|
Return
to Sulfentrazone Index Page
Activity:
Herbicide
(triazolone)
Structure:
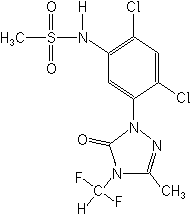
Adverse Effects:
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Endocrine: Prostate
Endocrine: Testicular
Endocrine: Vaginal
Liver
Spleen
Environmental
•
Persistent in soils
•
Groundwater Contaminant
• Highly Toxic to Estuarine/Marine
Organisms
•
Phototoxic
As
of February 12, 2005, this herbicide is permitted in
or on 51 food commodities
in the United States - see list below.
|
Anemia
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Subchronic toxicity.
A 90-day subchronic toxicity study was conducted in rats, with
dietary intake levels of 0, 3.3, 6.7, 19.9, 65.8, 199.3, or 534.9
mg/kg/day for males and 0, 4, 7.7, 23.1, 78.1, 230.5, or 404.3
mg/kg/day for females respectively. NOAELs of 19.9 mg/ kg/day
in males and 23.1 mg/kg/day in females were based on clinical
anemia.
Ref: Federal Register, March 7, 2003 (Volume
68, Number 45)] [Notices] [Page 11096-11100]. Notice of Filing
Pesticide Petitions to Establish Tolerances for a Certain Pesticide
Chemical in or on Food.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Sulfentrazone.FR.Mar.7.2003.htm
-- 90-Day oral toxicity
rodents (rats) - [870.3100] NOAEL = 19.9 milligrams/kilogram/day
(mg/ kg/day) for males and 23.1 mg/kg/ day for females LOAEL =
65.8 mg/kg/ day for males and 78.1 mg/kg/day for females based
on clinical signs of anemia (reduced
hematocrit, hemoglobin, mean cell volume, and mean cell hemoglobin
values during treatment)
-- Chronic toxicity dogs - [870.4100] NOAEL = 24.9 mg/kg/day for
males and 29.6 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL = 61.2 mg/kg/ day for
males and 61.9 mg/kg/day for females based on compensated normochromic
microcytosis
Ref:
Federal Register: September 24, 2003. Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
•
Definitions:
Normochromic:
Being normal in colour; referring especially to red blood cells
that possess the normal quantity of haemoglobin.
Microcytosis: a
blood disorder characterized by the presence of microcytes (abnormally
small red blood cells) in the blood; often
associated with anemia.
Blood
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- A 1-year feeding
oral study was performed on dogs. The induction of normochromic
microcytosis in animals fed diets containing 1800 ppm test material,
although compensated by increased red cell production, reflects
an adverse treatment-related effect. The microcytosis may
have arisen from the inhibition of heme synthesis as indicated
by the presence of brown to yellow/brown pigmentation in hepatocytes
and reticuloendothelial cells of the liver. The microcytosis induced
by sulfentrazone justifies an oral LOEL of 61.2 mg/kg/day for
males and 61.9 mg/kg/day for females. The NOEL is 24.9 mg/kg/day
for males and 29.6 mg/kg/day for females.
-- A 18-month feeding/carcinogenicity study in mice resulted a
LOEL of 160.5 mg/kg/day in males and 198.0 mg/kg/day in females,
based upon treatment-related decreases in
hemoglobin and hematocrit. The NOEL is 93.9 mg/kg/day in
males and 116.9 mg/kg/day in females.
-- A developmental toxicity study in rats resulted in a maternal
(systemic) LOEL of 50.0 mg/kg/day based upon increased relative
spleen weight and splenic extramedullary hematopoiesis. The
maternal (systemic) NOEL is 25.00 mg/kg/day...
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Sulfentrazone
Reason for Issuance: Registration of a New Chemical Date Issued:
February 27, l997.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/sulfentrazone.pdf
-- 90-Day oral toxicity
rodents (mice) - [870.3100] NOAEL = 60 mg/kg/day for males and
79.8 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL = 108.4 mg/ kg/day for males
and 143.6 mg/kg/ day for females based on decreased body weights,
body weight gains, red blood cells, hemoglobin,
hematocrit, and severity of splenic micropathology (increased
incidence and severity of extramedullary hematopoiesis)
-- 90-Day oral toxicity in nonrodents (dogs) - [870.3150] NOAEL
= 28 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 57 mg/kg/ day for males and 73 mg/kg/day
for females based on decreased body weights (7-10%) and body weight
gains during first 5 weeks of study; decreased
hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean cell volume, mean cell hemoglobin
and mean cell hemoglobin concentration, and increased absolute
liver weights and alkaline phosphatase levels, and microscopic
changes in the liver and spleen (pigmented sinusoidal microphages
in the liver, swollen centrilobular hepatocytes and pigmented
reticuloendotheli al cells in the spleen)
-- Carcinogenicity mice - [870.4200] NOAEL = 93.9 mg/kg/ day for
males and 116.9 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL = 160.5 mg/ kg/day
for males and 198.0 mg/kg/ day for females
based on dose- related decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit
by study termination. No evidence of carcinogenicity
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rats - [870.4300]
NOAEL = 40 mg/kg/day for males and 36.4 mg/kg/day in females LOAEL
= 82.2 mg/kg/ day for males and 67 mg/kg/day for females based
on dose-related decreased body weights (11 and 19%), body weight
gains (13 and 26%), food consumption (13 and 19%), hemoglobin,
hematocrit, mean cell volume, and mean cell hemoglobin. Increased
nucleated red blood cells and reticulocytes in bone of females
at 124.7 mg/kg/ day. No evidence of carcinogenicity
Ref:
Federal Register: September 24, 2003. Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- A developmental
toxicity study in rats resulted in
a maternal (systemic) LOEL of 50.0 mg/kg/day based upon increased
relative spleen weight and splenic extramedullary hematopoiesis.
