|
Return to
Index Page
ACTIVITY: List
2 Inert
Molecular Structure:
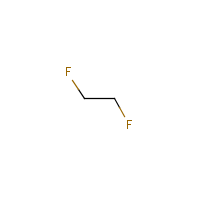
Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Heart
Kidney
Note:
Very little data available
|
Blood
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: The inhalation toxicity of a series of fluorinated
ethanes which are metabolized to fluoroacetate (144490) were studied
in the male CD-rat. When the rats were exposed
by inhalation to 1,2-difluoroethane (624-72-6), 1-chloro-2-fluoroethane
(762505), 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane (762492), or 1-chloro-1,2-difluoroethane
(338647) for 4 hours, the lethal concentrations for each compound
were less than 100 parts per million (ppm). Tests with
1,1-difluoroethane (75376) showed a 4 hour median lethal dose
of over 400,000ppm in rats. Clinical signs of fluoroacetate toxicity
were noted including lethargy, hunched posture, and convulsions.
Concentrations of citrate increased in serum and heart tissue
on exposure to 1,2-difluoroethane, 1-chloro-2-fluoroethane,
1-chloro-1,2-difluoroethane, and 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Fluoroacetate
was present in the urine of rats exposed to each of the toxic
compounds. Rats exposed to 1,2-difluoroethane showed fluorocitrate
in the kidneys. Rats exposed to 1,2-difluoroethane
showed a concentration related elevation of serum and heart citrate
up to 1000 ppm of the compound. Serum citrate was up five fold
and heart citrate 11 fold over control levels. The authors
suggest that the metabolism of the toxic fluoroethane was initiated
at the carbon/hydrogen bond, with metabolism to fluoroacetate
via an aldehyde or an acyl fluoride. The authors conclude that
1-(di)halo-2-fluoroethanes are highly toxic to rats and should
be viewed as a hazard to humans.
Ref: Fluoroacetate-Mediated Toxicity of
Fluorinated Ethanes; by Keller DA, Roe DC, Lieder PH. Fundamental
and Applied Toxicology, Vol. 30, No. 2, pages 213-219, 1996.
Abstract: The 18-year-old white male driver and 17-year-old white
male passenger of an automobile were killed when their vehicle
crossed the median of a 4-lane highway and collided with a minivan.
A can of airbrush propellant was found in the automobile of the
deceased. The only drug detected during initial toxicological
analyses was 130 mg/L ethanol in the blood of the driver. When
performing ethanol analysis by headspace gas chromatography, an
unidentified peak was observed in the blood of both deceased.
This peak was identified as difuoroethane (Freon
152), the propellant in the aerosol can found in the automobile.
The concentrations of difluoroethane in
the blood of the driver and passenger were 78 mg/L and 35 mg/L,
respectively. Based on a literature search we believe that this
is the first report of the quantitation of difluoroethane in biological
samples.
Publication Types: • Case Reports
Ref: Two traffic fatalities related to the
use of difluoroethane. Broussard LA, Brustowicz T, Pittman T,
Atkins KD, Presley L. J Forensic Sci. 1997 Nov;42(6):1186-7.
Heart
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: The inhalation toxicity of a series of fluorinated
ethanes which are metabolized to fluoroacetate (144490) were studied
in the male CD-rat. When the rats were exposed
by inhalation to 1,2-difluoroethane (624-72-6), 1-chloro-2-fluoroethane
(762505), 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane (762492), or 1-chloro-1,2-difluoroethane
(338647) for 4 hours, the lethal concentrations for each compound
were less than 100 parts per million (ppm). Tests with
1,1-difluoroethane (75376) showed a 4 hour median lethal dose
of over 400,000ppm in rats. Clinical signs of fluoroacetate toxicity
were noted including lethargy, hunched posture, and convulsions.
