|
Return
to Index Page
Activity:
Acaricide,
Insecticide (pyrethroid ester)
Structure:
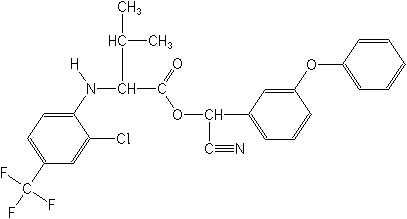
Adverse Effects:
Ataxia
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Dermal
Endocrine: Breast
Endocrine: Testicular
Fetotoxic
Teratogen
Tremors
Environmenal
Tau-fluvalinate
is a broad-spectrum insecticide/miticide in the pyrethroid
class of pesticides. It is registered for a single food
use (beehives/honey) and several non-food uses, including
ornamentals (outdoor and container-grown, greenhouse, interior
plantscapes, dip for cuttings), building surfaces/perimeters,
ant mounds and certain crops (carrots and brassica/cole
crops) grown for seed. Tau-fluvalinate was first registered
in one of its earlier forms, racemic fluvalinate, in 1983.
With an estimated 11,000 pounds of active ingredient (a.i.)
used per year, it has minimal domestic usage. The majority
of the usage is in commercial greenhouses and on outdoor
field- and container-grown ornamentals. The residential
uses are very limited (approximately 600 pounds a.i. annually
on spot application to ant mounds and outdoor building perimeters),
and no homeowner applications are allowed. Therefore, there
is little potential for residential exposure.
Ref: October 28, 2005. Reregistration
Eligibility Decision (RED) for Tau-fluvalinate. List A.
Case No. 2295. US EPA. Federal Register Docket No. OPP-2005-0230-0002.
(Page 1.)
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau-fluvalinate.red.2005.pdf
|
Ataxia
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
Neurotoxic effects of tau fluvalinate were seen in rats after
administration by gavage of 60 mg/kg bw/day in corn oil for 7
days. Body weight decrease, symptoms such as fear, ruffled fur,
ataxia, startle response hyperreactivity,
spasms, and signs of neurotoxicity (reduced grip strength, irritability,
reduced motion, spasms and abnormal gait) were observed, accompanied
by nerve fibre degeneration correlating to incidence and severity
of the symptoms. Severity and number of the lesions were reduced
in animals allowed to recover for 7 days. 10 mg/kg bw/day resulted
in a marginal increase in vocalisation when handled and hyperalgesia.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- In a 2-generation rat study with racemic fluvalinate
reproduction was subnormal in all groups, including controls.
At dietary doses of 100 ppm and 500 ppm body
weights were reduced. At 500 ppm, the offspring showed
reduced viability, survival and growth
rates and parent animals showed skin lesions and reduced
body weight gains. Beginning with the low dose (20 ppm),
a dose dependent impairment of spermatogenesis was observed in
males of the F0 generation.
-- A 2-generation reproductin toxicity study in rats with tsau
fluvalinate showed parental and developmental effects in the mid
and high dose group. 2 of 4 males of the F1-generation from the
mediam dose group failing to mate had atrophic seminiferous tubules
in both testes and spermatozoa were partly absent from the epididymides.
Litter and mean pup weights of the F2 generation
of the mediam dose group were lower between
days 8 and 21. Incidence of fur loss and scabbing was a marginally
increased among adults. F1 and F2 pups of the highest dose group
had tremors, mainly arond lactation day 14, indicating toxic effects
of tau fluvalinate excreted in rat milk. As toenails of all animals
were clipped prior to treatment and later at weekly intervals
a final NOEL can not be derived. No adverse substance related
effects were observed at 0.5 mg/kg bw/day.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
Teratogeniciity studies on tau fluvalinate in rabbits showed increased
incidences of delayed ossification, and
visceral and skeletal malformations at an overt maternotoxic
dose (125 mg/kg bw). This dose salso caused increased numbers
of resorptions and poorer viability of fetuses. No teratogenic
effects occurred at lower doses. No reproduction studies with
tau fluvalinate in other species were submitted and the compound
has to be classified as possibly teratogenic.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
Dermal
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- The acute dermal toxicity of tau fluvalinate
in rabbits was low (LD 50> 20 g/kg/bw) with little percutaneous
absorption...
