean Springs, MS.
Georgia State Univ., Atlanta.
Supporting
Agency: Environmental Research Lab., Gulf Breeze, FL. |
First-order biotic degradation rate constants of 14 pesticides
were determined in estuarine water and sediment/water slurry
systems. Test systems used environmentally realistic concentrations
of pesticides in sterile and nonsterile samples of water
and sediment taken directly from the field. Thiobencarb,
sulprofos, chlorothalonil, diclofop-methyl, fenthion, oxyfluorfen,
methoxychlor, phorate, and trifluralin all showed significantly
(p < = 0.01) more degradation in the presence of nonsterile
sediment than in the presence of sterile sediment. Most
of these nine pesticides biodegraded significantly faster
in flasks containing sediment than in those with water alone.
Endosulfan and PCNB, however, biodegraded faster in the
absence of sediment. EPN and chlorpyrifos were degraded
primarily by abiotic processes. Methomyl did not significantly
degrade under any test conditions. Oxyfluorfen and chlorpyrifos
were also slow to degrade, with half-lives of generally
over two weeks in nonsterile sediment.
Keywords:
Pesticides
Biodeterioration
Estuaries
Streams
Xenobiotics
|
| NTIS/PB89-178578
30p |
1988
- Light-Sensitized Decontamination of Groundwater Hazardous
Chemicals.
Authors:
Larson RA, Schlauch MB, Ellis DD, Marley KA, Ju HL
Illinois
Univ. at Urbana-Champaign. Environmental Research Labs. |
The
use of sunlight, oxygen, and dissolved organic compounds
active as 'photosensitizers' (substances capable of absorbing
sunlight and transforming it into chemically useful forms)
is a promising treatment for contaminated waters. Light
is absorbed by the sensitizing substance, raising it to
a higher energy excited state. Reaction with the excited
state substance converts molecular oxygen to a form much
more reactive with dissolved compounds. Riboflavin (Vitamin
B2), a naturally occurring compound and a known photosensitizer,
was investigated for use in this process. A series of kinetic
experiments explored its ability to photodegrade several
aromatic compounds, phenols and anilines, that are related
to some herbicides (such as carbaryl, 2, 4-D, alachlor,
atrazine, and trifluralin)
commonly found in polluted waters.
It was found that riboflavin when added to solutions of
phenols or anilines greatly accelerated the rate of their
loss in the presence of light. The sensitized photolysis
rates incr [abstract truncated] |
NTIS/PB88-245931
861p |
1988
-
Health Advisories for 50 Pesticides ...
Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC. Office of Drinking Water. |
The
documents summarize the health effects of 50 pesticides
including: acifluorfen, ametryn, ammonium sulfamate, atrazine,
baygon, bentazon, bromacil, butylate, carbaryl, carboxin,
chloramben, chlorothalonil, cyanazine, dalapon, dacthal,
diazinon, dicamba, 1,3-dichloropropene, dieldrin, dimethrin,
dinoseb, diphenamid, disulfoton, diuron, endothall, ethylene
thiourea, fenamiphos, fluometuron, fonofos, glyphosate,
hexazinone, maleic hydrazide, MCPA, methomyl, methyl parathion,
metalachlor, metribuzin, paraquat, picloram, prometon, pronamid,
propachlor, propazine, propham, simazine, 2,4,5-T, tebuthiuron,
terbacil, terbufos, and trifluralin.
Topics discussed include: General Information and Properties,
Pharmokinetics, Health Effects in Humans and Animals, Quantification
of Toxicological Effects, Other Criteria and Standards,
Analytical Methods, and Treatment Technologies. Supersedes
PB88-113543. |
NTIS/PB89-197081
66p |
1988
-
Feasibility of Land Application of Soils Contaminated with
Pesticide Waste as a Remediation Practice.
Authors:
Felsot A, Liebl R, Bicki T
Illinois
Univ. at Urbana-Champaign. Dept. of Agronomy.
Supporting
Agency: Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign
Illinois State Water Survey Div., Savoy. Hazardous Waste
Research and Information Center. |
The
feasibility of cleaning up soil contaminated with pesticide
waste by removing it from the contaminated site and applying
it to cropland was examined at the Galesville
Chemical Company (GCC) in Piatt Co., Illinois. Soil
contaminated with the herbicides alachlor, atrazine, metolachlor,
and trifluralin was excavated
and applied to an adjacent field divided into corn and soybean
plots. Soil was applied in amounts equivalent to an application
rate of 3, 7.5, or 15 lbs alachlor per acre. Dissipation
of residues, phytotoxicity to crops and weeds, bioaccumulation
in grain, and quality of shallow groundwater were monitored
after application of the contaminated soil. These data were
compared to data obtained when herbicides were freshly sprayed
at similar concentrations. Sponsored by Illinois Natural
History Survey, Champaign, and Illinois State Water Survey
Div., Savoy. Hazardous Waste Research and Information Center.
|
NTIS/PB88-136916
43p |
1987
- Pesticides in Water Supplies Using Surface Water Sources,
Authors:
Wnuk M, Kelley R, Breuer G, Johnson L
Iowa
Dept. of Natural Resources, Des Moines.
Iowa Univ., Iowa City. State Hygienic Lab.
Supporting
Agency: Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. |
Between
May and early July in 1986, samples of treated (finished)
water were collected after rainfall from 33 public water
supplies using surface water sources. These samples were
analyzed for 37 pesticide compounds. Fourteen water supplies
also collected samples from their surface water source prior
to treatment to determine the effectiveness of treatment
with regard to pesticide removal. Detectable concentrations
of one or more of ten pesticides were found in the treated
water from 30 of the 33 water supplies tested. Individual
pesticides and the number of supplies in which they were
detected were: atrazine, 30; cyanazine (Bladex), 26; metolachlor
(Dual), 21; alachlor (Lasso), 17; carbofuran (Furadan),
9; metribuzin (Sencor), 4; 2,4-D, 2; and, trifluralin
(Treflan), butylate (Sutan) and dicamba (Banvel),
1 each. Study results indicate that
current conventional water treatment technology is ineffective
at substantial reduction of pesticide concentrations or
elimination of pesticides from drinki [abstract truncated]
|
NTIS/PB87-201935
274p |
1987
- Guidance for the Reregistration of Pesticide Products
Containing Trifluralin as the Active Ingredient.
Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC. Office of Pesticide Programs. |
The
document contains information regarding the registration
of pesticide products containing the subject active ingredient.
The document includes how to register under a registration
standard, regulatory position and rationale, and summaries
of data requirements and data gaps. Also included is a bibliography
containing citations of all studies reviewed by EPA in arriving
at the positions and conclusions contained in the standard. |
NTIS/PB88-113543
820p |
1987
- Health Advisories for 50 Pesticides
Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC. Office of Drinking Water. |
These
documents summarize the health effects of 50 pesticides
including: acifluorfen, ametryn, ammonium sulfamate, atrazine,
baygon, bentazon, bromacil, butylate, carbaryl, carboxin,
chloramben, chlorothalonil, cyanazine, dalapon, dacthal,
diazinon, dicamba, 1,3-dichloropropene, dieldrin, dimethrin,
dinoseb, diphenamid, disulfoton, diuron, endothall, ethylene
thiourea, fenamiphos, fluometuron, fonofos, glyphosate,
hexazinone, maleic hydrazide, MCPA, methomyl, methyl parathion,
metolachlor, metribuzin, paraquat, picloram, prometon, pronamid,
propachlor, propazine, propham, simazine, 2,4,5-T, tebuthiuron,
terbacil, terbufos, and trifluralin.
Topics discussed include: General Information and Properties,
Pharmacokinetics, Health Effects in Humans and Animals,
Quantification of Toxicological Effects, Other Criteria
Guidance and Standards, Analytical Methods, and Treatment
Technologies. Draft rept. See also PB86-118338.
|
NTIS/PB88-204136
32p |
1987
- Drinking-Water Quality: Guidelines for Selected Herbicides.
World
Health Organization, Copenhagen (Denmark). Regional Office
for Europe. |
The
Guidelines cover eleven of the most commonly used herbicides
in Italy: Alachlor, Atrazine, Bentazon, MCPA, Metolachlor,
Molinate, Pendimethalin, Propanil, Pyridate, Simazine and
Trifluralin. Guideline values
for contamination by these herbicides are given, although
these should be considered as recommendations not standards.
The Guidelines were established during two Consultations
and should be considered as a guide for risk management
decisions and for setting standards for developing alternative
control procedures with regard to drinking-water quality.
Environmental health series |
NTIS/PB87-851846
59p |
1986
- Herbicide Residues: Methods for the Detection and Monitoring.
1970-November 1986 (Citations from Pollution Abstracts).
National
Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA. |
This
bibliography contains citations concerning techniques and
processes for the detection of herbicide residues. Specific
detection and monitoring methods for individual herbicides
such as trifluralin, D 2-4 herbicide, and the trazines
are discussed. Performance
evaluations are included. (This updated bibliography contains
156 citations, 48 of which are new entries to the previous
edition.) Rept. for 1970-Nov 86. Supersedes PB83-863225.
Prepared in cooperation with Cambridge Scientific Abstracts,
Washington, DC. |
NTIS/PB86-176781
9p |
1985
- Excised Barley Root Uptake of Several 14C Labeled Organic
Compounds.
Authors:
McFarlane C, Wickliff C
Corvallis
Environmental Research Lab., OR. |
Many
organic pollutants potentially are available for uptake
by plants and thus bioaccumulation and food contamination.
One method of studying uptake is with excised roots, a technique
extensively used with plant nutrients. A similar method
was developed and used to evaluate uptake patterns of several
14C-labeled organic chemicals. Uptake rate constants for
the chemicals tested occurred in the following order: captan
approximately equals phenol > aniline > ethanol approximately
equals indole approximately equals
trifluralin approximately equals propanil > 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene(TCB)
> nitrobenzene approximately equals atrazine > bromacil
> simazine > monuron. Journal article, Pub. in Environmental
Monitoring and Assessment 5, p385-391 Dec 85. |
NTIS/NTN85-0009
PB84-246370 |
1985
- Development of a Fateoxicity Screening Test.
Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC. |
This
citation summarizes a one-page announcement of technology
available for utilization. A shake-flask screening test
was designed to rapidly evaluate the relative degradation
rates of a wide spectrum of chemicals, each compared to
methyl parathion. Test chemicals evaluated were bolero,
bravo, dibutylphthalate, dimilin, dursban, endosulfan, hoelon,
pentachlorobenzene, phorate, and trifluralin.
Diverse regimes of salinity, pH, TOC, and microbial biomass
were encountered across space and time. The experimental
design for the screening test embodies four treatments:
active sediment, sterile sediment, active water, and sterile
water. Decay curves were produced and rate constants and
half-life values determined. ...FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
Detailed information about the technology described may
be obtained by ordering the NTIS report, order number: PB84-246370,
price: $8.50. For information not in the report, contact
Mr. C. Richard Cripe, Environmental Research Laboratory,
U.S. Environmental Prot [abstract truncated] |
NTIS/PB84-246370
39p |
1984
- Development of a Fateoxicity Screening Test,
Authors:
Walker WW
Gulf Coast Research Lab., Ocean Springs, MS. |
A
shake-flask screening test was designed to rapidly evaluate
the relative degradation rates of a wide spectrum of chemicals,
each compared to methyl parathion. Test chemicals evaluated
were bolero, bravo, dibutylphthalate, dimilin, dursban,
endosulfan, hoelon, pentachlorobenzene, phorate, and trifluralin.
