|
Return
to Fluoroglycofen-ethyl
Index Page
Activity: Herbicide
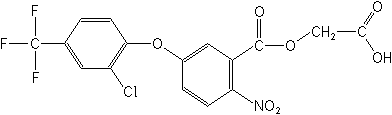
Structure
for "Fluoroglycofen"
Adverse
Effects:
Ataxia
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Embryotoxic / Fetotoxic - rabbits only
Kidney
Liver
Mode
of action: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl is a member of the diphenyl
ether group of herbicides. Its mode of action is thought
to be like acifluorfen another member of this group which
is a metabolite of fluoroglycofen-ethyl. Acifluorfen induces
the accumulation of tetrapyroles which, following absorbtion
of light, become excited and react with oxygen to create
biodestructive oxygen radicals which attack the cell membranes.
Ref:
Evaluation on: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl. May 1992. Issue No.
50. Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs,
Pesticides Safety Directorate, UK.
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/050_confirm-box.htm
|
Ataxia
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
In the main study,
fluoroglycofen-ethyl (97.8% pure) was administered by gavage to
groups of 18 New Zealant White rabbits at concentrations of 1
(water and vehicle controls), 10, 30 and 90 mg/kg bw/day on days
8-18 of gestation. The animals were killed on day 29.... Overt
signs of toxicity seen from days 10-29 in the 90 mg/kg bw/day
groups were an increased incidence of scant, red and/or soft faeces,
thin appearance, red vaginal discharge,
ataxia and lethargy. Maternal body
weights
in the 90 mg/kg bw/day group were decreased from day 12 to the
end of gestaion.
Ref:
Evaluation on: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl. May 1992. Issue No. 50. Department
for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate,
UK.
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
Blood
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
In the mouse
1 and 3 month study, the rat 1 month
study and the dog 52 week study,
reductions in haemoglobin levels, red blood
cell numbers and packed cell volume were variously seen,
predominantly at the top doses. Nucleated
and polychromatic red blood cell numbers were raised in
the rat study only. These effects appeared reversible, in both
the 1 month rat and mouse studies. It would appear that any potential
haemolytic effects, possibly from aniline-derivatives, are of
secondary importance to other subchronic effects...
Ref:
Evaluation on: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl. May 1992. Issue No. 50. Department
for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate,
UK.
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
Body
Weight Decrease
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
In the main study,
fluoroglycofen-ethyl (97.8% pure) was administered by gavage to
groups of 18 New Zealant White rabbits at concentrations of 1
(water and vehicle controls), 10, 30 and 90 mg/kg bw/day on days
8-18 of gestation. The animals were killed on day 29.... Overt
signs of toxicity seen from days 10-29 in the 90 mg/kg bw/day
groups were an increased incidence of scant, red and/or soft faeces,
thin appearance, red vaginal discharge,
ataxia
and lethargy. Maternal body weights
in the 90 mg/kg bw/day group were decreased from day 12
to the end of gesttion... The NOEL for embryo/fetotoxicity was
30 mg/kg bw/day, based on increased resorptions and abortions
and decreased fetal size and viability at 90 mg/kg bw/day. The
NOEL for maternal toxicity was 30 mg/kg bw/day, based on overt
signs of toxicity, decreased maternal body
weights, and maternal deaths at 90 mg/kg bw/day.
Ref:
Evaluation on: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl. May 1992. Issue No. 50. Department
for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate,
UK.
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
In the main study,
fluoroglycofen-ethyl (97.8% pure) was administered by gavage to
groups of 18 New Zealant White rabbits at concentrations of 1
(water and vehicle controls), 10, 30 and 90 mg/kg bw/day on days
8-18 of gestation. The animals were killed on day 29.... Overt
signs of toxicity seen from days 10-29 in the 90 mg/kg bw/day
groups were an increased incidence of scant, red and/or soft
faeces, thin appearance, red vaginal discharge, ataxia and lethargy.
Maternal body weights
in the 90 mg/kg bw/day group were decreased from day 12 to the
end of gesttion... Two animals in the 90 mg/kg bw/day group died
on day 19, ten aborted their litters between days 21 - 26, and
one litter was entirely resorbed at necropsy. Most of the resorptions
in this dose group were late resorptions. In the 90 mg/kg bw/day
group there was an increased number or resorptions and a decrease
in the number of viable fetuses, although the latter was not statistically
significant. As a result of this, the viability index (No. viable
fetuses/ No. corpora lutea) were reduced. The sex ratio of the
fetuses was not altered by fluoroglycofen-ethyl, but the mean
weights and
crown-to-rump lengths were decreased in
fetuses of both sexes at 90 mg/kg bw/day.
The decrease in fetal weight was reflected in a decrease in the
weight of the gravid uterus in the high dose group. There
was a treatment related increase in the
incidence of unossified talus in the high dose group, but
overall, fluoroglycofen-ethyl did not alter the incidences of
developmental variations or malformations. When administered to
New Zealand White rabbis by gavage on days 8-18 of gestation at
90 mg/kg bw/day, fluoroglycofen-ethyl was abortifacient, maternally
toxic, and feto- and embryotoxic. The NOEL for embryo/fetotoxicity
was 30 mg/kg bw/day, based on increased resorptions and abortions
and decreased fetal size and viability at 90 mg/kg bw/day. The
NOEL for maternal
toxicity was 30 mg/kg bw/day, based on overt signs of toxicity,
decreased maternal body weights, and maternal deaths at 90 mg/kg
bw/day.
Definition of Talus: the bone in the ankle
that articulates with the leg bones to form the ankle joint.
