|
Return
to
Index Page
Abstracts
Activity:
Fungicide
(pyrrole)
Structure:
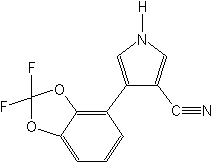
Adverse Effects:
Body Weight Decrease
Cancer: "currently
unclassifiable" - statistically significant trend for malignant
LYMPHOMAS in female mice; statistically
significant increases in LIVER tumors
in female rats
Cholesterol
Endocrine: Ovary
Endocrine: Thymus
Genotoxic
Kidney
Liver
Spleen
Environmental
Body
Weight Decrease
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- 1
Year chronic toxicity study - dog. NOAEL = 3.3 mg/kg/day.
LOAEL = 35.5 mg/kg/day based on decreased
weight gain in female dogs.
-- 13 Week Oral Feeding Study - rat.
Systemic. NOAEL= 64 mg/kg/day. LOAEL = 428 mg/kg/day based on
decreased body weight gain in both sexes,
chronic nephropathy in males, and centrilobular
hepatocyte hypertrophy in females.
Ref: Federal Register: September 12, 2001.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. Final
Rule. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Sept.12.2001.htm
A chronic oral toxicity
study in dogs dosed for 52 weeks at 0, 100, 1,000, and 8,000 ppm
in the diet (0, 3.1, 33.1, and 297.8 mg/kg/ day in males; 3.3,
35.5, and 330.7 mg/kg/day in females. The LEL is 297.8 mg/kg/day
for male dogs based on decreased body weight, hematology alterations
(increase in platelets and fibrin), clinical chemistry alterations
(increase in cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase) and
increased liver weight. The LEL is 35.5 mg/kg/day for female
dogs based on a marked decrease in body weight gain for weeks
1 - 13 and weeks 1 - 52 of the study. The NOEL is 33.1
mg/kg/day for male dogs and 3.3 mg/kg/day in female dogs.
Ref: Federal Register: October 29, 1997
[Page 56075-56082]. 4-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile;
Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Oct.29.1997.htm
Cancer:
"currently unclassifiable"
- statistically significant trend for malignant LYMPHOMAS in female
mice; and statistically significant increases in LIVER tumors in
female rats
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Combined Chronic
Toxicity/ Carcinogenicity in rats: NOAEL = 37 mg/kg/day (M) and
44 mg/kg/day (F) LOAEL = 113 mg/kg/day (M) and 141 mg/kg/day
(F) based on decreased mean body weight gain, slight anemia (F),
and increased incidence and severity of liver lesions (degeneration)
in both sexes. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity in male
rats, but there was a statistically significant increase, both
trend and pairwise, of combined hepatocellular tumors in female
rats. Classified as ``Group D'' by OPP Cancer Peer Review Committee.
Carcinogenicity mice: increased incidence of mice convulsing when
handled (M) and increased absolute liver weight and grossly enlarged
livers (F). Statistically significant trend
for malignant lymphomas in females...
-- 90-Day oral toxicity in NOAEL = 64 mg/kg/day (M) and 70 mg/kg/day
rats (F) LOAEL = 428 mg/kg/day (M) and 462 mg/kg/day (F) based
on decreased weight gain (both sexes), chronic nephropathy (M)
and centrilobular hepatocyte hypertrophy (F).
-- In vivo Rat hepatocyte Male rats were orally dosed 1250, 2500
and micronucleus assay 5,000 mg/kg and hepatocytes were harvested.
Micronucleated hepatocytes were found in Phase II at the low and
mid dose levels but not at the high dose level and not in Phase
I. Positive for mutagenicity in hepatocytes exposed in vivo.
Ref: Federal Register: December 29, 2000.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Dec.2000.htm
--
The EPA classified Fludioxonil as a Group D - not classifiable
as to human carcinogenicity. The evidence is inadequate and cannot
be interpreted as showing either the presence or absence of a
carcinogenic effect. In one mouse study, there was a significant
trend for malignant lymphomas in
female mice up to 3,000 ppm. However, in a second study up to
7,000 ppm, the limit dose, there was no evidence of carcinogenicity
for either sex. In rats, fludioxonil produced
a significant trend and pair- wise increase in hepatocellular
tumors, combined, in female rats at doses adequate to assess carcinogenicity.
