|
Return
to Flufenacet Index Page
Activity:
Herbicide (anilide)
Structure:
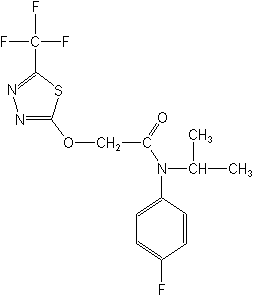
Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body
Weight Decrease
Bone
Brain
Cholesterol
Endocrine: Thyroid
Endocrine: Uterus
Eye
Heart
Kidney
Liver
Sciatic Nerve
Spinal Cord
Spleen
Environmental
As
of February 14, 2005, this herbicide is permitted in
or on over 500 food commodities
in the United States - see list at bottom of page.
"Based
on the toxicological findings for flufenacet relating to
endocrine disruption effects, flufenacet should be considered
as a candidate for evaluation as an endocrine disrupter
when the criteria are established."
Ref.
US EPA. Federal Register: March 29, 2000 (Volume 65, Number
61) [Notices] [Page 16602-16608]. Notice of Filing a Pesticide
Petition to Establish a Tolerance for Certain Pesticide
Chemicals in or on Food
http://www.epa.gov/fedrgstr/EPA-PEST/2000/March/Day-29/p7740.htm
•
LD50 Rat (male) oral 1365 mg/kg /FOE
5043 DF Herbicide/
• LD50
Rat (female) oral 371 mg/kg
/FOE 5043 DF Herbicide/
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact
Sheet. Flufenacet Reason for Issuance: Conditional Registration
Date Issued: April 1998. http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
|
Blood
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- In the rat chronic
feeding / carcinogenicity study the NOEL was less than 1.2 mg/kg/day
in males and less than 1.5 mg/kg/day in females and the LOEL was
1.2 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females based on methemoglobinemia
and multi-organ effects in blood,
kidney, spleen,
heart, and uterus.
Under experimental conditions the treatment did not alter the
spontaneous tumor profile. In the mouse carcinogenicity study
the NOEL was less than 7.4 mg/kg/day in males and was 9.4 mg/kg/day
for females and the LOEL was 7.4 mg/kg/day for males and was 38.4
mg/kg/day for females based on cataract
incidence and severity. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity
for flufenacet in this study.
-- Chronic Feeding/ Carcinogenicity (rat): NOEL < 25 ppm [1.2
mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females]. LOEL = 25 ppm
[1.2 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females] based on
methemoglobinemia and multi-organ effects
in blood, kidney, spleen, heart, and uterus.
Under experimental conditions the treatment did not alter
the spontaneous tumor profile.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Flufenacet
Reason for Issuance: Conditional Registration Date Issued: April
1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
Body
Weight Decrease (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Developmental Toxicity
(rat): Maternal NOEL = 25 mg/kg/day Maternal LOEL = 125 mg/kg/day
based on decreased body weight gain initially.
Developmental NOEL = 25 mg/kg/day Developmental LOEL = 125 mg/kg/day
based on decreased fetal body weight,
delayed development [mainly delays in ossification in the skull,
vertebrae, sternebrae, and appendages], and an increase in the
incidence of extra ribs.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Flufenacet
Reason for Issuance: Conditional Registration Date Issued: April
1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Reproductive and developmental
toxicity:
-- A rat developmental study with a maternal NOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day
and with a maternal LOAEL of 125 mg/kg/day based on decreased
body weight gain initially and a developmental NOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day
and a developmental LOAEL of 125 mg/kg/day based on decreased
fetal body weight, delayed development mainly
delays in ossification in the skull, vertebrae, sternebrae, and
appendages, and an increase in the incidence of extra ribs.
-- A rabbit developmental study with a maternal NOAEL of 5 mg/kg/
day and a maternal LOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day based on histopathological
finds in the liver and a developmental NOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day and
a developmental LOAEL of 125 mg/kg/day based on increased skeletal
variations.
Ref:
Federal Register. March 29, 2000. Notice of Filing a Pesticide
Petition to Establish a Tolerance for Certain Pesticide Chemicals
in or on Food.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flufenacet.FR.Mar.29.2000.htm
Brain
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
NOEL = 40 ppm [1.29
mg/kg/day in males and 1.14 mg/kg/day in females] LOEL = 800 ppm
[27.75 mg/kg/day in males and 26.82 mg/kg/day in females] based
on increased alkaline phosphatase, kidney, and liver weight in
both sexes, increased cholesterol in males, decreased T3, T4 and
ALT values in both sexes, and increased incidence of microscopic
lesions in the brain [axonal degeneration],
eye [vacuolization of the ciliary body epithelium], kidney [hyperplasia
of the epithelial cells], spinal cord [axonal degeneration], sciatic
nerve [axonal degeneration] and liver [hepatocytomegaly].
Ref: EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet, April 1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
•
Notes from FAN:
-- axonal degeneration is associated
with Multiple Sclerosis see
http://www.albany.net/~tjc/abstr05a-2g1.html#1
• "Interestingly, although about
30% of individuals with HIV/AIDS will develop the symptoms of
sensory neuropathy, axonal degeneration is almost universal at
autopsy."
Ref: Griffin, et al., Peripheral neuropathy
in AIDS: New Investigative Approaches. Technical advances in AIDS.
In: Major E, ed. Research in Human Nervous System. Plenum Press:
1994. -
http://www.hopkins-aids.edu/publications/report/may01_2.html
-- Chronic toxicity:
A 1-year dog chronic feeding study
with a NOAEL was 40 ppm (1.29 mg/kg/day in males and 1.14 mg/kg/day
in females), and a LOAEL of 800 ppm (27.75 mg/kg/day in males
and 26.82 mg/kg/day in females) based on increased alkaline phosphatase,
kidney, and liver weight in both sexes, increased cholesterol
in males, decreased T2, T4 and ALT values in both sexes, and increased
incidences of microscopic lesions in the
brain, eye, kidney, spinal cord, sciatic nerve, and liver.