The maternal (systemic) NOEL is 25.00 mg/kg/day. The developmental
(fetal) LOEL is 25.0 mg/kg/day based upon 1) decreased
mean fetal weight and 2) retardation in skeletal development
as evidenced by an increased number of litters with any variation
and by decreased numbers of caudal vertebral and metacarpal ossification
sites. The developmental (fetal) NOEL is 10.0 mg/kg/day. Evidence
of treatment-related developmental toxicity consisted of decreased
fetal viability, decreased fetal body weight,
and increased incidence of fetal alterations, comprised, for the
most part, of skeletal malformations and variations. A supplementary
prenatal oral developmental toxicity study in rats confirmed the
maternal and fetal findings of the previously conducted study
and did not alter the study conclusions.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Sulfentrazone
Reason for Issuance: Registration of a New Chemical Date Issued:
February 27, l997.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/sulfentrazone.pdf
-- 90-Day oral toxicity rodents (mice)
- [870.3100] NOAEL = 60 mg/kg/day for males and 79.8 mg/kg/day
for females LOAEL = 108.4 mg/ kg/day for males and 143.6 mg/kg/
day for females based on decreased body
weights, body weight gains, red blood cells, hemoglobin,
hematocrit, and severity of splenic micropathology (increased
incidence and severity of extramedullary hematopoiesis)
-- 90-Day oral toxicity in nonrodents (dogs)
- [870.3150] NOAEL = 28 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 57 mg/kg/ day for males
and 73 mg/kg/day for females based on decreased
body weights (7-10%) and body weight gains during first
5 weeks of study; decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean cell
volume, mean cell hemoglobin and mean cell hemoglobin concentration,
and increased absolute liver weights and alkaline phosphatase
levels, and microscopic changes in the liver and spleen (pigmented
sinusoidal microphages in the liver, swollen centrilobular hepatocytes
and pigmented reticuloendotheli al cells in the spleen)
-- 2-Generation reproduction and fertility effects (rats)
- [870.3800] Parental/Systemic NOAEL = 14 mg/kg/day for males
and 16 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL = 33 mg/kg/ day for males and
40 mg/kg/day for females based on decreased
maternal body weight/body weight gain during
gestation in both generation (P and F1) and reduced
premating body weight gain in second generation (F1) males
Reproductive NOAEL = 14 mg/kg/ day for males and 16 mg/kg/day
for females LOAEL = 33 mg/kg/ day for males and 40 mg/kg/day for
females based on increased duration of gestation in females and
degeneration and/ or atrophy of the germinal epithelium of the
testes and oligospermia and intratubular degenerated seminal material
in the epididymis of F1 males Offspring NOAEL = 14 mg/kg/ day
for males and 16 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL = 33 mg/kg/ day for
males and 40 mg/kg/day for females based on reduced prenatal viability
(fetal and litter), reduced litter size, increased number of stillborn
pups, reduced pup and litter postnatal survival and decreased
pup body weights throughout lactation
-- Reproduction and fertility effects (rat).
Nonguideline - [870.3800] Parental/Systemic NOAEL = 20 mg/kg/day
LOAEL = 51 mg/kg/ day (F1 females) based on decrease
in pre-mating body weight gain (10%) Offspring and Reproductive
NOAEL = 16 mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 40 mg/kg/ day based on reduced
gestation day 20 fetal weights; decreased
postnatal day 0, 4 and 7 pup weights; decreased pup survival;
delayed vaginal patency; reduced epididymal, prostate, and testicular
weights Additional information supports the conclusions reached
in the 2- generation reproduction study in rats
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rats
- [870.4300] NOAEL = 40 mg/kg/day for males and 36.4 mg/kg/day
in females LOAEL = 82.2 mg/kg/ day for males and 67 mg/kg/day
for females based on dose-related decreased
body weights (11 and 19%), body weight gains (13 and 26%), food
consumption (13 and 19%), hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean cell volume,
and mean cell hemoglobin. Increased nucleated red blood cells
and reticulocytes in bone of females at 124.7 mg/kg/ day. No evidence
of carcinogenicity
-- Subchronic neurotoxicity screening battery - [870.6200]. NOAEL
= 30 mg/kg/day for males and 37 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL =
150 mg/kg/ day for males and 180 mg/kg/day for females based on
increased incidence of clinical signs; decreased
body weight, body weight gains, and food consumption in
females; and increased motor activity in females. At 5,000 ppm,
included increased mortality; decreased
body weights, and body weight gains in males; decreased
hindlimb grip strength and increased tail flick latency in males
at week 8; distended bladders with red fluid and enlarged spleen.
No evidence of neuropathology at 2,500 and 5,000 ppm.
