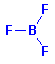|
Return
to
Boron trifluoride Index Page
Activity: Fumigant
(Inorganic)
Structure:
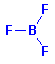
Adverse Effects:
Body
Weight Decrease
Blood
Bone
CNS
Eye
Kidney
Lung
Use:
Catalyst in organic synthesis, manufacture of boranes, soldering
flux, gas brazing, oxidation protectant, fumigant,
polymerizer of epoxy resins, casting and heat treating in
magnesium industry.
Other
Names:
ANCA 1040, trifluoroborane, trifluoroboron.
Ref: US EPA Emergency First
Aid Treatment Guide.
http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/boron.trifluoride.epa.htm
|
| Environmental releases
(in pounds) of boron trifluoride in the United States, 1995-2003
(Exhibit 3-3: Page 3-17) |
| Year |
Air Emissions |
Surface Water Discharges |
Underground Injection |
Releases to Land |
Off-Site Releases |
Total On- & Offsite
Releases |
| 1995 |
25,019 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
929 |
25,948 |
| 1996 |
29,881 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
29,881 |
| 1997 |
21,290 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
21,295 |
| 1998 |
37,802 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
37,807 |
| 1999 |
16,725 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
16,725 |
| 2000 |
11,595 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
250 |
11,845 |
| 2001 |
11,496 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
11,496 |
| 2002 |
10,114 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
10,114 |
| 2003 |
7,513 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4,295 |
11,808 |
| Source: REGULATORY
DETERMINATIONS SUPPORT DOCUMENT FOR SELECTED CONTAMINANTS FROM
THE SECOND DRINKING WATER CONTAMINANT CANDIDATE LIST (CCL 2).
US EPA, Office of Water. EPA 815-D-06-007. December 2006 DRAFT. |
Blood
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Target Organs: Lungs,
blood, bones
and teeth.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Boron
Trifluoride (BF3). May 2001.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Boron.Trifluoride.MSDS.htm
Body
Weight Decrease
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
- In a 2 week study,
all animals exposed to 180 mg/cu m died prior to the sixth exposure,
rats exposed at concn of 66 and 24 mg/cu m showed clinical signs
of respiratory irritation, body weight gain
depressions, increased lung weights, and depressed liver
weights.
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Bank for Boron Trifluoride.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Boron.Trifluoride.TOXNET.htm
Bone
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Target Organs: Lungs,
blood, bones and teeth.
-- Signs and Symptoms of Exposure: Acute exposure: coughing, shortness
of breath, headache, vertigo, chills and nausea. Subchronic: dental
fluorosis, increased bone, serum
and urinary fluoride levels, hypocalcemia.
-- Chronic and Subchronic Data: Two of forty rats exposed to 6
ppm for 6 hours/day, 5 days/week for 13 weeks exhibited renal
toxicity and signs of respiratory irritation. Six month exposures
of rats, rabbits and guinea pigs produced dental
fluorosis and pneumonitis at similar levels. This material
is listed in the Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances
(RTECS), but no information on its carcinogenicity is available.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Boron
Trifluoride (BF3). May 2001.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Boron.Trifluoride.MSDS.htm#Contents
[Note:
Dental fluorosis hasn't been included in the bone category even
though it was noted in many studies for this and other pesticides.
However, we will keep this study in to remind us that this category
was omitted.- EC]
... Exposure
of six animal species to 0.28 mg/L of boron trifluoride for 4
to 7 hours a day, 5 days a week killed all animals within 30 days.
Rats, rabbits, and guinea pigs were exposed to boron trifluoride
via inhalation. Guinea pigs died of respiratory failure after
being exposed to 0.036 mg/L for 19 days; rats experienced fluorosis
of the teeth at this concentration.
Ref.
USEPA/OPPT. Support Document for the Health and Ecological Toxicity
Review of TRI Expansion Chemicals. U. S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC (1993). As cited by US EPA in:
Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV. 40 CFR Part 372. Addition
of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical Release Reporting; Community
Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
-- Boron trifluoride
is primarily a respiratory irritant which predisposed the exposed
/guinea pigs/ to respiratory infection. Exposure at 100 ppm (277
mg/cu m) was fatal to all animals. Physiological responses prior
to death included respiratory irritation and infection, kidney
damage, retarded growth, and severe progressive
fluorosis in rat teeth...