-- Metabolite toxicology. A 55-day
dog study with subcutaneous administration of thiadone
flufenacet metabolite supports the hypothesis that limitations
in glutathione interdependent pathways and antioxidant stress
result in metabolic lesions in the brain
and heart following flufenacet exposure.
-- A rat subchronic neurotoxicity study with a NOAEL of 120 ppm
(7.3 mg/kg/day in males and 8.4 mg/kg/day in females), and a LOAEL
of 600 ppm (38.1 mg/kg/day in males and 42.6 mg/kg/day in females)
based on microscopic lesions in the cerebellum/medulla
and spinal cords.
Ref:
Federal Register. March 29, 2000. Notice of Filing a Pesticide
Petition to Establish a Tolerance for Certain Pesticide Chemicals
in or on Food. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flufenacet.FR.Mar.29.2000.htm
Chronic feeding studies
in dog and rat showed structural or functional alterations in
liver, kidney, haematology, spleen, and
thyroid. Flufenacet induces neuropathogical changes in the brain
and spinal cord (axonal swelling)
in rat and dog. The overall evaluation of the observed
changes demonstrates that these effects occur only after repeated
and prolonged exposure to high dose levels of flufenacet, which
saturate metabolic pathways, and exceed the animal capacity to
rapidly metabolise and excrete it. The liver was considered the
primary target organ, with increases in organ weight, cell size
and number, and/or associated changes in liver function tests.
Ref: European Commission, Health & Consumer
Protection Directorate-General, Scientific Committee on Plants,
October 17, 2001. SCP/FLUFEN/002-Final.
http://europa.eu.int/comm/food/fs/sc/scp/out112_ppp_en.pdf
Special Studies: In
a 55-day dog study subcutaneous via mini-pump with Thiadone [flufenacet
metabolite] support the hypothesis that
limitations in glutathione interdependent pathways and antioxidant
stress result in metabolic lesions in the brain and heart
following flufenacet exposure.
Ref:
US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Flufenacet Reason for Issuance:
Conditional Registration Date Issued: April 1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
Cholesterol
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
A 1-year dog chronic
feeding study with a NOEL was 40 ppm (1.29 mg/kg/day in males
and 1.14 mg/kg/day in females) and a LOEL of 800 ppm (27.75 mg/kg/day
in males and 26.82 mg/kg/day in females) based on increased alkaline
phosphatase, kidney, and liver weight in both sexes, increased
cholesterol in males, decreased T2, T4 and ALT values in
both sexes, and increased incidences of microscopic lesions in
the brain, eye, kidney, spinal cord, sciatic nerve and liver.
Ref: Federal Register: September 23, 1998.
Flufenacet; Time-Limited Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flufenacet.FR.Sept.23.1998.htm
Endocrine:
Thyroid (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 21-day dermal (rats):
Dermal Irritation NOEL = 1000 mg/kg/day (males and females) Systemic
NOEL = 20 mg/kg/day (males) Systemic NOEL = 150 mg/kg/day (females)
Systemic LOEL = 150 mg/kg/day for males and 1000 mg/kg/day for
females based on clinical chemistry data (decreased
T4 and FT4 levels in both sexes) and centrilobular
hepatocytomegaly in females.
-- Special Studies: In a 55-day dog study subcutaneous via mini-pump
with Thiadone [flufenacet metabolite] support the hypothesis that
limitations in glutathione interdependent pathways and antioxidant
stress result in metabolic lesions in the
brain and heart following flufenacet exposure. Non guideline
studies provide evidence supporting hypothesis of an extra
thyroidal mechanism to explain alterations in circulating thyroid
hormone concentrations.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Flufenacet
Reason for Issuance: Conditional Registration Date Issued: April
1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
A 84-day rat feeding
study with a No Observed Effect Level (NOEL) less than 100 ppm
(6.0 mg/kg/day) for males and a NOEL of 100 ppm (7.2 mg/kg/day)
for females and with a Lowest Observed Effect Level (LOEL) of
100 ppm (6.8 mg/kg/day) for males based on suppression
of thyroxine (T4) level and a LOEL of 400 ppm (28.8 mg/kg/day)
for females based on hematology and clinical chemistry findings.
Ref: Federal Register. September 23, 1998.
Flufenacet; Time-Limited Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flufenacet.FR.Sept.23.1998.htm
-- Based on the toxicological findings for flufenacet relating
to endocrine disruption effects, flufenacet
should be considered as a candidate for evaluation as an endocrine
disrupter when the criteria are established ... there is concern
for thyroid hormone disruption.
Subchronic toxicity:
-- A 13-week mouse feeding study with a NOAEL of 100 ppm (18.2
mg/ kg/day for males and 24.5 mg/kg/day for females), and a LOAEL
of 400 ppm (64.2 mg/kg/day for males and 91.3 mg/kg/day for females)
based on histopathology of the liver,
spleen and thyroid.
-- A 13-week dog dietary study with a NOAEL
of 50 ppm (1.70 mg/ kg/day for males and 1.67 mg/kg/day for females),
and a LOAEL of 200 ppm (6.90 mg/kg/day for males and 7.20 mg/kg/day
for females), based on evidence that the bio-transformation capacity
of the liver has [[Page 16601]] been exceeded (as indicated by
increase in LDH, liver weight, ALK and hepatomegaly), globulin
and spleen pigment in females, decreased
T4 and ALT values in both sexes, decreased albumin in males,
and decreased serum glucose in females.
-- A 21-day rabbit dermal study with the dermal irritation NOAEL
of 1,000 mg/kg/day for males and females, and a systemic NOAEL
of 20 mg/kg/day for males and 150 mg/kg/day for females, and a
systemic LOAEL of 150 mg/kg/day for males and 1,000 mg/kg/day
for females based on clinical chemistry data (decreased
T4 and FT4 levels in both sexes) and centrilobular hepatocytomegaly
in females.