Ref:
Federal Register: September 24, 2003. Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
Bone
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
-- A developmental
toxicity study in rats resulted in
a maternal (systemic)... The developmental (fetal) LOEL is 25.0
mg/kg/day based upon 1) decreased
mean fetal weight and
2) retardation in skeletal development as
evidenced by an increased number of litters with any variation
and by decreased numbers of caudal vertebral and metacarpal ossification
sites. The developmental (fetal) NOEL is 10.0 mg/kg/day.
Evidence of treatment-related developmental toxicity consisted
of decreased fetal viability, decreased
fetal body weight, and increased incidence of fetal alterations,
comprised, for the most part, of skeletal
malformations and variations. A supplementary prenatal
oral developmental toxicity study in rats confirmed the maternal
and fetal findings of the previously conducted study and did not
alter the study conclusions.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Sulfentrazone
Reason for Issuance: Registration of a New Chemical Date Issued:
February 27, l997.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/sulfentrazone.pdf
-- Developmental Study
in rats. Developmental LOAEL = 25
mg/kg/day based on decreased fetal weight and retarded skeletal
development as evidenced by an increased number of litters with
any variation and by decreased numbers of caudal vertebral and
metacarpal ossification sites.
-- In the dermal developmental study in rats,
the maternal (systemic) NOAEL was 250 mg/kg/day and a LOAEL was
not determined. The developmental (fetal) NOAEL was 100 mg/kg/day,
based on decreased fetal weight and increased fetal variations
(hypoplastic or wavy ribs, incompletely
ossified lumbar vertebral arches,
incompletely ossified ischia or pubes,
and reduced numbers of thoracic vertebral
and rib ossification sites) at the LOAEL of 250 mg/kg/day.
Ref: Federal Register. August 1, 2001. Sulfentrazone;
Pesticide Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.aug1.2001.htm
A developmental toxicity
study in rabbits was conducted at
gavage dose levels of 0, 100, 250, or 375 mg/kg/day... The maternal
(systemic) NOEL is 100 mg/kg/day. Skeletal
evaluation in fetuses revealed dose- and treatment-related
findings at the 375 mg/kg/day dose level. These included
significant increases in both the fetal and litter incidences
of fused caudal vertebrae (a malformation) and of partially fused
nasal bones (a variation). In addition, at 375 mg/kg/day,
significant treatment-related reductions in ossification site
averages were observed for metacarpals and both fore- and hindpaw
phalanges
Ref: Federal Register: March 10, 1997. Sulfentrazone;
Establishment of Tolerances. Final Rule. Federal Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Sulfentrazone.FR.Mar10.1997.htm
Prenatal developmental
in rodents (rats) - [870.3700] LOAEL
= 25 mg/kg/ day based on decreased mean fetal weights, and retardation
in skeletal development evidenced by an increased number
of litters with any variation and by decreased
number of caudal vertebral and metacarpal ossification sites Maternal
NOAEL = 250 mg/kg/day LOAEL was not established. Developmental
NOAEL = 100 mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 250 mg/kg/ day based on decreased
fetal body weight; increased incidence of fetal variations: hypoplastic
or wavy ribs, incompletely ossified lumbar vertebral arches, and
incompletely ossified ischia or pubis [see
definitions below]; and reduced number of thoracic vertebral
and rib ossification sites.
-- Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity
rats - [870.4300] NOAEL = 40 mg/kg/day
for males and 36.4 mg/kg/day in females LOAEL = 82.2 mg/kg/ day
for males and 67 mg/kg/day for females based on dose-related decreased
body weights (11 and 19%), body weight gains (13 and 26%), food
consumption (13 and 19%), hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean cell volume,
and mean cell hemoglobin. Increased nucleated red blood cells
and reticulocytes in bone of females at
124.7 mg/kg/ day. No evidence of carcinogenicity
Ref:
Federal Register: September 24, 2003. Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
•
Definitions:
Ischia (plural of Ischium):
The
ventral and posterior of the three principal bones composing
either half of the pelvis; seat bone; the huckle bone.
Pubis: one of the
three sections of the hipbone; together the two pubic bones
form the front of the pelvis
52988-0047 220351 (EPA MRID#: unknown), Freeman, C., “F6285
Technical: Teratology study in rats (oral),” FMC Corporation
Toxicology Laboratory, Princeton, NJ; and Argus Research Laboratories,
Inc., Horsham, PA, Aug. 4, 1993. Laboratory Study #: FMC Study
No. A91-3410. Pregnant Crl:CD®BR VAF/Plus® dams, 25/group,
were dosed by gavage (5 ml/kg corn oil vehicle) with 0, 1, 10,
25, or 50 mg/kg/day Sulfentrazone (F6285 Technical), purity 94.2%,
during gestation days 6-15 in a standard developmental toxicity
study. Maternal NOEL = 25 mg/kg/day. At 50 mg/kg/day there were
decreased maternal body weight gains during late gestation, attributable
to decreased gravid uterine weights due to increased resorptions
(6.0 resorptions/dam in the 50 mg/kg/day group, compared to a
range of 0.3 to 0.9/dam in controls and lower dose groups).
About 22% of 50 mg/kg/day group resorptions
were late resorptions, which normally occur only in about 0.02%
of implantations (based on historical control data).
There were three fetal deaths at 50 mg/kg/day, also an uncommon
occurrence in historical controls. Vaginal bleeding was
observed in ten 50 mg/kg/day dams compared to 0 controls (considered
by investigators as associated with the increased resorptions).