Diverse regimes of salinity, pH, TOC, and microbial biomass
were encountered across space and time. The experimental
design for the screening test embodies four treatments:
active sediment, sterile sediment, active water and sterile
water. Decay curves were produced and rate constants and
half-life values determined. Half-life values for the 10
chemicals evaluated varied substantially with time and geographic
sampling site. In active systems, 8 of the 10 chemicals
degraded more rapidly than methyl parathion. Nine dibutylphthalate
screens were run involving six geographic sites. Disappearance
was quite rapid in active treatments in all screens. Disappearance
curves describing DBP abatement eith |
NTIS/PB88-162375
67p |
1984
- Health and Environmental Effects Profile for Trifluralin.
Environmental
Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH. Environmental Criteria
and Assessment Office. |
The Health
and Environmental Effects Profile for trifluralin was prepared
by the Office of Health and Environmental Assessment, Environmental
Criteria and Assessment Office, Cincinnati, OH for the Office
of Solid Waste to support listings of hazardous constituents
of a wide range of waste streams under Section 3001 of the
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). Both published
literature and information obtained from Agency program office
files were evaluated as they pertained to potential human
health, aquatic life and environmental effects of hazardous
waste constituents. Quantitative estimates have been presented
provided sufficient data are available. Trifluralin has been
evaluated as a carcinogen. The human carcinogen potency factor
(ql*) for trifluralin is .029 per (mg/kg bw/day) for oral
exposure. |
NTIS/PB84-175306
10p |
1984
- Histopathology and Enlargement of the Pituitary of a Teleost
Exposed to the Herbicide Trifluralin.
Authors:
Couch JA
Environmental
Research Lab., Gulf Breeze, FL. |
Pituitary
glands of sheepshead minnows, Cyprinodon
variegatus, exposed for 19 months to 1-5 micrograms/l trifluralin
were significantly enlarged and possessed histopathologic
characteristics (when compared to glands of controls) such
as pseudocysts, congestion of blood vessels and edema.
Most of the fish with enlarged pituitaries
also had diffuse vertebral hyperostosis
and other dysplastic vertebral changes. Several speculative
mechanistic paths are suggested for the mode of the effect
of trifluralin on the vertebral and pituitary tissues. Study
of the form and function of pituitary glands of teleosts from
natural populations might provide indications of chronic physiological
stress, particularly in relation to chemical pollutant stress.
Journal article, Pub. in the Jnl. of Fish Diseases, v7 p157-163,
1984. |
NTIS/PB84-226513
15p |
1984
-
Usefulness of 'Cyprinodon variegatus' and 'Fundulus grandis'
in Carcinogenicity Testing: Advantages and Special Problems.
Authors:
Courtney LA, Couch JA
Environmental
Research Lab., Gulf Breeze, FL. |
Cyprinodon
variegatus and Fundulus grandis, two species of Cyprinodontid
fishes extensively studied and used in toxicological and
biological investigations, are reviewed and compared as
laboratory test animals. Their ecology and general biology,
and suitability for various types of experimentation are
examined. A laboratory system for exposing critical life
stages (e.g., embryos, fry, juveniles) of these species
to suspect carcinogens is described. A discussion of the
use, findings and potential of these species in oncological
studies and carcinogen assays is presented, particularly
in regard to responses to three known or suspect carcinogen
chemicals (e.g., trifluraline,
benzidine, and aflatoxin). Finally, advantages and disadvantages
or special problems in using the species as carcinogen test
animals are reviewed. Journal article, Pub. in National
Cancer Institute Monograph, n65 p83-96 1984. |
NTIS/PB84-111772
115p |
1983
- Herbicides in Runoff from Agricultural Watersheds in a
High-Winter-Rainfall Zone,
Authors:
Hickman JS, Harward ME, Montgomery ML
Oregon
State Univ., Corvallis. Water Resources Research Inst.
Oregon State Univ., Corvallis. Coll. of Agricultural Sciences.
Supporting
Agency: Office of Water Research and Technology, Washington,
DC. |
Relatively few studies have been made on the behavior of
pesticides in relation to runoff from agricultural watersheds
in the high-winter-rainfall zone of the northwestern United
States. This study was designed to quantify runoff losses
of two herbicides, diclofop-methyl (methyl 2-(4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy)propanoate)
and trifluralin (alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-N,N-dipropyl-p-toluidine),
from small agricultural watersheds in the Willamette Valley,
Oregon and identify factors and processes influencing herbicide
transport in this region. Various diclofop-methyl soil interactions
were also studied under conditions typically following a
winter application of diclofop-methyl in western Oregon.
Final technical rept., Prepared
in cooperation with Oregon State Univ., Corvallis. Coll.
of Agricultural Sciences.
|
NTIS/PB83-863225
107p |
1983
- Herbicide Residues: Methods for the Detection and Monitoring.
1970-April, 1983 (Citations from Pollution Abstracts).
National
Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA. |
This bibliography contains citations concerning techniques
and processes for the detection of herbicide residues. Specific
methods for individual herbicides such as trifluralin,
D 2-4 herbicide, and the trazines are discussed. Performance
evaluations are included. (This updated bibliography contains
108 citations, 27 of which are new entries to the previous
edition.) Rept. for 1970-Apr 83. Supersedes PB81-869372.Prepared
in cooperation with Cambridge Scientific Abstracts, Washington,
DC.
|
NTIS/PB82-263252
97p |
1982
- Trifluralin (TREFLAN (Trade Name)), alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-N,N-dipropyl-p-toluidine.
Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC. Office of Pesticides
and Toxic Substances. |
Contents:
Elanco's chronic feeding study;
Revised exposure estimate; Revised cancer risk estimate;
Ecological effects; Comments relating to risk; Comments
relating to benefits; Comments relating to testing requirements/regulatory
options. Position document 4.