The EPA determined that based on the increase
in liver tumors in female rats that was statistically significant
for combined adenoma/carcinoma only, the lack of tumorogenic
response in male rats or in either sex of mice, and the need for
additional mutagenicity studies, a Group D classification was
appropriate. However, the Agency has since received the
additional mutagenicity studies and based on the negative preliminary
findings of the studies, the fact that the statistical increase
in liver tumors in female rats occurred only at the highest dose,
the lack of tumorigenic response in male rats and mice, the Agency
has concluded that fludioxonil does not
pose a significant cancer risk.
Ref: Federal Register: September 12, 2001.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. Final
Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Sept.12.2001.htm
Cholesterol
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
A chronic oral toxicity
study in dogs dosed for 52 weeks at 0, 100, 1,000, and 8,000 ppm
in the diet (0, 3.1, 33.1, and 297.8 mg/kg/ day in males; 3.3,
35.5, and 330.7 mg/kg/day in females. The LEL is 297.8 mg/kg/day
for male dogs based on decreased body weight, hematology alterations
(increase in platelets and fibrin), clinical chemistry alterations
(increase in cholesterol and alkaline
phosphatase) and increased liver weight. The LEL is 35.5 mg/kg/day
for female dogs based on a marked decrease in body weight gain
for weeks 1 - 13 and weeks 1 - 52 of the study. The NOEL is 33.1
mg/kg/day for male dogs and 3.3 mg/kg/day in female dogs.
Ref: Federal Register: October 29, 1997
[Page 56075-56082]. 4-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile;
Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Oct.29.1997.htm
Endocrine:
Ovary (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Gene mutation and
other genotoxic effects were studied using fludioxonil technical:
... iii. Chromosome aberrations assay (in
vitro) in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells with and without S9
activation provided convincing evidence that
fludioxonil is a clastogen and polyploidy inducer.
Ref: Federal Register. October 7, 1998.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Oct.1998.htm
--
In vitro Chromosome aberration. Chinese hamster ovary cells were
tested with and without metabolic activation from 1.37 to 700
g/mL. Positive for nondisjunction of chromosomes both in the presence
and absence of activation.
-- Fludioxonil was not mutagenic in the tests for gene mutations.
However, because of the powerful induction of polyploidy in the
in vitro Chinese hamster ovary cell cytogenetic assay
and the suggestive evidence of micronuclei induction in
rat hepatocytes in vivo, additional mutagenicity testing was performed
in an in vivo study specifically designed for aneuploidy analysis.
Ref: Federal Register: December 29, 2000.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Dec.2000.htm
Genotoxicity. Mutagenicity
potential of fludioxonil was tested in several studies.
In the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell assay, some clastogenic
and polyploidogenic effects were seen at or near the precipitating
concentration of the test substance. However, results were
negative in the Ames assay, CHO V79 cell assay, hepatocyte DNA
repair assay, rat hepatocyte micronucleus test, mouse bone marrow
test, and Chinese hamster bone marrow test. A dominant lethal
test conducted in the mouse was also negative.
Ref: Federal Register. March 29, 2000. [Page
16602-16608]. Notice of Filing a Pesticide Petition to Establish
a Tolerance for Certain Pesticide Chemicals in or on Food.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.March29.2000.htm
Endocrine:
Thymus
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- A carcinogenicity
study in mice administered technical fludioxonil in the diet at
0, 10, 100, 1,000, and 3,000 ppm (0, 1.1, 11.3, 112, and 360 mg/kg/day
for males and 0, 1.4, 13.5, 133, and 417 mg/kg/day for females)...