Also, 50 mg/kg/day dams had increased spleen weights and increased
severity of splenic extramedullary hematopoiesis compared to controls
and lesser dose groups. Developmental toxicity NOEL = 10 mg/kg/day.
Dose related findings at 25 and 50 mg/kg/day included diminished
body weights of fetuses (reductions of 7% and 19%, respectively,
compared to concurrent controls). Statistically
significant skeletal observations at 25 and 50 mg/kg/day were
reduced ossification sites of caudal vertebrae and metacarpals.
Developmental toxicity at 50 mg/kg/day was marked by malformations
[whole body edema (anasarca) in 4 fetuses (4 litters),
short ribs in 2 fetuses (1 litter), and bent radius and ulna in
3 fetuses (2 litters): all of these considered treatment-related
because of low concurrent and historical control incidences].
Also common at 50 mg/kg/day were wavy ribs
[30 fetuses (16 litters), compared with 1 or 0 fetuses
per group in controls and lower dose groups] and wide-spread
additional ossification delays. This study indicates a
“possible adverse effect” and
was flagged as such by investigators under 40 CFR 158.34, because
the fetal NOEL is lower than the maternal NOEL. Overall,
developmental toxicity findings at 25 mg/kg/day were modest, and
the dose-response between 25 and 50 mg/kg/day was quite sharp.
Study is acceptable. Aldous, 11/29/05.
Ref: January
13, 2006: Summary of toxicology data: Sulfentrazone (F2685). California
EPA. Department of Pesticide Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.ca.epa.2006.pdf
Brain
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
TERATOLOGY, RABBIT **52988-0038 217369, “F6285 Technical,
Teratology Study in Rabbits (Oral)”, ©. Freeman, FMC
Corporation, Toxicology Laboratory, Princeton, NJ., Study No.
A92-3540, 22 June 1993). 20 mated female New Zealand White rabbits
per group received F6285 Technical (94.2 ± 0.5% sulfentrazone)
by oral gavage at 0 (corn oil), 100, 250, and 375 mg/kg/day on
gestation days 7 through 19. There were no treatment-related deaths.
Two dams per group at 100 and 250 mg/kg/day died due to misdosing.
One 375 mg/kg/day dam was sacrificed due to misdosing. Five dams
at 375 mg/kg/day aborted (two on day 21 and one each on days 22,
23, and 24). The mean number of implants and the mean number of
early resorptions were significantly increased at 250 and 375
mg/kg/day. 13, 13, 16, and 18 dams at 0, 100, 250, and 375 mg/kg/day
respectively exhibited decreased feces during the study and hematuria
was recorded for 1 and 16 dams at 250 and 375 mg/kg/day respectively.
Significantly reduced bodyweights were recorded for dams at 250
and 375 mg/kg/day on gestation days 19 and 29 compared to controls
and bodyweight gains were significantly reduced during the dosing
period and overall for days 0 through 29. Fetal weights were significantly
reduced at 250 and 375 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related findings
for fetal external and internal exams. Two treatment related skeletal
malformations were noted at 375 mg/kg/day. One
fetus had incompletely or not ossified frontals,
parietals, interparietals, suppraoccipital bones, and execenphaly.
Although not statistically significant, the findings were considered
treatment-related since they occurred only at the high dose and
because execenphaly is uncommon in the rabbit strain.
Additionally, 3 fetuses from 3 different dams had fused caudal
vertebrae. The incidence was statistically significant and was
higher than the historical control values. Treatment-related skeletal
variations included statistically significant litter and fetal
incidences of partially fused nasal bones at 375 mg/kg/day. Also,
4 litter mates at 375 mg/kg/day had unossified pubes. Finally,
the average number of ossified sternal centers, tarsal bones,
forepaw and hindpaw phlanges and metacarpal bones was significantly
reduced in fetuses at 375 mg/kg/day. Maternal NOEL = 100 mg/kg/day
(reduced bodyweight). Developmental NOEL = 100 mg/kg/day (reduced
fetal weight, increased early resorptions). No teratogenicity.
Acceptable. (Green and Leung, 12/13/05)
Was execenphaly a spelling error? Should
it read exencephaly? Definition exencephaly
- A condition in which the skull is defective, causing exposure
or extrusion of the brain.
Ref: January
13, 2006: Summary of toxicology data: Sulfentrazone (F2685). California
EPA. Department of Pesticide Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.ca.epa.2006.pdf
Endocrine:
Prostate
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproduction and fertility
effects (rat) Nonguideline - [870.3800] Parental/Systemic NOAEL
= 20 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 51 mg/kg/ day (F1 females) based on decrease
in pre-mating body weight gain (10%) Offspring and Reproductive
NOAEL = 16 mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 40 mg/kg/ day based on reduced gestation
day 20 fetal weights; decreased postnatal day 0, 4 and 7 pup weights;
decreased pup survival; delayed vaginal
patency; reduced epididymal, prostate,
and testicular weights Additional information supports the conclusions
reached in the 2- generation reproduction study in rats
Ref:
Federal Register: September 24, 2003. Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
Endocrine:
Testicular
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Toxicological Profile...
A two-generation reproduction study in the rat at dietary levels
of 14, 33, or 46 mg/kg/day in males and 16, 40, or 56 mg/kg/day
in females established a NOEL for systemic and reproductive/ developmental
parameters of 14 mg/kg/day for males and 16 mg/kg/day for females.
