|
Return to Cyfluthrin
Index Page
ACTIVITY: Insecticide
(pyrethroid)
Note: CAS
No. 68359-37-5 for cyfluthrin and beta-cyfluthrin
is the same
Structure:
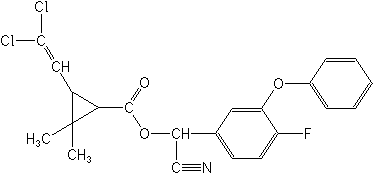
Adverse
Effects:
Ataxia
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Brain
Endocrine: Adrenal
Endocrine: Ovary
Endocrine: Thymus
Eye - Microphthalmia
Genotoxic
Kidney
Lung
Salivary Glands
Sciatic nerve
Tremors
Environmental
•
As of February 12, 2005, this insecticide is permitted in
or on over 200 food commodities
in the United States - see list at http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/mrl.cyfluthrin.htm
There
are also two tolerances of 0.05 ppm for residues
of the insecticide cyfluthrin
from
general surface, spot, and/or crack and crevice applications
in
• food commodities exposed
to the insecticide during treatment of food-handling establishments
where food and food products are held, processed, prepared,
or served.
and
in
•
feed commodities exposed
to the insecticide during treatment of feed-handling establishments
where feed and feed products are held, processed, prepared,
or served.
|
Rationale
for US EPA to add Cyfluthrin to the Toxic Release Inventory
In
a 14-day rat study, oral administration of 60 mg/kg/day
produced tremors, uncoordinated gait, salivation, slight
brain hemorrhages, necrosis of the skeletal muscle fibers,
and death. The NOEL was not defined. In another study, salivation,
straddled gait, axonal degeneration of sciatic nerve, microtubular
dilation, and mitochondria degeneration in the sciatic and
femoral nerves were observed in rats administered 80 mg/kg/day
orally for 5 days and 40 mg/kg/day for the following 9 days.
No NOEL was established. Liver and adrenal weight increases
were observed in rats orally administered 40 to 80 mg/kg/day
for 28 days. The highest dose of 80 mg/ kg/day was reduced
to 40 mg/kg/day. The NOEL was 20 mg/kg/day. Liver weight
changes and urobilinogen and ketone bodies in the urine
were observed in rats fed 15 mg/kg/day for 28 days. No NOEL
was established. In a 28-day mouse feeding study, increased
liver weight was observed at 50 mg/kg/day (LOEL). The NOEL
was 15 mg/kg/day. Inflammatory foci in the kidneys of females
were observed at 7.5 mg/kg/day in a 2-year rat feeding study.
The NOEL was 2.5 mg/kg/day. Based on the NOEL of the study,
an oral RfD of 0.025 mg/kg/day was determined. Increased
alkaline phosphatase activity•
was observed in males at 7.5 mg/kg/day in a 23-month mouse
feeding study. EPA believes that there is sufficient evidence
for listing cyfluthrin on EPCRA section 313 pursuant to
EPCRA section 313(d)(2)(B) based on the available neurological,
hepatic, and renal toxicity data. Aquatic acute toxicity
values for cyfluthrin include a rainbow trout 96-hour LC
50 of 0.68 ppb, a bluegill 96-hour LC 50 of 1.5 ppb, and
a daphnid 48-hour EC 50 of 0.14 ppb. EPA believes that there
is sufficient evidence for listing cyfluthrin on EPCRA section
313 pursuant to EPCRA section 313(d)(2)(C) based on the
available environmental toxicity data.
Ref:
USEPA/OPP. Support Document for the Addition of Chemicals
from Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, Rodenticide Act (FIFRA)
Active Ingredients to EPCRA Section 313. U. S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC (1993).
As cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV. 40 CFR Part 372.
Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical Release Reporting;
Community Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
•
Note from FAN:
Alkaline phosphatase: An enzyme
that hydrolyses phosphate esters, is secreted into the serum
by osteoblasts and is used as a diagnostic marker for increased
osteoblastic metabolic activity. Ref: http://www.kumc.edu/instruction/medicine/pathology/ed/keywords/kw_alkaline.html
|
2004-2006
- US EPA CHEERS study in Jacksonville, Duval County, Florida.
