|
Return
to Tolylfluanid Index Page
Activity:
Fungicide,
Insecticide (phenylsulfamide)
Structure:
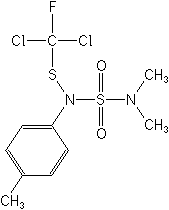
Adverse
Effects:
Body
Weight Decrease
Bone - including Arthrogryposis
Cancer: Likely to be Carcinogenic to
Humans - THYROID
Clastogenic
Cytotoxic
Endocrine: Thyroid
Eye
Kidney
Liver
Reproductive/Developmental
Thyroid
Environmental
•
In 2001, Tolylfluanid ranked 9th out of the ten most frequently
found pesticides in fruits and vegetables. There were 151
samples with residues at or above reporting level.
Ref:
September 2002 Report
of Pesticide Residue Monitoring Results of the Netherlands
for 2001. Inspectorate
of Health Protection, Commodities and Veterinary Public
Health Food Inspection Service Den Haag - Amsterdam Hoogte
Kadijk 401 1018 BK Amsterdam The Netherlands
•
On
September 25, 2002, US EPA established an import
tolerance for residues of tolylfluanid in or on imported
Apple,
Grape, Tomato, Hop
-
see list at bottom of page.
|
In a
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) on the product "Mipa
Holzgrund" an unusual effect was noted:
"Repeated
or prolonged contact with the preparation may cause removal
of natural fat from the skin resulting in non-allergic
contact dermatitis and absorption through the skin."
- page 4
Other
ingredients in this product include:
Zinkcarboxylat (Hexanoic acid, 2-ethyl, zinc salt - CAS
No. 136-53-8)
Naptha (petroleum), hydrotreated heavy - CAS No. 64742-48-9
1-Butanol - CAS No. 71-36-3.
The
company name on the MSDS is Miap
AG, a producer of car paint systems.
|
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 90-Day oral toxicity
rodents (rat). NOAEL = 20.1 milligram/kilogram/ day (mg/kg/day)
male (M) LOAEL = 108 mg/kg/ day, based on changes
in clinical blood chemistry associated with the liver and thyroid
(M) NOAEL = 131 mg/kg/day female (F) LOAEL = 736.1
mg/kg/ day, based on changes in clinical blood chemistry associated
with the liver and thyroid and decreased
body weights (F)
-- 90-Day oral toxicity
in nonrodents
(dog). NOAEL = 23.1/25 mg/kg/
day (F/M) LOAEL = 67.2/69.4 (F/ M) mg/kg/day, based on decreased
body weight gains and changes in liver structure and function
in both sexes
-- Prenatal developmental in rodents (rat). Maternal NOAEL = not
determined LOAEL = 100 mg/kg/ day, based on decreased
body weight gains and food consumption.
-- Prenatal developmental in rodents (rat). Maternal NOAEL = 100
mg/kg/day LOAEL = 300 mg/kg/ day, based on dose- related decreased
body weight gains during the dosing interval. Developmental
NOAEL > 1,000 mg/kg/day (HDT) LOAEL = not identified
-- Prenatal developmental in nonrodents (rabbit). Maternal NOAEL
= 25 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 70 mg/kg/day, based on evidence of hepatotoxicity
(increased glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH) and triglyceride levels
and gross and microscopic liver pathology) and decreased
food consumption and equivocal decreases in body weight gain.
Developmental NOAEL = 25 mg/kg/day LOAEL= 70 mg/kg/day, based
on increased malformations (arthrogryposis
of front extremities and small orbital cavity/folded retina) and
variations (floating rib and accelerated ossification).
-- 2-Generation reproduction and fertility effects (rat). Parental/systemic
NOAEL = 7.9-10.5 mg/ kg/day LOAEL = 57.5-78.0 mg/ kg/day, based
on decreased body weights, body weight
gains, and liver weights in the P females
Reproductive NOAEL = 7.9-10.5 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 57.5-78.0
mg/ kg/day, based on reduced litter size Offspring NOAEL = 7.9-
10.5 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 57.5-78.0 mg/ kg/day, based on
decreased pup weights, increased pup deaths and related
pup viability indices.