Other macroscopic changes in female mice were an increased incidence
of enlarged thymus, spleen, mediastinal
lymph node, and liver and an increased incidence
of lymphoma in these organs. The LOAEL is 112 mg/ kg/day
for male mice, based on the increased incidence of clinical toxicity
and 417 mg/kg/day for female mice, based on the increased liver
weight and the increased incidence of macroscopic pathology.
Ref: Federal Register.
October 7, 1998. Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Oct.1998.htm
--
In a 4 week dermal toxicity study, where the animals were treated
5 days per week, there were no signs of skin irritation at up
to 1000 mg/kg bw/day. The NOAEl was 200 mg/kg bw/day, based on
the presence of enlarged macrophages in the thymic
cortices of all females at 1000 mg/kg bw/day. This finding
is unexpected since it has not been reproduced in any other study
where the animals have been systemically exposed to high doses
of fludioxonil for long periods. It may be a phenomenon of high
dose exposure via the dermal route.
-- The plant metabolites CGA 192155, CGA 265378, CGA 308103, and
the chicken metabolite CGA 309565, were of low acute oral toxicity
to the rate with LD50's of >2000 mg/kg bw, except for CGA 309103
where the LD50 was >1000 mg/kg bw. At gross necropsy, spotted
thymuses were noted in all females (all of which died within
one day of dosing) treated at 2000 mg/kg bw CGA 308103, but not
at the lower dose levels, 200, 500 and 1000 mg/kg bw. The
significance of the findings in the thymuses of the animals which
died was not investigated further. In Salmonella typhimurium
reverse mutation assays, the 4 above mentioned plant metabolites
showed no evidence of mutagenic potential. The above results give
further assurance that consumer risk from exposure to these metabolites
is acceptable.
Ref: Evaluation of Fludioxonil. UK Department
for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate,
Mallard House, Kings Pool, 3 Peasholme Green, York YO1 7PX. March
1995.
Note: this pdf document is large
with no search engine.
Available
at:
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/PSD_PDFs/Evaluations/126_fludioxonil.pdf
Genotoxic
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Gene mutation and
other genotoxic effects were studied
using fludioxonil technical: ... iii. Chromosome
aberrations assay (in vitro) in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells
with and without S9 activation provided convincing evidence that
fludioxonil is a clastogen and polyploidy inducer.
Ref: Federal Register. October 7, 1998.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Oct.1998.htm
Kidney
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Fludioxonil safety.
a. Ciba has submitted over 25 separate toxicology studies in support
of tolerances for fludioxonil. According to Ciba, fludioxonil
has a low order of acute toxicity by the oral, dermal, and inhalation
exposure routes. The compound is slightly irritating to the eye,
non-irritating to skin, and is not a dermal sensitizer. It is
not a teratogen and does not affect reproduction or fertility.
The kidney and liver have been identified
as target organs in subchronic and chronic toxicity studies.
No mutagenic activity has been seen in vivo.
Ref: Federal Register. February 5, 1997.
[PF-695; FRL-5584-1]
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Feb.5.1997.htm
A combined chronic
toxicity/carcinogenicity study in rats fed 0, 10, 30, 100, 1,000
and 3,000 ppm for either 12 or 24 months (males: 0, 0.37, 1.1,
3.7, 37 and 113 mg/kg/day, respectively; females: 0, 0.44, 1.3,
4.4, 44 and 141 mg/kg/day respectively)... At necropsy, [[Page
56078]] males at the 3,000 ppm dose level exhibited an increased
incidence of enlarged livers, and kidneys
with discolored foci or general discoloration and an increased
severity of progressive nephropathy;
kidneys with cysts were reported
at both the 1,000 and 3,000 ppm dose levels. For females in the
1,000 and 3,000 ppm dose levels there was an increase incidence
of general discoloration of the the kidneys.
Ref: Federal Register.October 29, 1997.
4-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile;
Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Oct.29.1997.htm
-- 13
Week Oral Feeding Study - rat. Systemic. NOAEL= 64 mg/kg/day.