This
2-year study of children's exposure to selected pesticides
and chemicals has ignited enormous controversy. Cyfluthrin
(I,
II, III, IV, total)
was
one of 16 pesticides selected to be monitored in children
(ages 0-3 years). See FAN's
updates on this study. Also,
4-fluoro-3-phenoxybenzoic acid,
(CAS No. 77279-89-1), a metabolite
of Cyfluthrin, will be analyzed
in biological media. It's molecular structure is
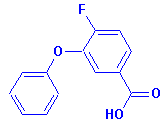
[Note:
the CDC's "Third National Report on Human Exposure
to Environmental Chemicals," expected to be released
sometime in 2005, includes
4-fluoro-3-phenoxybenzoic acid
in its list of chemicals.]
••
Abstract on 4-fluoro-3-phenoxybenzoic
acid:
Toxicology
Letters Volume 134, Issues 1-3 , 5 August 2002,
Pages 141-145
Pyrethroid
exposure of the general population—is this due to
diet
Thomas
Schettgen (a), Ursel Heudorf (b), Hans Drexler (a) and Jürgen
Angerer (a)
(a)
Institute and Outpatient Clinic of Occupational, Social
and Environmental Medicine, Friedrich-Alexander-University
of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Schillerstraße 25/29, D-91054,
Erlangen, Germany
(b) Public Health Department of the City of Frankfurt am
Main, Braubachstr. 18–22, D-60311, Frankfurt am Main,
Germany
Received 21 September 2001; accepted 20 February 2002.
Available online 13 September 2002.
Inhabitants
(1177) of a residential area in Frankfurt/Main have been
investigated with respect to internal exposure to pyrethroids.
Biological monitoring revealed a body burden of pyrethroids.
The 95th‰ for the urinary metabolites of pyrethroids,
such as permethrin and cypermethrin, cis and trans-3-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylic
acid (cis-DCCA and trans-DCCA), was determined to be 0.5
and 1.4 g/l, respectively. 95th‰ for cis-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylic
acid (DBCA), a specific metabolite of deltamethrin, and
4-fluoro-3-phenoxybenzoic acid (F-PBA),
a metabolite of cyfluthrin, were 0.3 and 0.27 g/l,
respectively. The metabolic pattern found for these samples
points out that pyrethroids are probably ingested orally
with daily diet.
|
Ataxia
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Chronic toxicity--
i. 1 Year dog study. Cyfluthrin was fed to beagle dogs at 0, 40,
160, or 640 ppm (equivalent to 0, 1, 4, or 16 mg/ kg/day) for
52 weeks. The NOEL was 4 mg/kg bw/day. The LOEL was 16 mg/ kg/day
for both sexes, based on slight ataxia
in two dogs on single occasions, decreased body weight in males,
and on observations of increased vomiting and diarrhea at the
high dose. The NOEL is 4 mg/kg/ day. This study was classified
as core minimum.
Ref: Federal Register: November 26, 1997.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Nov.26.1997.htm
Blood
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Cyfluthrin. 28-Day
oral toxicity NOAEL = 15.0 (males & females) based on minimal
decrease in
blood glucose.
LOAEL = 50 based on, gait abnormalities, salivation, nervousness,
decrease in body weight, food consumption, changes
in hematological, clinical chem. & urinalysis parameters,
increases in selected organ wts., cytoplasmic swelling of glandular
epithelium of submaxillary gland, minimal
degrees of fiber degeneration in sciatic nerve (# not reported)
which disappeared after recovery period.
-- Cyfluthrin (93.8% a.i.). 4-Week inhalation toxicity study--rats.
NOAEL = 0.00044 mg/L (0.12 mg/kg/day; males & females) LOAEL =
0.006 mg/L (1.6 mg/kg/day; males & females) based on
decreases in body weight and body weight gain in males, hypothermia,
reduction in leukocyte counts (F)
and low serum protein.
Ref: Federal Register.
September 27, 2002. Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Sept.27.2002.htm
Groups of 18 rats (strain
unspecified) of each sex received diets containing 0, 100, 300,
or 1000 mg/kg cyfluthrin for one month, when 12 rats of each sex
per group were sacrificed; the remainder were killed after one
month of recovery on control diet... Total protein and blood glucose
levels were significantly decreased
in male rats given 300 mg/kg feed. No effects were seen
on macroscopic examination... On the basis of the depressed
blood glucose levels in male rats at 300 mg/kg feed, the
NOEL was 100 mg/kg feed, equivalent to 5 mg/kg bw (Watanabe et
al., 1982a)...