-- In 13-week toxicity studies in rats tau fluvalinate was given
in the diet or per gavage in corn oil. Pharmacotoxic effects and
skin lesions were observed at a dose of
1 mg/kg bw/day by gavage (NOEL proposed by expert). Dietary
exposure to the same dose also produced skin
lesions... Similar findings were recorded in mice receiving
tau fluvalinate in the diet for 13 weeks (lowest dose tested:
1 mg/kg bw). The NOEL in the rat study was
0.3 mg/kg bw.
-- 6-month toxicity studies on tau fluvalinate were not submitted.
Administratin of racemic fluvalinate in gelatine capsules for
6 months to dogs resulted in skin lesions
at the lowest dose tested and emesis, depression, diarrhoea,
and dehydration at higher doses.
-- A NOEL of 1 mg/kg bw for tau fluvalinate, derived from a 13-week
gavage study in rats is not acceptable as this dose led to pharmacodynamic
effects and skin problems. Only limited
information about biological effects of tau fluvalinate in mammals,
particularly in regard to acute neurotoxicity is given.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
Endocrine:
Breast
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
A 2-year study in mice showed no tumorigenic effects of dietary
tau fluvalinate. An increase of mammary
fibroadenomas in female rats in a 2-year gavage study is
judged to be a chance effect.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
Endocrine:
Testicular
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
--
In a 2-generation rat study with racemic fluvalinate reproduction
was subnormal in all groups, including controls... Beginning with
the low dose (20 ppm), a dose dependent impairment of spermatogenesis
was observed in males of the F0 generation.
-- A 2-generation reproduction toxicity study in rats with tau
fluvalinate showed parental and developmental effects in the mid
and high dose group. 2 of 4 males of the F1-generation from the
median dose group failing to mate had strophic
seminiferous tubles in both testes and spermatozoa
were partly absent from the epididymides. Litter and mean
pup weights of the F2 generation of the median dose group were
lower between days 8 and 21. Incidence of fur loss and scabbing
was a marginally increased among adults. F1 and F2 pups of the
highest groups had tremors, mainly around lactation day 14, indicating
toxic effects of tau fluvalinate excreted in rat milk. As
toenails of all animals were clipped prior to treatment and later
at weekly intervals a final NOEL can not be derived. No adverse
substance related effects were observed at 0.5 mg/kg bw/day.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
Eye (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Acute & Chronic Dietary (general population). LOAEL = 1 mg/kg/day.
Clinical signs in the rat chronic feeding study coupled with a
LOAEL of 2 mg/kg/day based on excessive grooming and bulging
eyes in the subchronic neurotoxicity study.
Ref:
October 28, 2005. Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) for
Tau-fluvalinate. List A. Case No. 2295. US EPA. Federal Register
Docket No. OPP-2005-0230-0002. (Page
1).
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau-fluvalinate.red.2005.pdf
Fetotoxic
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Teratogenicity studies on tau fluvalinate in rabbits showed
incidences of delayed ossification, and visceral and skeletal
malformations at an overt maternotoxic dose (125 mg/kg bw). This
dose also caused increased numbers of resorptions and poorer viability
of fetuses. No teratogenic effects occurred at lower
doses. No reproduction studies with tau fluvalinate in other species
were submitted and the compound has to be classified as possibly
teratogenic. No teratogenic effects of the less toxic racemic
fluvalinate were seen in rats. Doses of
10 and 50 mg/kg bw/day were materno- and fetotoxic.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
Lung
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Although the inhalation MOEs exceed 100
for all occupational scenarios at baseline level of protection
(long sleeve shirt, long pants, shoes and socks, and no respirator),
tau-fluvalinate labels also currently require respirators for
applicators and all other handlers for both indoor and outdoor
applications. Tau-fluvalinate may have a
special problem with regard to the unknown consequences resulting
from the property of this chemical to cause the “pyrethroid
reaction” once the respiratory tract is exposed to the chemical.
In particular, persons with asthma and emphysema may be especially
sensitive. Prevention of possible respiratory hazard associated
with the “pyrethroid reaction” will be accomplished
by maintaining the current label requirement for the use of respirators
for those product uses where spray mists or other potentially
respirable atmospheres containing tau-fluvalinate occur. In addition,
to confirm that the established restricted-entry interval (REI)
of 12 hours is adequate, the Agency will require the registrant
to conduct an inhalation post-application exposure study (OPPTS
Guideline 875.2500). (Page 33).