-- 2-Generation reproduction and effects (rat). Parental/Systemic
NOAEL = 20.1-26.3 mg/ fertility kg/day LOAEL = 83.4-109.5 mg/
kg/day, based on decreased body weights
and body weight gains Reproductive NOAEL = 83.4 - 109.5
mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 335.6-492.4 mg/kg/day, based on decreased mean
litter size Offspring NOAEL = 20.1-26.3 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 83.4-109.5
mg/ kg/day, based on decreased pup weights
-- 2-Generation reproduction and fertility effects (rat). Parental/Systemic
NOAEL = 75 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 375 mg/kg/ day, based on decreased
body weights and body weight gains for both generations
Reproductive NOAEL > 375 mg/kg/day (HDT) LOAEL not established
Offspring NOAEL = 75 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 375 mg/kg/ day, based on
decreased survival and reduced body weights
during lactation
-- Chronic toxicity (dog).
NOAEL = 12.5 mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 62.5 mg/kg/
day (M), based on decreased body weight
gains
Ref:
Federal Register: September 25, 2002. Tolylfluanid; Pesticide
Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolylfluanid.FR.Sept25.2002.htm
Bone
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
See Tables on accumulation in bone and
teeth excerpted from:
February 2005 European Commission Report:
Final addendum to the Draft Assessment Report (DAR) - public version
- Initial risk assessment provided by the rapporteur Member State
Finland for the existing active substance TOLYLFLUANID of the
second stage of the review programme referred to in Article 8(2)
of Council Directive 91/414/EEC
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/epage.tolylfluanid.bone.eu.html
In all species tested, the concentrations
of fluoride in the bone and teeth were increased in a dose-related
manner. At high doses, this increase was associated with
discolouration, particularly of the skull
cap and incisors, in both sexes but starting at lower doses in
male rats. In long-term studies, rats at 7500 ppm, equal
to 500 mg/kg bw per day, required treatment for overgrown incisors
more frequently than controls, presumably because fluoride deposition
in the incisors had increased their strength and thus decreased
the wear on these teeth. Hyperostosis of
the skull and sternum was seen at high doses in mice and rats
of either sex, and histopathological changes were seen in the
bones of female mice at 300 ppm (equal to 120 mg/kg bw
per day) and female rats at 1500 ppm (equal to 100 mg/kg bw per
day). In both sexes, increased fluoride
deposition was seen at 300 ppm, equal to 76 mg/kg bw per day,
in mice and 18 mg/kg bw per day in rats. The NOAEL for
fluoride deposition was 60 ppm, equal to 15 mg/kg bw per day,
in mice, and 60 ppm, equal to 3.6 mg/kg bw per day, in rats. In
dogs, the fluoride concentration in bone was increased in males
at doses of 80 mg/kg bw per day and in females at 20 mg/kg bw
per day and above, while the fluoride concentration in teeth was
increased in males at 80 mg/kg bw per day and in females at all
doses including the lowest one tested, 5 mg/kg bw per day, although
not in a dose-related manner. The increase in fluoride deposition
raises concern because mottling of dental enamel (or dental fluorosis)
occurs in humans after exposure to high concentrations of fluoride,
particularly where water has a high concentration of fluoride
or has been inappropriately supplemented. While this is mainly
a cosmetic defect, it is generally recognized as adverse. (page
254-255)
..........The Meeting established
an ADI of 0–0.08 mg/kg bw on the basis of the NOAEL of 60
ppm, equal to 3.6 mg/kg bw per day, in the 2-year study in rats,
in which increased fluoride deposition was seen at higher doses,
and a safety factor of 50. This safety factor
was used because of the limited differences noted between species
in the deposition of fluoride in bones and teeth after administration
of tolylfluanid. The NOAEL in the 2-year study in rats
treated in the diet was used in preference to the LOAEL of 5 mg/kg
bw per day in the 1-year study in dogs given tolylfluanid by capsule,
as increased fluoride concentrations were seen only in the teeth
and the low dose in the study in dogs, without a clear dose–response
relationship... (page 256)
..........Metabolism involves cleavage
of the fluorodichloromethylthio group from tolylfluanid to form
N,N-dimethyl-N’-p-tolysulfamide (dimethylaminosulfotoluidine,
DMST). The fluorodichloromethylsulfenyl side-chain undergoes further
metabolism to form thiazolidine-2-thioxo-4-carboxylic acid, which
is the main metabolite in the urine of rats and is of toxicological
significance because of its potential anti-thyroid effects. Dimethyltolylsulfamide
is also further metabolized, producing a range of metabolites
that are not of toxicological significance. The
release of the fluoride ion and its distribution in the body have
not been clearly characterized. (page 254)
..........Studies that would provide
information useful for continued evaluation of the compound (page
257)
• Further characterization of the
distribution and excretion of fluoride and thiazolidine-2-thione4-carboxylic
acid, particularly in milk
• Investigation of the cause of decreased pup survival during
lactation
• Further observations in humans
Ref: Pesticide residues in food - 2002.
