|
Return
to Butafenacil
Index Page
Activity: Herbicide
(uracil)
Structure:
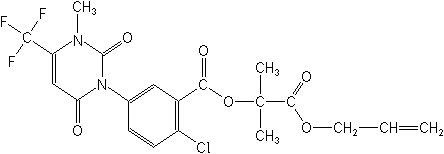
Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Liver
Spleen
Blood
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
The
most susceptible species in long term studies was the mouse. A
NOEL for butafenacil-allyl of 0.36 mg/kg bw/day was found for
males in an 18 month study, essentially based on
haematological effects mostly in males and liver toxicity
in animals of both sexes. A rat 2-year study revealed a NOEL of
1.14 mg/kg bw/day for males, based on liver toxicity in animals
of both sexes. A safety factor of 100 is considered appropriate
for the ADI, due to the extensive toxicology database for butafenacil-allyl.
This results in an ADI of 0.004 mg/kg bw/day (p 10).
-- Long-Term Studies. Mice received butafenacil in the diet at
concentrations of 0, 1, 3, 10 and 60 ppm over 18 months.
Haematological effects included lower mean values for erythrocyte
count, haemoglobin concentration and haematocrit in males at 60
ppm at weeks 53 and 79, respectively, and for erythrocyte count,
haemoglobin and haematocrit at week 79 in males at 10 ppm. Males
also had slightly increased neutrophil and monocyte counts at
60 ppm, and a slight thrombocytosis. Mean absolute and
relative liver weights were increased in both sexes at 60 ppm.
The incidence of enlarged liver was increased in males at 60 ppm
and in females at 10 and 60 ppm. Microscopic examination revealed
an increased incidence of hepatocyte necrosis and hyperplasia
of Kupffer cells in the liver of males at 10 and 60 ppm, and of
females at 60 ppm. In addition, an increased incidence of lipofuscin
deposition, and inflammatory cell infiltration was seen in males
at 60 ppm. There was no treatment-related increase in the incidence
of neoplasms at any dose. Butafenacil was not carcinogenic in
mice. The NOEL was 3 ppm in males and 10 ppm in females, equivalent
to 0.36 and 1.20 mg/kg bw/day for males and females, respectively
(p7-8)....
Ref:
Public Release Summary on Evaluation of the new active BUTAFENACIL
in the products LOGRAN B-POWER HERBICIDE & TOUCHDOWN B-POWER HERBICIDE.
National Registration Authority for Agricultural and Veterinary
Chemicals. Australia. February 2002. Available at:
http://www.nra.gov.au/publications/prsbuta.pdf
Some
excerpts from Table 3.--Toxicological Dose and Endpoints for
Butafenacil
- a summary of the toxicological endpoints used for human
risk assessment
Ref: Butafenacil; Pesticide Tolerance.
Final Rule. Federal Register. September
19, 2003.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/butafenacil.fr.sept.19.2003.htm
|
-- Exposure Scenario
-- Dose Used in Risk Assessment, UF
-- Special FQPA SF* and Level of Concern
for Risk Assessment |
Study
and Toxicological Effects |
-- Chronic
dietary (All populations)
-- NOAEL= 1.2 mg/kg/day UF = 100
-- Chronic RfD = 0.012 mg/ kg/day.
-- Special FQPA SF = 1 cPAD = chronic
RfD
-- Special FQPA SF = 0.012 mg/kg/day. |
Mouse
oncogenicity study.
The LOAEL is 6.96 mg/kg/. day, based on enlarged
livers with increased
weights, and hepatic microscopic lesions including Kupffer
cell hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltration, and single
cell necrosis in both sexes and on deposits of
lipofuscin in males |
-- Short-term
inhalation (1 to 30 days)
-- Oral NOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/ day
-- Residential LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = 100 |
90-day
rat feeding study.
The LOAEL for this study is 62.3 mg/kg/ day based on decreased
hemoglobin,
hematocrit, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular
volume, increased red cell volume distribution width,
and increased incidence of bone marrow
hypercellularity |
-- Short-term
incidental oral (1 to 30 days)
-- Intermediate-term incidental oral (1- 6 months)
-- LOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/day
-- Residential LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = NA |
90-day
rat feeding study.
