|
Return
to Fluorouracil
Index Page
Activity:
Former
insect chemosterilant; now used as a chemotherapeutic drug
Structure:
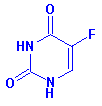
Adverse
Effects:
Note:
While this substance was cited as a a former insect chemosterilant,
we list a very limited selection of
the adverse effects noted in the literature
for its use as a chemotherapy drug.
Anemia
Ataxia
Blood
Bone
Brain
Developmental Toxicant
Embryotoxic
Endocrine: Gonadotoxicity / Spermatogenesis
Endocrine: Ovary
Endocrine: Thymus
Gastrointestinal tract
Genotoxic
Heart
Lung
Teratogen
Urinary
Tract
Anemia
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Major toxic effects
result from myelosuppressive action. Clinical effects are leukopenia,
thrombocytopenia, and anemia. Loss
of hair, occasionally progressing to total alopecia, nail changes,
dermatitis, and increased pigmentation and atrophy of skin may
occur.
Ref: OXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base for FLUOROURACIL.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
•
Definition
for Leukopenia - an
abnormal lowering of the white blood cell count
Ataxia
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Human Toxicity Excerpts:
... APHTHOUS ULCERATION MAY OCCUR ... OTHER TOXIC EFFECTS INCL
... HYPERPIGMENTATION, PHARYNGITIS, ESOPHAGITIS,
CEREBELLAR ATAXIA, & EPISTAXIS. LASSITUDE & ASTHENIA, LASTING
FROM 12-36 HR AFTER INJECTION, MAY OCCUR. WHEN ... DEATH /OCCURS/
IT IS USUALLY FROM SEPTICEMIA ... TOPICALLY, /IT/ ... MAY INDUCE
PHOTOSENSITIZATION ... . [Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.).
Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania:
Mack Publishing Co., 1975. 1079]
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
Blood
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Major toxic effects
result from myelosuppressive action. Clinical effects are leukopenia,
thrombocytopenia,
and anemia. Loss of hair, occasionally
progressing to total alopecia, nail changes, dermatitis, and increased
pigmentation and atrophy of skin may occur.
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base for FLUOROURACIL.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
•
Definitions
Leukopenia - an abnormal
lowering of the white blood cell count
Thrombocytopenia
- a
blood disease
characterized by an abnormally small number of platelets in the
blood
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- A major use of fluorouracil
is in the palliative treatment of carcinoma of the colon, rectum,
breast, stomach, and pancreas that is not amenable to surgery
or irradiation. The major toxic effects
of fluorouracil are on the normal, rapidly proliferating tissues
particularly of the bone marrow and lining of the gastrointestinal
tract. Leukopenia, predominantly of the granulocytopenic type,
thrombocytopenia, and anemia occur commonly with intravenous fluorouracil
therapy at doses ranging from 6 to 12 mg/kg. Pancytopenia and
agranulocytosis also have occurred...
-- EPA believes that there is sufficient evidence for listing
fluorouracil on EPCRA section 313 pursuant to EPCRA section 313(d)(2)(B)
based on the toxicity of this substance to bone marrow, and on
the developmental and chronic neurotoxicity data for this chemical.
Ref:
USEPA/OPPT. Support Document for the Health and Ecological Toxicity
Review of TRI Expansion Chemicals. U. S. Environmental Protection
Agency, Washington, DC (1993). As cited by US EPA in:
Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV.
40 CFR Part 372. Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical
Release Reporting; Community Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
•
Definition
for Leukopenia - an
abnormal lowering of the white blood cell count
Potential Adverse Effects
on Fetus: Exposure in first trimester: skeletal
abnormalities; hypoplasia of aorta, lungs, thymus, and
gastrointestinal tract; and urinary tract abnormalities. Fetus
exposed in third trimester had cyanosis and clonus... the incidence
of malformations,
particularly
those affecting the tail, hindlimb bud, and brain, was increased.
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
Brain
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic neurotoxic
effects were noted in dogs fed fluorouracil at a dietary dose
of 2 mg/kg/day for 6 months. In this study, animals were examined
at the end of 3 months and 6 months. At the end of the experiment,
or at death, the brain was removed and examined (only one dog
survived the entire 6-month period). Histological
sections of the brain showed the presence large multiple monolocular
vacuoles in the wall of the fornix of the third ventricle.
Ref: USEPA/OPPT. Support Document
for the Health and Ecological Toxicity Review of TRI Expansion
Chemicals. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington,
DC (1993). As cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV.