In separate studies, the NOEL in rats ranged from 5 mg/kg bw per
day on the basis of depressed blood glucose
levels to 20 mg/kg bw per day on the basis of mortality
and decreased body-weight gain.
Ref: Toxicological evaluation of certain
veterinary drug residues in food. 1997. WHO FOOD ADDITIVES SERIES
39. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.WHO.Tox.Eval.97.htm
Body
Weight Decrease
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Two rat developmental
toxicity studies via the inhalation route of exposure were also
conducted... In the second study, the maternal NOAEL and LOAEL
were < 0.46 mg/ M3, based on decreased
body weight gain and reduced relative food efficiency.
The developmental NOAEL was 0.46 mg/M3 and the developmental LOAEL
was 2.55 mg/M3, based on reduced
fetal and placental weight, and reduced ossification in
the phalanx, metacarpals,
and vertebrae.
Ref: Federal Register: November 26, 1997.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Nov.26.1997.htm
-- Cyfluthrin.
28-Day oral toxicity NOAEL = 15.0 (males & females) based on minimal
decrease in blood glucose. LOAEL = 50 based on, gait abnormalities,
salivation, nervousness, decrease
in body weight, food consumption, changes
in hematological, clinical chem. & urinalysis parameters, increases
in selected organ wts., cytoplasmic swelling of glandular epithelium
of submaxillary gland, minimal degrees of fiber degeneration
in sciatic nerve (# not reported) which disappeared after recovery
period.
-- Cyfluthrin (94.9% a.i.). 90-Day inhalation toxicity study--rats.
NOAEL = 0.00009 mg/liter (L) (0.02 mg/kg/day; both sexes) LOAEL
= 0.00071 mg/L (0.16 mg/kg/day) based on decreased
body weights and body weight gains in males and clinical
signs in females
-- Cyfluthrin (93.8% a.i.). 4-Week inhalation toxicity study--rats.
NOAEL = 0.00044 mg/L (0.12 mg/kg/day; males & females) LOAEL =
0.006 mg/L (1.6 mg/kg/day; males & females) based on
decreases in body weight and body weight gain in males,
hypothermia, reduction in
leukocyte counts (F) and low serum protein.
-- Cyfluthrin (96% a.i.). Prenatal
developmental toxicity--rabbits.
Maternal NOAEL = 20.0 Developmental NOAEL
= 180.0 Maternal LOAEL = 60.0 based on decreased body weight gain
and food consumption during the dosing period Developmental LOAEL
> 180 mg/kg/day
-- Cyfluthrin (96.2%). Prenatal developmental
toxicity via inhalation- rat .
Maternal NOAEL <0.00046 mg/L (< 0.125 mg/kg/
day)Developmental NOAEL = 0.00046 mg/L (0.125 mg/ kg/day) Maternal
LOAEL = 0.00046 mg/L (0.125 mg/kg/ day) based on decreased body
weight gain and relative food efficiency Developmental LOAEL =
0.00255 mg/L (0.692 mg/ kg/day) based on reduced fetal and placental
weights and reduced ossification in phalanx, metacarpals, vertebrae
-- Cyfluthrin (95.4%
a.i.). Reproduction and fertility
effects study-- rat (dietary). Parental
NOAEL = Parental: 3/4 (M/F) Offspring NOAEL = 7 (M/F) Parental
LOAEL = 9/10 (M/F) based on reductions in body weights and food
consumption. Offspring LOAEL = 19 based on coarse tremors
in pups during lactation and decreases in mean litter weight
.
-- Cyfluthrin (95.7-96.2%
a.i.).
Pilot 1-generation reproduction
study--rat. Parental
systemic NOAEL = 22.9 Offspring systemic NOAEL = 7.8 Parental
systemic LOAEL = 59.6 based on hind leg splay, ataxia,
reduction in body weight gain. Pup systemic LOAEL = 22.9
based on tremors during lactation
and pup weight decreases.
-- Cyfluthrin. Multigeneration
reproduction study--rats.
Parental NOAEL = 12.3/15.1 Offspring NOAEL
= 5.4 Parental LOAEL = 37.2/48.5 based on decreased body weight
gain. Offspring LOAEL = 15.1 based on decreased viability during
lactation period and decreased body weight gains
-- Cyfluthrin (93.9% a.i.). Carcinogenicity feeding study--mice.
