|
Return to Boron
trifluoride Adverse Effects
ACTIVITY: Fumigant
(Inorganic)
Structure:
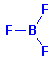
| Adverse
Effects:
Body
Weight Decrease
Blood
Bone
CNS
Eye
Kidney
Lung |
Hazard
Ranking:
Ranked as one of the most hazardous compounds (worst 10%) to
human health.
Ref: Scorecard
for Boron Trifluoride |
Regulatory
Information
(only comprehensive for the US) |
| US
EPA Registered: |
No |
| US
NIOSH IDLH (Immediately Dangerous
to Life and Health) |
25 ppm |
| Other
Information |
| Molecular
Formula: |
B
F3
INORGANIC |
| Other Names: |
ANCA
1040
Trifluoroborane
Trifluoroboron |
| Manufacturer: |
Allied
Signal;
Pennwalt subsidiary
Ozark Mahoning |
| Of special interest: |
| TOXNET
profile from Hazardous Substances Data Bank |
| November 14, 2003
- The TV program "20-20"
aired a segment on the vulnerability of US chemical factories
to terrorist attack. One of the large facilities they spent
a considerable amount of time at produced Boron trifluoride.
We made a copy of this program, and when time allows we will
add the transcript to this site. |
| 1998
- In this report Boron trifluoride was identified: "Very
high acute toxicity." The report, entitled Examples
of substances requiring particular attention, was issued
by the Swedish National Chemicals Inspectorate in collaboration
with the Swedish Environmental Protection Agency and the Swedish
National Board of Occupational Safety and Health. NATIONAL CHEMICALS
INSPECTORATE. Order No 510 622. Second, revised edition, 1998.
See list of the specific Fluorine
and organofluorine pesticides cited in the report. |
| Toxic
Release Inventory. Brief Summary of
1995-2000 data. |
| US
EPA - Emergency
First Aid Treatment Guide. |
| May
2001 - Material
Safety Data Sheet. |
Rationale
for US EPA to add Boron Trifluoride
to the Toxic Release Inventory
Boron
trifluoride is a colorless gas that is corrosive to tissues
due to its rapid hydrolysis to hydrofluoric acid and boric
acid. The principal acute effect in animals is irritation
of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and eyes;
post mortem examination also revealed pneumonia and degenerative
changes in renal tubules. The kidneys are most severely
affected because boric acid concentrates in this organ.
Exposure of six animal species to 0.28 mg/L of boron trifluoride
for 4 to 7 hours a day, 5 days a week killed all animals
within 30 days. Rats, rabbits, and guinea pigs were exposed
to boron trifluoride via inhalation. Guinea pigs died of
respiratory failure after being exposed to 0.036 mg/L for
19 days; rats experienced fluorosis of the teeth at this
concentration. All three species were minimally affected
at 0.004 mg/L. In a 2-week rat inhalation study, all animals
died after 6 daily exposures to 0.18 mg/L. Rats exposed
to 0.024 mg/L showed signs of respiratory irritation, increased
lung weights, and depressed liver weights. Rats exposed
to 0.17 mg/L of boron trifluoride 6 hours/day, 5 days a
week for 13 weeks developed necrosis of the proximal tubular
epithelium of the kidneys. Guinea pigs exposed to 0.035
mg/L, 7 hours/day, 5 days a week for 3 months developed
severe pneumonitis and pulmonary changes indicating chemical
irritation.
Ref.
USEPA/OPPT. Support Document for the Health and Ecological
Toxicity Review of TRI Expansion Chemicals. U. S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC (1993). As cited by US
EPA in:
Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part
IV. 40 CFR Part 372. Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic
Chemical Release Reporting; Community Right-to-Know; Proposed
Rule.
|
Uses:
Catalyst in organic synthesis, manufacture of boranes, soldering
flux, gas brazing, oxidation protectant, fumigant,
polymerizer of epoxy resins, casting and heat treating in
magnesium industry.
Ref: US EPA. Emergency
First Aid Treatment Guide.
|
| Environmental releases
(in pounds) of boron trifluoride in the United States, 1995-2003
(Exhibit 3-3: Page 3-17) |
| Year |
Air Emissions |
Surface Water Discharges |
Underground Injection |
Releases to Land |
Off-Site Releases |
Total On- & Offsite
Releases |
| 1995 |
25,019 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
929 |
25,948 |
| 1996 |
29,881 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
29,881 |
| 1997 |
21,290 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
21,295 |
| 1998 |
37,802 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
37,807 |
| 1999 |
16,725 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
16,725 |
| 2000 |
11,595 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
250 |
11,845 |
| 2001 |
11,496 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
11,496 |
| 2002 |
10,114 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
10,114 |
| 2003 |
7,513 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4,295 |
11,808 |
| Source: REGULATORY
DETERMINATIONS SUPPORT DOCUMENT FOR SELECTED CONTAMINANTS FROM
THE SECOND DRINKING WATER CONTAMINANT CANDIDATE LIST (CCL 2).
US EPA, Office of Water. EPA 815-D-06-007. December 2006 DRAFT. |
Occupational
exposure to boron trifluoride
Year
of Publication: 1977
Authors:
NIOSH Working Group
Source:
TA:Criteria for a recommended standard PG:83 p YR:1977 IP:
VI:NIOSH 77-122
Abstract:
This report presents the criteria and recommended standard
based thereon which were prepared to meet the need for preventing
occupational diseases arising from exposure to boron trifluoride
and resultant mists. The biological effects of exposure
are reviewed including effects on humans, epidemiological
studies, and animal toxicity. Tables are presented which
detail the animal mortality from single acute inhalation
exposure to boron trifluoride and the effects of repeated
inhalation. A review is made of the sampling and analytical
methods used thus far to determine environmental levels
of boron trifluoride. Recommendations are made for standards
in the following areas: medical surveillance of workers;
labeling and posting of warning signs; personal protective
clothing and equipment; information given to employees regarding
the hazards inherent in boron trifluoride; work practices
including emergency procedures, engineering controls, cylinder
handling, service lines, and general work practices; sanitation
practices; and monitoring and record keeping requirements.
Keywords:
ANIMAL
HUMAN
occupational exposure
epidemiological study
Respiratory system
dose effect
CAS
Registry Numbers: 7637-07-2
|
|