The LOEL for systemic and reproductive/development parameters
was 33 mg/kg/day for males and 40 mg/kg/day for females. Systemic
effects were comprised of decreased body weight gains, while reproductive/developmental
effect at the LOEL included degeneration
and/or atrophy in the testes, with epididymal sperm deficits,
in the second (F1) generation males. Male
fertility in the F1 generation was reduced at higher doses;
litter size, pup survival, and pup body weight for both generations
were also effected at higher doses.
Ref: Federal Register: March 10, 1997. Sulfentrazone;
Establishment of Tolerances. Final Rule. Federal Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Sulfentrazone.FR.Mar10.1997.htm
-- Chronic dietary (all populations) NOAEL= 14.0 mg/kg/day. 2-Generation
Reproduction in Rats. LOAEL = 33/44 mg/kg/day in males and females,
respectively, based on: (1) Decreased maternal body weight and/or
body weight gain during gestation in both P and F1 generations,
(2) reduced premating body weight gains in the second generation
(F1 adults), (3) increased duration of gestation in both F1 and
F2 dams, (4) reduced prenatal viability (fetal and litter), (5)
reduced litter size, (6) increased number of stillborn pups, (7)
reduced pup and litter postnatal survival, and (8) decreased pup
body weights throughout gestation. In males, effects included
decreased fertility in F1 generation
and/or atrophy of the germinal epithelium
of the testes, oligospermia and intratubular degeneration of the
seminal product in the epididymis.
Ref: Federal Register. August 1, 2001. Sulfentrazone;
Pesticide Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Sulfentrazone.FR.Aug1.2001.htm
-- Reproduction and
fertility effects (rat) Nonguideline - [870.3800] Parental/Systemic
NOAEL = 20 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 51 mg/kg/ day (F1 females) based
on decrease in pre-mating body weight gain (10%) Offspring and
Reproductive NOAEL = 16 mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 40 mg/kg/ day based
on reduced gestation day 20 fetal weights; decreased postnatal
day 0, 4 and 7 pup weights; decreased pup survival;
delayed vaginal patency; reduced epididymal,
prostate, and testicular weights.
Additional information supports the conclusions reached
in the 2- generation reproduction study in rats
-- 2-Generation reproduction and fertility effects (rats) - [870.3800]
Parental/Systemic... Reproductive NOAEL = 14 mg/kg/ day for males
and 16 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL = 33 mg/kg/ day for males and
40 mg/kg/day for females based on increased duration of gestation
in females and degeneration and/ or atrophy
of the germinal epithelium of the testes and oligospermia and
intratubular degenerated seminal material in the epididymis of
F1 males...
Ref:
Federal Register: September 24, 2003. Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
Endocrine:
Vaginal
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproduction and fertility
effects (rat) Nonguideline - [870.3800] Parental/Systemic NOAEL
= 20 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 51 mg/kg/ day (F1 females) based on decrease
in pre-mating body weight gain (10%) Offspring and Reproductive
NOAEL = 16 mg/kg/ day LOAEL = 40 mg/kg/ day based on reduced gestation
day 20 fetal weights; decreased postnatal day 0, 4 and 7 pup weights;
decreased pup survival; delayed vaginal
patency; reduced epididymal, prostate, and testicular weights
Additional information supports the conclusions reached in the
2- generation reproduction study in rats
Ref:
Federal Register: September 24, 2003. Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Chronic toxicity. A 12-month feeding study in dogs was dosed
at levels of 0.0, 24.9, or 61.2 mg/kg/day for male dogs and 0.0,
10.4, 29.6, or 61.9 [[Page 11100]] mg/kg/day for female dogs in
the control through high-dose groups, respectively, with a NOAEL
of 24.9 mg/kg/day for males and 29.6 mg/kg/ day for females based
on hematology effects and microscopic
liver changes.
-- In a 90-day subchronic feeding study in dogs administered
by dietary admix at doses of 0, 10, 28, or 57 mg/kg/day for males
and 0, 10, 28, or 73 mg/kg/day for females, a NOAEL of 28 mg/kg/day
was determined for both males and females based on decreases
in Hgb and HCT, elevated alkaline phosphatase levels, increased
liver weights and microscopic liver as well as splenic changes.
Ref: Federal Register, March 7, 2003 (Volume
68, Number 45)] [Notices] [Page 11096-11100]. Notice of Filing
Pesticide Petitions to Establish Tolerances for a Certain Pesticide
Chemical in or on Food.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Sulfentrazone.FR.Mar.7.2003.htm
-- 90-Day oral toxicity
in nonrodents (dogs) - [870.3150]
NOAEL = 28 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 57 mg/kg/ day for males and 73 mg/kg/day
for females based on decreased body weights
(7-10%) and body weight gains during first 5 weeks of study; decreased
hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean cell volume, mean cell hemoglobin
and mean cell hemoglobin concentration, and increased
absolute liver weights and alkaline phosphatase levels,
and microscopic changes in the liver
and spleen (pigmented sinusoidal microphages
in the liver, swollen centrilobular hepatocytes and pigmented
reticuloendotheli al cells in the spleen)
Ref:
Federal Register: September 24, 2003. Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
Spleen
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
A prenatal oral developmental
toxicity study in the rat with dose levels at 25.0 or 50.0 mg/kg/day
established a maternal NOEL of 25 mg/kg/day based on decreased
body weight gain, increased spleen
weight, and microscopic changes in the spleen,
and a fetal NOEL of 10 mg/kg/day was based on fetal death, reduced
body weights, and alterations in skeletal development at higher
doses... Risk to infants and children was determined by use of
developmental toxicity studies in rats and a two-generation reproduction
study in rats. The oral developmental toxicity studies resulted
in a maternal NOEL of 25 mg/kg/day based on decreased body weight
gain, increased spleen weight, and
microscopic changes in the spleen,
and a fetal NOEL of 10 mg/kg/day based on fetal death, reduced
body weights, and alterations in skeletal development at higher
doses.