Keywords:
Pesticides
Toxicology
Trifluralin |
NTIS/PB82-237942
91p |
1982
-
Pesticide Rebuttable Presumption against
Registration, Treflan (Trade Name) Position Document 4
Environmental
Protection Agency, Arlington, VA. Special Pesticide Review
Div. |
This
document details the final determination regarding the Rebuttable
Presumption Against Registration (RPAR) of products containing
the above chemical. The responses by EPA to comments on
the preliminary determination by the Scientific Advisory
Panel and the United States Department of Agriculture are
contained in the document. A bibliography of citations used
in this final determination is also provided. |
NTIS/PB82-156035
21p |
1982
-
The Determination of Dinitroaniline Pesticides in Industrial
and Municipal Wastewater: Method 627
Authors:
Pressley TA, Longbottom JE
Environmental
Monitoring and Support Lab.-Cincinnati, OH. |
This
is a gas chromatographic (GC) method applicable to the determination
of selected pesticides in municipal and industrial discharges
as provided under 40CFR 136.1. A sample is solvent extracted
with methylene chloride using a separatory funnel. The extract
is exchanged to hexane during concentration. GC conditions
are described which permit measurement with an electron
capture detector. The compounds included in the method scope
are: benfluralin; ethalfluralin; isopropalin; profluralin;
and trifluralin. Final rept. |
NTIS/PB82-221391
33p |
1982
- Pesticide Use on Soybeans in the Southeast, 1980
Authors:
Hanthorn M, Osteen C, McDowell R, Roberson L
Economic
Research Service, Washington, DC. Natural Resource Economics
Div. |
Farmers
reported that 18.1 million pounds active ingredient (a.i.)
of pesticides were applied to soybeans in the Southeast
during 1980. This consisted of 11.3 million pounds (a.i.)
of herbicides, 5.1 million pounds (a.i.) of insecticides,
1.4 million pounds (a.i.) of nematicides, and 234,000 pounds
(a.i.) of fungicides. Pesticide acre-treatments totaled
16.4 million and consisted of 9.7 million with herbicides,
5.8 million with insecticides, 555,000 with nematicides,
and 384,000 with fungicides. The primary
herbicides were alachlor, bentazon, metribuzin, and
trifluralin. The major insecticides
were carbaryl and methomyl. |
NTIS/PB82-220112
37p |
1982
- Pesticide Used on Soybeans in the North Central States
(1980)
Authors:
Hanthorn M, Osteen C, McDowell R, Roberson L
Economic
Research Service, Washington, DC. Natural Resource Economics
Div. |
Farmers
reported that 77.8 million pounds (a.i.) of pesticides were
applied to soybeans in the North Central States during 1980.
This consisted of 77.1 million pounds (a.i.) of herbicides
and 700,000 pounds (a.i.) of insecticides. Pesticide acre-treatments
totaled 58.1 million and consisted of 44.8 million with
single material herbicides, 12.6 million with herbicide
mixes, and 700,000 with insecticides. The
primary herbicides were alachlor, bentazon, metribuzin,
and trifluralin. The major
insecticide was carbaryl. |
NTIS/DE83000305
69p |
1982
- Long-Term Biobarriers to Plant and Animal Intrusions of
Uranium Tailings.
Authors:
Cline JF, Burton FG, Cataldo DA, Skiens WE
Gano KA
Battelle
Pacific Northwest Labs., Richland, WA.
Supporting
Agency: Department of Energy, Washington, DC. |
The
objective of this project was to develop and evaluate the
effectiveness of physical and chemical barriers designed
to prevent plant and animal breachment of uranium mill tailings
containment systems for an extended period of time. A polymeric
carrier/biocide delivery system was developed and tested
in the laboratory, greenhouse and field. A continuous flow
technique was established to determine the release rates
of the biocides from the PCD systems; polymeric carrier
specifications were established. Studies were conducted
to determine effective biocide concentrations required to
produce a phytotoxic response and the relative rates of
phytotoxin degradation resulting from chemical and biological
breakdown in soils. The final PCD
system developed was a pelletized system containing 24%
trifluralin, 18% carbon black and 58% polymer.
Pellets were placed in the soil at the Grand Junction
U-tailings site at one in. and two in. intervals. Data obtained
in the field determined that the pellets releas [abstract
truncated] |
NTIS/PB80-177751
11p |
1981
- Vertebral Dysplasia in Young Fish Exposed to the Herbicide
Trifluralin
Authors:
Couch J, Winstead JT, Hansen DJ, Goodman LR
Environmental
Research Lab., Gulf Breeze, FL |
Sheepshead
minnows, Cyprinodon variegatus Lacepede, exposed to 5-5 to
31 micrograms/l of the herbicide trifluralin, throughout their
first 28 days of life, developed a heretofore, undescribed
vertebral dysplasia. This dysplasia
consisted of semisymmetrical hypertrophy of vertebrae (three
to 20 times normal), characterized by foci of osteoblast and
fibroblasts actively laying down bone and bone precursors.
Effects of the abnormal vertebral development were dorsal
vertebral growth into the neural canal, ventral compression
of renal ducts, and longitudinal fusion of vertebrae. Fish,
exposed for 51 days to 16-6 micrograms/l trifluralin and thereafter
depurated for 41 days, showed no increase in vertebral dysplasia
during depuration; however, residual
spinal column damage was evident. Serum calcium concentrations
were elevated in adult fish exposed for 4 days to 16-6 micrograms/l
trifluralin. Fluorosis or mimicry of
hypervitaminosis A are considered possible mechanisms for
the osseous effect, but are [abstract
truncated] |
NTIS/PNL-SA-8872
18p |
1981
- Application of Controlled Release Technology to Uranium
Mill Tailings Stabilization
Authors:
Burton FG, Cataldo DA, Cline JF, Skiens WE
Battelle
Pacific Northwest Labs., Richland, WA.
Supporting
Agency: Department of Energy, Washington, DC. |
A
trifluralin (herbicide) releasing device was developed with
a theoretical effective lifetime in excess of 100 years.
