We are on X

About Fluoride
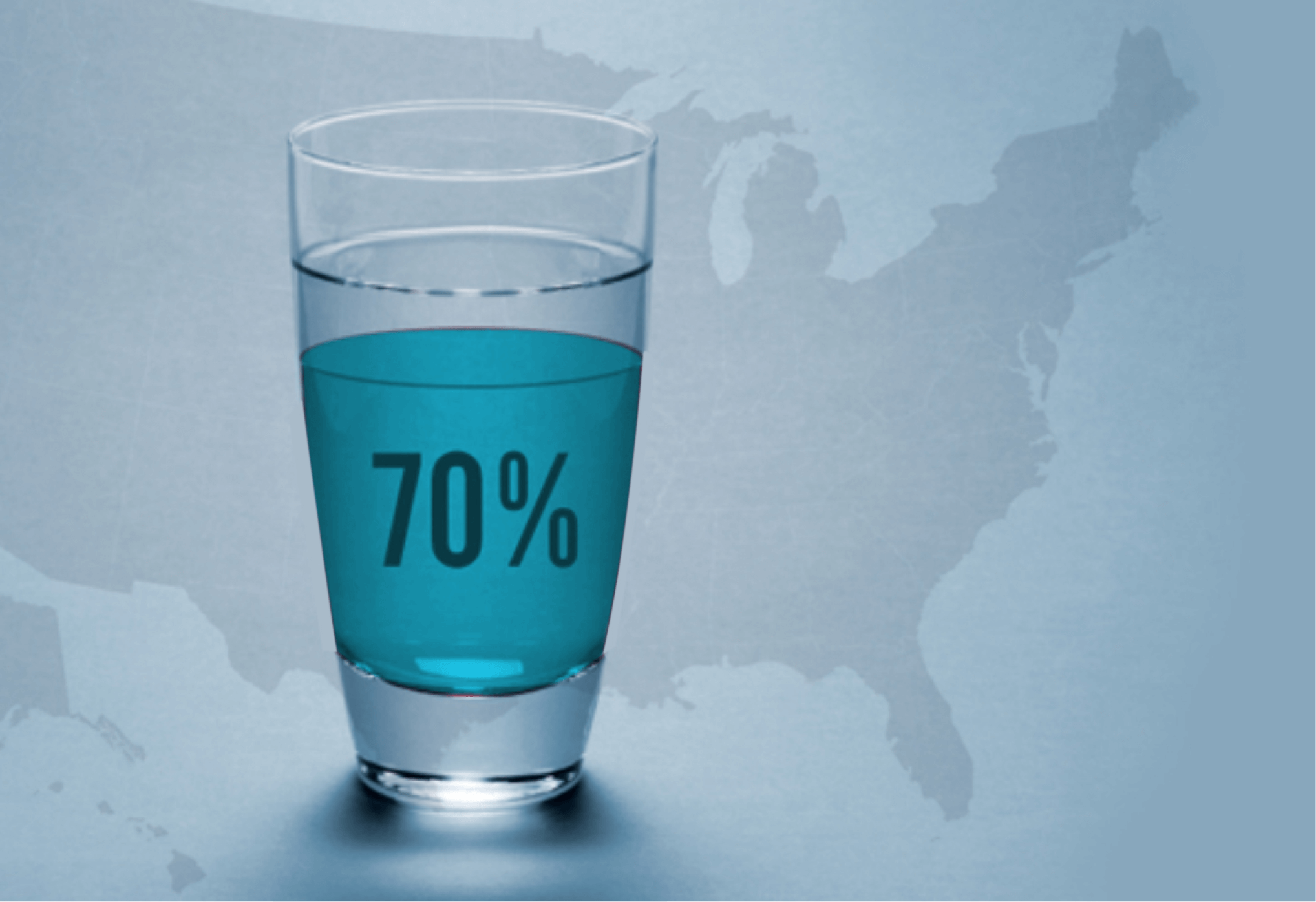
What is Water Fluoridation?
Unlike all other water treatment processes, fluoridation does not treat the water itself, but the person consuming it. It’s outdated, unnecessary, and harmful.