Ref: Federal Register: March 10, 1997.
Sulfentrazone; Establishment of Tolerances. Final Rule. Federal
Register.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Sulfentrazone.FR.Mar10.1997.htm
-- 90-Day oral toxicity
rodents (mice) - [870.3100] NOAEL
= 60 mg/kg/day for males and 79.8 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL
= 108.4 mg/ kg/day for males and 143.6 mg/kg/ day for females
based on decreased body weights, body weight gains, red blood
cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and severity
of splenic micropathology (increased incidence and severity of
extramedullary hematopoiesis)
-- 90-Day oral toxicity in nonrodents (dogs)
- [870.3150] NOAEL = 28 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 57 mg/kg/ day for males
and 73 mg/kg/day for females based on decreased body weights (7-10%)
and body weight gains during first 5 weeks of study; decreased
hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean cell volume, mean cell hemoglobin
and mean cell hemoglobin concentration, and increased absolute
liver weights and alkaline phosphatase levels, and microscopic
changes in the liver and spleen (pigmented
sinusoidal microphages in the liver, swollen centrilobular hepatocytes
and pigmented reticuloendotheli al cells in the spleen)
-- Prenatal developmental in rodents (rats)
- [870.3700] Maternal NOAEL = 25 mg/kg/day LOAEL = 50 mg/kg/ day
based on increased relative splenic extramedullary
hematopoiesis
-- Subchronic neurotoxicity screening battery - [870.6200] NOAEL
= 30 mg/kg/day for males and 37 mg/kg/day for females LOAEL =
150 mg/kg/ day for males and 180 mg/kg/day for females based on
increased incidence of clinical signs; decreased body weight,
body weight gains, and food consumption in females; and increased
motor activity in females. At 5,000 ppm, included increased mortality;
decreased body weights, and body weight gains in males; decreased
hindlimb grip strength and increased tail flick latency in males
at week 8; distended bladders with red fluid and enlarged
spleen. No evidence of neuropathology at 2,500 and 5,000
ppm.
Ref: Federal Register: September 24, 2003.
Sulfentrazone; Pesticide Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.fr.sept24.03.htm
Teratogen (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
52988-0047 220351 (EPA MRID#: unknown), Freeman, C., “F6285
Technical: Teratology study in rats (oral),” FMC Corporation
Toxicology Laboratory, Princeton, NJ; and Argus Research Laboratories,
Inc., Horsham, PA, Aug. 4, 1993. Laboratory Study #: FMC Study
No. A91-3410. Pregnant Crl:CD®BR VAF/Plus® dams, 25/group,
were dosed by gavage (5 ml/kg corn oil vehicle) with 0, 1, 10,
25, or 50 mg/kg/day Sulfentrazone (F6285 Technical), purity 94.2%,
during gestation days 6-15 in a standard developmental toxicity
study. Maternal NOEL = 25 mg/kg/day. At 50 mg/kg/day there were
decreased maternal body weight gains during late gestation, attributable
to decreased gravid uterine weights due to increased resorptions
(6.0 resorptions/dam in the 50 mg/kg/day group, compared to a
range of 0.3 to 0.9/dam in controls and lower dose groups).
About 22% of 50 mg/kg/day group resorptions were late resorptions,
which normally occur only in about 0.02% of implantations (based
on historical control data). There were three fetal deaths
at 50 mg/kg/day, also an uncommon occurrence in historical controls.
Vaginal bleeding was observed in ten 50 mg/kg/day dams compared
to 0 controls (considered by investigators as associated with
the increased resorptions). Also, 50 mg/kg/day dams had increased
spleen weights and increased severity of splenic extramedullary
hematopoiesis compared to controls and lesser dose groups. Developmental
toxicity NOEL = 10 mg/kg/day. Dose related findings at 25 and
50 mg/kg/day included diminished body weights
of fetuses (reductions of 7% and 19%, respectively, compared
to concurrent controls). Statistically significant
skeletal observations at 25 and 50 mg/kg/day were reduced ossification
sites of caudal vertebrae and metacarpals. Developmental
toxicity at 50 mg/kg/day was marked by malformations
[whole body edema (anasarca) in 4 fetuses (4 litters), short ribs
in 2 fetuses (1 litter), and bent radius and ulna in 3 fetuses
(2 litters): all of these considered treatment-related
because of low concurrent and historical control incidences].
Also common at 50 mg/kg/day were wavy ribs
[30 fetuses (16 litters), compared with 1 or 0 fetuses
per group in controls and lower dose groups] and wide-spread
additional ossification delays. This study indicates a
“possible adverse effect” and
was flagged as such by investigators under 40 CFR 158.34, because
the fetal NOEL is lower than the maternal NOEL. Overall,
developmental toxicity findings at 25 mg/kg/day were modest, and
the dose-response between 25 and 50 mg/kg/day was quite sharp.