When placed in a layer in soil, the PCD system will prevent
root penetration through that layer without harming the
overlying vegetation. Equilibrium concentrations of trifluralin
in soil can be adjusted (along with the theoretical life
of the device) to suit specific needs. The present system
was designed specifically to protect the asphalt layer or
clay/aggregate barriers on uranium mill tailings piles;
PCD devices composed of pellets could also be implanted
over burial sites for radioactive and/or toxic materials,
preventing translocation of those materials to plant shoots,
and thence into the biosphere. (ERA citation 06:013491)
ANS waste management conference, Tucson, AZ, USA, 23 Feb
1981. |
NTIS/PB82-127523
7p |
1981
- Fate of Selected Herbicides in a Terrestrial Laboratory
Microcosm
Authors:
Gile JD, Collins JC, Gillett JW
National
Heart, Lung, and Blood Inst., Bethesda, MD. |
The
transport and metabolism of 14C-labeled herbicides (simazine,
bromacil, trifluralin, and
2,4,5-T) applied as a foliar spray (0.28 kg/ha) was examined
in a terrestrial microcosm chamber (TMC). These chemicals
were compared to a reference compound, the insecticide dieldrin.
The TMC contained a synthetic soil medium, Douglas fir and
red alder seedlings, rye grass, numerous invertebrates,
and a gravid gray-tailed vole (Microtus canicaudus). By
20 days posttreatment, total soil residues (parent and metabolites
and bound residues) averaged 0.14 ppm for all chemicals.
Except for dieldrin little extractable parent material was
detected for any of the chemicals in the soil. Concentrations
of 14C material in the rye grass shoots ranged from an average
of 2.5 ppm for 2,4,5-T to 16.8 ppm for simazine. 2,4,5-T
and trifluralin were more rapidly degraded than the other
chemicals with 2,4,5-T present primarily as extractable
metabolites. 14C materials of dieldrin was accumulated to
a much greater extent tha [abstract truncated] |
NTIS/AD-A098
281/9
39p |
1981
- Pesticide Use in the Lake Erie Basin and the Impact of
Accelerated Conservation Tillage on Pesticide Use and Runoff
Losses
Authors:
Logan TJ
Ohio
State Univ., Columbus. Dept. of Agronomy. |
A
major shift from conventional tillage to conservation tillage
will be required to reduce soil loss and diffuse sources
of phosphorus in the Lake Erie drainage basin. This shift
will require some changes in the kinds and amounts of pesticides
used and may change the losses of these compounds in runoff.
Alachlor, atrazine and butylate account for about 77% of
the herbicide used in Indiana, Michigan and Ohio, and carbofuran,
fonofos and terbufos represent about 86% of the insecticide
use. Most of the pesticides in use in the basin today are
relatively nonpersistent and have low mammalian and fish
toxicities. A major shift to conservation
tillage will increase use of paraquat and glyphosate herbicides
and reduce the use of soil-incorporated materials such as
butylate and trifluralin. About 1% of applied pesticide
is lost in runoff, much of it in the first event after the
compound is applied. Pesticide losses are reduced with increased
surface cover, but this effect decreases with pesticides
that a
[abstract truncated] |
NTIS/PB81-869372
83p |
1981
- Methods for the Detection and Monitoring of Herbicide
Residues. January, 1970-June, 1981 (Citations from Pollution
Abstracts)
National
Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA. |
This
retrospective bibliography contains citations concerning
methodology for the detection of herbicide residues. Specific
methods for individual herbicides are discussed. These include
methodology for the detection of trifluralin,2,4-D, the
trazines and fluidone. Many others are also considered.
(Contains 81 citations fully indexed and including a title
list.) Rept. for Jan 70-Jun 81.
|
NTIS/DE82006167
17p |
1981
- Use of Controlled Release Herbicides in Waste Burial Sites
Authors:
Burton FG, Cataldo DA, Cline JF, Skiens WE
Battelle
Pacific Northwest Labs., Richland, WA.
Supporting
Agency: Department of Energy, Washington, DC |
Controlled-release
formulations of herbicides have been applied to the soil
in the manner traditional for herbicides: on the surface
or mixed into the top few inches of soil. The controlled-release
formulation allows another option that we propose to use:
to place herbicides, contained in controlled-release formulations,
in a layer at least a foot below the surface of the soil,
in order to prevent root penetration below that level. Ideally,
the herbicide will prevent root tip cell division but will
not translocate within the plant, thus assuring that the
plant will survive, preserving the ground cover. Trifluralin
is one of the herbicides which does not translocate and
was chosen for use in this study. A number of applications
for this technology are possible; particularly in waste
management. In the present studies, we used two different
forms of polymeric carrier/delivery (PCD) systems to investigate
the controlled release of herbicides. In the initial study,
a sheet was made of homogeneous mi
Keywords:
Mill tailings
Herbicides
Radioactive waste disposal
. |
NTIS/PB83-133058
327p |
1981
- Aromatic Amines: An Assessment of the Biological and Environmental
Effects.
National
Research Council, Washington, DC.
Supporting
Agency: Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. |
Aromatic
amines and compounds related through metabolism are used
widely in industry. As a result of such applications, they
are also dispersed into the environment, thereby creating
a potential for human exposure. Four aromatic are known
to lead to urinary tract cancer in exposed humans, and some
are also responsible for the induction of methemoglobinemia.
Some other structurally similar amines are carcinogenic
to one or more tissues in laboratory animals. This report
summarizes the key information concerning the occurrence,
analysis, and toxicology of the aromatic amines and then
considers six specific amines in detail. The following substances
were studied: Aniline, 4,4'Methylene-Bis (2Chloraniline),
2,4-Diaminotoluene, trifluralin,
p-Cresidine, and furazolidone. The following topics are
covered: occurrence in the environment, general analysis,
metabolism, carcinogenc potency and risk estimation, and
epidemiology. Final rept.
|
NTIS/PB81-111056
124p |
1980
-
Adsorption, Movement, and Biological Degradation of Large
Concentrations of Selected Pesticides in Soils
Authors:
Davidson JM, Rao PSC, Ou LT, Wheeler WB, Rothwell DF
Florida
Univ., Gainesville. Dept. of Soil Science.
