|
Return to
Index Page
Adverse
Effects
ACTIVITY:
Herbicide (Diphenyl
ether)
CAS Name:
2-ethoxy-1-methyl-2-oxoethyl
5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-nitrobenzoate
Structure:
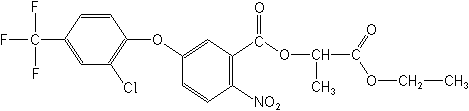
Based
on mechanistic studies with transgenic mice, lactofen
has been classified as a non-genotoxic hepatocarcinogen
in rodents with peroxisome proliferation being a plausible
mode of action. Lactofen is currently classified
as likely to be carcinogenic to humans at high enough
doses to cause the biochemical and histopathological changes
in the liver of rodents, but unlikely to be carcinogenic
to humans below those doses causing these changes.
Ref: Sept
24, 2004, US EPA. Final
Rule for Pesticide Tolerances.
Lactofen
is a member of the diphenyl ether group of herbicides,
which includes acifluorfen (lactofen's major metabolite),
nitrofen,
oxyfluorfen, and fomefasen. In addition, lactofen degrades
to acifluorfen in the environment. The Agency has evidence
that these compounds induce similar toxic effects but
has not yet determined whether these compounds exhibit
a common mechanism of toxicity. The
Agency
[US EPA] defers the cumulative risk assessment of lactofen
and the other diphenyl ethers to a later date.
Ref: Sept 24, 2004, US EPA. Final
Rule for Pesticide Tolerances.
|
| |
| Published
Date |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| June 20, 2007
|
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0178 |
IR-4.
Pesticide
Tolerance. FINAL RULE.
| Okra |
0.02 ppm |
Vegetables, fruiting, group
08
This group includes
17 commodities.
chili, postharvest • eggplant • groundcherry
• pepino • pepper • pepper, bell
• pepper, nonbell • pepper, nonbell, sweet
• tomatillo • tomato • tomato, concentrated
products • tomato, dried pomace • tomato,
paste • tomato, puree • tomato, wet pomace
• vegetable, fruiting • vegetable, fruiting,
group
|
0.02 ppm |
DOCUMENTS MADE AVAILABLE WITH
THIS FINAL RULE:
• Lactofen:
Company Notice of Filing. Docket ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0178-0002
• Lactofen
Acute, Chronic, and Cancer Aggregate Dietary and Drinking
Water Exposure and Risk Assessments for the Section 3 Registration
Action. Docket ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0178-0004
• Drinking
water and aquatic exposure water assessments for IR4 Tolerance
petition for the new use (R17) of lactofen on the fruiting
vegetable group and okra. Docket ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0178-0005
• Lactofen.
Addition of New Uses: Fruiting Vegetables (Crop Group 8)
and Okra. PRIA R17. Summary of Analytical Chemistry and
Residue Data. Docket ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0178-0006
• Data
Evaluation Record. Docket ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0178-0007
• Lactofen:
Revised Human Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on
Fruiting Vegetables and Okra. Docket ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0178-0008
• Cancer. Lactofen
has been classified as ``not likely'' to be carcinogenic in
humans because of available data on lactofen support activation
of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARa)
as the mode of action which induced liver tumors in rodents.
While the proposed mode of action for
liver tumors in rodent is qualitatively possible in humans,
it is quantitatively implausible and unlikely to take place
in humans based on quantitative species toxicodynamic differences
in PPARa activation. The quantification
of risk is not required.
• Exposure assessment for acifluorfen.
Lactofen degrades in the environment to acifluorfen. Sodium
acifluorfen is a registered agricultural pesticide. Accordingly,
an aggregate assessment for acifluorfen exposure resulting
from both use of lactofen and sodium acifluorfen was also
conducted.
• EPA determined that an additional
safety factor was needed to address the lack of a NOAEL in
the rabbit developmental study. Although sufficient reliable
information has been submitted on developmental effects of
lactofen in rabbits, no NOAEL was identified in one of the
two rabbit developmental studies submitted.