-- Chronic toxicity - A 1-year dog chronic feeding study with
a NOAEL was 40 ppm (1.29 mg/kg/day in males and 1.14 mg/kg/day
in females), and a LOAEL of 800 ppm (27.75 mg/kg/day in males
and 26.82 mg/kg/day in females) based on increased alkaline phosphatase,
kidney, and liver weight in both sexes, increased cholesterol
in males, decreased T2, T4 and ALT values
in both sexes, and increased incidences
of microscopic lesions in the brain, eye, kidney, spinal cord,
sciatic nerve, and liver.
Ref: Federal Register. March 29, 2000. Notice
of Filing a Pesticide Petition to Establish a Tolerance for Certain
Pesticide Chemicals in or on Food.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flufenacet.FR.Mar.29.2000.htm
Endocrine:
Uterus (click on for
all fluorinated pesticides)
-- In the rat chronic
feeding / carcinogenicity study the NOEL was less than 1.2 mg/kg/day
in males and less than 1.5 mg/kg/day in females and the LOEL was
1.2 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females based on
methemoglobinemia and multi-organ effects
in blood, kidney, spleen, heart, and uterus.
Under experimental conditions the treatment did not alter the
spontaneous tumor profile. In the mouse carcinogenicity study
the NOEL was less than 7.4 mg/kg/day in males and was 9.4 mg/kg/day
for females and the LOEL was 7.4 mg/kg/day for males and was 38.4
mg/kg/day for females based on cataract
incidence and severity. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity
for flufenacet in this study.
-- Chronic Feeding/ Carcinogenicity (rat): NOEL < 25 ppm [1.2
mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females]. LOEL = 25 ppm
[1.2 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females] based
on methemoglobinemia and
multi-organ effects in blood, kidney, spleen,
heart, and uterus.
Under experimental conditions the treatment did not alter the
spontaneous tumor profile.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Flufenacet
Reason for Issuance: Conditional Registration Date Issued: April
1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
Eye
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
A 1-year dog chronic
feeding study with a NOEL was 40 ppm (1.29 mg/kg/day in males
and 1.14 mg/kg/day in females) and a LOEL of 800 ppm (27.75 mg/kg/day
in males and 26.82 mg/kg/day in females) based on increased alkaline
phosphatase, kidney, and liver weight in both sexes, increased
cholesterol in males, decreased T2, T4 and ALT values in both
sexes, and increased incidences of microscopic lesions in the
brain, eye, kidney, spinal cord,
sciatic nerve and liver.
Ref: Federal Register: September 23, 1998.
Flufenacet; Time-Limited Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flufenacet.FR.Sept.23.1998.htm
In a mouse carcinogenicity
study the NOAEL was less than 50 ppm (7.4 mg/kg/day) for males
and the NOAEL was 50 ppm (9.4 mg/kg/day) for females. The LOAEL
was 50 ppm (7.4 mg/kg/day) for males and the LOAEL was 200 ppm
(38.4 mg/kg/day) for females based on cataract
incidence and severity. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity
for flufenacet in this study.
Ref:
Federal Register. March 29, 2000. Notice of Filing a Pesticide
Petition to Establish a Tolerance for Certain Pesticide Chemicals
in or on Food.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flufenacet.FR.Mar.29.2000.htm
Heart
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- In the rat chronic
feeding / carcinogenicity study the NOEL was less than 1.2 mg/kg/day
in males and less than 1.5 mg/kg/day in females and the LOEL was
1.2 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females based
on methemoglobinemia and multi-organ effects in blood, kidney,
spleen,
heart, and uterus.
Under experimental conditions the treatment did not alter the
spontaneous tumor profile. In the mouse carcinogenicity study
the NOEL was less than 7.4 mg/kg/day in males and was 9.4 mg/kg/day
for females and the LOEL was 7.4 mg/kg/day for males and was 38.4
mg/kg/day for females based on cataract incidence and severity.
There was no evidence of carcinogenicity for flufenacet in this
study.
-- A 55-day dog study subcutaneous via mini-pump with Thiadone
[flufenacet metabolite] supports the hypothesis that limitations
in glutathione interdependent pathways and antioxidant stress
result in metabolic lesions in the brain
and heart following flufenacet exposure. Non-guideline
studies provide evidence supporting the hypothesis of an extra
thyroidal mechanism to explain alterations in circulating thyroid
hormone concentrations.
-- Chronic Feeding/ Carcinogenicity (rat): NOEL < 25 ppm [1.2
mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females]. LOEL = 25 ppm
[1.2 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females] based on
methemoglobinemia and multi-organ effects
in blood, kidney, spleen, heart,
and uterus.
Under experimental
conditions the treatment did not alter the spontaneous tumor profile.
-- Special Studies: In a 55-day dog study subcutaneous via mini-pump
with Thiadone [flufenacet metabolite] support the hypothesis that
limitations in glutathione interdependent pathways and antioxidant
stress result in metabolic lesions in the
brain and heart following flufenacet exposure. Non guideline
studies provide evidence supporting hypothesis of an extra thyroidal
mechanism to explain alterations in circulating thyroid hormone
concentrations.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Flufenacet
Reason for Issuance: Conditional Registration Date Issued: April
1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
Kidney
(click on for all
fluorinated pesticides)
NOEL = 40 ppm [1.29
mg/kg/day in males and 1.14 mg/kg/day in females] LOEL = 800 ppm
[27.75 mg/kg/day in males and 26.82 mg/kg/day in females] based
on increased alkaline phosphatase, kidney,
and liver weight in both sexes, increased cholesterol in males,
decreased T3, T4 and ALT values in both sexes, and increased incidence
of microscopic lesions in the brain [axonal
degeneration], eye [vacuolization of the ciliary body epithelium],
kidney [hyperplasia of the epithelial cells], spinal cord
[axonal degeneration], sciatic nerve [axonal degeneration] and
liver [hepatocytomegaly].