NOAEL = 31.9 (males) and 140.6 (females) LOAEL = 114.8 (males)
based on ear skin lesions and reduced body
weight gains. 309.7 (females) based on clinical signs;
macroscopic and microscopic pathology findings; and reduced
body weights, body weight gains, and food consumption.
Under the conditions of this study, there was no evidence of carcinogenic
potential.
-- Cyfluthrin (94.7% a.i.). Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity
feeding study--rat. NOAEL = 2.6 (males), 3.3 (females) LOAEL =
11.6 (males), 14.4 (females) based on overall
declines in body weight gain by 12 and 10% in males and females,
respectively. No carcinogenic effects.
-- Cyfluthrin (49.7-51.0%).. Combined chronic toxicity/ carcinogenicity
feeding study--rat. NOAEL = 6.19 (males), 8.15 (females) LOAEL
= 19.20 (M), 25.47 (F) based on decreased
body weights and body weight gains. No carcinogenic effects.
Ref: Federal Register. September 27, 2002.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Sept.27.2002.htm
Bone
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
-- Rat developmental
studies via inhalation: In the second study, the dams were exposed
to analytical concentrations of 0, 0.09, 0.25, 0.59 or 4.2 mg/m3
of the test material. The dams were sacrificed on day 20 and their
pups removed by caesarian section. The maternal NOEL was 1.1 mg/
m3 and the maternal LOEL was 4.7 mg/m3 (reduced
motility, dyspnea, piloerection, ungroomed coats and eye irritation.
The developmental NOEL was 0.59 mg/m3 and the developmental
LOEL was 1.1 mg/m3 (increases in the incidence of runts
and skeletal anomalies in the sternum
(1.1 mg/m3 and above); increases in post-implantation
losses and decreases in pup weights (4.7 mg/m3 and
above) and increased incidences of late embryonic deaths, in skeletal
anomalies in the extremities, pelvis and skull and in microphthalmia
(23.7 mg/m3).
--Two rat developmental toxicity studies via the inhalation route
of exposure were also conducted... In the second study, the maternal
NOAEL and LOAEL were < 0.46 mg/ M3, based on decreased body
weight gain and reduced relative food efficiency. The developmental
NOAEL was 0.46 mg/M3 and the developmental LOAEL was 2.55 mg/M3,
based on reduced fetal and placental weight,
and reduced ossification in the phalanx, metacarpals, and vertebrae.
Ref: Federal Register: November 26, 1997.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Nov.26.1997.htm
Brain
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
... A group of 12 hens
received a single oral dose of cyfluthrin in PEG 400 at 4300 mg/kg
bw and were observed for three weeks. A second group of 16 hens
received two doses of 4300 mg/kg bw three weeks apart by gavage
and were allowed to recover for eight weeks. A final group of
12 hens received doses of 1500 mg/kg bw per day by gavage for
five consecutive days and were allowed to recover for eight weeks.
All animals were autopsied after the recovery periods.
Neurotoxic esterase activity was determined
in the brains and spinal cords from five hens of each group
24, 48, and 72 h and seven days after treatment.
... Groups of five male and five female Wistar (SPF-Cpb) rats
received cyfluthrin at 0 or 60 mg/kg bw per day for two weeks
by gavage, and a supplementary group of male rats received doses
of 0 or 50 mg/kg bw per day... Symptoms of acute toxicity were
observed in all treated animals, including tremor, altered gait,
and increased vocalization. Four males at 60 mg/kg bw per day
died between treatment days 5 and 8, but gross pathologicam examination
revealed no specific alterations. The body-weight gain of females
was not affected by treatment, but decreases were seen for males
at 50 or 60 mg/kg bw per day. Small, fresh brain
haemorrhages were seen in all four males that died on test.
The authors concluded that the 'most likely explanation is that
these are the result of a terminal cardiovascular disorder with
necrosis of the vascular walls'. Since this finding was not seen
in control animals, a treatment-related effect could not be ruled
out. A NOEL was not identified (Heimann & Kaliner, 1983).
Ref: Toxicological evaluation of certain
veterinary drug residues in food. 1997. WHO FOOD ADDITIVES SERIES
39.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.WHO.Tox.Eval.97.htm
Endocrine:
Adrenal
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Subchronic toxicity--
i. 28-Day oral toxicity study in rats. Cyfluthrin was administered
to SPF-Wistar rats via gavage at 0, 5, 20, or 80 (40) mg/kg/day.