Ref:
October 28, 2005. Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) for
Tau-fluvalinate. List A. Case No. 2295. US EPA. Federal Register
Docket No. OPP-2005-0230-0002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau-fluvalinate.red.2005.pdf
Teratogen
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Teratogenicity studies on tau fluvalinate in rabbits showed incidences
of delayed ossification, and visceral and skeletal malformations
at an overt maternotoxic dose (125 mg/kg bw). This dose also caused
increased numbers of resorptions and poorer viability of fetuses.
No teratogenic effects occurred at lower doses. No reproduction
studies with tau fluvalinate in other species were submitted and
the compound has to be classified as possibly
teratogenic. No teratogenic effects of the less toxic racemic
fluvalinate were seen in rats. Doses of 10 and 50 mg/kg bw/day
were materno- and fetotoxic.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
Tremors
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--
A 2-generation reproduction toxicity study in rats with tau fluvalinate
showed parental and developmental effects in the mid and high
dose group. 2 of 4 males of the F1-generation from the median
dose group failing to mate had strophic seminiferous tubles in
both testes and spermatozoa were partly absent from the epididymides.
Litter and mean pup weights of the F2 generation of the median
dose group were lower between days 8 and 21. Incidence of fur
loss and scabbing was a marginally increased among adults. F1
and F2 pups of the highest groups had tremors,
mainly around lactation day 14, indicating toxic effects of tau
fluvalinate excreted in rat milk....
-- Neurotoxic effects of tau fluvalinate were seen in rats after
administration by gavage of 60 mg/kg bw/day in corn oil for 7
days. Body weight decrease, symptoms such as fear, ruffled fur,
ataxia, startle response hyperreactivity, spasms,
and signs of neurotoxicity (reduced grip strength, irritability,
reduced motion, spasms and abnormal gait) were observed, accompanied
by nerve fibre degeneration correlating to incidence and severity
of the symptoms. Severity and number of the lesions were reduced
in animals allowed to recover for 7 days. 10 mg/kg bw/day resulted
in a marginal increase in vocalisation when handled and hyperalgesia.
Ref: Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation of
Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
|
Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Considerable
accumulation of tau fluvalinate was observed in wax. Depending
on the location of the samples tau fluvalinate concentrations
varied from 0.2 mg/kg - 5.5 mg/kg, with a maximum of 26.9
mg/kg in one wax sample collected from a frame positioned
next to a strip.
Accumulation
in wax is the result of the stability of tau fluvalinate
in this matrix, its lipophilic character and the fact that
wax is normally reused over several seasons. Monitoring
of tau fluvalinate residues in honey and wax in Belgium
in 1989-1992 revealed that residues
in wax increased exponentially when the wax was reused over
the years. Transfer of tau fluvalinate residues from
wax to honey was shown to be negligible. However, the high
tau fluvalinate residues in wax should be taken into consideratin
in the evaluation of tau fluvalinate since contamination
of honey with wax particles has to be expected (0.5 % content
of water insoluble particles in honey is allowed).
Ref:
Revised
Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/021-REV1/95. Committee for Veterinary
Medicinal Products. The European Agency for the Evaluation
of Medicinal Products.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.1995.review.pdf
--
Environmental hazards:
Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse
effects in the aquatic environment.
-- Ecological
Information:
Very toxic to aquatic organisms.
Ecotoxicity:
Fish: LC 50 > 0.024 mg/l, 96 hours (rainbow trout).
Algae: EC 50 = >100 mg/l (72 hours).