The endpoints of concern identified in available studies are:
Decreased live young/ litter, increased embryonic death/litter,
and increased incidence of post-implantation loss. These effects
were noted at all dose levels (5, 15, 50 mg/kg/day) thus a
NOAEL was not established. Consequently, a LOAEL to
NOAEL factor is appropriate and the risk assessment applies
a 3X uncertainty factor. A FQPA uncertainty factor of infants
and children and will be used for the LOAEL to NOAEL extrapolation.
The 3X factor is considered to be protective because the incidence
of the effects at the lowest dose tested was only marginally
higher than the historical controls.
For sodium acifluorfen, the available
toxicology database provides sufficient information for selecting
various toxicity endpoints and doses for assessing the risks.
The Agency evaluated the hazard and exposure data for sodium
acifluorfen and recommended retaining
the safety factor at 10X due to the data gap for the developmental
neurotoxicity study in rats. In accordance with the current
EPA policy, the 10x factor will be applied to all exposure
durations.
• The drinking water assessment of lactofen
is complicated by the fact that lactofen has a major degradate
in common with another registered herbicide, sodium acifluorfen.
Lactofen and sodium acifluorfen also have common use sites.
The Agency considered the contribution of acifluorfen as an
environmental degradate of lactofen and from sodium acifluorfen
in the aggregate assessment. The drinking water residues used
in the dietary risk assessment were incorporated directly
into this dietary exposure from drinking water assessment.
Therefore, EPA estimated drinking water concentrations for
both lactofen and acifluorfen from lactofen applications. |
| April 13, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0005 |
Notice
of Receipt of Requests to Voluntarily Cancel Certain Pesticide
Registrations.
| Registration No. |
Product Name |
Registrant |
| 059639 WA-01-0006 |
Cobra Herbicide |
Valent U.S.A.
Corp.
PO Box 8025
Walnut Creek, CA 94596 |
|
| February 2, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287 |
Pesticide
Registration Review; New Dockets Opened for Review and Comment.
EPA is opening the public comment period for lactofen's registration
review. Registration review is EPA's periodic review of pesticide
registrations to ensure that each pesticide continues to satisfy
the statutory standard for registration, that is, the pesticide
can perform its intended function without unreasonable adverse
effects on human health or the environment.
| Document Date |
Document |
| Jan 2007 |
Summary
Document.
-- Preliminary Work Plam
-- Fact Sheet
-- Ecological Risk Assessment Problem Formulation
-- Human Health Effects Scoping Document
-- Glossary of Terms and Abbreviations
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0002
(45 pages) |
| Dec 19, 2006 |
Human
Health Assessments. Scoping document to support registration
review
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0003
(9 pages) |
| Dec 13, 2006 |
Problem
Formulation for lactofen registration review
-- the methods that will likely be used in the ecological
risk assessment of lactofen
-- anticipated LOC exceedances
-- data gaps
-- additional data needs
Docket Number:
EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0004 (26
pages) |
| Oct 18, 2006 |
Screening-level
usage analysis (SLUA)- Available estimates used on
US agricultural crops
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0005
(2 pages) |
| Oct 31, 2005 |
Appendix
A - Food/Feed & Non-Food/Non–Feed Uses Eligible
for Registration - Partial Listing.
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0006
(2 pages) |
| Oct 25, 2005 |
Section
3, IR4 Tolerance petition for the new use of lactofen
as Cobra Herbicide 2EC on the fruiting vegetable group
and okra.