The high dose was 80 mg/kg/day during the first and third weeks
and 40 mg/kg/day during the second and fourth weeks. The LOEL
was 80 (40) mg/kg/day in both sexes based on clinical signs of
nerve toxicity, decreases in body weight gain, and changes in
liver and adrenal weights. The NOEL
was 20 mg/kg/day. This study was classified as core minimum.
Ref: Federal Register: November 26, 1997.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Nov.26.1997.htm
-- Rats Four groups
of 30 male and 24 female Mura:SPRA (SPF 68 Han) rats received
14C radiolabelled cyfluthrin as either oral doses of 0.5 or 10
mg/kg bw or intravenous or intraduodenal doses of 0.5 mg/kg bw.
Another group received unlabelled cyfluthrin orally once a day
for 14 consecutive days, followed by a single oral dose of 0.5
mg/kg bw 14C-cyfluthrin... The residues found in the organs and
tissues were influenced by the route of administration, as the
mean relative concentration of cyfluthrin in the bodies of males
and females at sacrifice was lower after oral administration (0.013)
than after intravenous injection (0.06). Female rats had higher
plasma concentrations after oral administration of the single
high or low dose; 48 h after administration, lower concentrations
were detected in the bone and muscle of animals of each sex and
in the testes of males rats. The
sciatic nerve showed a similar relative concentration value, which
may explain the toxic effects observed on the peripheral nervous
system. Higher concentrations were detected in the spleen, adrenal
glands, liver, and plasma of both males and females and
in the ovaries. The renal fatty tissue concentration
was about seven times higher after either oral or intravenous
administration, whereas the mean concentration in brain was significantly
lower ( p = 0.0006-0.006) (Klein et al., 1983).
-- Groups of 28 male and 28 female Sprague-Dawley rats received
diets containing 0, 100, 300, or 1000 mg/kg cyfluthrin (purity,
95%) incorporated into the powdered diet on a 0.4% maximum clay
carrier, daily for three months... The food consumption and body-weight
gains of females and males at the highest dose were significantly
lower than those of the control group. The body-weight gain depression
in females appeared to recover after cessation of treatment, while
that of the males remained significantly low... The absolute weights
of the liver, heart, and lung were decreased in male rats at the
high dose, and females at this dose had depressed liver, kidney,
adrenal, and ovarian
weights. In both males
and females at the high dose, the relative weight of the submaxillary
gland was increased...
Ref: Cyfluthrin. Toxicological evaluation
of certain veterinary drug residues in food. WHO FOOD ADDITIVES
SERIES 39 Prepared by: The forty-eighth meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO
Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). World Health Organization,
Geneva 1997. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.WHO.Tox.Eval.97.htm
Endocrine:
Ovary
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Rats Four groups
of 30 male and 24 female Mura:SPRA (SPF 68 Han) rats received
14C radiolabelled cyfluthrin as either oral doses of 0.5 or 10
mg/kg bw or intravenous or intraduodenal doses of 0.5 mg/kg bw.
Another group received unlabelled cyfluthrin orally once a day
for 14 consecutive days, followed by a single oral dose of 0.5
mg/kg bw 14C-cyfluthrin... The residues found in the organs and
tissues were influenced by the route of administration, as the
mean relative concentration of cyfluthrin in the bodies of males
and females at sacrifice was lower after oral administration (0.013)
than after intravenous injection (0.06). Female rats had higher
plasma concentrations after oral administration of the single
high or low dose; 48 h after administration, lower concentrations
were detected in the bone and muscle of animals of each sex and
in the testes of males rats. The sciatic
nerve showed a similar relative concentration value, which may
explain the toxic effects observed on the peripheral nervous system.
Higher concentrations were detected in the spleen, adrenal glands,
liver, and plasma of both males and females and in the
ovaries. The renal fatty tissue concentration
was about seven times higher after either oral or intravenous
administration, whereas the mean concentration in
brain was significantly lower ( p = 0.0006-0.006) (Klein
et al., 1983).
-- Groups of 28 male and 28 female Sprague-Dawley rats received
diets containing 0, 100, 300, or 1000 mg/kg cyfluthrin (purity,
95%) incorporated into the powdered diet on a 0.4% maximum clay
carrier, daily for three months... The food consumption and body-weight
gains of females and males at the highest dose were significantly
lower than those of the control group. The body-weight gain depression
in females appeared to recover after cessation of treatment, while
that of the males remained significantly low... The absolute weights
of the liver, heart, and lung were decreased in male rats at the
high dose, and females at this dose had depressed liver, kidney,
adrenal, and
ovarian weights. In both males and females at the high
dose, the relative weight of the submaxillary gland was increased...