Ref: EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet, April 1998
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
Liver
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic feeding studies
in dog and rat showed structural or functional alterations in
liver, kidney, haematology, spleen,
and thyroid. Flufenacet induces neuropathogical changes in the
brain and spinal cord (axonal swelling) in rat and dog. The overall
evaluation of the observed changes demonstrates that these effects
occur only after repeated and prolonged exposure to high dose
levels of flufenacet, which saturate metabolic pathways, and exceed
the animal capacity to rapidly metabolise and excrete it. The
liver was considered
the primary target organ, with increases in organ weight,
cell size and number, and/or associated changes in
liver function tests.
Ref: European Commission, Health & Consumer
Protection Directorate-General, Scientific Committee on Plants,
October 17, 2001. SCP/FLUFEN/002-Final.
http://europa.eu.int/comm/food/fs/sc/scp/out112_ppp_en.pdf
-- 21-day dermal (rats): Dermal Irritation NOEL = 1000 mg/kg/day
(males and females) Systemic NOEL = 20 mg/kg/day (males) Systemic
NOEL = 150 mg/kg/day (females) Systemic LOEL = 150 mg/kg/day for
males and 1000 mg/kg/day for females based on clinical chemistry
data (decreased T4 and FT4 levels in both
sexes) and centrilobular hepatocytomegaly
in females.
-- Two Generation Reproduction (rat): Parental Systemic NOEL =
20 ppm [1.4 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females] Parental
Systemic LOEL = 100 ppm [7.4 mg/kg/day in males and 8.2 mg/kg/day
in females] based on increased liver weight
in F1 females and hepatocytomegaly
in F1 males. Reproductive NOEL = 20 ppm [1.3 mg/kg/day] Reproductive
LOEL = 100 ppm [6.9 mg/kg/day] based on increased pup death in
early lactation (including cannibalism) for F1 litters and the
same effects in both F1 and F2 pups at the high dose level of
500 ppm [37.2 mg/kg/day in F1 males and 41.5 mg/kg/day in F1 females,
respectively].
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Flufenacet
Reason for Issuance: Conditional Registration Date Issued: April
1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
- Reproductive and developmental toxicity--
---- A 2-generation rat reproduction study with a parental systemic
no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) of 20 ppm (1.4 mg/kg/day
in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females) and a reproductive NOAEL
of 20 ppm (1.3 mg/kg/day) and a parental systemic lowest observed
adverse effect level (LOAEL) of 100 ppm (7.4 mg/kg/day in males
and 8.2 mg/kg/day in females), based on increased
liver weight in F1 females and hepatocytomegaly in F1 males,
and a reproductive LOAEL of 100 ppm (6.9 mg/kg/ day) based on
increased pup death in early lactation (including cannibalism)
for F1 litters and the same effects in both F1 and F2 pups at
the high dose level of 500 ppm (37.2 mg/kg/day in males and 41.5
mg/kg/day in females), respectively.
---- A rabbit developmental study with a maternal NOAEL of 5 mg/kg/
day and a maternal LOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day based on histopathological
finds in the liver and a developmental
NOAEL of 25 mg/kg/day and a developmental LOAEL of 125 mg/kg/day
based on increased skeletal variations.
Subchronic toxicity:
----- A 13-week mouse feeding study with a NOAEL of 100 ppm (18.2
mg/ kg/day for males and 24.5 mg/kg/day for females), and a LOAEL
of 400 ppm (64.2 mg/kg/day for males and 91.3 mg/kg/day for females)
based on histopathology of the liver,
spleen and thyroid.
---- A 13-week dog dietary study with a NOAEL of 50 ppm (1.70
mg/ kg/day for males and 1.67 mg/kg/day for females), and a LOAEL
of 200 ppm (6.90 mg/kg/day for males and 7.20 mg/kg/day for females),
based on evidence that the bio-transformation capacity of the
liver has been exceeded (as indicated by increase in LDH,
liver weight, ALK and hepatomegaly),
globulin and spleen pigment in females, decreased T4 and ALT values
in both sexes, decreased albumin in males, and decreased serum
glucose in females.
- Chronic toxicity
---- A 1-year dog chronic feeding study with a NOAEL was 40 ppm
(1.29 mg/kg/day in males and 1.14 mg/kg/day in females), and a
LOAEL of 800 ppm (27.75 mg/kg/day in males and 26.82 mg/kg/day
in females) based on increased alkaline phosphatase, kidney, and
liver weight in both sexes, increased
cholesterol in males, decreased T2, T4 and ALT values in both
sexes, and increased incidences of microscopic lesions in the
brain, eye, kidney, spinal cord, sciatic nerve, and
liver.
Ref:
Federal Register. March 29, 2000. Notice of Filing a Pesticide
Petition to Establish a Tolerance for Certain Pesticide Chemicals
in or on Food.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flufenacet.FR.Mar.29.2000.htm
Sciatic
Nerve (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
NOEL = 40 ppm [1.29 mg/kg/day in males and 1.14 mg/kg/day in
females] LOEL = 800 ppm [27.75 mg/kg/day in males and 26.82 mg/kg/day
in females] based on increased alkaline phosphatase, kidney, and
liver weight in both sexes, increased cholesterol in males, decreased
T3, T4 and ALT values in both sexes, and increased incidence of
microscopic lesions in the brain [axonal degeneration], eye [vacuolization
of the ciliary body epithelium], kidney [hyperplasia of the epithelial
cells], spinal cord [axonal degeneration], sciatic
nerve [axonal degeneration] and liver [hepatocytomegaly].