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0007
(9 pages) |
| Jan 8, 2007 |
Human
Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Fruiting
Vegetables and Okra
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0008
(39 pages) |
| Sept 2003 |
Lactofen
TRED Fact Sheet )
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0009
(4 pages) |
| Sept 24, 2003 |
Report
of the Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA) Tolerance Reassessment
Progress and Risk Management Decision (TRED) for Lactofen
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0010
(9 pages) |
| Oct 12, 2000 |
Preliminary
Human Health Risk Assessment for Tolerance Reassessment
Incorporating Revised Cancer Unit Risks
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0011
(30 pages) |
| May 4, 2000 |
Tolerance
Reassessment of Lactofen: Product and Residue Chemistry
Considerations
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0012
(38 pages) |
| Jan 21, 2003 |
Drinking
Water Exposure Assessment for Lactofen, Updated for
Prospective Ground Water (PGW) Monitoring Study
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0013
(40 pages) |
| July 14, 2000 |
Revised
Drinking Water Exposure Assessment for Lactofen
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0014
(34 pages) |
| July 22, 2004 |
Occupational
and Residential Risk Assessment for Lactofen on Cotton
and Peanuts
Docket Number: EPA-HQ-OPP-2005-0287-0015
(27 pages) |
|
| April 12, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0178 |
IR-4.
Pesticide
petition; New Tolerance PP 5E6930.
in or on various food commodities
-- vegetable, fruiting, group at 0.01 pp
This group (group 8) includes
17 commodities.
chili, postharvest • eggplant • groundcherry
• pepino • pepper • pepper, bell •
pepper, nonbell • pepper, nonbell, sweet • tomatillo
• tomato • tomato, concentrated products •
tomato, dried pomace • tomato, paste • tomato,
puree • tomato, wet pomace • vegetable, fruiting
• vegetable, fruiting, group
-- okra at 0.01 ppm. |
| Sept
24, 2004 |
OPP-2004-0293 |
Valent.
Pesticide Tolerance.
FINAL RULE.
The proposed and established tolerances are corrected to conform
to the Food and Feed Commodity Vocabulary Database and
to lower the established tolerances for snap
bean and soybean to 0.01 ppm as required by the Lactofen Tolerance
Reassessment. Section
180.432 is revised to read as follows:
Sec. 180.432 Lactofen; tolerances for residues.
(a) Tolerances are established for residues of the herbicide
lactofen, 1-(carboethoxy)ethyl 5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-
2- nitrobenzoate, in or on the following raw agricultural
commodities:
| Commodity
|
Parts
per million |
| Beans,
snap, succulent (excluding limas) |
0.01 |
| Cotton,
gin byproducts |
0.02 |
| Cotton,
undelinted seed |
0.01 |
| Peanut |
0.01 |
| Soybean,
seed |
0.01 |
| Table
2.--Summary of Toxicological Dose and Endpoints for lactofen
for Use in Human Risk Assessment |
| Exposure
Scenario |
Dose
Used in Risk
Assessment, Interspecies and Intraspecies and any Traditional
UF |
Special
FQPA SF and Level of Concern for Risk Assessment
|
Study
and Toxicological Effects |
| Acute
Dietary (Females 13-50 years of age) |
NOAEL
= 50 mg/kg/day UF
= 100 Acute RfD = 0.5 mg/kg/day |
Special
FQPA SF = 3 aPAD = acute RfD/ Special FQPA SF = 0.17 mg/kg/day |
Rat
Developmental Toxicity Study
LOAEL = 150 mg/kg/day based on decreased
fetal weight and skeletal
abnormalities. |
| Acute
Dietary (General population including infants and children). |
An
endpoint attributable to a single dose (exposure) was
not identified from the available studies, including the
developmental toxicity studies in rats and rabbits. |
| Chronic
Dietary (All populations) |
NOAEL
= 0.79 mg/kg/day
UF = 100 Chronic RfD = 0.008 mg/kg/day |
Special
FQPA SF = 1 cPAD = chronic RfD/ Special FQPA SF = 0.008
mg/kg/day |
Dog
chronic toxicity LOAEL = 3.96 mg/kg/day based on increased
incidence of
proteinaceous casts in the kidneys,
and
statistically significant increases
in the absolute weights of the thyroid and adrenal glands
in males. |
| Cancer
(Oral, dermal, inhalation) |
Lactofen
acts via a peroxisome proliferation mechanism of action.