Supporting
Agency: Municipal Environmental Research Lab., Cincinnati,
OH. |
Because
of the importance of soil in biologically reducing the quantity
and retarding the rate of pollutant movement into groundwater,
this laboratory study was initiated to evaluate the adsorption,
mobility, and degradation of large concentrations of the
pesticide atrazine, methyl parathion, terbacil, trifluralin,
and 2, 4-D in soils representing four major soil orders
in the United States. Solution concentrations ranged from
zero to the aqueous solubility limit for each pesticide.
The mobility of each pesticide increased as its concentration
in the soil solution phase increased. These results were
in agreement with the adsorption isotherm data. Pesticide
degradation rates and soil microbial populations generally
declined as the pesticide concentration in soil increased;
however, some soils were able to degrade a pesticide at
all concentrations studied, while others remained essentially
sterile throughout the incubation period (60 to 80 days).
As shown by measurements of 14CO2 evolution, total [abstract
truncated]
|
NTIS/PB80-151533
39p |
1980
-
Freshwater Micro-Ecosystem Development and Testing of Substitute
Chemicals
Authors:
Isensee AR, Yockim RS
Science
and Education Administration, Beltsville, MD. Pesticide
Degradation Lab.
Supporting
Agency: Environmental Research Lab.-Duluth, MN. |
The
objective of the study was to develop better techniques
for studying pesticides in aquatic model ecosystems. To
achieve this objective, a model ecosystem was designed and
built that utilizes the continuous dosing, flow-through
system routinely used for chronic fish toxicity testing
in combination with the organisms used in static model ecosystem
testing. A previously developed recirculating static model
ecosystem (simulating a sediment or erosional pesticide
source) was simultaneously used with the flowing water system
(simulating an effluent pesticide source) to test the behavior
of three pesticides (pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB), simazine,
and trifluralin). Conditions
in the static system favored pesticide degradation while
the flowing system insured continuous pesticide exposure
to the organisms.
|
NTIS
PB Rep. PB-151,533:
39p |
1980
- Freshwater micro-ecosystem development and testing of
substitiute chemicals.
Authors:
Isensee AR , Yockim RS
Pestic.
Degrad. Lab., SEA, Beltsville, MD |
The
objective of the study was to develop better techniques
for studying pesticides in aquatic model ecosystems. To
achieve this objective, a model ecosystem was designed and
built that utilizes the continuous dosing, flow-through
system routinely used for chronic fish toxicity testing
in combination with the organisms used in static model ecosystem
testing. A previously developed recirculating static model
ecosystem (simulating a sediment or erosional pesticide
source) was simultaneously used with the flowing water system
(simulating an effluent pesticide source) to test the behavior
of 3 pesticides [pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB; quintozene),
simazine, and trifluralin].
Conditions in the static system favored pesticide degradation
while the flowing system insured continuous pesticide exposure
to the organisms. (Author abstract by permission) |
| US
NTIS PB Rep. PB80-811,532: p. 15 |
1980
- Freshwater micro-ecosystem development and testing of
substitute chemicals.
Authors:
Isensee AR , Yockim RS
SEA,
USDA, Beltsville, MD |
The
objective of the study was to develop better techniques
for studying pesticides in aquatic model ecosystems. To
achieve this objective, a model ecosystem was designed and
built that utilizes the continuous dosing, flow-through
system, routinely used for chronic fish toxicity testing,
in combination with the organisms used in static model ecosystem
testing. A previously developed recirculating static model
ecosystem (simulating a sediment or erosional pesticide
source) was simultaneously used with the flowing water system
(simulating an effluent pesticide source) to test the behavior
of 3 pesticides [pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB; quintozene),
simazine, and trifluralin]. Conditions in the static system
favored pesticide degradation while the flowing system insured
continuous pesticide exposure of the organisms. (Author
abstract by permission)
CAS
Registry Numbers:
82-68-8
82-68-8
122-34-9
1582-09-8 |
NTIS/PB80-213937
83p |
1979
- Trifluralin (Treflan): Position 1/2/3
Environmental
Protection Agency, Arlington, VA. Special Pesticide Review
Div. |
The
report is a preliminary risk assessment for trifluralin.
It gives a preliminary examination of its use, environmental
residues, and health effects including toxicology data.
Limited information is provided for exposure and extent
of risk. Results of a literature search are provided. |
NTIS/PB80-130883
15p |
1979
- Toxicity of the Herbicides 2,4-D, DEF, Propanil and Trifluralin
to the Dungeness Crab, 'Cancer magister'
Authors:
Caldwell RS, Buchanan DV, Armstrong DA, Mallon MH, Millemann
RE
Oregon
State Univ., Corvallis. Agricultural Experiment Station.
Supporting
Agency: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration,
Rockville, MD. Office of Sea Grant. |
Lethal
and sublethal responses to the herbicides 2,4-D, DEF, propanil,
and trifluralin of various life history stages of the Dungeness
crab, Cancer magister, were examined to estimate maximum
acceptable toxicant concentrations (MATC) of each compound
for this species. Zoeae were found, in long term tests,
to be the most sensitive stage. Based on the experiments
with this stage, MATCs were concluded to be greater than
0.95, less than 6.9 micro g for DEF, = 26, less than 220
micro g/L for trifluralin, = 80, less than 1,700 microgram/L
for propanil, and less than 1,000 micro g/L for the free
acid form of 2.4-D.
|
NTIS
PB Rep. PB-293,167
298
pp |
1979
- Design and evaluation of a terrestrial model ecosystem
for evaluation of substitute pesticide chemicals.
Authors:
Metcalf RL , Cole LK , Wood SG , Mandel DJ , Milbrath ML
Inst.