Ref: EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet, April 1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
-- Chronic toxicity dogs: NOAEL = 1.29(m), 1.14(f) mg/kg/day
LOAEL = 27.75 (m), 26.82(f) mg/kg/day based on increased alkaline
phosphatase, kidney, and liver weight in both sexes, increased
cholesterol in males, decreased T3, T4, and ALT values in both
sexes, and increased incidences of microscopic lesions in the
brain, eye, kidney, spinal cord, sciatic
nerve, and liver.
Ref: Federal Register. Flufenacet (Bayer). June 25, 2003. Pesticide
Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/flufenacet.fr.june.25.2003.htm
Spinal
Cord (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic toxicity. A 1-year dog chronic
feeding study with a NOEL was 40 ppm [1.29 mg/kg/day in males
and 1.14 mg/kg/day in females] and a LOEL of 800 ppm [27.75 mg/kg/day
in males and 26.82 mg/kg/day in females] based on increased alkaline
phosphatase, kidney, and liver weight in both sexes, increased
cholesterol in males, decreased T2, T4 and ALT values in both
sexes, and increased incidences of microscopic
lesions in the brain, eye, kidney, spinal
cord, sciatic nerve and liver. A rat chronic feeding/carcinogenicity
study with a NOEL less than 25 ppm [1.2 mg/kg/day in males and
1.5 mg/kg/day in females] and a LOEL of 25 ppm [1.2 mg/kg/day
in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day in females] based on methemoglobinemia
and multi-organ effects in blood, kidney,
spleen, heart, and uterus. Under experimental conditions the treatment
did not alter the spontaneous tumor profile. In a mouse carcinogenicity
study the NOEL was less than 50 ppm [7.4 mg/kg/day] for males
and the
NOEL was 50 ppm [9.4 mg/kg/day] for females and the LOEL was 50
ppm [7.4 mg/kg/day] for males and the LOEL was 200 ppm [38.4 mg/kg/day]
for females based on cataract incidence and severity. There was
no evidence of carcinogenicity for flufenacet in this study.
Ref: Federal Register. June 23, 1998. Pesticide
Tolerance Petition.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/flufenacet.fr.june.23.1998.htm
In an acute rat neurotoxicity study
the NOEL was less than 75 mg/kg and the LOEL was 75 mg/kg/day
based on decreased motor activity in males. In a rat subchronic
neurotoxicity study the NOEL was 7.3 mg/kg/day in males and 8.4
mg/kg/day in females and the LOEL was 38.1 mg/kg/day in males
and 42.6 mg/kg/day in females based on microscopic
lesions in the cerebellum/medulla and spinal cords.
Ref: Flufenacet. Pesticide Fact Sheet.
US EPA, April 8, 1998.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/flufenacet.factsheet.epa.98.htm
Spleen
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic feeding studies
in dog and rat showed structural or functional alterations in
liver, kidney, haematology, spleen,
and thyroid. Flufenacet induces neuropathogical changes in the
brain and spinal cord (axonal swelling) in rat and dog. The overall
evaluation of the observed changes demonstrates that these effects
occur only after repeated and prolonged exposure to high dose
levels of flufenacet, which saturate metabolic pathways, and exceed
the animal capacity to rapidly metabolise and excrete it. The
liver was considered the primary target organ, with increases
in organ weight, cell size and number, and/or associated changes
in liver function tests.
Ref: European Commission, Health & Consumer
Protection Directorate-General, Scientific Committee on Plants,
October 17, 2001. SCP/FLUFEN/002-Final.
http://europa.eu.int/comm/food/fs/sc/scp/out112_ppp_en.pdf
-- In the rat chronic feeding / carcinogenicity study the NOEL
was less than 1.2 mg/kg/day in males and less than 1.5 mg/kg/day
in females and the LOEL was 1.2 mg/kg/day in males and 1.5 mg/kg/day
in females based on methemoglobinemia
and multi-organ effects in blood, kidney,
spleen,
heart, and uterus.
Under experimental conditions the treatment did not alter the
spontaneous tumor profile. In the mouse carcinogenicity study
the NOEL was less than 7.4 mg/kg/day in males and was 9.4 mg/kg/day
for females and the LOEL was 7.4 mg/kg/day for males and was 38.4
mg/kg/day for females
based on cataract incidence and severity.
There was no evidence of carcinogenicity for flufenacet
in this study.
Ref: US EPA. Pesticide Fact Sheet. Flufenacet
Reason for Issuance: Conditional Registration Date Issued: April
1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
| Environmental
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
--
Flufenacet is highly toxic to terrestrial, semi-aquatic,
and aquatic plants.
Adverse effects to surrounding plant communities may occur
if flufenacet moves off the treatment site. Endangered mammals
and plants also may be affected. Environmental hazard precautionary
statements are required. Bayer Corporation will conduct
a product stewardship program to assist growers in reducing
the herbicide's impact on non-target organisms.
Ref: US EPA Pesticide Fact
Sheet. April 1998.
http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/factsheets/flufenacet.pdf
--
... The study implies that, because
of its moderate to high adsorption, flufenacet is likely
to persist in soil for some time. However, the possibility
of its movement by leaching or surface run off is less.
Ref: PubMed abstract: Gajbhiye
VT et al. (2001).
Adsorption-desorption behaviour of flufenacet in five different
soils of India. Pest Manag Sci.
Jul;57(7):633-9.
|
A
February 13, 2005, check at the Code
of Federal Regulations for Flufenacet: this herbicide
is permitted in or on over
500 food commodities in
the United States. The
following list identifies these crops for which EPA has set
pesticide tolerances.
|
| [Code
of Federal Regulations]
[Title 40, Volume 22]
[Revised as of July 1, 2004]
From the U.S. Government Printing Office via GPO Access
[CITE: 40CFR180.527]
[Page 492-493]
TITLE 40--PROTECTION OF ENVIRONMENT
CHAPTER I--ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY (CONTINUED)
PART 180_TOLERANCES AND EXEMPTIONS FROM TOLERANCES FOR PESTICIDE
CHEMICALS
IN FOOD--Table of Contents
Subpart C_Specific Tolerances
Sec. 180.527 N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[[5-(trifluoromethyl)-
1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]oxy]acetamide; tolerances for residues.