Report of the Joint Meeting of the FAO Panel of Experts on Pesticide
Residues in Food and the Environment and the WHO Core Assessment
Group on Pesticide Residues. Rome, Italy. 16- 25 September 2002.
ISBN 92-5-104858-4.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tolylfluanid.fao.2002.pdf
Toxicity - General:
The skeletal system (bones and teeth),
liver and thyroid were identified as target
organs in the animal studies.
Ref: US EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet. Reason
for Issuance: Import Tolerance. September 2002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tolylfluanid.epa.facts.2002.pdf
Chronic toxicity studies
on tolylfluanid were done in the rat, mouse and dog. Tolylfluanid
was tested in two rat chronic dietary studies.
Increased growth of the incisors of the upper jaw and skeletal
changes (hyperostosis in the skull and ribs) resulted from the
high fluorine content of the compound...
Ref: Federal Register: August 11, 1997 (Volume
62, Number 154). Page 42980-42986. Notice of Filing of Pesticide
Petitions.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolyfluanid.FR.August.1997.htm
-- Prenatal developmental
in nonrodents (rabbit). Developmental NOAEL = 25 mg/kg/day LOAEL=
70 mg/kg/day, based on increased malformations
(arthrogryposis
[see definition below]
of front extremities and small orbital cavity/folded
retina) and variations (floating
rib and accelerated ossification).
-- 2-Generation reproduction and fertility effects (rat). Parental/systemic
NOAEL not established LOAEL = 15.9-21.5 mg/ kg/day, based on
hardened crania of P generation animals Reproductive NOAEL
not established LOAEL = 15.9-21.5 mg/ kg/day, based on increased
clinical signs of toxicity Offspring NOAEL > 15.9-21.5 mg/kg/day
(HDT) LOAEL not established
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rodents (rat): NOAEL
= 18.1/21.1 mg/ kg/day (M/F); LOAEL = 90.1/105.2 mg/ kg/day (M/F),
based on skeletal changes. Evidence
of thyroid follicular cell adenomas and/or carcinomas in high-
dose males and females.
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rodents (rat): NOAEL
= 20/20 mg/kg/ day (M/F); LOAEL = 80/110 mg/kg/day (M/F),
based on bone hyperostosis in males and females. Evidence
of thyroid follicular cell adenomas and/or carcinomas in high-
dose males and females.
-- -- Carcinogenicity rodents (mouse): NOAEL = 76.3/123.9 mg/kg/day
(M/F) LOAEL = 375.8/610.8 mg/kg/day (M/F), based
on skeletal, liver, and kidney changes.
No evidence of carcinogenicity.
Ref: Federal Register: September 25, 2002.
Tolylfluanid; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolylfluanid.FR.Sept25.2002.htm
WHAT
IS ARTHROGRYPOSIS?