Likely to be carcinogenic to humans at high enough doses
to cause these biochemical and histopathological effects
(peroxisome proliferation) in the livers of rodents but
unlikely to be carcinogenic at doses below those causing
these changes. Lactofen
is considered to be a threshold carcinogen.
NOAEL = 0.3 mg/kg/day based on increased
activities of liver enzymes and increased incidence of
liver histopathological findings at the LOAEL of 1.5 mg/kg/day. |
••
The toxicology database for lactofen
is complete for FQPA purposes except for a developmental toxicity
study in rabbits. Based on the quality
of the exposure data, EPA determined
that the 10X SF to protect infants and children should be
reduced to 3X
•• The available rabbit
developmental toxicity study was considered unacceptable because
dosing was not done at a high enough level to observe significant
toxicity.
••
Endpoints for other risk assessments (chronic and cancer)
utilize NOAELs significantly lower than 20mg/kg/day; therefore
the developmental rabbit study will not affect these assessments.
Based on mechanistic studies with transgenic mice, lactofen
has been classified as a non-genotoxic hepatocarcinogen in
rodents with peroxisome proliferation being a plausible mode
of action. Lactofen is currently classified as likely
to be carcinogenic to humans at high enough doses to cause
the biochemical and histopathological changes in the liver
of rodents, but unlikely to be carcinogenic to humans below
those doses causing these changes. |
| Jan
28, 2004 |
OPP-2003-0294 |
Report
of the Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA) Tolerance Reassessment
and Risk Management Decision (TRED)
for Lactofen; Notice of Availability.
• This document announces availability of and starts
a 30-day public comment period for the FQPA TRED for Lactofen.
•
Tolerances for lactofen in or on raw
agricultural commodities for plants are currently established
for the combined residues of lactofen and its associated metabolites
containing the diphenyl ether linkage, but will be revised
to include only lactofen per se. The
two existing tolerances for lactofen have been reassessed
and will be lowered from 0.05 ppm to 0.01 ppm. There
are currently no tolerances for lactofen in processed commodities
or animal commodities, and the available residue data indicate
that tolerances for these commodities are not necessary.
Documents
available:
1.
Sept 2003: Lactofen
TRED Facts - (4 pages)
2.
Sept 24, 2003: Report
of the Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA) Tolerance Reassessment
Progress and Risk Management Decision (TRED) for Lactofen
- (9 pages)
3.
Sept 24, 2003: Overview
of Lactofen FQPA Risk Assessment for Tolerance Reassessment
- (9 pages)
4.
Aug 12, 2003: Lactofen.
Revisions to HED Tolerance Reassessment Risk Assessment
- (3 pages)
5.
May 22, 2002: Lactofen
- Report of the Cancer Assessment Review Committee - (38
pages)
6.
March 12, 2001: LACTOFEN:
Report of the Mechanism of Toxicity Assessment Review Committee
- (17 pages)
7.
Feb 26, 2003: EFED
Review of Lactofen Small-Scale Prospective Ground-Water Monitoring
Study 166-1 DER MRID #456717-01, 02, and -03. - (40
pages)
8.
Jan 21, 2003: DRINKING
WATER EXPOSURE ASSESSMENT FOR LACTOFEN, UPDATED FOR
PROSPECTIVE GROUND WATER (PGW) MONITORING STUDY - (40
pages)
9.
Sept 15, 2003: Addendum
to EFED RED Chapter for sodium acifluorfen. Addendum to TRED
for lactofen - (41 pages) |
| July
30, 2003 |
OPP-2002-0327 |
US
EPA's Pesticide Reregistration Performance Measures and Goals.
Candidate for Tolerance Reassessment Progress and Interim Risk
Management Decision (TRED) in Fiscal Year 2004
which
runs
from October 1, 2003, through September 30, 2004. |
| Jan
29, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0001 |
VALENT
- Pesticide
Petitions to Establish Tolerances in
or on the raw agricultural commodities (RACs) cottonseed at
0.01 ppm, cotton gin byproducts at 0.02 ppm, and peanut nutmeats
at 0.01 ppm.