Study is acceptable. Aldous, 11/29/05.
Ref: January
13, 2006: Summary of toxicology data: Sulfentrazone (F2685). California
EPA. Department of Pesticide Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.ca.epa.2006.pdf
| Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Phototoxic
Pesticide.
Light-dependent peroxidizing herbicides (LDPHs).
US EPA identified the organofluorine herbicides
Acifluorfen, Azafenidin, Carfentrazone-ethyl, Flumiclorac-penty,
Flumioxazin, Fluthiacet-methyl, Fomesafen, Lactofen, Oxadiargyl,
Oxadiazon, Oxyfluorfen, Sulfentrazone,
Thidiazimin as phototoxic
pesticides that act by inhibiting protoporphyringen
oxidase in the heme and chlorophyll biosynthetic pathway.
[10 out of the 13 pesticides that EPA identified are organofluorines].
SEE http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/PHOTOTOXICITY.PAGE.htm
Ref: December 11, 2001 - US EPA. Revised
Environmental Fate and Effects Division Preliminary Risk
Assessment for the Oxyfluorfen Reregistration Eligibility
Decision Document - also at: http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/reregistration/oxyfluorfen/oxyefedchap.pdf
Persistent
in Soil.
Enviornmental Fate: A typical
half-life for sulfentrazone in soils is 541 days...
Sulfentrazone's potential to leach to groundwater is high;
surface runoff potential is high, and potential for loss on
eroded soil is intermediate.
Ref:
Sulfentrazone. Roadside Vegetation Management Herbicide Fact
Sheet. Washington State Department of Transportation.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfentrazone.wa.state.facts.pdf
--
Environmental Characteristics. Acceptable information from
environmental fate studies with respect to the persistence
and mobility of sulfentrazone under laboratory and field
conditions has been reviewed. Based on the current environmental
fate data base, sulfentrazone has the following characteristics:
1) moderately soluble, 2) not susceptible to hydrolysis,
3) extremely susceptible to direct photolysis in water,
4) very stable to photolysis on soil, 5) aerobic half-life
of 1.5 years, 6) anaerobic half-life of 9 years, 7) very
high mobility in soil (average Koc = 43, Kd < 1), and 8)
low volatility from soils and water. With these properties,
it appears that sulfentrazone is highly
mobile and persistent, and has a strong potential to leach
into groundwater and move offsite to surface water.
-- Potential to Contaminate Groundwater. A groundwater exposure
estimate for sulfentrazone was conducted based on findings
from a prospective groundwater monitoring study in North
Carolina. Although the study was incomplete, enough data
were collected to confirm that sulfentrazone
leaches substantially to groundwater in areas with sandy
soils.
-- Aquatic. Sulfentrazone is practically non-toxic to the
rainbow trout (LC50 ) greater 120 ppm) and slightly toxic
to the bluegill sunfish (93.8 ppm). The results indicate
that sulfentrazone is slightly toxic to fish on an acute
basis. The chronic results indicate that sulfentrazone significantly
affects young fish survival and growth at aquatic concentrations
as low as 5.93 ppm. Sulfentrazone is slightly toxic to aquatic
invertebrates on an acute basis. The results from data from
chronic freshwater invertebrates indicate that survival
of young daphnids is adversely affected
at sulfentrazone concentrations as low as 0.51 ppm.
The results from acute estuarine and marine animals study
are incomplete but indicate that sulfentrazone is
highly toxic to estuarine/marine organisms.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact
Sheet. Sulfentrazone Reason for Issuance: Registration of
a New Chemical Date Issued: February 27, l997.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/sulfentrazone.pdf
|
A
February 12, 2005, check at the Code
of Federal Regulations for Sulfentrazone: this
herbicide is permitted in or on
51 food commodities in
the United States. The
following list identifies these crops for which EPA has
set pesticide tolerances.
|
| [Code
of Federal Regulations]
[Title 40, Volume 22]
[Revised as of July 1, 2004]
From the U.S. Government Printing Office via GPO Access
[CITE: 40CFR180.498]
[Page 481-482]
TITLE 40--PROTECTION OF ENVIRONMENT
CHAPTER I--ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY (CONTINUED)
PART 180_TOLERANCES AND EXEMPTIONS FROM TOLERANCES FOR PESTICIDE
CHEMICALS
IN FOOD--Table of Contents
Subpart C_Specific Tolerances
Sec. 180.498 Sulfentrazone; tolerances for residues.