Concentrations of citrate increased in serum and heart tissue
on exposure to 1,2-difluoroethane, 1-chloro-2-fluoroethane,
1-chloro-1,2-difluoroethane, and 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Fluoroacetate
was present in the urine of rats exposed to each of the toxic
compounds. Rats exposed to 1,2-difluoroethane showed fluorocitrate
in the kidneys. Rats exposed to 1,2-difluoroethane
showed a concentration related elevation of serum and heart citrate
up to 1000ppm of the compound. Serum citrate
was up five fold and heart citrate 11 fold over control
levels. The authors suggest that the metabolism of the
toxic fluoroethane was initiated at the carbon/hydrogen bond,
with metabolism to fluoroacetate via an aldehyde or an acyl fluoride.
The authors conclude that 1-(di)halo-2-fluoroethanes are highly
toxic to rats and should be viewed as a hazard to humans.
Ref: Fluoroacetate-Mediated Toxicity of
Fluorinated Ethanes; by Keller DA, Roe DC, Lieder PH. Fundamental
and Applied Toxicology, Vol. 30, No. 2, pages 213-219, 1996.
Kidney
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Abstract: The inhalation toxicity of a series of fluorinated
ethanes which are metabolized to fluoroacetate (144490) were studied
in the male CD-rat. When the rats were exposed
by inhalation to 1,2-difluoroethane (624-72-6), 1-chloro-2-fluoroethane
(762505), 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane (762492), or 1-chloro-1,2-difluoroethane
(338647) for 4 hours, the lethal concentrations for each compound
were less than 100 parts per million (ppm). Tests with
1,1-difluoroethane (75376) showed a 4 hour median lethal dose
of over 400,000ppm in rats. Clinical signs of fluoroacetate toxicity
were noted including lethargy, hunched posture, and convulsions.
Concentrations of citrate increased in serum and heart tissue
on exposure to 1,2-difluoroethane, 1-chloro-2-fluoroethane, 1-chloro-1,2-difluoroethane,
and 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Fluoroacetate was present in the urine
of rats exposed to each of the toxic compounds. Rats
exposed to 1,2-difluoroethane showed fluorocitrate in the kidneys.
Rats exposed to 1,2-difluoroethane showed
a concentration related elevation of serum and heart citrate up
to 1000ppm of the compound. Serum citrate was up five fold and
heart citrate 11 fold over control levels. The authors
suggest that the metabolism of the toxic fluoroethane was initiated
at the carbon/hydrogen bond, with metabolism to fluoroacetate
via an aldehyde or an acyl fluoride. The authors conclude that
1-(di)halo-2-fluoroethanes are highly toxic to rats and should
be viewed as a hazard to humans.
Ref: Fluoroacetate-Mediated Toxicity of
Fluorinated Ethanes; by Keller DA, Roe DC, Lieder PH. Fundamental
and Applied Toxicology, Vol. 30, No. 2, pages 213-219, 1996.
| Toxicity.
|
Organism
|
Test Type |
Route |
Reported
Dose (Normalized Dose) |
Effect |
Source |
mouse
|
LC50 |
inhalation |
977gm/m3/2H
(977000 mg/kg) |
- |
National
Technical Information Service. Vol. OTS0534607 |
rat
|
LCLo |
inhalation |
75ppm/4H
(75 mg/kg) |
- |
National
Technical Information Service. Vol. OTS0534607 |
| Ref:
ChemIDplus for 1,2-Difluoroethane at Toxnet |
Reports
available from
The National Technical Information Service (NTIS)
Order from NTIS by: phone at 1-800-553-NTIS (U.S. customers);
(703)605-6000 (other countries); fax at (703)605-6900; and
email at orders@ntis.gov. NTIS is located at 5285 Port Royal
Road, Springfield, VA, 22161, USA.
••
If you have copies of any of the reports listed below, please
share them with FAN. |
| NTIS
Order Number / Source |
Title |
Keywords
/ Abstract |
NTIS/OTS0523799
EPA/OTS;
Doc #40-7834109 |
2000.
FLUOROCARBONS - AN INDUSTRIAL HYGIENE SURVEY OF WORKERS EXPOSURE
IN FOUR FACILITIES |
NIOSH
FLUOROALKENES
HEALTH EFFECTS
INDUSTRIAL HYGIENE |
NTIS/OTS0520115
EPA/OTS;
Doc #86-890000971 |
2000.