LOAEL = 428 mg/kg/day based on decreased
body weight gain in both sexes, chronic
nephropathy in males,
and centrilobular
hepatocyte hypertrophy in females.
Ref: Federal Register: September 12, 2001.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. Final
Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Sept.12.2001.htm
Liver
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Combined Chronic
Toxicity/ Carcinogenicity in rats: NOAEL = 37 mg/kg/day (M) and
44 mg/kg/day (F) LOAEL = 113 mg/kg/day (M) and 141 mg/kg/day (F)
based on decreased mean body weight gain, slight anemia (F), and
increased incidence and severity of liver
lesions (degeneration) in both sexes. There was no evidence of
carcinogenicity in male rats, but there was a statistically significant
increase, both trend and pairwise, of combined hepatocellular
tumors in female rats. Classified as ``Group D'' by OPP
Cancer Peer Review Committee. Carcinogenicity mice: increased
incidence of mice convulsing when handled (M) and increased absolute
liver weight and grossly enlarged
livers (F). Statistically significant
trend for malignant lymphomas in females...
-- 90-Day oral toxicity in NOAEL = 64 mg/kg/day (M) and 70 mg/kg/day
rats (F) LOAEL = 428 mg/kg/day (M) and 462 mg/kg/day (F) based
on decreased weight gain (both sexes), chronic nephropathy (M)
and centrilobular hepatocyte hypertrophy
(F).
-- In vivo Rat hepatocyte Male rats were orally dosed 1250, 2500
and micronucleus assay 5,000 mg/kg and hepatocytes were harvested.
Micronucleated hepatocytes were found in Phase II at the low and
mid dose levels but not at the high dose level and not in Phase
I. Positive for mutagenicity in hepatocytes exposed in vivo.
Ref: Federal Register: December 29, 2000.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Dec.2000.htm
The kidney and liver
have been identified as target organs in subchronic and chronic
toxicity studies... In a 90-day subchronic dietary toxicity study
in rats, the NOEL was 10 ppm based on liver
toxicity.
Ref: Federal Register. Februry 5, 1997.
[PF-695; FRL-5584-1]
http://www.epa.gov/docs/fedrgstr/EPA-PEST/1997/February/Day-05/p2711.htm
-- 13
Week Oral Feeding Study - rat. Systemic. NOAEL= 64 mg/kg/day.
LOAEL = 428 mg/kg/day based on decreased
body weight gain in both sexes, chronic nephropathy in males,
and centrilobular
hepatocyte hypertrophy in females.
-- The EPA classified Fludioxonil as a Group D - not classifiable
as to human carcinogenicity. The evidence is inadequate and cannot
be interpreted as showing either the presence or absence of a
carcinogenic effect. In one mouse study, there was a significant
trend for malignant lymphomas in female mice up to 3,000 ppm.
However, in a second study up to 7,000 ppm, the limit dose, there
was no evidence of carcinogenicity for either sex. In rats, fludioxonil
produced a significant trend and pair- wise
increase in hepatocellular tumors, combined, in female rats at
doses adequate to assess carcinogenicity. The EPA determined
that based on the increase in liver tumors
in female rats that was statistically
significant for combined adenoma/carcinoma only, the lack
of tumorogenic response in male rats or in either sex of mice,
and the need for additional mutagenicity studies, a Group D classification
was appropriate. However, the Agency has since received the additional
mutagenicity studies and based on the negative preliminary findings
of the studies, the fact that the statistical increase in liver
tumors in female rats occurred only at the highest dose, the lack
of tumorigenic response in male rats and mice, the Agency has
concluded that fludioxonil does not pose a significant cancer
risk.
Ref: Federal Register: September 12, 2001.