The LOAEL for this study is 62.3 mg/kg/ day, based on decreased
hemoglobin, hematocrit,
mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular volume, increased
red cell volume distribution width, and increased
incidence of bone marrow hypercellularity |
-- Short-term
inhalation (1 to 30 days)
-- Intermediate-term inhalation (1 to 6 months)
-- Oral NOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/day
-- Residential
LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = 100 |
Same
as above |
Some excerpts from Table 2.--Subchronic,
Chronic, and Other Toxicity
Ref:
Butafenacil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
Federal Register. September 19, 2003.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/butafenacil.fr.sept.19.2003.htm
|
Study
type
[Guideline number] |
Results |
90-Day
oral (dietary) toxicity rodents
(rat) - [870.3100] |
NOAEL
= 300 ppm (18.8/20.6 mg/kg/ day M/F). LOAEL = 1,000 ppm (62.3/69.3
mg/kg/ day M/F) based on decreased body weight gains, decreased
hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH),
mean corpuscular volume (MCV), increased red cell volume,
increased bone marrow hypercellularity;
increased bilirubin and urobilinogen; increased alanine
aminotransferase; hepatocyte necrosis;
inflammatory liver cell infiltration |
| 90-Day
oral (capsule) toxicity in non- rodents (dog)
- [870.3150] |
NOAEL
= 200 mg/kg/ day M/F LOAEL = 1,000 mg/kg/ day M/F, based on
decreases in MCV and MCH in males;
increases in RDW, HDW, platelets and
triglycerides in males; and hemosiderosis in spleen
and liver and extramedullary hematopoiesis the spleen
in males |
1-Year
chronic oral (capsule) toxicity
(dog) - [870.4100] |
NOAEL
= 500 mg/kg/day M/F LOAEL = 1,000 mg/kg/ day M/F, based
on decreased body weight gain in males, decreased
MCV, MCH, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC);
increased thrombocytes and red cell volume distribution width;
hepatic histopathology: glycogen disposition, inclusion bodies
in cytoplasm, and pigment disposition in both sexes, and
focal vaculolation in females |
18-Month
carcinogenicity dietary study
(mouse) - [870.4200] |
NOAEL
= 10 ppm (1.17/1.20 mg/kg/day M/F) LOAEL = 60 ppm (6.96/ 6.59
mg/kg/day M/ F), based on enlarged livers
with increased weights, and hepatic microscopic lesions
including Kupffer cell hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltration,
and single cell necrosis in both sexes and on deposits of
lipofuscin in males No evidence
of carcinogenicity |
| Mechanistic
studies - [870.7485] |
Effects
on enzymes of cultured mouse, rat, and/or human hepatocytes
involved with heme biosynthesis |
| Mechanistic
studies - [870.7485] |
Effects
on liver microsomal and plasma
protox activity and its metabolic
conversion |
| Mechanistic
studies - [870.7485] |
Effects
on porphyrin profile in rats; treatment induced porphyria,
consisting of accumulation of selected porphyrins in the
liver, spleen, and plasma
and increased excretion in urine and feces |
| Mechanistic
studies - [870.7485] |
Test
substance interferes with heme
biosynthesis in rats, as evidenced
by dose- dependent, pronounced porphyria in the
liver, spleen, and plasma;
increased porphyrin excretion, and decreased activity of various
isoenzymes of the hepatic microsomal cytochrome P450 system |
Body
Weight Decrease
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Some excerpts from Table 2.--Subchronic,
Chronic, and Other Toxicity
Ref:
Butafenacil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
Federal Register. September 19, 2003.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/butafenacil.fr.sept.19.2003.htm
|
Study
type
[Guideline number] |
Results |
90-Day
oral (dietary) toxicity rodents
(rat) - [870.3100] |
NOAEL
= 300 ppm (18.8/20.6 mg/kg/ day M/F). LOAEL = 1,000 ppm (62.3/69.3
mg/kg/ day M/F) based on decreased body
weight gains, decreased hemoglobin,
hematocrit, mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular
volume (MCV), increased red cell volume, increased bone marrow
hypercellularity; increased bilirubin and urobilinogen; increased
alanine aminotransferase; hepatocyte necrosis; inflammatory