(a)(1) General. A tolerance is established
for combined residues of
the herbicide sulfentrazone N-[2,4-dichloro-5-[4-(difluoromethyl)-4,5-
dihydro-3-methyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]phenyl]methanesulfonamide
and its major metabolite 3-hydroxymethyl
sulfentrazone N-[2,4-dichloro-
5-[4-(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-3-hydroxymethyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-
triazol-1-yl]phenyl]methanesulfonamide in or on the following
raw agricultural commodity: |
| Commodity |
As
of January 2002
PPM |
As
of September 2003
PPM |
As
of January 2004
PPM |
As
of
February 2005
PPM |
US
Code of Federal Regulations
CFR |
| Soybean,
seed |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
180.498
|
| (2)
Tolerances are established for combined
residues of the
herbicide sulfentrazone and its metabolites HMS (N-(2,4-dichloro-5-(4-
(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-3-hydroxymethyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-
1-
yl)phenyl)methanesulfonamide) and DMS
(N-(2,4-dichloro-5-(4-
(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-
yl)phenyl)methanesulfonamide in or on the following food commodities: |
| Asparagus |
- |
- |
0.15 |
0.15 |
180.498 |
Bean,
lima, succulent
|
- |
- |
0.15 |
0.15 |
180.498 |
| Cabbage |
- |
- |
0.2 |
0.20 |
180.498 |
| Corn,
field, forage |
- |
- |
0.2 |
0.20 |
180.498
|
| Corn,
field, grain |
- |
- |
0.15 |
0.15 |
180.498
|
| Corn,
field, stover |
- |
- |
0.3 |
0.30 |
180.498
|
| COWPEAS,
W/OUT POD |
0.1 |
- |
- |
Not
listed |
180.498
|
| COWPEA,
SUCCULENT |
0.1 |
0.10 |
same |
Not
listed |
180.498
|
| Horseradish,
roots |
0.1 |
same |
same |
0.20 |
180.498
|
| PEA, DRY |
0.10 |
same |
- |
Not
listed |
180.498
|
Pea
and bean, dried shelled, except soybean, subgroup 6C
This
group includes 27 commodities:
bean, adzuki
bean, broad dry
bean, dry
bean, kidney
bean, lablab
bean, lima dry
bean, moth
bean, mung
bean, navy
bean, pink
bean, pinto
bean, rice
bean, tepary
bean, urd
catjang
chickpea
cowpea
guar
lentil
lupin, grain
lupin, sweet
pea, blackeyed
pea, crowder
pea, field
pea, field seed
pea, pigeon
pea, southern
|
- |
- |
0.15 |
0.15 |
180.498 |
| Peanut |
- |
- |
0.2 |
0.20 |
180.498 |
| Peanut,
meal |
- |
- |
0.4 |
0.40 |
180.498 |
| Peppermint,
tops |
- |
- |
0.3 |
0.30 |
180.498 |
| Potato |
- |
0.10 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
180.498
|
| POTATO,
GRANULES/FLAKES |
- |
0.20 |
- |
Not
listed |
180.498
|
| POTATO,
WET PEEL |
- |
0.15 |
- |
Not
listed |
180.498
|
| Spearmint,
tops |
- |
- |
0.3 |
0.30 |
180.498
|
| Sugarcane,
cane |
0.05 |
same |
same |
0.15 |
180.498
|
| Sugarcane,
molasses |
- |
- |
0.2 |
0.20 |
180.498
|
| SUNFLOWER,
FORAGE |
0.1 |
same |
- |
Not
listed |
180.498
|
| Sunflower,
seed |
0.1 |
0.10 |
0.2 |
0.20 |
180.498
|
(b)
Section 18 emergency exemptions. Time-limited
tolerances are
established for residues of the herbicide N-[2,4-dichloro-5-[4-
(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-3-methyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-y-
l]phenyl] methanesulfonamide and its
metabolites 3-hydroxymethyl
sulfentrazone and 3-desmethyl sulfentrazone, in connection
with use of
the pesticide under section 18 emergency exemptions granted
by EPA. The
tolerance is specified in the following table. The tolerances
expire and
will be revoked by EPA on the date specified in the table.
[[Page
482]]
|
| Commodity |
As
of January 2002
PPM |
As
of September 2003
PPM |
As
of January 2004
PPM |
As
of
February 2005
PPM |
Expiration/
revocation date |
Flax,
seed |
- |
- |
0.20 |
0.20 |
12/31/07 |
Strawberry |
0.60 |
0.60 |
- |
0.60 |
12/31/07 |
| BEAN,
LIMA, (SUCCULENT), W/OUT POD (lima bean & cowpea) |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
- |
12/31/04 |
CHICKPEA,
SEED |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.1 |
- |
12/31/04 |
(c)
Tolerances with regional registrations. [Reserved]
(d) Indirect or inadvertent residues.
Tolerances are established for
inadvertent and indirect combined residues of the herbicide
sulfentrazone (N-[2,4-dichloro-5-[4-(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-3-
methyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]phenyl]methanesulfonamide)
and its
metabolites 3-hydroxymethyl sulfentrazone (N-[2,4-dichloro-5-[4-
(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-3-hydroxymethyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-
yl]phenyl]methanesulfonamide) and 3-desmethyl sulfentrazone
(N-[2,4-
dichloro-5-[4-(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-l-
yl]phenyl]methanesulfonamide) in or on the following raw
agricultural
commodities when present therein as a result of the application
of sulfentrazone to growing crops.
|
| Commodity |
As
of January 2002
PPM |
As
of September 2003
PPM |
As
of January 2004
PPM |
As
of
February 2005
PPM |
CFR |
| Grain,
cereal (excluding sweet corn), Bran |
0.15 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
180.498
|
| Grain,
cereal (excluding sweet corn), Forage |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
180.498
|
| Grain,
cereal (excluding sweet corn), Grain |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.498
|
| Grain,
cereal (excluding sweet corn), Hay |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
180.498
|
| Grain,
cereal (excluding sweet corn), Hulls |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.30 |
180.498
|
| Grain,
cereal (excluding sweet corn), Stover |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.498
|
| Grain,
cereal (excluding sweet corn), Straw |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
180.498
|
|