-- In the developmental toxicity study
in rats, effects were observed at the 150 mg/kg/day dose level
consisting of decreases in fetal weight
as well as skeletal abnormalities.
This dose level also elicited signs
of toxicity in the parental group.
-- Chronic toxicity. Lactofen
causes adverse health effects when administered to animals
for extended periods of time. These effects include proliferative
changes in the liver, spleen, and kidney; hematological changes;
and blood biochemistry changes.
-- Subchronic toxicity... Mice
3-month. Groups of male and female mice
were fed diets containing lactofen technical at concentrations
of 0, 40, 200, 1,000, 5,000, and 10,000 for 13 weeks. At week
5, the dosage of the 40 ppm, groups was increased to 2,000
ppm. Treatment related mortality occurred at dosages above
1,000 ppm. The LOAEL was 200 ppm, 28.6 mg/kg/day based on:
¥ Increased WBC; decreased hematocrit,
hemoglobin and RBC. ¥ Increased alkaline phosphatase, serum
glutamic-oxloacetic transaminase (SGOT), SGPT, cholesterol
and total serum protein levels. ¥ Increased weights or enlargement
of the spleen, liver, adrenals, heart, and kidney; histopathological
changes of the liver, kidney, thymus, spleen, ovaries, and
testes.
-- Peroxisome
proliferation. Butler et al (1988)
studied the effects of lactofen on peroxisome proliferation
in mice exposed for 7 weeks to dietary concentrations of 2,
10, 50, and 250 ppm. Liver-weight
to body-weight ratio, liver catalase, liver acyl-CoA oxidase,
liver cell cytoplasmic eosinophilia, nuclear, and cellular
size, and peroxisomal staining were increased by the tumorigenic
dose of lactofen, i.e. 250 ppm.
-- The Cancer Peer Review Committee (CPRC) evaluated the relevant
data on the carcinogenic potential of lactofen in 1987 and
classified lactofen as a B2 carcinogen Probable Human
Carcinogen. The B2 classification
is based on an increase in the combined
incidence of liver adenomas and carcinomas in mice and increases
in liver neoplastic nodules and foci of cellular alteration
(possible precursor of tumors) in rats.
-- EPA has recently determined that
lactofen acts via a peroxisome proliferation mechanism
and is currently reevaluating its approach
to the quantification of the cancer risk for lactofen.
-- Carcinogenicity. As a member of the
diphenyl ether chemical family, lactofen is structurally
related to four other chemicals that are oncogenic in rodents:
--- Sodium acifluorfen (acifluorfen
is a lactofen metabolite), nitrofen, oxyfluorfen, and fomesafen.
--- Sodium acifluorfen produces hepatocellular
adenomas and carcinomas in mice but is negative in rats.
--- Nitrofen produces hepatocellular carcinomas in mice and
pancreatic carcinomas in rats.
--- Oxyfluorfen produces marginally positive liver tumors
in mice but is negative in rats.
--- Fomesafen produces hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas
in mice. |
| Sept
13, 2002 |
OPP-2002-
0121 |
EPA
status of reregistration and tolerance reassessment. |
| July
26, 2001 |
OPP-34240 |
Availability
of Risk Assessment. These documents are the human health
risk assessment and related documents for lactofen (Cobra).