liver cell infiltration |
| 2-Generation
reproduction and fertility effects - [870.3800]
|
Parental/systemic
NOAEL = 30 ppm (2.4/ 2.5 mg/kg/day M/F) Parental/systemic
LOAEL = 300 ppm (23.8/25.2 mg/kg/ day M/F), based on decreased
body weights and food consumption
and on increased incidences of bile duct hyperplasia and liver
necrosis in males and females of both generations Offspring
NOAEL = 300 ppm (23.8/25.2 mg/kg/day M/F) Offspring LOAEL
= 1,000 ppm (79.6/ 83.8 M/F), based on decreased pup body
weight and body weight gain in both generations Reproductive
NOAEL = 30 ppm (2.4/2.5 mg/ kg/day M/F) Reproductive LOAEL
= 300 ppm (23.8/25.2 mg/kg/day M/F) based on an increase in
the number of days to mating in both generations |
1-Year
chronic oral (capsule) toxicity
(dog) - [870.4100] |
NOAEL
= 500 mg/kg/day M/F LOAEL = 1,000 mg/kg/ day M/F, based on
decreased body weight gain in males,
decreased MCV, MCH, and mean corpuscular
hemoglobin concentration (MCHC); increased thrombocytes and
red cell volume distribution width; hepatic histopathology:
glycogen disposition, inclusion bodies in cytoplasm, and pigment
disposition in both sexes, and focal vaculolation in females |
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Some excerpts from Table 2.--Subchronic,
Chronic, and Other Toxicity
Ref:
Butafenacil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
Federal Register. September 19, 2003.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/butafenacil.fr.sept.19.2003.htm
|
Study
type
[Guideline number] |
Results |
90-Day
oral (dietary) toxicity rodents
(rat) - [870.3100] |
NOAEL
= 300 ppm (18.8/20.6 mg/kg/ day M/F). LOAEL = 1,000 ppm (62.3/69.3
mg/kg/ day M/F) based on decreased body
weight gains, decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular
hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), increased
red cell volume, increased bone marrow
hypercellularity; increased bilirubin and urobilinogen;
increased alanine aminotransferase; hepatocyte necrosis; inflammatory
liver cell infiltration |
| Some
excerpts from Table 3.--Toxicological Dose and Endpoints
for Butafenacil
- a summary of the toxicological endpoints used for human
risk assessment
Ref:
Butafenacil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
Federal Register. September 19, 2003.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/butafenacil.fr.sept.19.2003.htm
|
-- Exposure Scenario
-- Dose Used in Risk Assessment, UF
-- Special FQPA SF* and Level of Concern
for Risk Assessment |
Study
and Toxicological Effects |
-- Short-term
inhalation (1 to 30 days)
-- Oral NOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/ day
-- Residential LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = 100 |
90-day
rat feeding study.
The LOAEL for this study is 62.3 mg/kg/ day based on decreased
hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean
corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular volume, increased
red cell volume distribution width, and increased
incidence of bone marrow hypercellularity |
-- Short-term
incidental oral (1 to 30 days)
-- Intermediate-term incidental oral (1- 6 months)
-- LOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/day
-- Residential LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = NA |
-- Short-term
inhalation (1 to 30 days)
-- Intermediate-term inhalation (1 to 6 months)
-- Oral NOAEL = 18.8 mg/kg/day
-- Residential
LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = 100 |
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- The most susceptible
species in long term studies was the mouse. A NOEL for butafenacil-allyl
of 0.36 mg/kg bw/day was found for males in an 18 month study,
essentially based on haematological effects mostly in males and
liver toxicity in animals of both
sexes. A rat 2-year study revealed a NOEL of 1.14 mg/kg bw/day
for males, based on liver toxicity
in animals of both sexes. A safety factor of 100 is considered
appropriate for the ADI, due to the extensive toxicology database
for butafenacil-allyl. This results in an ADI of 0.004 mg/kg bw/day
(p 10).