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Bank for Boron Trifluoride.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Boron.Trifluoride.TOXNET.htm
CNS
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Animal Toxicity Studies:
Non-Human Toxicity Excerpts: The principal feature in acute action
... is the irritation of mucous membranes of respiratory tract
& eyes. In animal acute experiments, a concn of 42 mg/cu m proved
fatal in some cases. Exam revealed a fall in inorg phosphorus
level in blood & autopsy showed pneumonia & degenerative changes
in renal tubules. Long-term (4 mo) exposure to 3 & 10 mg/cu m
... produced irritation of resp tract, dysproteinemia, reduction
in cholinesterase activity &
increased nervous system lability.
Exposure to high concn results in reduction of acetyl carbonic
acid & inorg phosphorus levels in blood, & dental fluorosis. [International
Labour Office. Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety.
Vols. I&II. Geneva, Switzerland: International Labour Office,
1983. 320]
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Bank for BORON TRIFLUORIDE.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Boron.Trifluoride.TOXNET.htm
Eye
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Boron trifluoride
is a colorless gas that is corrosive to tissues due to its rapid
hydrolysis to hydrofluoric acid and boric acid. The principal
acute effect in animals is irritation of the mucous membranes
of the respiratory tract and eyes;
post mortem examination also revealed pneumonia and degenerative
changes in renal tubules.
Ref. USEPA/OPPT. Support Document for the
Health and Ecological Toxicity Review of TRI Expansion Chemicals.
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC (1993).
As
cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV. 40 CFR Part 372. Addition
of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical Release Reporting; Community
Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
Kidney
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Exposure of 6 animal
species to 100 ppm, 4-7 hr/day, 5 days/wk in a 30 day experiment
killed all animals, most within the test period. Guinea pigs were
most susceptible ... dogs least ... The primary site of damage
was the lung ... Kidney damage ...
also occurs. [Mackison, F. W., R. S. Stricoff, and L. J. Partridge,
Jr. (eds.). NIOSH/OSHA - Occupational Health Guidelines for Chemical
Hazards. DHHS(NIOSH) PublicationNo. 81-123 (3 VOLS). Washington,
DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, Jan. 1981.
-- An acute study of boron trifluoride (BF3) in rats indicated
the 4 hr LC50 to be 1.21 mg/l. In a 2 week study, all animals
exposed to 180 mg/cu m died prior to the sixth exposure, rats
exposed at concn of 66 and 24 mg/cu m showed clinical signs of
respiratory irritation, body weight gain depressions, increased
lung weights, and depressed liver weights. Histopathology showed
necrosis and pyknosis of the proximal tubular
epithelium of the kidneys. This effect was limited to the
high-concn exposure group. Based on the results of these studies,
Fischer 344 rats were exposed 6 hr/day, 5 days/week for 13 weeks
to a respirable, liquid aerosol of BF3 at concn of 0, 2.0, 6.0,
and 17 mg/cu m. One rat in the high exposure group died. The
most significant finding in this group was necrosis of the proximal
tubular epithelium of the kidneys....
-- Boron trifluoride is primarily a respiratory irritant which
predisposed the exposed /guinea pigs/ to respiratory infection.
Exposure at 100 ppm (277 mg/cu m) was fatal to all animals. Physiological
responses prior to death included respiratory irritation and infection,
kidney damage, retarded growth, and
severe progressive fluorosis in rat teeth...
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Bank for Boron Trifluoride.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Boron.Trifluoride.TOXNET.htm
-- The principal
acute effect in animals is irritation of the mucous membranes
of the respiratory tract and eyes; post mortem examination also
revealed pneumonia and degenerative changes in renal tubules.
The kidneys are most severely affected because
boric acid concentrates in this organ.
Ref.