40 CFR Part 372. Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical
Release Reporting; Community Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
-- Absorption, Distribution
& Excretion : Fluorouracil is distributed into tumors, intestinal
mucosa, bone marrow, liver, and other tissues. Despite its limited
lipid solubility, the drug readily crosses
the blood-brain barrier and distributes
into CSF and brain tissue... [McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American
Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 93. Bethesda, MD:
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1993 (Plus Supplements,
1993).
-- Potential Adverse Effects on Fetus: Exposure in first trimester:
skeletal abnormalities; hypoplasia of aorta, lungs, thymus, and
gastrointestinal tract; and urinary tract abnormalities. Fetus
exposed in third trimester had cyanosis and clonus... the incidence
of malformations, particularly those affecting the tail,
hindlimb bud, and brain, was increased.
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
-- PubMed
abstract: Two metabolites of 5-fluorouracil
(FU), monofluoroacetic acid (FA) and alpha-fluoro-beta-alanine
(FBAL), were continuously administered into the left ventricle
of the brain in cats for up to 1 month to investigate the mechanism
of neurotoxicity of FU and its derivatives. The cumulative doses
of FU and FBAL over a 1-month period were 1.5-45 mg (20 cats)
and 0.2-4.8 mg (21 cats), respectively. As controls for each experimental
group, acetic acid (AA) and beta-alanine (BAL) were administered.
In terms of survival time in relation to the cumulative dose and
molecular weight, FBAL was more toxic than FA. Neuropathologically,
two types of change, vacuoles and
necrosis/softening-like change, were found.
The vacuoles
were 20-50 microns in diameter, and distributed mainly in the
cerebellar nuclei, white matter and the tectum and tegmentum of
the brain stem in both experimental groups. Electron microscopically,
these vacuoles were due to splitting of the myelin intraperiod
line or separation between the axon and the innermost layer of
myelin. Necrosis/softening-like change occurred preferentially
in the FBAL group and was located symmetrically in the superior
and inferior colliculi, oculomotor nuclei and thalamus.
Both types of neuropathological change, especially those in the
FBAL group, were similar to those found in cats orally administered
with FU and its derivatives.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Ref: Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1990;81(1):66-73;
Experimental
neurotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil and its derivatives is due
to poisoning by the monofluorinated organic metabolites, monofluoroacetic
acid and alpha-fluoro-beta-alanine; Okeda R, Shibutani
M, Matsuo T, Kuroiwa T, Shimokawa R, Tajima T.
Developmental
toxicant (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Developmental
abnormalities
or other effects on newborns were reported in offspring of women
receiving 150 or 240 mg/kg fluorouracil intravenously during weeks
11 to 14 or 20 to 31 of pregnancy. In addition, maternal toxicity
to the reproductive organs, toxicity to the fetus, and developmental
abnormalities have been reported in mice, rats, and hamsters receiving
oral, intraperitoneal, or intramuscular doses of fluorouracil
ranging from 10 to 700 mg/kg.
Ref: USEPA/OPPT. Support Document for the
Health and Ecological Toxicity Review of TRI Expansion Chemicals.
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC (1993).
As cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV.
40 CFR Part 372. Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical
Release Reporting; Community Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
Abstract: Biologically
based dose-response (BBDR) models are a way to incorporate mechanistic
information into dose-response assessment. The chemotherapeutic
drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) has been used as a prototypic compound
for the construction of a BBDR model for
developmental toxicity (Shuey et al. 1994). Previous work
(Lau et al. 2000) has provided data and a general mechanistic
framework for the development toxicity of 5-FU when it was administered
to pregnant rats subcutaneously on gestation day 14. Here we develop
a mathematical model relating maternally administered dose to
embryonal thymidylate synthetase (TS) inhibition, and thymidylate
synthetase inhibition to various measures of deoxyribonucleotide
(dNTP) pool perturbation, and estimate parameters and the uncertainty
of subsequent predictions using the previously collected data.
The strategy used was to develop semi-empirical submodels for
5-FU pharmacokinetics, 5-FU metabolism and TS inhibition, and
nucleotide pool perturbation, and to estimate model parameters
from the dose-response data described in Lau et al. (2000). Even
for the relatively simple models described here, not all parameters
could be uniquely estimated using data from dose-response and
time-course studies, and some values had to be assigned based
on plausible guesses. The models developed predict that even minimal
doses of 5-FU should result in some perturbation of dNTP pools.