Environ. Studies, Univ. Illinois, Urbana, IL 61807 |
This
grant was established to design a terrestrial model ecosystem
that was simple, inexpensive, and suitable for examining
the total environmental fate of radiolabeled pesticides
in a soil crop model e.g. soil-corn or soil-soybean. This
was accomplished with the practical development of a system
in which corn or soybeans are grown on 3 kg of typical Illinois
soil types contained in a 19 l wide-mouth glass carboy fitted
with airtight lid and impingers to sample pesticide content
in aspirated air, and a bottom petcock to sample leachate
water. The units are housed in an environmental growth chamber
under 12 hr simulated daylight, at 26êC. Emphasis
was placed on tracing the fate of the pesticide chemical
and its degradation products in soil, air, water, phytoplankton
and in the major food chain organisms of the model ecosystems,
e.g. Zea mays, Glycine max, Lumbricus terrestris, Limax
maximus, Armadillidium vulgare, Estigmene acrea, and, Microtus
ochregaster in the soil-plant phase; and Daphnia magna,
Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus, Physa spp., and Gambusia
affinis in the leachate water. The 14C-labeled pesticides
examined included DDT, methoxychlor, aldrin, dieldrin, fonofos,
phorate, parathion, methyl parathion, simazine, trifluralin,
2,4,5-T iso-octyl ester, hexachlorobenzene, pentachlorophenol
(PCP), pentachloronitrobenzene (quintozene), and captan.
Detailed summaries of their fate and degradation, based
on more than 20,000 analyses, are presented. (Author abstract
by permission) |
| NTIS
PB Rep. PB-285,134: 386 |
1978
- Transport of agricultural chemicals from small upland
Peidmont watersheds.
Authors:
Smith CN, Leonard RA, Langdale GW, Bailey GW
Environ.
Res. Lab., US EPA, Athens, GA |
Data
were collected from four small watersheds (1.3 to 2.7 ha)
located in the Southern Piedmont region. Total losses of
applied herbicides were affected by the occurrence of runoff
in close proximity to application data, mode of application,
and persistence in the soil runoff zone. Most of the total
annual losses by runoff were in the first three runoff events
for all compounds except paraquat. Runoff of trifluralin
was very low (0.1 to 0.3% of the annual application). Total
runoff losses of other herbicides were commonly less than
1.0% except when runoff occurred shortly after application.
Sediment yield from terraced watersheds was significantly
less than from watersheds managed without terraces. Except
for paraquat, however, pesticide yields in runoff were not
reduced in proportion to sediment reduction because solution
transport was the major mode of loss for the soluble herbicide
phase. Annual runoff losses of soluble plant nutrients were
5.0 and 1.3 kg/ha for chloride and nitrate, respectively.
Losses of soluble phosphorus from both watersheds were very
low, about 380 g/ha. (Author abstract by permission)
CAS
Registry Numbers:
1582-09-8
1582-09-8
4685-14-7 |
NTIS/PB81-232530
9p |
1978
- Concentration and Toxicity of Trifluralin in CD-1 Mice,
Presented Intragastrically of Intraperitoneally
Authors:
Beck SL
Wheaton
Coll., Norton, MA. Dept. of Biology. |
This
report presents the results of experiments involving administration
of the herbicide Trifluralin, dissolved in corn oil, delivered
at different concentrations for each dose, either by intragastric
intubation or intraperitoneal injection. The investigations
produced several surprising results. These included the
fact that, in per ora administration there were clear cut
differences in toxicity such that for each dose which did
cause death, there was inverse relationship between toxicity
and concentration. This relationship was not seen in the
intraperitoneal treatment groups. Further, there was no
apparent difference in LD-50 in the two routes, and the
time to death was greater in the intraperitoneally treated
animals. Journal article |
NTIS
PS Rep. PS-790,109
pg.
24 |
1979
-
Chronic toxicity of chlordane, trifluralin, and pentachlorophenol
to sheepshead minnows (Cyprinodon variegatus).
Authors:
Parrish PR , Dyar EE , Enos JM , Wilson WG
Mar.
Res. Lab., EG & G, Bionomics, Pensacola, FL |
Sheepshead
minnows (Cyprinodon variegatus) were exposed to 3 chemicals
- chlordane, trifluralin, or pentachlorophenol (PCP) - in
flowing, natural seawater to determine acute and chronic
(full life-cycle) effects. Mortality of parental fish exposed
to mean measured chlordane concentrations was significantly
greater than that of control fish. Hatch of juveniles from
embryos of exposed parental fish was significantly less
than hatch of control juveniles. The estimated maximum acceptable
toxicant concentration (MATC) was 0.5- 0.8 mug/l and the
application factor (AF) limits, 0.04 - 0.06.
Exposure to mean measured trifluralin concentrations of
9.6 mug/l significantly decreased growth of parental fish.
Fecundity of exposed parental fish was significantly less
than that of control fish. Survival and growth of second
generation fish were significantly less than the control.
The estimated MATC was 1.3 4.8 mug/l and the AF limits 0.007-0.025.
Mortality of parental sheepshead minnows exposed
to mean measured pentachlorophenol concentrations of 88
mug/l was significantly greater than mortality of control
fish. The estimated MATC was 47 88 mug/l and the AF limits,
0.11-0.20. [Abstract from Ecology of Insecticides Water
Pollution] (Author abstract by permission)
CAS
Registry Numbers:
57-74-9
57-74-9
1582-09-8
87-86-5 |
| NTIS
PS Rep. PS-790,109 pg. 33 |
1979
-
Biological effects of pesticides on the Dunegrass crab.
Authors:
Caldwell RS
Marine
Sci. Cent., Oregon State Univ., Newport, OR |
The
toxicity of 9 pesticides to various life history stages
of the Dunegrass crab, Cancer magister, was examined to
establish the most sensitive life stage of the crab, and
the highest concentration of each pesticide having no discernible
effect on that most sensitive stage during prolonged exposures.