Ref: Cyfluthrin. Toxicological evaluation
of certain veterinary drug residues in food. WHO FOOD ADDITIVES
SERIES 39 Prepared by: The forty-eighth meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO
Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). World Health Organization,
Geneva 1997. http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.WHO.Tox.Eval.97.htm
Endocrine:
Thymus
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
28-day rat
inhalation study (short-term): Decreases
in body and thymus
weights,
hypothermia
and clinical
pathology in rats
in a 28-day study (short-term) and behavioral effects in rats
in a 90-day study (intermediate/ chronic)
Ref: Federal Register: May 17,
2001, Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions.
Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.May17.2001.htm
Eye
- Microphthalmia
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Rat developmental studies
via inhalation. In the first two studies, pregnant female rats
at day 0 gestation were exposed head-only to cyfluthrin concentrations
of 0, 1.1, 4.7 or 23.7 mg/m3/ day (milligrams/per cubic
meter/day) for 6 hours/day on gestation days 6 through 15. In
the second study, the dams were exposed to analytical concentrations
of 0, 0.09, 0.25, 0.59 or 4.2 mg/m3 of the test material.
The dams were sacrificed on day 20 and their pups removed by caesarian
section. The maternal NOEL was 1.1 mg/ m3 and the maternal
LOEL was 4.7 mg/m3 (reduced motility, dyspnea, piloerection,
ungroomed coats and eye irritation.
The developmental NOEL was 0.59 mg/m3 and the developmental
LOEL was 1.1 mg/m3 (increases in the incidence of runts
and skeletal anomalies in the sternum (1.1 mg/m3 and
above); increases in post-implantation losses and decreases in
pup weights (4.7 mg/m3 and above) and increased incidences
of late embryonic deaths, in skeletal anomalies in the extremities,
pelvis and skull and in microphthalmia
[abnormal smallness of the eye] (23.7
mg/m3). The study was graded core minimum.
Ref: Federal Register: November 26, 1997.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerances. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Nov.26.1997.htm
Genotoxic
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: ...
Our study describes the genotoxic effects
of PCP, lindane, transfluthrin,
cyfluthrin, and natural pyrethrum
on human mucosal cells of the inferior and
middle nasal conchae.
METHODS: Epithelial cells were isolated from nasal mucosa, which
was removed in the surgical treatment of chronic sinusitis and
nasal concha hyperplasia. After the cells had been tested for
vitality using the trypan blue exclusion test, the short-term
culture method was used. The material was incubated with PCP (0.3,
0.75, and 1.2 mmol), lindane (0.5, 0.75, and 1.0 mmol), transfluthrin
(0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.0 mmol), cyfluthrin (0.05, 0.1, 0.5,
0.75, and 1.0 mmol), natural pyrethrum (0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05,
and 0.1 mmol), and N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine for 60
minutes. Substance-induced DNA damage (single-strand and double-strand
breaks) were determined using single-cell microgel electrophoresis.
A fluorescence microscope was used together with an image processing
system to analyze the results obtained.
RESULTS: After exposure to all tested substances, a high percentage
of the cells of the middle nasal concha in particular were found
to have severely fragmented DNA as a result of strong genotoxic
effects. Although the reaction of the cells of the inferior nasal
concha was significantly less strong (p < 0.001), the tested
substances were nevertheless found to have a notable genotoxic
effect on these cells too.
CONCLUSION: Our study strongly suggests
that exposure to PCP, lindane, transfluthrin, cyfluthrin, and
natural pyrethrum has a genotoxic effect on the epithelial cells
of human nasal mucosa. In addition, we have shown that
nasal structures differ in susceptibility to the various pesticides
used in the tests. Thus, the study provides new evidence supporting
the biological plausibility of PCP- and lindane-induced effects,
thereby helping evaluate potential PCP- and lindane-induced mucous
membrane carcinomas of these parts of the nose. In addition, our
study shows that other substances that today are widely used for
controlling pests have a considerable genotoxic effect on human
target cells. The results obtained indicate the need for additional
studies on the genotoxicity of these substances and their adverse
effects on human health.