Published by AVENUES A National Support Group for Arthrogryposis
Multiplex Congenita - http://www.sonnet.com/avenues/pamphlet.html
"Arthrogryposis" (Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita) is
a term describing the presence of multiple joint contractures
at birth. A contracture is a limitation in the range of
motion of a joint. In some cases, few joints maybe affected
and the range of motion may be nearly normal. In the "classic"
case of Arthrogryposis, hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders,
hips, feet, and knees are affected. In the most severe cases,
nearly every body joint may be involved, including the jaw
and back. Frequently, the joint contractures are accompanied
by muscle weakness which further limits movement.
Arthrogryposis is relatively rare, occurring in perhaps
one in 3,000 births... There is a wide variation
in the degree to which muscles and joints are affected in
those with Arthrogryposis. In some
cases, Arthrogryposis may be accompanied by other conditions,
such as central nervous system disorders, which complicate
the picture... In general, there are four causes for limitation
of joint movement before birth:
(1) Muscles do not develop properly (atrophy). In most cases,
the specific cause for muscular atrophy cannot be identified.
Suspected causes include muscle diseases (for example, congenital
muscular dystrophies), maternal fever during pregnancy,
and viruses which may damage cells which transmit nerve
impulses to the muscles.
(2) There is not sufficient room in the uterus for normal
movement. For example, the mother may lack normal amount
of amniotic fluid, or have an abnormally shaped uterus.
(3) Central nervous system and spinal cord are malformed.
In these cases, Arthrogryposis is usually accompanied by
a wide range of other conditions.
(4) Tendons, bones, joints or joint linings may develop
abnormally. For example, tendons may not be connected to
the proper place in a joint. |
Cancer:
Likely to be Carcinogenic to Humans - THYROID
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Likely
to be Carcinogenic to Humans. Thyroid tumors
in male and female Wistar rats. Linear low-dose extrapolation
approach recommended.
Ref: April
26, 2006 . Chemicals Evaluated for Carcinogenic Potential by the
Office of Pesticide Programs. From: Jess Rowland, Chief Science
Information Management Branch Health Effect Division (7509C) Office
of Pesticide Programs, USEPA.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/pesticides.cancer.potential.2006.pdf
--
Cancer Classification: ``Likely to be carcinogenic to humans''
by the oral route, based
on thyroid tumors in high-dose male and female rats. The
FQPA SF Committee further recommended a linear low-dose extrapolation
approach for the quantification of human cancer risk based on
the thyroid tumors in rats. Q1* = 1.59 x 10-\3\ based upon male
rat thyroid adenomas and/or carcinomas combined... Cancer. A partially
refined, cancer dietary exposure assessment was conducted for
the general U.S. population using the same assumptions as were
used in the chronic risk assessment (listed in the preceding section).
Import share data generated within the Agency were used in the
assessment to estimate what proportion of the grape, apple, hop,
and tomato consumed in the United States are imported. Modified
DEEM\TM\ processing factors based on the results of processing
studies were used for raisins and apple and grape juice/juice
concentrates. Default DEEM\TM\ processing factors were used for
all other processed commodities The cancer risk estimate is 1.2
x 10-\6\ for the general U.S. population.
Ref: Federal Register: September 25, 2002.
Tolylfluanid; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolylfluanid.FR.Sept25.2002.htm
Clastogenic
and
Cytotoxic
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
Bacterial gene mutation assay. Tolylfluanid was cytotoxic
to all strains at = 8 [mu]g/plate +/ - S9 and precipitated from
solutions in all strains at 5,000 [mu]g/plate +/- S9. There were
no reproducible, dose- related differences in the number of revertant
colonies in any strain or dose over the background. Positive controls
induced appropriate response.
-- Metabolite--WAK 6698. Bacterial gene mutation assay. Metabolite
was cytotoxic at doses £=158 [mu]g/plate in the initial assay
and 1,581 [mu]g/plate in the repeat assay. There was no evidence
of a significant increase in mutant colonies over background in
any strains tested in the initial or repeat mutagenicity assays.
Positive controls induced appropriate response.