In particular, the relationship between dNTP pool perturbation
and fetal weight deficit suggests that if there is a biological
threshold for the effect of 5-FU on fetal weight, the responsible
repair or compensation mechanism must be downstream of dNTP pool
perturbation, and saturable at 5-FU doses lower than 10 mg/kg,
the lowest dose examined for developmental effects in these studies.
Ref: Setzer RW et al. (2001). Creating a
biologically-based dose-response model for developmental toxicity
of 5-fluorouracil in the rat. Toxicologist 2001 Mar;60(1):145.
As cited on Toxnet.
Embryotoxic
(click on
for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: The chemotherapeutic
agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is a known developmental toxicant
in the rat both in vivo and in vitro. The mechanism of the drug's
embryotoxic effect is unclear, but it has been postulated that
5-FU inhibits thymidylate synthase activity, leading to a deficiency
of thymidine and a decrease in DNA synthesis. If this is the case,
addition of excess exogenous thymidine should reverse the drug's
embryotoxicity. Rat embryos were
cultured beginning on day 10 of gestation (for 48 hours) in a
whole embryo culture system. For the initial three hours of the
culture period, 5-FU was present at a final concentration of 3
ug/mL. Following removal of 5-FU, various concentrations of thymidine
were added for the remainder of the culture period. Treatment
with 5-FU decreased the morphological score, number of somite
pairs, crown-rump and head lengths, as well as DNA and protein
contents; the incidence of malformations, particularly those affecting
the tail, hindlimb bud, and brain, was increased. With addition
of thymidine, there was attenuation of all parameters examined
and fewer malformations. Exogenous thymidine was not able to reverse
the effects of 5-FU completely, even if it was present for the
entire 48 hour culture period, including the three hour 5-FU treatment
phase. These results suggest that 5-FU may induce a thymidine
deficiency in treated rat embryos, but some other effect(s) also
appear to be involved in the embryotoxicity
induced by the drug.
Ref: Hansen DK et al. (1988-89). Attenuation
of 5-fluorouracil-induced embryotoxicity by exogenous thymidine
in vitro. Attenuation of 5-fluorouracil-induced embryotoxicity
by exogenous thymidine in vitro. As cited on Toxnet.
Abstract:
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is a widely used antitumor agent that is
embryotoxic in rats at maternal therapeutic levels. A biologically
based dose-response model (BBDR) was developed that relates a
single dose of 5-FU on gestation day 14 in rats to cell cycle
effects in developing fetuses, specifically the inhibition of
thymidylate synthetase (TS; due to formation of a FdUMP/TS/folate
complex) with subsequent reduction in thymidylate (dTMP) levels,
thymidine-5'-triphosphate (dTTP; a DNA precursor) and, ultimately,
disruption of DNA synthesis. The initial modeling of the pharmacokinetic
component of the BBDR model was based upon a two-compartment PBPK
model (Collins et al., 1980) for the maternal kinetics with an
added compartment for the fetal kinetics of 5-FU. This BBDR model
described well the 5-FU concentration data from gestation day
19, but fetal compartment concentrations on day 14 and the time
course of the inhibition were modeled empirically rather than
mechanistically. To incorporate more physiological information,
a pregnant rat PBPK model developed by O'Flaherty et al. (TAP
112:245-256, 1992) for the weak acid dimethyloxazolidine-2,4-dione
(DM0) was adapted for use in the 5-FU BBDR model. The O'Flaherty
model adjusts for changes in the dam and fetal body weights, blood
flows, and organ volumes as the gestation progresses. Metabolism
of 5-FU and tissue partitioning was also added to the model. Sensitivity
analysis and use of different data sets as the basis for parameter
estimates in this more detailed PBPK component provided insights
into the importance of 5-FU pharmacokinetics to the resulting
changes in thymidylate synthesis compared with other potential
pharmacodynamic interactions.
Ref: Setzer RW et al. (2000). Incorporating
a validated PBPK pregnant rat model into a BBDR model for the
embryotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil. Toxicologist 2000 Mar;54(1):93.
As cited on Toxnet.
Endocrine:
Ovary
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Fluorouracil has not
been adequately studied in animals to determine its effects on
fertility and general reproductive performance. Following intraperitoneal
administration of 125 or 250 mg/kg in rats,
chromosomal aberrations and changes in chromosomal organization
of spermatogonia were induced; spermatogonial
differentiation was also inhibited, resulting in transient infertility.