Ref:
Evaluation on: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl. May 1992. Issue No. 50. Department
for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate,
UK.
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
Embryotoxic
/ Fetotoxic (rabbits only) (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
The teratogenic potential
and maternal toxicity of fluoroglycofen-ethyl was investigated
in rats and rabbits. In rats, fluoroglycofen-ethyl was not embryotoxic,
fetotoxic or teratogenic at doses of up to 200 mg/kg bw/day. It
was maternally toxic at doses of 60 mg/kg bw/day upwards, as seen
by overt signs and decreased body weight gain. In
rabbits, it was abortifacient (increased abortions) feto- and
embyotoxic (increased resorptions, decreased fetal size
and viability) and maternally toxic (maternal deaths and decreased
maternal weights) at 90 mg/kg bw/day. There was no evidence of
teratogenicity in rabbits. The NOEL for embryo/fetotoxicity was
30 mg/kg bw/day in rabbits and >200 mg/kg bw/day in rats. The
NOEL for maternal toxicity was 30 mg/kg bw/day in rabbits and
18 mg/kg bw/day in rats.
Ref:
Evaluation on: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl. May 1992. Issue No. 50. Department
for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate,
UK.
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
Kidney
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
--In
the mouse 1 and 3 month study, the rat 1 month study and the dog
52 week study, reductions in haemoglobin levels, red blood cell
numbers and packed cell volume were variously seen, predominantly
at the top doses. Nucleated and polychromatic red blood cell numbers
were raised in
the rat study only. These effects appeared reversible, in both
the 1 month rat and mouse studies. It would appear that any potential
haemolytic effects, possibly from aniline-derivatives, are of
secondary importance to other subchronic effects. In dogs there
were initial decreases in body weight and food consumption, which
returned to normal with time, and increased liver and kidney weights.
There was a brown pigment of unknown aetiology
in the renal cortical tubule epithelial cells, which was
PAS and iron-negative.
-- The chronic toxicity and oncongenicity of fluoroglycofen-ethyl
was investigated in mice (2 studies) and rats. In both species,
the systemic toxicity was much the same as had been seen in the
sub-acute studies, the main effects being on the
liver and kidneys... In the
rat study, brown pigment was observed in
the renal tubular cells from week 14 to termination in
the high dose group. A decrease in packed
cell volume, haemoglobin and red cell counts were also seen at
the top dose.
--
A satellite group which was treated for 14 weeks and then given
a 13 week recovery
period showed that the compound related effects were at least
partially reversible. The NOEL for chronic oral exposure to fluoroglycofen-ethyl
was 0.95 mg/kg bw/da (20 ppm) based on the hepatic
and renal effects at 100 ppm.
Ref:
Evaluation on: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl. May 1992. Issue No. 50. Department
for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate,
UK.
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- The pertinent study
proposed for consumer risk assessment was the rat chronic study.
However, 2 mouse chronic/oncongenicity studies were performed.
The first showed liver neoplasia
at <> 50 ppm, whilst histopatholical and organ weight effects
were seen at all doses (10-250 ppm). Hence a NOEL could not be
determined. The second sudy failed to find effects at up to 10
ppm. The mouse NOEL was therefore cncluded to be 10 ppm based
on the second study, which allowed for the NOEL for neoplasia
as seen in the first study. It should be noted that the
second study employed technical material with lower levels of
impurities. The technical fluoroglycofen-ethyl used in the initial
mouse study was used in the rat chronic study without any treatment-related
carcinogenicity. Peroxisome proliferation
has been implicated by the applicant as the cause of hepatic neoplasia
in mice. Subchronic studies in mice have shown peroxisome
proliferation, along with biochemical
and morphological changes in liver attributable to peroxisome
proliferation, at similar doses to those which have caused
hepatic neoplasia in the chronic
study. It is important to note that this assessment is based only
on fluoroglycofen-ethyl and its mammalian metabolites in which
the diphenyl ether bond remains intact.
-- The pertinent no effect level from subacute/subchronic studies
was 9 mg/kg bw/day (80 ppm) taken from the 14 day rat study, based
primarily on enlarged livers and altered
liver enzyme function at 800 ppm. This figure is above
the no observed effect levels for the 3 month dietary mouse study
and the 14 days perosxome prolifertion study. However, these figures
were based on slight increases in hepatocellular
hypertrophy at the next dose, which in the 3 month mouse
study were shown to be reversible, especially at the lower dose.
Hence the no adverse effect level for mice was concluded to be
9.6 mg/kg bw/day. The rat 8 mg/kg bw/day NEL is also lower than
the dog 52 week study NEL (9.9-9.9 mg/kg bw/day) which was based
on increased liver and kidney weights at higher doses.
-- The chronic toxicity and oncongenicity of fluoroglycofen-ethyl
was investigated in mice (2 studies) and rats. In both species,
the systemic toxicity was much the same as had been seen in the
sub-acute studies, the main effects being on the liver
and kidneys. In the first mouse study, carcinogenicity,
as seen by primary liver neoplasms,
was increased at 50 and 250 pm but not at 10 ppm...
-- A satellite group which was treated for 14 weeks and then given
a 13 week recovery period showed that the compound related effects
were at least partially reversible. The NOEL for chronic oral
exposure to fluoroglycofen-ethyl was 0.95 mg/kg bw/da (20 ppm)
based on the hepatic and renal effects
at 100 ppm.
Ref:
Evaluation on: Fluoroglycofen-ethyl. May 1992. Issue No. 50. Department
for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate,
UK.
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/citizen/evaluations/evallist_alphabet.htm
|