-- Technical. In vitro mammalian cell gene mutation assay. Cytotoxicity
was observed at concentrations 1 to 10 [mu]g/milliliter (mL) -S9
and 5 to 10 [mu]g/mL +S9. Over the ranges tested clastogenic effects
included increased incidences of metaphases with aberrations including
gaps, metaphases excluding gaps, metaphases with exchanges, and
metaphases with polyploidy were observed. Tolyfluanid
is clastogenic both in the presence and in the absence of S9 activation.
Ref: Federal Register: September 25, 2002.
Tolylfluanid; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolylfluanid.FR.Sept25.2002.htm
Endocrine:
Thyroid (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Toxicity - General: The skeletal
system (bones and teeth),
liver and thyroid were identified
as target organs in the animal studies.
Ref: US EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet. Reason
for Issuance: Import Tolerance. September 2002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tolylfluanid.epa.facts.2002.pdf
-- Cancer Classification:
``Likely to be carcinogenic to humans''
by the oral route, based
on thyroid tumors in high-dose male and
female rats. The FQPA SF Committee
further recommended a linear low-dose extrapolation approach for
the quantification of human cancer risk based on the thyroid tumors
in rats. Q1*
= 1.59 x 10-\3\ based upon
male rat thyroid adenomas and/or carcinomas combined.
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rodents (rat): NOAEL
= 18.1/21.1 mg/ kg/day (M/F); LOAEL = 90.1/105.2 mg/ kg/day (M/F),
based on skeletal changes. Evidence
of thyroid follicular cell adenomas and/or carcinomas in high-
dose males and females.
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rodents (rat): NOAEL
= 20/20 mg/kg/ day (M/F); LOAEL = 80/110 mg/kg/day (M/F),
based on bone hyperostosis in males and
females Evidence of thyroid follicular cell adenomas and/or
carcinomas in high- dose males and females.
-- Non-guideline (rat) thyroid function: Thyroid-stimulating
hormone
levels significantly
increased (168-425%) in high-dose males and females. Slightly
increased T3 levels in males rats above 119.3 mg/ kg/day.
--
Metabolite Non-guideline (mice).
In
vitro investigation
of TTCA goitrogenic
properties.
Tolylfluanid's
metabolite TTCA was shown to reversibly inhibit thyroid peroxidase
(TPO)- mediated reactions involved with the initial stages of
thyroid hormone synthesis... TTCA, unlike tolylfluanid, behaves
as a goitrogenic compound with a potency approximately equal to
propylthiouracil (PTU), a known thionamide inhibitor of initial
thyroid hormone synthesis.
Ref: Federal Register: September 25, 2002.
Tolylfluanid; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tolylfluanid.fr.sept25.2002.htm
Eye
(click on for
all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Prenatal developmental
toxicity/rabbit LOAEL = 70 mg/kg/day based
on increased
malformations (arthrogryposis of front extremities and small
orbital cavity/folded retina) and variations
(floating ribs and accelerated ossification).
Ref: Federal Register: September 25, 2002.
Tolylfluanid; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolylfluanid.FR.Sept25.2002.htm
Kidney
(click on for
all fluorinated pesticides)
--
Carcinogenicity
rodents (mouse).
NOAEL = 76.3/123.9 mg/ kg/day (M/F) LOAEL
= 375.8/610.8 mg/kg/day (M/F), based on skeletal, liver, and kidney
changes No evidence of carcinogenicity
Ref:
Federal Register: September 25, 2002. Tolylfluanid; Pesticide
Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolylfluanid.FR.Sept25.2002.htm
Chronic toxicity. Chronic
toxicity studies on tolylfluanid were done in the rat, mouse and
dog. Tolylfluanid was tested in two rat chronic dietary studies.