Daphnia: LC 50 = 0.011 mg/l (48 hours)
Ref: Material Safety Data
Sheet for Klartan. : Code no. R-10834.G. Makhteshim Agan
(UK) Limited Unit 16, Thatcham Business Village, Colthrop
Way, Thatcham Berkshire RG19 4LW.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau.fluvalinate.msds.klarta.pdf
Table
8. Fish and Invertebrate Acute Risk Estimates
|
| Test
Species |
Crop
|
EEC
(ppb) |
EC50/LC50
(Ref. 2) |
Toxicity
Classification |
RQ
(Ref. 2) |
Freshwater
|
| Fish
(Carp) |
CA
carrots |
0.46
|
0.35 |
Highly
toxic |
1.3
|
| Fish
(Carp) |
OR
ornamental |
0.25 |
0.35 |
Highly
toxic |
0.7
|
Invertebrate
(Red swamp crayfish) |
CA
carrots |
0.46 |
0.31 |
Highly
toxic |
1.5 |
Invertebrate
(Red swamp crayfish) |
OR
ornamental |
0.25 |
0.31 |
Highly
toxic |
0.8 |
Marine/Estuarine
|
| Fish
(Sheepshead minnow) |
CA
carrots |
0.46
|
10.8
|
Slightly
toxic |
0.04 |
| Fish
(Sheepshead minnow) |
OR
ornamental |
0.25 |
10.8
|
Slightly
toxic |
0.02 |
| Invertebrate
(Mysid shrimp) |
CA
carrots |
0.46
|
0.02 |
Very
Highly toxic |
23.0
|
| Invertebrate
(Mysid shrimp) |
OR
ornamental |
0.25 |
0.02 |
Very
Highly toxic |
12.5 |
| Invertebrate
(Eastern oyster) |
CA
carrots |
0.46
|
12 |
Slightly
toxic |
0.04 |
| Invertebrate
(Eastern oyster) |
OR
ornamental |
0.25 |
12 |
Slightly
toxic |
0.02 |
1.
A statistically derived concentration that can be expected
to cause death in 50% of test animals.
2. Acute Risk Quotients are calculated using the following
formula: EEC/LC50. Acute LOC = 0.5. |
Ref:
October 28, 2005. Reregistration Eligibility Decision
(RED) for Tau-fluvalinate. List A. Case No. 2295. US
EPA. Federal Register Docket No. OPP-2005-0230-0002.
(Page
23-24).
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau-fluvalinate.red.2005.pdf
|
Risk
to Federally Listed Endangered and Threatened Species
Based on a screening-level assessment, tau-fluvalinate will
have no direct acute or chronic effect on listed avian species.
However, there is some evidence that suggests there is a
potential for sublethal effects to avian species. The screening
level assessment further indicates there is a potential
concern for direct effects to a variety of taxa, should
exposure actually occur at modeled level. These are as follows:
• Freshwater fish – exceeds
acute and chronic LOCs for California carrots and
nationwide ornamentals
• Marine/estuarine fish –
exceeds chronic LOC for California carrots and nationwide
ornamentals
• Freshwater invertebrates –
exceeds acute and chronic LOCs for California carrots
and nationwide ornamentals
• Marine/estuarine invertebrates
– exceeds acute LOC (Mysid) for California
carrots and nationwide ornamentals
• Mammals – exceeds acute
LOC for small mammals feeding on short grass for
nationwide ornamentals. Exceeds chronic
LOC for all size mammals (short and tall grass, broadleaf
plants and small insects for California carrots and nationwide
ornamentals); all size mammals
(fruits, pods and large insects for nationwide ornamentals);
and small mammals feeding on seeds
for nationwide ornamentals.
As a pyrethroid, tau-fluvalinate has
a tendency to adsorb to glass. Thus, there is uncertainty
surrounding the data that was used to determine toxicity
to aquatic organisms, and it is possible that calculated
risks to aquatic species may be underestimated. Additional
data is being required to address this uncertainty. Because
of this uncertainty, we can not currently preclude the possibility
of effects to aquatic species. Although the Agency expects
taufluvalinate to pose an acute risk to nontarget insects
because tau-fluvalinate is highly toxic to honeybees (acute
contact LD50 is 0.2 g/bee), an assessment method for estimating
the risk to bees is not yet available; therefore, we can
not preclude the possibility of potential effects to listed
insect species. The Agency currently does not have data
to quantify risks for taufluvalinate at the screening-level
and can not preclude potential direct effects to plants
or chronic effects to estuarine/marine invertebrates. Finally,
the Agency can not preclude the potential for indirect effects
to listed species that may be dependent upon taxa that experience
direct effects from the use of tau-fluvalinate. These findings
are based solely on EPA’s screening-level assessment
and do not constitute “may affect” findings
under the Endangered Species Act (ESA) for any listed species
(page 28-29).
Ref:
October 28, 2005. Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED)
for Tau-fluvalinate. List A. Case No. 2295. US EPA. Federal
Register Docket No. OPP-2005-0230-0002.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/tau-fluvalinate.red.2005.pdf
|
|