Long-Term Studies. Mice received butafenacil in the diet at concentrations
of 0, 1, 3, 10 and 60 ppm over 18 months. Haematological effects
included lower mean values for erythrocyte count, haemoglobin
concentration and haematocrit in males at 60 ppm at weeks 53 and
79, respectively, and for erythrocyte count, haemoglobin and haematocrit
at week 79 in males at 10 ppm. Males also had slightly increased
neutrophil and monocyte counts at 60 ppm, and a slight thrombocytosis.
Mean absolute and relative liver
weights were increased in both sexes at 60 ppm. The incidence
of enlarged liver was increased in
males at 60 ppm and in females at 10 and 60 ppm. Microscopic examination
revealed an increased incidence of hepatocyte
necrosis and hyperplasia of Kupffer cells in the liver
of males at 10 and 60 ppm, and of females at 60 ppm. In addition,
an increased incidence of lipofuscin deposition, and inflammatory
cell infiltration was seen in males at 60 ppm. There was no treatment-related
increase in the incidence of neoplasms at any dose. Butafenacil
was not carcinogenic in mice. The NOEL was 3 ppm in males and
10 ppm in females, equivalent to 0.36 and 1.20 mg/kg bw/day for
males and females, respectively (p7-8).... Rats were administered
butafenacil in the diet at doses of 0, 10, 30, 100 and 300 ppm
for 24 months. At interim sacrifice, the incidence
and/or severity of liver necrosis was increased in both sexes
at 100 and 300 ppm. In addition, increased incidence of
hepatocellular single cell necrosis (300 ppm) and increased incidence
(100 and 300 ppm) and severity (300 ppm) of cholangiofibrosis
were noted in females. At the end of the study, higher incidences
and slightly increased severity of fatty change in the
liver, and slightly higher incidences of increased mitotic
activity of hepatocytes were observed in females at 300 ppm. There
was no treatment-related increase in the incidence of neoplasms
at any dose. Butafenacil was not carcinogenic in rats. The NOEL
was 30 ppm, equivalent to 1.14 mg/kg bw/day for males and 1.30
mg/kg bw/day in females, respectively... Butafenacil was administered
to rats in the diet at concentrations of 0, 100, 300 and 1,000
ppm for a period of 90 days. Observations and functional tests
conducted during the Functional Observation Battery did not show
any effects of toxicological significance. No morphological changes
in the central or peripheral nervous system were revealed at neuropathological
examination. Microscopic examination of the
liver showed inflammatory cell infiltration, cholangiofibrosis
of the intrahepatic bile ducts, pigments within Kupffer
cells, necrosis of single hepatocytes, cytoplasmic vacuolation,
hypertrophy of centrilobular hepatocytes, and an increased mitotic
activity of hepatocytes of males at 1,000 ppm. Slight effects
were seen at 300 ppm, indicating the beginning of liver
necrosis.
Ref: Public Release Summary on Evaluation
of the new active BUTAFENACIL in the products LOGRAN B-POWER HERBICIDE
& TOUCHDOWN B-POWER HERBICIDE. National Registration Authority
for Agricultural and Veterinary Chemicals. Australia. February
2002.
http://www.nra.gov.au/publications/prsbuta.pdf
Some excerpts from Table 2.--Subchronic,
Chronic, and Other Toxicity
Ref: Butafenacil; Pesticide
Tolerance. Final Rule. Federal Register.