In a strain of mouse that is sensitive to the induction
of sperm head abnormalities after
exposure to a number of chemical mutagens and carcinogens, no
abnormalities were produced at oral dosages of up to 80 mg/kg
daily. Following intraperitoneal administration at weekly doses
of 25 or 50 mg/kg weekly for 3 weeks during the preovulatory phases
of oogenesis in female rat, the incidence
of fertile matings was substantially reduced,
development of preimplantation and postimplantation embryos was
delayed, and the incidence of preimplantation lethality and chromosomal
anomalies in the embryos was increased. In a limited study in
rabbits, a single 25 mg/kg dose or daily doses of 5 mg/kg for
5 days had no effect on ovulation, appeared not to affect implantation,
and had only a limited effect in producing zygote
destruction. Drugs that inhibit DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis
like fluorouracil might be expected to have adverse effects on
gametogenesis. [McEvoy, G.K. (ed.).
American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 93. Bethesda,
MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1993 (Plus
Supplements, 1993). 576]
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base for FLUOROURACIL.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
•
Definitions:
Gametogenesis: The meiotic process by which mature gametes
(ova and sperm) are formed.
Oogenesis refers specifically to the production of ova
and spermatogenesis to the production of sperm. [ Definition from:
GeneTests from the University of Washington and Children's Health
System, Seattle]
Endocrine:
Testes and Spermatogenesis
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Fluorouracil has not
been adequately studied in animals to determine its effects on
fertility and general reproductive performance. Following intraperitoneal
administration of 125 or 250 mg/kg in rats,
chromosomal aberrations and changes in chromosomal organization
of spermatogonia were induced;
spermatogonial differentiation was also inhibited, resulting
in transient infertility. In a strain of mouse that is sensitive
to the induction of sperm head abnormalities
after exposure to a number of chemical mutagens and carcinogens,
no abnormalities were produced at oral dosages of up to 80 mg/kg
daily. Following intraperitoneal administration at weekly doses
of 25 or 50 mg/kg weekly for 3 weeks during the preovulatory phases
of oogenesis in female rat, the incidence
of fertile matings was substantially reduced,
development of preimplantation and postimplantation embryos was
delayed, and the incidence of preimplantation lethality and chromosomal
anomalies in the embryos was increased. In a limited study in
rabbits, a single 25 mg/kg dose or daily doses of 5 mg/kg for
5 days had no effect on ovulation, appeared not to affect implantation,
and had only a limited effect in producing zygote
destruction. Drugs that inhibit DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis
like fluorouracil might be expected to have adverse effects on
gametogenesis. [McEvoy, G.K. (ed.).
American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 93. Bethesda,
MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1993 (Plus
Supplements, 1993). 576]
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base for FLUOROURACIL.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
•
Definitions
Gametogenesis:
The meiotic process by which mature gametes (ova and sperm) are
formed.
Oogenesis refers specifically to the production of ova
and spermatogenesis to the production of sperm. [ Definition from:
GeneTests from the University of Washington and Children's Health
System, Seattle]
Abstract: Introduction:
Anticancer drugs have variable effects on male gonadal function.
There were many reports regarding gonadotoxicity
induced by drugs like vinblastine, procarbazine and methotrexate.
However, literature of 5-fluorouracil induced gonadotoxicity appears
to be lacking. The present study investigates the sperm shape
anomalies induced by 5-fluorouracil at various doses on Swiss
albino mice. Methods: Mice were treated with therapeutic (12 mg/kg
body weight) and high dose (24 mg/kg body weight) of 5-fluorouracil
for 5 consecutive days. Mice were sacrificed on 35th day after
the first injection. Epididymis were minced with normal saline
and stained with eosin. One thousand sperms/animal were counted
including the control groups. Normal and abnormal sperms were
recorded. Results: A mean abnormality of 13.26% at therapeutic
dose and 8.76% at high dose was observed. Conclusion: 5-fluorouracil
was found to be gonadotoxic to mice which is directly proportional
to the dosage. Hence care must be taken before commencing
5-fluorouracil therapy.
Ref: D'Souza AS (2001). 5-Fluorouracil induced
sperm shape anomalies in Swiss albino mice. Indian J Pharmacol
Aug;33(4):308. As cited on Toxnet.