The compounds tested were the insecticides carbofuran, chlordane,
malathion and methoxychlor; the herbicides 2,4-D, DEF, propanil
and trifluralin; and the fungicide
captan. For each pesticide the zoeal stages were found to
be the most sensitive in long-term tests, approximately
5-10 times and 10-100 times more sensitive than juvenile
and adult crabs, respectively, and were also affected at
lower concentrations than those that affected egg hatching
and prezoel development. The maximum acceptable toxicant
concentrations for continuous exposures of C. magister zoeae
to each of the 9 pesticides are: methoxychlor, 0.005 mug/l;
chlordane, 0.015 mug/l; malathion, 0.02 mug/l; carbofuran,
0.05 mug/l; captan, 2 mug/l; DEF, 4 mug/l; trifluralin,
15 mug/l; propanil, 80 mug/l; and 2,4-D 1000 mug/l.
The toxicity of each of these pesticides to crabs is compared
with literature reports of their toxicity to other aquatic
species. [Abstract from Ecology of Insecticides Water Pollution]
(Author abstract by permission) |
| NTIS
PB REPORT PB-268647:251
PP |
1977
- EVALUATION OF SELECTED PESTICIDES AS CHEMICAL MUTAGENS
IN VITRO AND IN VIVO STUDIES
Authors:
SIMMON VF, MITCHELL AD, JORGENSON TA |
Taxonomic
Name:
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA1535
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA1537
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA1538
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA100
ESCHERICHIA COLI,WP2(UVRA)
ESCHERICHIA COLI,W3110
ESCHERICHIA COLI,P3478(POLA)
BACILLUS SUBTILIS,H17
BACILLUS SUBTILIS,M45(REC)
SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE,D3
MUS,ICR/SIM
HOMO SAPIENS
Test Object: BACTERIA
FUNGUS,YEAST
MAMMAL,MOUSE
MAMMAL,HUMAN CELL CULTURE
Sex Treated: MALE
Tissue Cultured: WI-38 CELLS
Cells Treated: GERM CELLS, SPERM
SOMATIC CELLS
Cells Observed: SOMATIC CELLS
Name
of Agent (CAS RN):
[too many to list, but includes]
TRIFLURALIN ( 1582-09-8 )
Inducer
(CAS Rn):
AROCLOR 1254 ( 11097-69-1 )
Assay:
Test Category: EFFECTS ON CHROMOSOMES
Specific Test/Endpoint: GENE CONVERSION
Test Category: EFFECTS ON CHROMOSOMES
Specific Test/Endpoint: CHROMOSOME ABERRATIONS-TRANSLOCATIONS
Test Category: EFFECTS ON CHROMOSOMES
Specific Test/Endpoint: DOMINANT LETHAL TEST
Test Category: EFFECTS ON CHROMOSOMES
Specific Test/Endpoint: HERITABLE TRANSLOCATION TEST
Test Category: EFFECTS ON NUCLEIC ACIDS
Specific Test/Endpoint: DIFFERENTIAL KILLING-REC ASSAY
Test Category: EFFECTS ON NUCLEIC ACIDS
Specific Test/Endpoint: DIFFERENTIAL KILLING-POL TEST
Test Category: EFFECTS ON NUCLEIC ACIDS
Specific Test/Endpoint: DNA REPAIR-UDS
Test Category: GENE MUTATIONS
Specific Test/Endpoint: AMES TEST
Test Category: GENE MUTATIONS
Specific Test/Endpoint: REVERSION-TRP
Test Category: FERTILITY AND STERILITY STUDIES
Specific Test/Endpoint: REPRODUCTIVE PERFORMANCE |
NTIS
PB REPORT EPA-600/1-76-022 114
PP
EMICBACK/25227 |
1976
- RELIABILITY OF BACTERIAL MUTAGENESIS TECHNIQUES TO DISTINGUISH
CARCINOGENIC AND NONCARCINOGENIC CHEMICALS
Authors:
COMMONER B |
Taxonomic
Name:
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA1535
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA1536
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA1537
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA1538
SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM,TA100
Test Object: BACTERIA
Name
of Agent (CAS RN):
[too many to list, but includes]
TRIFLURALIN ( 1582-09-8 ) |
NTIS
PB-244-734
73
pages
NIOSH/00136490 |
1975
- Screening Study To Develop Background Information And
Determine The Significance Of Air Contaminant Emissions
From Pesticide Plants
Authors:
Ifeadi CN
Office
of Pesticide Programs, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency,
Washington, D.C. |
A
screening study to develop background information on air
emissions from pesticide producing facilities was conducted.
Data on methyl-parathion (298000) (MP), toxaphene (8001352),
monosodium-methanearsenate (2163806) (MSA),
trifluralin (1582-09-8), pentachlorophenol (87865)
(PCP), and paradichlorobenzene (106467) (PDB) was obtained
by surveys of published reports and questionnaires sent
to pesticide manufacturing firms. The
manufacturers of each pesticide were listed. Manufacturing
processes, raw and waste material handling, air pollution
emission sources, amounts emitted, and pertinent control
methods were analyzed. The significance of air contaminant
emissions in the production of each compound was evaluated.
In the production of MP, only one company controlled the
primary emissions, such as those of hydrogen-sulfide (7783064),
mercaptans, and phosphorus-pentoxide (1314563). In the production
of toxaphene, significant quantities of hydrogen-chloride
(7647010) (HCl) and toxaphene particulates were emitted
by the producers. In the manufacture of MSA, arsenic-trioxide
(1327533) emissions were controlled by all manufacturers,
but the extent of control was not known. In
the production of trifluralin, trifluralin was the jor toxic
material emitted to the environment. No data on emission
rates was obtained. PCP was the major toxic agent
emitted in PCP manufacture. The method of using bag filters
to control PCP emissions was inadequate. In PDB manufacture,
emissions of toxic compounds such as HCl, benzene (71432),
and chlorobenzenes were 90 to 95 percent controlled by water
scrubbers and absorption columns. Production
projections for the compounds were estimated for 1980
in millions of pounds: MP,
98.0; toxaphene, 232.9; MSA, 131.0; trifluralin,
38.4; PCP, 74.9; and PDB, 111.7. |
|