TOXICITY OF SOME HALOGENATED COMPOUNDS
|
TRICHLOROFLUOROMETHANE
(359-28-4)
HEALTH EFFECTS
ACUTE TOXICITY
MAMMALS
RATS
INHALATION
MICE
CATS
SUBCHRONIC TOXICITY
RABBITS
GUINEA PIGS
DOGS
HUMANS |
NTIS/OTS0534607-1
EPA/OTS; Doc #89-920000139 |
1992.
SUPPLEMENT:
LETTER FROM DUPONT REPORTING TOXICOLOGICAL RESULTS FROM REPEATED
LOW-LEVEL EXPOSURE TO 1,2-DIFLUOROETHANE IN MICE |
E I DUPONT
DE NEMOURS & CO
1,2-DIFLUOROETHANE
HEALTH EFFECTS
SUBCHRONIC TOXICITY
MAMMALS
MICE
INHALATION |
NTIS/OTS0571557
EPA/OTS;
Doc #88-920009904 |
1992.
INITIAL SUBMISSION: INHALATION TOXICITY STUDIES OF VARIOUS FREON
COMPOUNDS WITH COVER LETTER DATED 10-15-92
|
DUPONT
CHEM
VARIOUS FREON COMPOUNDS
HEALTH EFFECTS
ACUTE TOXICITY
MAMMALS
RATS
INHALATION
CAS Registry
Numbers:
75-63-8
353-59-3
624-72-6
1511-62-2 |
NTIS/OTS0571579
EPA/OTS;
Doc #88-920009924 |
1992.
INITIAL SUBMISSION: INHALATION TOXICITY STUDIES OF VARIOUS FREON
COMPOUNDS WITH COVER LETTER DATED 10-15-92
|
DUPONT
CHEM
VARIOUS FREON COMPOUNDS
HEALTH EFFECTS
ACUTE TOXICITY
MAMMALS
RATS
INHALATION
CAS Registry
Numbers:
75-63-8
353-59-3
624-72-6
1511-62-2 |
NTIS/OTS0534607
EPA/OTS;
Doc #88-920000157 |
1991.
INITIAL SUBMISSION: LETTER SUBMITTING PRELIMINARY RESULTS OF
INHALATION STUDIES IN RATS ON 1,2-DIFLUOROETHANE
|
E I DUPONT
DE NEMOURS & CO
1,2-DIFLUOROETHANE
HEALTH EFFECTS
ACUTE TOXICITY
MAMMALS
RATS
INHALATION |
NTIS/OTS0520938
EPA/OTS;
Doc #86-890000822 |
1989.
INHALATION TOXICITY STUDIES OF VARIOUS FREON COMPOUNDS WITH
ATTACHMENTS AND COVER SHEET DATED 06-12-89
Corporate
Name: HASKELL LABORATORIES |
Abstract:
Results of inhalation toxicity studies with rats on 6 freon
compounds (containing 1,1-difluoroethane) are provided. Brom-12
at a concentration of 100,000 ppm for 7 minutes was lethal,
while exposure to 19,000 ppm for 3 hours induced transient
violent trembling but not lethality. Chlorbrom-12 was lethal
at 500,000 ppm for 5 minutes, whereas at 62,000 ppm for 3
hours it was non- lethal but caused occasional transient nervous
movements and slight lung injury. Brom-13 was lethal at 300,000
ppm for 40 minutes, while at 200,000 ppm for 2 hours no adverse
effects were noted. Freon-152 was not lethal at a concentration
of 200,000 ppm for 2 hours, but occasional trembling and incoordination
were observed. Freon F-0316 and Freon F-C317 each produced
no observable effects at a concentration of 10,000 ppm for
at least 40 6-hour exposures. Summary data tables are provided.
Keywords:
E I DUPONT DE NEMOURS & CO
1,1-DIFLUOROETHANE (75-37-6)
HEALTH EFFECTS
ACUTE TOXICITY
MAMMALS
RATS
INHALATION
SUBCHRONIC TOXICITY
CAS Registry Numbers:
75-37-6
75-71-8
75-72-9
624-72-6
62253-21-8 |
|