Endocrine:
Thymus
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
POTENTIAL
ADVERSE EFFECTS ON FETUS: Exposure in first trimester resulted
in skeletal abnormalities; hypoplasia of aorta, lungs, thymus,
and gastrointestinal tract; and urinary tract abnormalities. Fetus
exposed in third trimester had cyanosis and clonus.
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
Gastrointestinal
tract
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
A major use of fluorouracil
is in the palliative treatment of carcinoma of the colon, rectum,
breast, stomach, and pancreas that is not amenable to surgery
or irradiation. The major toxic effects of fluorouracil are on
the normal, rapidly proliferating tissues particularly of the
bone marrow and lining of the gastrointestinal tract. Leukopenia,
predominantly of the granulocytopenic type, thrombocytopenia,
and anemia occur commonly with intravenous fluorouracil therapy
at doses ranging from 6 to 12 mg/kg. Pancytopenia and agranulocytosis
also have occurred.
Ref:
USEPA/OPPT. Support Document for the Health and Ecological Toxicity
Review of TRI Expansion Chemicals. U. S. Environmental Protection
Agency, Washington, DC (1993). As cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV.
40 CFR Part 372. Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical
Release Reporting; Community Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
POTENTIAL
ADVERSE EFFECTS ON FETUS: Exposure in first trimester resulted
in skeletal abnormalities; hypoplasia of aorta, lungs, thymus,
and gastrointestinal tract; and urinary
tract abnormalities. Fetus exposed in third trimester had cyanosis
and clonus.
Ref:
TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances Data Base.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
Genotoxic
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Ref:
Gene-Tox from Toxnet.
GENE-TOX Evaluation B (post-1980):
| Species/Cell
Type: |
Human
lymphocytes |
| Assay
Type: |
Sister-chromatid
exchange (SCE) in vivo |
| Assay
Code: |
SCY+ |
| Results: |
Positive |
| Panel
Report: |
EMIC/91392;
Mutat Res 1993 Sep;297(2):101-80 |
| Reference: |
EMICBACK/31689;
MUTAT RES 67:289-294,1979 |
GENE-TOX
Evaluation A (pre-1980):
| Species/Cell
Type: |
Mouse
(C3H/10T1/2) cells |
| Assay
Type: |
Cell
transformation |
| Assay
Code: |
CTH+ |
| Results: |
Positive |
| Panel
Report: |
EMICBACK/50076;
MUTAT RES 114:283-385,1983 |
| Species/Cell
Type: |
Mammalian
polychromatic erythrocytes |
| Assay
Type: |
Micronucleus
test, chromosome aberrations |
| Assay
Code: |
MNT+ |
| Results: |
Positive |
| Panel
Report: |
EMICBACK/50890;
MUTAT RES 123:61-118,1983 |
| Species/Cell
Type: |
Tradescantia
species |
| Assay
Type: |
Chromosome
aberrations |
| Assay
Code: |
TRC+D |
| Results: |
Positive |
| Dose
Response: |
With
dose response |
| Panel
Report: |
EMICBACK/48094;
MUTAT RES 99:293-302,1982 |
Heart
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
POTENTIAL
ADVERSE EFFECTS ON FETUS: Exposure in first trimester resulted
in skeletal abnormalities; hypoplasia of
aorta, lungs, thymus, and gastrointestinal tract; and urinary
tract abnormalities. Fetus exposed in third trimester had cyanosis
and clonus.
Ref:
TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances Data Base.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
Lung
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
POTENTIAL
ADVERSE EFFECTS ON FETUS: Exposure in first trimester resulted
in skeletal abnormalities; hypoplasia of aorta, lungs,
thymus, and gastrointestinal tract; and urinary tract abnormalities.
Fetus exposed in third trimester had cyanosis and clonus.
Ref:
TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances Data Base.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
Teratogenic
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
REPRODUCTIVE HAZARDS.
Fluorouracil is known to be teratogenic
in animals, as well as causing degenerative effects in male test
animals' reproductive system.
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Base for Fluorouracil.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
Urinary
Tract (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
POTENTIAL
ADVERSE EFFECTS ON FETUS: Exposure in first trimester resulted
in skeletal abnormalities; hypoplasia of aorta, lungs,
thymus, and gastrointestinal tract; and
urinary tract abnormalities. Fetus exposed in third trimester
had cyanosis and clonus.
Ref:
TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances Data Base.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fluorouracil.TOXNET.HSDB.htm
|