(a) General. Tolerances are established for
the combined residues of
the herbicide N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[(5-
(trifluoromethyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)oxy]acetamide and
its
metabolites containing the 4-fluoro-N-methylethyl benzenamine
moiety in
or on the following raw agricultural commodities: |
| Commodity |
As
of October 4, 2003
PPM |
As
of February 14, 2005
PPM |
US
Code of Federal Regulations
CFR |
| Corn,
field, forage |
0.4 |
0.4 |
180.527
|
| Corn,
field, grain |
0.05 |
0.05 |
180.527
|
| Corn,
field, stover |
0.4 |
0.4 |
180.527
|
| Soybean,
seed |
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.527
|
| (b)
Section 18 emergency exemptions. Time-limited
tolerances are
established for the combined residues
of N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-
methylethyl)-2-[[5-(trifluoromehtyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]oxy]acetamide
and its metabolites containing the 4-fluoro-N-methylethyl
benzenamine
moiety in or on the following food commodities. |
| Commodity |
As
of October 4, 2003
PPM |
As
of February 14, 2005
PPM |
Expiration/
Revocation Date |
| Cattle,
fat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Cattle,
kidney |
0.50 |
0.50
|
6/30/05
|
| Cattle,
meat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Cattle,
meat byproducts |
0.10 |
0.10 |
6/30/05
|
| Goat,
fat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Goat,
kidney |
0.50 |
0.50
|
6/30/05 |
| Goat,
meat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Goat,
meat byproducts |
0.10 |
0.10 |
6/30/05
|
| Hog,
fat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Hog,
kidney |
0.50 |
0.50
|
6/30/05 |
| Hog,
meat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Hog,
meat byproducts |
0.10 |
0.10 |
6/30/05
|
| Horse,
fat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Horse,
kidney |
0.50 |
0.50
|
6/30/05
|
| Horse,
meat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Horse,
meat byproducts |
0.10 |
0.10 |
6/30/05
|
| Sheep,
fat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Sheep,
kidney |
0.50 |
0.50
|
6/30/05
|
| Sheep,
meat |
0.05 |
0.05 |
6/30/05
|
| Sheep,
meat byproducts |
0.10 |
0.10 |
6/30/05
|
| Wheat,
forage |
10 |
10.0 |
6/30/05
|
| Wheat,
grain |
1.0 |
1.0 |
6/30/05
|
| Wheat,
hay |
2.0 |
2.0
|
6/30/05
|
| Wheat,
straw |
0.50 |
0.50
|
6/30/05
|
| (c)
Tolerances with regional registrations. [Reserved]
(d) Indirect or inadvertent residues. Tolerances are established
for
indirect or inadvertent residues of the herbicide N-(4-fluroophenyl)-N-
(1-methylethyl)-2-[(5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-
yl)oxy]acetamide and its metabolites containing the 4-fluoro-N-
methylethyl benzenamine moiety in or on the raw agricultural
commodities
listed in paragraph (a) of this section. |
| Alfalfa,
forage |
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.527
|
| Alfalfa,
hay |
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.527
|
| Alfalfa,
seed |
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.527
|
| Clover,
forage |
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.527
|
| Clover,
hay |
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.527
|
Grain,
cereal, forage, fodder, and straw, group 16, except rice
This
group includes 50 commodities - see Ref.
1.
|
Not
listed in this way |
0.1 |
180.527
|
| GRAIN,
CEREAL, FORAGE,FODDER&STRAW (CROP GROUP 16) |
0.1 |
Not
listed in this way |
180.527
|
Grain,
cereal, group 15, except rice
This
group includes 100 commodities - see Ref.
2.
|
Not
listed in this way |
0.1 |
180.527
|
| GRAIN,
CEREAL, GROUP 15 |
0.1 |
Not
listed in this way |
180.527
|
Grass,
forage, fodder, and hay, group 17
This
group includes 360 commodities - see Ref.
3.
|
0.1 |
0.1 |
180.527
|
| References. |
(Ref
1 ) Grain,
cereal, forage, fodder, and straw, group 16. This
group includes 50 commodities.
•
barley, hay • barley,
straw • corn, field •
corn, field, aspirated grain fractions •
corn, field, forage •
corn, field, hay • corn,
field, stover • corn,
pod • corn, pod, stover
• corn,
pop • corn, pop, stover •
corn, sweet, cannery waste •
corn, sweet, forage •
corn, sweet, stover •
grain, cereal, forage, fodder and straw, group, for
forage, except sweet corn, forage •
grain. cereal, group •
grass, hay • millet,
forage • millet, hay
• millet,
pearl, forage • millet, pearl, hay •
millet, pearl, straw •
millet, proso, forage •
millet, proso, hay •
millet, proso, straw •
millet, straw • oat
• oat, forage •
oat, hay • oat,
straw • rice, forage •
rice, hulls • rice,
straw • rice, wild •
ricegrass, indian • rye,
forage • rye, straw •
sorghum, forage • sorghum,
forage, forage • sorghum,
forage, hay • sorghum,
forage, silage • sorghum,
grain • sorghum, grain,
forage • sorghum, grain,
stover • wheat, forage
• wheat, hay •
wheat, straw • wheat,
vavilovi, straw • wheat,
wild einkorn, straw • wheat,
wild emmer, straw
|
(Ref
2 )
Grain, cereal, group 15. This
group includes 100 commodities.