Increased growth of the incisors of the upper jaw and skeletal
changes (hyperostosis in the skull and ribs) resulted from the
high fluorine content of the compound. Hepatotoxicity and renal
toxicity were seen in rats, mice, and dogs. Hepatotoxicity
was evidenced by hepatocellular cytoplasmic changes, vacuolation,
and focal fatty changes in rats, hepatocellular hypertrophy and
single cell necrosis in mice, decreased liver enzymes in rats,
and increased liver enzymes in mice and dogs. Renal
toxicity (microscopic kidney lesions, increased relative kidney
weights, effects on urinalysis parameters) was probably
attributable to the effects of fluoride on renal tubules. A second
chronic toxicity study in dogs is currently ongoing (results not
yet available).
Ref: Federal Register: August 11, 1997 (Volume
62, Number 154). Page 42980-42986. Notice of Filing of Pesticide
Petitions.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolyfluanid.FR.August.1997.htm
Liver
(click on for
all fluorinated pesticides)
Toxicity - General: The skeletal
system (bones and teeth),
liver and thyroid were identified
as target organs in the animal studies.
Ref: US EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet. Reason
for Issuance: Import Tolerance. September 2002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tolylfluanid.epa.facts.2002.pdf
-- 90-Day oral toxicity
rodents (rat). NOAEL = 20.1 milligram/kilogram/ day (mg/kg/day)
male (M) LOAEL = 108 mg/kg/ day, based on changes
in clinical blood chemistry associated with the liver and thyroid
(M) NOAEL = 131 mg/kg/day female
(F) LOAEL = 736.1 mg/kg/ day, based
on changes in clinical blood chemistry associated with the liver
and thyroid and decreased body weights
(F)
-- 90-Day oral toxicity in
nonrodents (dog). NOAEL
= 23.1/25 mg/kg/ day (F/M) LOAEL = 67.2/69.4 (F/ M) mg/kg/day,
based on decreased body weight gains and
changes in liver structure and function in both sexes
-- Prenatal developmental in nonrodents (rabbit). Maternal NOAEL
= 25 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 70 mg/kg/day, based on evidence of hepatotoxicity
(increased glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH) and triglyceride levels
and gross and microscopic liver pathology) and
decreased food consumption and equivocal decreases in body weight
gain. Developmental NOAEL = 25 mg/kg/day LOAEL= 70 mg/kg/day,
based on increased malformations (arthrogryposis of front extremities
and small orbital cavity/folded retina) and variations (floating
rib and accelerated ossification).
-- 2-Generation reproduction and fertility effects (rat). Parental/systemic
NOAEL = 7.9-10.5 mg/ kg/day LOAEL = 57.5-78.0 mg/ kg/day, based
on decreased body weights, body weight
gains, and liver weights in the P
females Reproductive NOAEL = 7.9-10.5 mg/kg/day LOAEL =
57.5-78.0 mg/ kg/day, based on reduced litter size Offspring NOAEL
= 7.9- 10.5 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 57.5-78.0 mg/ kg/day, based on
decreased pup weights, increased pup deaths and related pup viability
indices.
-- Carcinogenicity rodents (mouse). NOAEL
= 76.3/123.9 mg/ kg/day (M/F) LOAEL = 375.8/610.8 mg/kg/day (M/F),
based on skeletal, liver, and kidney changes
No evidence of carcinogenicity
Ref: Federal Register:
September 25, 2002. Tolylfluanid; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
Federal Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolylfluanid.FR.Sept25.2002.htm
Reproductive
/ Developmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Prenatal developmental
in nonrodents (rabbit). Developmental NOAEL = 25 mg/kg/day LOAEL=
70 mg/kg/day, based on increased malformations
(arthrogryposis
[see definition below•] of front extremities and small orbital cavity/folded
retina) and variations (floating
rib and accelerated ossification).
-- 2-Generation reproduction and fertility effects (rat). Parental/systemic
NOAEL not established LOAEL = 15.9-21.5 mg/ kg/day, based on
hardened crania of P generation animals Reproductive NOAEL
not established LOAEL = 15.9-21.5 mg/ kg/day, based on increased
clinical signs of toxicity Offspring NOAEL > 15.9-21.5 mg/kg/day
(HDT) LOAEL not established
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rodents (rat): NOAEL
= 18.1/21.1 mg/ kg/day (M/F); LOAEL = 90.1/105.2 mg/ kg/day (M/F),
based on skeletal changes. Evidence
of thyroid follicular cell adenomas and/or carcinomas in high-
dose males and females.