September 19, 2003.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/butafenacil.fr.sept.19.2003.htm
|
Study
type
[Guideline number] |
Results |
90-Day
oral (dietary) toxicity rodents
(rat) - [870.3100] |
NOAEL
= 300 ppm (18.8/20.6 mg/kg/ day M/F). LOAEL = 1,000 ppm (62.3/69.3
mg/kg/ day M/F) based on decreased body
weight gains, decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular
hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), increased
red cell volume, increased bone marrow hypercellularity;
increased bilirubin and urobilinogen; increased alanine aminotransferase;
hepatocyte necrosis; inflammatory
liver cell infiltration |
| 90-Day
oral (dietary) toxicity in rodents (mouse)
- [870.3100] |
NOAEL
= 30 ppm (4.11/5.67 mg/kg/day M/F) LOAEL = 100 ppm (13.8/20.1
mg/kg/ day M/F), based on hepatic histopathology:
fatty change, glycogen deposition, and hypertrophy in both
sexes |
| 90-Day
oral (capsule) toxicity in non- rodents (dog)
- [870.3150] |
NOAEL
= 200 mg/kg/ day M/F LOAEL = 1,000 mg/kg/ day M/F, based on
decreases in MCV and MCH in males; increases in RDW, HDW,
platelets and triglycerides in males; and hemosiderosis
in spleen and liver
and extramedullary hematopoiesis the spleen in males |
1-Year
chronic oral (capsule) toxicity
(dog) - [870.4100] |
NOAEL
= 500 mg/kg/day M/F LOAEL = 1,000 mg/kg/ day M/F, based on
decreased body weight gain in males,
decreased MCV, MCH, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
(MCHC); increased thrombocytes and red cell volume distribution
width; hepatic histopathology:
glycogen disposition, inclusion bodies in cytoplasm, and pigment
disposition in both sexes, and focal
vaculolation [liver]
in females |
18-Month
carcinogenicity dietary study
(mouse) - [870.4200] |
NOAEL
= 10 ppm (1.17/1.20 mg/kg/day M/F) LOAEL = 60 ppm (6.96/ 6.59
mg/kg/day M/ F), based on enlarged livers
with increased weights, and hepatic microscopic lesions including
Kupffer cell hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltration,
and single cell necrosis in both sexes and on deposits of
lipofuscin in males No evidence of carcinogenicity |
Combined
2-Year chronic/ carcinogenicity dietary study
(rat) - [870.4300] |
NOAEL
= 100 ppm (3.76/4.43 mg/kg/ day M/F) LOAEL = 300 ppm (11.4/13.0
mg/kg/ day M/F), based on minimal hepatic
abnormalities in the females, including a fatty change
and increased mitotic activity No evidence of carcinogenicity |
|
Mechanistic studies - [870.7485]
|
Effects
on enzymes of cultured mouse, rat, and/or human hepatocytes
involved with heme biosynthesis |
| Effects
on liver microsomal and plasma
protox activity and its metabolic conversion |
|
Effects on porphyrin profile in rats; treatment induced porphyria,
consisting of accumulation of selected porphyrins in the liver,
spleen, and plasma and increased excretion in urine and feces |
| Test
substance interferes with heme biosynthesis
in rats, as evidenced by dose- dependent, pronounced porphyria
in the liver,
spleen, and plasma; increased porphyrin excretion,
and decreased activity of various isoenzymes of the hepatic
microsomal cytochrome P450 system |
Some
excerpts from Table 3.--Toxicological Dose and Endpoints for
Butafenacil
- a summary of the toxicological endpoints used for human
risk assessment
Ref: Butafenacil; Pesticide Tolerance.
Final Rule. Federal Register. September
19, 2003.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/butafenacil.fr.sept.19.2003.htm
|
-- Exposure Scenario
-- Dose Used in Risk Assessment, UF
-- Special FQPA SF* and Level of Concern
for Risk Assessment |
Study
and Toxicological Effects |
| --
Chronic dietary (All populations)
-- NOAEL= 1.2 mg/kg/day UF = 100
-- Chronic RfD = 0.012 mg/ kg/day.
-- Special FQPA SF = 1 cPAD = chronic
RfD
-- Special FQPA SF = 0.012 mg/kg/day.
--
Long-term inhalation (>6 months)
-- Oral NOAEL = 1.2 mg/kg/day
-- Residential
LOC for MOE = 100
-- Occupational = 100 |
Mouse
oncogenicity study.