This notice also starts a 60- day public comment period for
the risk assessment. copies of the risk assessment and certain
related documents for lactofen may also be accessed at http://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/lactofen/ |
| Feb
25, 1998 |
PF-789 |
VALENT
- Petition to
extend a time-limited tolerance for residues on cottonseed
at 0.05 ppm. The tolerance would expire on December 31,
1999. The time limitation on the tolerance would allow Valent
to complete, and EPA to evaluate, additional prospective groundwater
study data. |
| Aug
4, 1997 |
OPP-300523 |
Pesticides
Subject to Tolerance Reassessment. |
| Dec
12, 1996 |
PF-677 |
VALENT
- Petition
for Renewal of Time-Limited Tolerance for residues on cottonseed
at 0.05 ppm. |
| June
19, 1996 |
na |
Emergency
Exemption. US EPA has granted specific exemptions to the
Oregon Department of Agriculture for the use of lactofen on
snap beans to control nightshade and pigweed; April 3, 1996,
to July 31, 1996. |
| May
8, 1996 |
PP
4E4418/R2231 |
IR-4*
- Petition
for Pesticide Tolerance. - FINAL RULE. This document
establishes a tolerance for combined residues of the herbicide
lactofen and its metabolites in or on the raw agricultural
commodity snap beans of 0.05 ppm. |
| May
3, 1996 |
PP
9F3798/R2229 |
VALENT
- Petition
for Pesticide Tolerance. - FINAL RULE. USEPA extends
a time-limited tolerance for residues on the raw agricultural
commodity cottonseed at 0.05 ppm. |
| March
8, 1996 |
PP
4E4418/P643 |
IR-4*
- Petition
for Proposed Pesticide Tolerance. EPA proposes to establish
a tolerance for the combined residues of the herbicide lactofen
in or on the raw agricultural commodity snap beans at 0.05
ppm. |
| Feb
21, 1996 |
na |
Emergency
Exemption. US EPA has granted specific exemption to Florida
Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services for use on snap
beans to control nightshade and common ragweed; September 1,
1995, to May 31, 1996. |
| Feb
14, 1996 |
PP
9F3798/P642 |
VALENT
- Petition
to renew a time-limited tolerance for residues on cottonseed
at 0.05 ppm, The tolerance would establish the maximum
permissible level of residues on this commodity. |
| July
26, 1995 |
OPP-180976 |
Request
for Emergency Exemption from the Florida Department of Agriculture
Consumer Services for use of the pesticide, lactofen (Cobra
Herbicide), to control nightshade Solanum spp. and parthenium
Parthenium spp. on up to 10,000 acres of row middle tomatoes
and 5,000 acres of row middle green peppers in Florida. |
| Mar
29, 1995 |
na |
Request
for Emergency Exemption. EPA has received a specific exemption
request from the Oregon Department of Agriculture for use of
the pesticide Lactofen (Cobra Herbicide) (EPA Reg. No. 59639-34)
manufactured by Valent U.S.A. Corp., to control black nightshade,
hairy nightshade, and redroot pigweed on up to 2,000 acres of
snap beans. |
| Dec
28, 1994 |
na |
Emergency
Pesticide Use Exemptions. US EPA has granted specific exemption
to Oregon Department of Agriculture for the use of lactofen
on snap beans to control weeds; May 31, 1994, to July 10, 1994.
US EPA has denied Texas Department of Agriculture for the use
of lactofen on peanuts to control eclipta. This specific exemption
was denied because an urgent nonroutine situation does not exist
in spite of increased infestations of the weed eclipta. |
| Dec
13, 1995 |
na |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions. US EPA authorized the following: Florida
Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services for the use
of lactofen on tomatoes and green peppers to control nightshade;
Sept 1, 1995, to August 31, 1996. A notice of receipt published
in the Federal Register of July 26, 1995 (60 FR 38335). The
use of lactofen has been requested for the past 4 years and
was granted. A complete application for registration of the
use has not yet been submitted to the Agency. Oregon Department
of Agriculture for the use of lactofen on snap beans to control
weeds; April 28, 1995, to July 31, 1995. |
| Jan
12, 1994 |
OPPTS-400082 |
EPA's
proposal to add 41
fluorine and organofluorine chemicals to the Toxics Release
Inventory (TRI). See excerpt in box
above. Also available at http://www.epa.gov/tri/frnotices/59fr1788.htm |
| *
Interregional Research Project No. 4 (IR-4) |
|