barley
• barley,
bran • barley, cereal
• barley, flour •
barley, grain •
barley, pearled barley • buckwheat
• buckwheat, flour •
buckwheat, fodder • buckwheat,
forage • buckwheat, grain
• cereal, cooked •
cereal, flour • cereal,
flour and related products • corn
• corn, cereal •
corn, field • corn,
field, aspirated grain fractions • corn,
field, dry milling • corn,
field, flour • corn,
field, grain • corn,
field, grits • corn,
field, meal • corn, field,
milled byproducts • corn,
field, refined oil • corn,
field, soapstock • corn,
field, starch • corn,
field, wet milling • corn,
pod, grain • corn, pop
• corn, pop, grain •
corn, sweet • corn,
sweet, kernel plus cob with husks removed •
grain, aspirated grain fractions •
grain, cereal • grain,
crops • grain, crops,
except corn, fresh and rice, grain • grain,
crops, except wheat • grain,
forage and stover • macaroni
products • millet •
millet, flour • millet,
grain • millet, pearl
• millet, pearl, grain
• millet, proso •
millet, proso, flour •
millet, proso, grain •
noodle products • oat
• oat and barley animal
feed mixture, 97% oats, 3% barley • oat,
bran • oat, cereal •
oat, flour • oat,
grain • oat, groats/rolled
oats • rice •
rice, bran • rice,
cereal • rice, cracked
• rice, cracked, malted
beverage • rice, flour
• rice, grain •
rice, hulls • rice,
polished rice • rice,
wild • rice, wild, grain
• rye •
rye, bran • rye,
cereal • rye, flour •
rye, grain • sorghum,
grain • sorghum, grain,
aspirated grain fractions • sorghum,
grain, brain • sorghum,
grain, flour • sorghum,
grain, grain • sorghum,
milled fractions, except flour • teosinte
• teosinte, grain •
triticale • triticale,
grain • wheat •
wheat, aspirated grain fractions •
wheat, bran • wheat,
cereal • wheat, flour
• wheat, germ •
wheat, gluten, postharvest in australia
• wheat, grain •
wheat, middlings • wheat,
milled byproducts • wheat,
shorts • wheat, vavilovi
• wheat, vavilovi, grain
• wheat, wild einkorn
• wheat, wild einkorn,
grain • wheat, wild emmer
• wheat, wild emmer,
grain
|
(Ref
3) Grass,
forage, fodder and hay, group 17. This
group includes 360 commodities.
This
group includes:
alkali sacaton • alkali sacaton, forage • alkali
sacaton, hay • alkaligrass • alkaligrass, forage
• alkaligrass, hay • arizona cottontop •
arizona cottontop, forage • arizona cottontop, hay
• bahiagrass • bahiagrass, forage • bahiagrass,
hay • bahiagress, hay • beachgrass • beachgrass,
forage • beachgrass, hay • bentgrass •
bentgrass, forage • bentgrass, hay • bentgrass,
spike • bentgrass, spike, forage • bentgrass,
spike, hay • bermudagrass • bermudagrass, forage
• bermudagrass, hay • bermudagrass, silage •
blowoutgrass • blowoutgrass, forage • blowoutgrass,
hay • bluegrass • bluegrass, forage •
bluegrass, hay • bluegrass, silky • bluegrass,
silky, forage • bluegrass, silky, hay • bluestem,
australian • bluestem, australian, forage •
bluestem, australian, hay • bluestem, big •
bluestem, big, forage • bluestem, big, hay •
bluestem, caucasian • bluestem, caucasian, forage
• bluestem, caucasian, hay • bluestem, diaz
• bluestem, diaz, forage • bluestem, diaz, hay
• bluestem, little • bluestem, little, forage
• bluestem, little, hay • bluestem, sand •
bluestem, sand, forage • bluestem, sand, hay •
bluestem, silver • bluestem, silver, forage •
bluestem, silver, hay • bluestem, south african •
bluestem, south african, forage • bluestem, south
african, hay • bluestem, yellow • bluestem,
yellow, forage • bluestem, yellow, hay • bristlegrass,
plains • bristlegrass, plains, forage • bristlegrass,
plains, hay • bromegrass • bromegrass, forage
• bromegrass, hay • bromegrass, silage •
broomsedge • broomsedge, forage • broomsedge,
hay • buffalograss • buffalograss, forage •
buffalograss, hay • buffelgrass • buffelgrass,
forage • buffelgrass, hay • canarygrass, annual
• canarygrass, annual, forage • canarygrass,
annual, hay • canarygrass, annual, seed • canarygrass,
reed • canarygrass, reed, forage • canarygrass,
reed, hay • canarygrass, reed, silage • caribgrass
• caribgrass, forage • caribgrass, hay •
carpetgrass • carpetgrass, broadleaf • carpetgrass,
broadleaf, forage • carpetgrass, broadleaf, hay •
carpetgrass, forage • carpetgrass, hay • centipedegrass
• centipedegrass, forage • centipedegrass, hay
• cordgrass, marshhay • cordgrass, marshhay,
forage • cordgrass, marshhay, hay • crabgrass
• crabgrass, forage • crabgrass, hay •
curly mesquite • curly mesquite, forage • curly
mesquite, hay • dallisgrass • dallisgrass, forage
• dallisgrass, hay • dropseed, pine •
dropseed, pine, forage • dropseed, pine, hay •
dropseed, sand • dropseed, sand, forage • dropseed,
sand, hay • dropseed, tall • dropseed, tall,
forage • dropseed, tall, hay • fescue •
fescue, forage • fescue, hay • fingergrass,
feather • fingergrass, feather, forage • fingergrass,
feather, hay • foxtail, creeping • foxtail,
creeping, forage • foxtail, creeping, hay •
foxtail, meadow • foxtail, meadow, forage •
foxtail, meadow, hay • gamagrass, eastern •
gamagrass, eastern, forage • gamagrass, eastern, hay
• grass • grass, forage • grass, galleta
• grass, galleta, forage • grass, galleta, hay
• grass, grama • grass, grama, forage •
grass, grama, hay • grass, hay • grass, muhly
• grass, muhly, forage • grass, muhly, hay •
grass, pasture • grass, pasture, forage • grass,
pasture, hay • grass, pasture, seed screenings •
grass, pasture, silage • grass, pasture, straw •
grass, rangeland • grass, rangeland, forage •
grass, rangeland, hay • grass, rangeland, seed screenings
• grass, rangeland, silage • grass, rangeland,
straw • grass, seed screenings • grass, seed,
straw • grass, silage • grass, st. augustine
• grass, st. augustine, forage • grass, st.