USEPA/OPPT. Support Document for the Health and Ecological Toxicity
Review of TRI Expansion Chemicals. U. S. Environmental Protection
Agency, Washington, DC (1993). As cited by US EPA in: Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part IV. 40 CFR Part 372. Addition
of Certain Chemicals; Toxic Chemical Release Reporting; Community
Right-to-Know; Proposed Rule.
Lung
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Target Organs: Lungs,
blood, bones and teeth.
-- Signs and Symptoms of Exposure: Acute exposure: coughing, shortness
of breath, headache, vertigo, chills and nausea. Subchronic: dental
fluorosis, increased bone, serum and urinary fluoride levels,
hypocalcemia.
-- Chronic and Subchronic Data: Two of forty rats exposed to 6
ppm for 6 hours/day, 5 days/week for 13 weeks exhibited renal
toxicity and signs of respiratory irritation. Six month exposures
of rats, rabbits and guinea pigs produced dental fluorosis and
pneumonitis at similar levels. This
material is listed in the Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical
Substances (RTECS), but no information on its carcinogenicity
is available.
Ref: Material Safety Data Sheet for Boron
Trifluoride (BF3). May 2001.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Boron.Trifluoride.MSDS.htm
-- Clinical Effects:
SUMMARY OF EXPOSURE 0.2.1.1 ACUTE EXPOSURE o Boron trifluoride
is a severe irritant to the lungs
and eyes and corrosive on skin contact. Effects are similar to
that of hydrogen fluoride but less severe.
-- CHRONIC EXPOSURE o Lowered pulmonary function, dried mucous
membranes and nosebleeds, severe irritation of the eyes and eyelids,
as well as inflammation and congestion of
the lungs may occur with chronic exposure to this compound
(HSDB, 1992).
-- Exposure of 6 animal species to 100 ppm, 4-7 hr/day, 5 days/wk
in a 30 day experiment killed all animals, most within the test
period. Guinea pigs were most susceptible ... dogs least ...
The primary site of damage was the lung ... Kidney damage
... also occurs. [Mackison, F. W., R. S. Stricoff, and L. J. Partridge,
Jr. (eds.). NIOSH/OSHA - Occupational Health Guidelines for Chemical
Hazards. DHHS(NIOSH) PublicationNo. 81-123 (3 VOLS). Washington,
DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, Jan. 1981. 1]
-- Boron trifluoride is primarily a respiratory
irritant which predisposed the exposed /guinea pigs/ to
respiratory infection. Exposure at 100 ppm (277 mg/cu m) was fatal
to all animals. Physiological responses prior to death included
respiratory irritation and infection, kidney damage, retarded
growth, and severe progressive fluorosis
in rat teeth. Exposure at 15 ppm (41.5 mg/cu m) did not produce
fluorosis, but did predispose guinea pigs to a rate of
respiratory infection greater than that found in controls. [NIOSH;
Criteria Document: Boron trifluoride p.27 (1976) DHEW Pub. NIOSH
77-122]
-- Ten male guinea pigs and 14 female rats were exposed to boron
trifluoride at a nominal concentration of 12.8 ppm (35 mg/cu m),
7 hours/day, 5 days/week, for up to 3 months. Examinations showed
the guinea pigs had difficulty in breathing and appeared
asthmatic. Exposed guinea pigs had increased lung
weights averaging 0.80 g/100 g of body weight, compared to lung
weights of 0.64 g/100 of body weight for the control animals.
Gross examination revealed pneumonitis, suggesting chemical damage,
in the hilar region of the lungs.
Examined microscopically, the lung showed
areas of collapse and emphysema adjacent to the areas of more
severe pneumonitis. The exposed rats were considered to
have normal appearance and organ weights, but gross and microscopic
tissue examination showed pulmonary changes indicating chemical
irritation. The hilar regions of the lung
were the most affected and the injuries were manifested as pneumonitis.
[NIOSH; Criteria Document: Boron trifluoride p.29-30 (1976)
DHEW Pub. NIOSH 77-122]
Ref: TOXNET profile from Hazardous Substances
Data Bank for Boron Trifluoride.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Boron.Trifluoride.TOXNET.htm
|