Ref: Genotoxic effects of pentachlorophenol,
lindane, transfluthrin, cyfluthrin, and natural pyrethrum on human
mucosal cells of the inferior and middle nasal conchae; by Tisch
M, Faulde MK, Maier H. Am J Rhinol. 2005 Mar-Apr;19(2):141-51.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=15921213&query_hl=2
Kidney
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
A 24 month chronic
feeding/carcinogenicity study in rats demonstrated a NOAEL of
2.5 mg/kg/bwt/day and LEL of 6.2 mg/kg/bwt/day, based on decreased
body weights in males, decreased food consumption in males, and
inflammatory foci in the kidneys in females...
4. Subchronic toxicity. Thirteen-week dietary toxicity studies
in rats, mice and dogs were conducted. The primary
target organs identified in these studies were the kidneys (rat),
and the liver (rat, mouse and dog)... Chronic toxicity. In a 2-year
combined chronic toxicity/ oncogenicity study in the rat, the
NOAEL for chronic toxicity was 5 mg/ kg/day based upon kidney
effects characterized as slight, subtle alteration in kidney tubular
morphology, mostly within the corticomedullary junction which
likely represented more a physiologic adaptation than a pathological
change indicative of a toxic injury... In a 2-year dietary
feeding study in B6C3F1 mice conducted at 50, 100, 250 and 500
mg/kg/ day, 50 mg/kg/day was considered the NOAEL in males and
the NOAEL in females based upon histologic
changes in the kidney. The lesion
noted in male mice was a reduced vacuolation of the kidney tubular
epithelium at all dose levels. Decreased absolute and relative
kidney weights were seen at 100 mg/kg/day and above. In female
mice, focal dilation with hyperplasia of the lining epithelium
of the renal cortical tubules was seen at 100 mg/kg/day and above.
Ref: Federal Register. November 20, 1998.
[PF-836; FRL-6030-9]
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Nov20.1998.htm
Lung
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Prenatal and postnatal
sensitivity. There are no data gaps for reproductive and developmental
toxicity studies. Evidence of increased sensitivity of young rats
following pre- and/or post-natal exposure to cyfluthrin was observed
in the three-generation reproduction study in rats. There was
suggestive sensitivity of rats to in utero exposure based on
bradypnea seen in dams in
the developmental inhalation studies. In addition, the reproductive
NOAEL of 2.5 mg/kg/day and the LOAEL of 7.5 mg/kg/day established
in the three-generation reproduction study in rats are identical
to the systemic NOAEL/LOAEL of 2.5/7.5 mg/ kg/day established
in the chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity study in rats. This NOAEL
(2.5 mg/kg/day) and a UF of 100 was used in deriving the RfD (0.025
mg/kg/day) and the RfD does not provide protection for infants
and children.
Ref: Federal Register. May 17, 2001, Pesticide
Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.May17.2001.htm
Salivary
Glands
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Cyfluthrin. 28-Day
oral toxicity NOAEL = 15.0 (males & females) based on
minimal decrease in blood glucose. LOAEL = 50 based on, gait abnormalities,
salivation, nervousness, decrease in body weight, food consumption,
changes in hematological, clinical chem. & urinalysis parameters,
increases in selected organ wts., cytoplasmic swelling of glandular
epithelium of submaxillary gland,
minimal degrees of fiber degeneration in sciatic nerve (# not
reported) which disappeared after recovery period.
Ref: Federal Register. September 27, 2002.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Sept.27.2002.htm
•
Definition:
[n] a salivary gland inside the lower jaw on either side that
produces most of the nocturnal saliva; discharges saliva into
the mouth under the tongue Synonyms: mandibular gland, submandibular
gland, submandibular salivary gland, submaxillary
salivary gland
Sciatic
nerve
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Cyfluthrin. Neurotoxicity
oral studies--hen. In the single-dose study, at 5,000 mg/kg, five
of the ten hens died. Moderate fiber alterations (axon
fragmentation, occasional swelling and eosinophilia of the axon
fragments and vacuolation of the myelin sheaths) in the sciatic
nerve were observed in two hens. Six hens at 2,500 mg/kg
showed signs of excitation during the first 3 days following treatment.
In the two-dose study, hens showed initial signs of intoxication
during the first 3 days but were normal until the second dose
was administered when four hens died. Symptoms following the second
treatment subsided; however, a second set of symptoms developed
in 4/30 hens. These symptoms resembled delayed type neurotoxicity.