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rodents (rat): NOAEL
= 20/20 mg/kg/ day (M/F); LOAEL = 80/110 mg/kg/day (M/F),
based on bone hyperostosis in males and females. Evidence
of thyroid follicular cell adenomas and/or carcinomas in high-
dose males and females.
Ref:
Federal Register: September 25, 2002. Tolylfluanid; Pesticide
Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Tolylfluanid.FR.Sept25.2002.htm
Thyroid
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Likely
to be Carcinogenic to Humans. Thyroid tumors
in male and female Wistar rats. Linear low-dose extrapolation
approach recommended.
Ref: April
26, 2006 . Chemicals Evaluated for Carcinogenic Potential by the
Office of Pesticide Programs. From: Jess Rowland, Chief Science
Information Management Branch Health Effect Division (7509C) Office
of Pesticide Programs, USEPA.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/pesticides.cancer.potential.2006.pdf
| Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Water-sediment
systems.
In a study of hydrolysis, tolylfluanid was readily hydrolyzed
into DMST [dimethylaminosulfotoluidine] under all conditions
used (pH 4, 7 and 9; 20, 30 and 40°C). The half life
of tolylfluanid was calculated to be 11.7 days at pH 4 and
29.1 hours at pH 7 at 22°C in respective sterile buffer
solutions. Tolylfluanid was so unstable at pH 9 that no
parent compound was left to be detected even in immediate
analysis of the sample making the estimation of half life
impossible. Another hydrolysis study
demonstrated that tolylfluanid was hydrolyzed into DMST,
fluoride ion, chloride ion,
sulfur and carbon dioxide. DMST, on the other hand, was
stable at pH 4, 7 and 9 up to 55°C in respective sterile
buffer solutions. The half life of DMST was calculated to
be > 1 year at 22°C at pH 4, 7 and 9.
Ref: Pesticide residues in food -
2002. Report of the Joint Meeting of the FAO Panel of Experts
on Pesticide Residues in Food and the Environment and the
WHO Core Assessment Group on Pesticide Residues. Rome, Italy.
16- 25 September 2002. ISBN 92-5-104858-4.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tolylfluanid.fao.2002.pdf
|
A
February
16, 2005,
check at the Code
of Federal Regulations for Toylfluanid: this fungicide
is permitted in or on 4
food
commodities imported into the
United States.
Note:
On
September 25, 2002, US EPA established a
tolerance for residues of tolylfluanid in or on imported
apple, grape, hop, and tomato.
Bayer Corporation requested this tolerance under the Federal
Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA), as amended by the
Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA) of 1996.
|
| [Code
of Federal Regulations]
[Title 40, Volume 22]
[Revised as of July 1, 2004]
From the U.S. Government Printing Office via GPO Access
[CITE: 40CFR180.584]
[Page 514]
TITLE 40--PROTECTION OF ENVIRONMENT
CHAPTER I--ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY (CONTINUED)
PART 180_TOLERANCES AND EXEMPTIONS FROM TOLERANCES FOR PESTICIDE
CHEMICALS
IN FOOD--Table of Contents
Subpart C_Specific Tolerances
Sec. 180.584 Tolylfluanid; tolerances for residues.
(a) General. Tolerances are established for residues of
tolylfluanid, 1,1-dichloro-N-[(dimethylamino)-sulfonyl]-1-fluoro-N-(4-
methylphenyl)methanesulfenamide in or on the following commodities. |
| Commodity |
Parts
Per Million |
| Apple\1\. |
5.0 |
| Grape\1\ |
11 |
| Hop\1\ |
30 |
| Tomato\1\ |
2.0 |
| \1\
No U.S. registration as of August 31, 2002. |
| (b)
Section 18 emergency exemptions. [Reserved]
(c) Tolerances with regional registrations. [Reserved]
(d) Indirect or inadvertent residues. [Reserved] |
|