Fludioxonil; Pesticide Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. Final
Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Sept.12.2001.htm
Spleen
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
A carcinogenicity study
in mice administered in the diet nominal dose levels at 0, 10,
100, 1,000, and 3,000 ppm (0, 1.1, 11.3, 112, and 360 mg/kg/day
for male mice; 0, 1.4, 13.5, 133, and 417 mg/kg/day for female
mice). Male mice at the 3,000 ppm level exhibited clinical toxicity
in the form of an incidence of male mice which ``convulsed'' when
handled. No significant effects on body weight, weight gain, food
consumption, hematology, or microscopic non-neoplastic pathology
was reported in either sex. Increased liver weight (9%) and spleen
weight (34%) were observed in male mice at the 3,000 ppm dose
level, which correlated with the macroscopic observations of enlarged
spleen and raised foci of their liver.
Female mice showed a statistically significant increase in liver
weight at the 3,000 ppm dose level, and this is also supported
by the macroscopic observation of enlarged liver at the 3,000
ppm dose level in female mice. Other macroscopic changes in female
mice were an increased incidence of enlarged thymus, spleen,
mediastinal lymph node, and liver, and an increased incidence
of lymphoma in these organs.
Ref: Federal Register: October 29, 1997
(Volume 62, Number 209) [Rules and Regulations] [Page 56075-56082].
4-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile;
Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Fludioxonil.FR.Oct.29.1997.htm
| Environmental
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
All
references from: Evaluation
of Fludioxonil. UK Department for Environment, Food and Rural
Affairs, Pesticides Safety Directorate, Mallard House, Kings
Pool, 3 Peasholme Green, York YO1 7PX. March 1995.
Note: this pdf document is large with no search engine. Available
at:
http://www.pesticides.gov.uk/PSD_PDFs/Evaluations/126_fludioxonil.pdf
--
According to the SSLRC [Soil Survey and Land Research Centre]
soil
persistence classification, fludioxonil is classed as 'very
persistent' (page 100).
--
Fludioxonil is very persistent in
soil (see Section 12), therefore, there is a chronic risk
to earthworms...
--
Data on the acute toxicity of the
active ingredient to aquatic organims indicate that fludioxonil
is of relatively high aquatic toxicity to fish, aquatic
invertebrates and aquatic plants - see
Table below
|
| Table
13.2 Acute Toxicity of technical fludioxonil to fish,
aquatic invertebrates and algae (pages 119-120) |
| Fish
species |
Test
type |
96
hour LC50 mg ai/l |
NOEC
mg ai/l |
Nominal/Acutal |
| Rainbow
Trout |
static |
0.50 |
<0.26 |
Actual |
| Bluegill
Sunfish |
static |
0.31 |
<0.14 |
Actual |
| Common
Carp |
static |
1.5 |
<1.0 |
Actual |
| Catfish |
static |
0.63 |
<0.58 |
Actual |
| Rainbow
Trout |
flow-through |
0.23 |
<0.06 |
Actual |
| Rainbow
Trout |
flow-through |
0.47 |
<0.17 |
Actual |
| Sheepshead
Minnow |
flow-through |
0.54 |
<0.39 |
Actual |
| Sheepshead
Minnow |
flow-through |
1.3 |
<0.38 |
Actual |
| Aquatic
Invertebrates |
Test
Type |
48
hour EC50 mg ai/l |
NOEC
mg ai/l |
Nominal/Actual |
| Daphnia
magna |
static |
1.1 |
0.32 |
Nominal |
| Daphnia
magna |
flow-through |
0.90 |
<0.50 |
Actual |
| Daphnia
magna |
flow-through |
0.82 |
<0.12 |
Actual |
| Daphnia
magna |
flow-through |
0.27
[96 hr EC50] |
0.075 |
Actual |
| Aquatic
Plants |
EC50
mg ai/l |
NOEC
mg ai/l |
Nominal/Actual |
| Scenedesmus
subspicatus |
72
hr EC 50 = 0.93 |
72
hr NOEC = 0.05 |
Actual |
| Raphidocellis
subcapitata |
120
hr EC 50 = 0.092 |
120
NOEC ² 0.028 |
Actual |
|
|