Nerve fiber degeneration was present in
the majority of the hens. The myelin sheath was distended and
the myelin sheath was described as being optically void or granularly
disintegrated. The axons were described as swollen or fragmented
and in some areas activated or proliferated Schwann's cells were
noted. The nerves also contained macrophages in which cytoplasm
contained granular material. In the 5-day study, 4/10 hens died.
All hens showed initial toxic responses which eventually disappeared.
Behavioral disorders accompanied by drowsiness and a cramped gait
were observed in 3 of the 6 survivors. Mottled kidneys and brittle
livers were noted at necropsy. Treatment-related fiber degeneration
(distension or granular disintigration of the medullary sheath,
swollen or fragmented axis cylinders and proliferated Schwann's
cell in the sciatic
nerve
were reported.
One hen had similar lesions in the spinal
marrow.
-- Cyfluthrin. Neurotoxicity dermal studies--hen. In the first
study there were 2 deaths on the 3rd and 10th day. All other hens
had symptoms (apathy and disturbed behavior) but recovered. Local
irritation and weight loss were also noted.
Two hens had minimal segment-like nerve fiber degeneration (sciatic
nerve), but this type is often found in hens. In the second
study, the hens were apathetic. These symptoms disappeared after
the first week in all hens except 2, in which they persisted until
the 38th and 51st day after the start of the treatment, respectively.
Local irritation and body weight loss were also observed.
No other neurologic effects were observed, including microscopic.
Ref: Federal Register. September 27, 2002.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Sept.27.2002.htm
Tremors
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
In
a 14-day rat study, oral administration of 60 mg/kg/day produced
tremors, uncoordinated gait, salivation,
slight brain hemorrhages, necrosis of the skeletal muscle fibers,
and death. The NOEL was not defined.
Ref:
USEPA/OPP. Support Document for the Addition of Chemicals from
Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) Active
Ingredients to EPCRA Section 313. U. S. Environmental Protection
Agency, Washington, DC (1993). As cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV. 40 CFR Part 372. Addition
of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical Release Reporting; Community
Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
--
Cyfluthrin
(95.4% a.i.). Reproduction
and fertility
effects study-- rat (dietary).
Parental NOAEL = Parental: 3/4 (M/F) Offspring
NOAEL = 7 (M/F) Parental LOAEL = 9/10 (M/F) based on reductions
in body weights and food consumption. Offspring
LOAEL = 19 based on coarse tremors
in pups during lactation and decreases in mean litter weight .
-- Cyfluthrin
(95.7-96.2% a.i.).
Pilot 1-generation reproduction
study--rat. Parental
systemic NOAEL = 22.9 Offspring systemic NOAEL = 7.8 Parental
systemic LOAEL = 59.6 based on hind leg splay, ataxia,
reduction in body weight gain. Pup systemic LOAEL = 22.9
based on tremors during lactation
and pup weight decreases.
Ref: Federal Register. September 27, 2002.
Cyfluthrin; Pesticide Tolerance. Final Rule.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Cyfluthrin.FR.Sept.27.2002.htm
| Environmental
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Aquatic
acute toxicity
values for cyfluthrin include a rainbow trout 96-hour LC
50 of 0.68 ppb, a bluegill 96-hour LC
50 of 1.5 ppb, and a daphnid 48-hour EC 50 of 0.14
ppb. EPA believes that there is sufficient evidence
for listing cyfluthrin on EPCRA section 313 pursuant to
EPCRA section 313(d)(2)(C) based on the available environmental
toxicity data.
Ref:
USEPA/OPP. Support Document for the Addition of Chemicals
from Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, Rodenticide Act (FIFRA)
Active Ingredients to EPCRA Section 313. U. S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC (1993). As cited by US
EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV. 40 CFR Part 372.
Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical Release Reporting;
Community Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
Environmental
Quality Standards (EQSs) for the protection of saltwater
life have been proposed (and were put into legislation in
1989) for the following chemicals used as mothproofing agents;
PCSDs; cyfluthrin; sulcofuron; flucofuron and permethrin...
toxicity of cyfluthrin to saltwater
life at concentrations above the EQS of 0.001 mg l-1 in
the water column.
Ref:
UK Marine Special Areas of Conservation. Mothproofing chemicals.
http://www.ukmarinesac.org.uk/activities/water-quality/wq8_25.htm
or http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Flucofuron.UK.Moth.water.htm
|
|