augustine, hay • grass, straw • grass, wildrye
• grass, wildrye, forage •grass, wildrye, hay
• grass, zoysia • grass, zoysia, forage •
grass, zoysia, hay • hairgrass, tufted • hairgrass,
tufted, forage • hairgrass, tufted, hay • hardinggrass
• hardinggrass, forage • hardinggrass, hay •
indiangrass • indiangrass, forage • indiangrass,
hay • junegrass • junegrass, forage •
junegrass, hay • limpograss • limpograss, forage
• limpograss, hay • lovegrass • lovegrass,
forage • lovegrass, hay • maidencane •
maidencane, forage • maidencane, hay • mannagrass
• mannagrass, forage • mannagrass, hay •
millet, foxtail • millet, foxtail, forage •
millet, foxtail, hay • millet, japanese • millet,
japanese, forage • millet, japanese, hay • molassesgrass
• molassesgrass, forage • molassesgrass, hay
• napiergrass • napiergrass, forage •
napiergrass, hay • needlegrass • needlegrass,
forage • needlegrass, hay • oat, sand •
oat, sand, forage • oat, sand, hay • oat, slender
• oat, slender, forage • oat, slender, hay •
oat, wild • oat, wild, forage • oat, wild, hay
• oatgrass • oatgrass, forage • oatgrass,
hay • oatgrass, tall • oatgrass, tall, forage
• oatgrass, tall, hay • oniongrass • oniongrass,
forage • oniongrass, hay • orchardgrass •
orchardgrass, forage • orchardgrass, hay • orchardgrass,
silage • pangolagrass • pangolagrass, forage
• pangolagrass, hay • panicgrass • panicgrass,
forage • panicgrass, hay • paspalum •
paspalum, forage • paspalum, hay • polargrass
• polargrass, forage • polargrass, hay •
quackgrass • quackgrass, forage • quackgrass,
hay • redtop • redtop, forage • redtop,
hay • reedgrass • reedgrass, forage •
reedgrass, hay • rhodesgrass • rhodesgrass,
forage • rhodesgrass, hay • rhodesgrass, multiflower
false • rhodesgrass, multiflower false, forage •
rhodesgrass, multiflower false, hay • ricegrass, indian
• ricegrass, indian, forage • ricegrass, indian,
hay • ryegrass, forage • ryegrass, hay •
ryegrass, italian • ryegrass, italian, forage •
ryegrass, italian, hay • ryegrass, perennial •
ryegrass, perennial, forage • ryegrass, perennial,
hay • sandreed, prairie • sandreed, prairie,
forage • sandreed, prairie, hay • sixweeks threeawn
• sixweeks threeawn, forage • sixweeks threeawn,
hay • sloughgrass • sloughgrass, forage •
sloughgrass, hay • smilograss • smilograss,
forage • smilograss, hay • sorghum, forage •
sorghum, grain, stover • spikeoat • spikeoat,
forage • spikeoat, hay • sprangletop, green
• sprangletop, green, forage • sprangletop,
green, hay • squirreltail • squirreltail, forage
• squirreltail, hay • sudangrass • sudangrass,
forage • sudangrass, hay • sunolgrass •
sunolgrass, forage • sunolgrass, hay • tanglehead
• tanglehead, forage • tanglehead, hay •
timothy • timothy, alpine • timothy, alpine,
forage • timothy, alpine, hay • timothy, forage
• timothy, hay • timothy, seed • timothy,
silage • trisetum, spike • trisetum, spike,
forage • trisetum, spike, hay • vaseygrass •
vaseygrass, forage • vaseygrass, hay • veldtgrass,
perennial • veldtgrass, perennial, forage •
veldtgrass, perennial, hay • velvetgrass • velvetgrass,
forage • velvetgrass, hay • wheatgrass •
wheatgrass, bluebunch • wheatgrass, bluebunch, forage
• wheatgrass, bluebunch, hay • wheatgrass, crested
• wheatgrass, crested, forage • wheatgrass,
crested, hay • wheatgrass, fairway • wheatgrass,
fairway, forage • wheatgrass, fairway, hay •
wheatgrass, forage • wheatgrass, hay •wheatgrass,
intermediate • wheatgrass, intermediate, forage •
wheatgrass, intermediate, hay • wheatgrass, pubescent
• wheatgrass, pubescent, forage • wheatgrass,
pubescent, hay • wheatgrass, siberian •wheatgrass,
siberian, forage • wheatgrass, siberian, hay •
wheatgrass, slender • wheatgrass, slender, forage
• wheatgrass, slender, hay • wheatgrass, streambank
• wheatgrass, streambank, forage • wheatgrass,
streambank, hay • wheatgrass, tall • wheatgrass,
tall, forage • wheatgrass, tall, hay • wheatgrass,
thickspike • wheatgrass, thickspike, forage •
wheatgrass, thickspike, hay • wheatgrass, western
• wheatgrass, western, forage • wheatgrass,
western, hay • windmillgrass, hooded • windmillgrass,
hooded, forage • windmillgrass, hooded, hay
|
|