The LOAEL is 6.96 mg/kg/. day, based on enlarged
livers with increased
weights, and hepatic microscopic lesions including Kupffer
cell hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltration, and
single cell necrosis in both sexes and on deposits of lipofuscin
in males |
Spleen
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Some excerpts from Table 2.--Subchronic,
Chronic, and Other Toxicity
Ref:
Butafenacil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
Federal Register. September 19, 2003.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/butafenacil.fr.sept.19.2003.htm
|
Study
type
[Guideline number] |
Results |
| 90-Day
oral (capsule) toxicity in non- rodents (dog)
- [870.3150] |
NOAEL
= 200 mg/kg/ day M/F LOAEL = 1,000 mg/kg/ day M/F, based
on decreases in MCV and MCH in males; increases in RDW, HDW,
platelets and triglycerides in males; and hemosiderosis
in spleen and
liver and extramedullary
hematopoiesis the spleen in males |
|
Mechanistic studies - [870.7485]
|
Effects
on porphyrin profile in rats; treatment induced porphyria,
consisting of accumulation of selected porphyrins in the
liver, spleen,
and plasma and
increased excretion in urine and feces |
| Test
substance interferes with heme biosynthesis
in rats, as evidenced by dose- dependent, pronounced porphyria
in the liver, spleen,
and plasma; increased porphyrin excretion, and decreased activity
of various isoenzymes of the hepatic microsomal cytochrome
P450 system |
A
February
15, 2005,
check at the Code
of Federal Regulations for Butafenacil: this herbicide
is permitted in or on 12
food
commodities in the United States.
Note:
•
On September
19, 2003, US EPA approved the first time use of Butafenacil
on food commodities.
•
The metabolite, or dimer of butafenacil, is included in
the tolerances for residues for livestock commodoties: CGA-293731.
The
following list identifies these crops for which EPA has set
pesticide tolerances. |
| [Code
of Federal Regulations]
[Title 40, Volume 22]
[Revised as of July 1, 2004]
From the U.S. Government Printing Office via GPO Access
[CITE: 40CFR180.592]
[Page 517]
TITLE 40--PROTECTION OF ENVIRONMENT
CHAPTER I--ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY (CONTINUED)
PART 180_TOLERANCES AND EXEMPTIONS FROM TOLERANCES FOR PESTICIDE
CHEMICALS
IN FOOD--Table of Contents
Subpart C_Specific Tolerances
Sec. 180.592 Butafenacil; tolerances for residues.
(a) General. (1) Tolerances are established for residues of
the
herbicide butafenacil, (1,1-dimethyl-2-oxo-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl
2-
chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3-methyl-2,6-dioxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1(2H)-
pyrimidinyl] benzoate) in or on the following raw agricultural
commodities: |
| Commodity |
Parts
Per Million |
CFR |
Cotton,
gin byproducts
|
10 |
180.592 |
| Cotton,
undelinted seed |
0.50 |
180.592 |
| (2)
Tolerances are established for residues
of the herbicide
butafenacil, (1,1-dimethyl-2-oxo-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl
2-chloro-5-[3,6-
dihydro-3-methyl-2,6-dioxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1(2H)-pyrimidinyl]
benzoate) and its metabolite CGA-293731
(1-carboxy-1-methylethyl 2-
chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3-methyl-2,6-dioxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1(2H)-
pyrimidinyl] benzoate), in or on the following livestock commodities: |
Cattle,
kidney
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
Cattle,
liver
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
Goats,
kidney
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
Goats,
liver
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
Hog, kidney
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
Hog, liver
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
Horse,
kidney
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
Horse,
liver
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
Sheep,
kidney
|
0.05 |
180.592 |
| Sheep,
liver |
0.05 |
180.592 |
| (b)
Section 18 emergency exemptions. [Reserved]
(c) Tolerances with regional registrations. [Reserved]
(d) Indirect and inadvertant residues. [Reserved] |
|