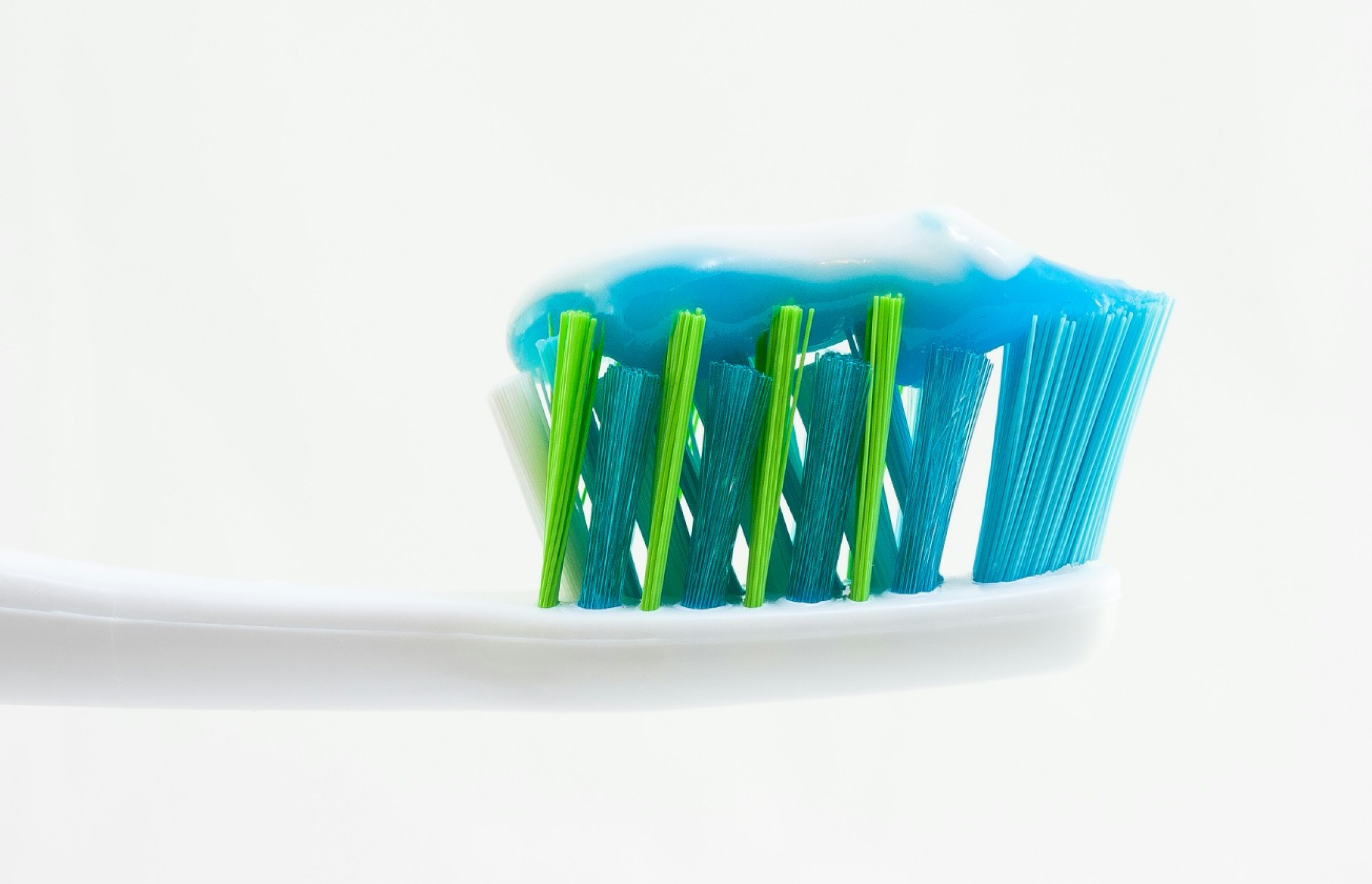


Sources of Fluoride
Fluoridated water is the largest source of exposure for most people, but it is not the only source of exposure to fluoride.
Health Effects of Fluoride
Fluoride is a highly toxic substance that can cause a range of adverse health effects. Certain members of the public are at particularly high risk of harm.
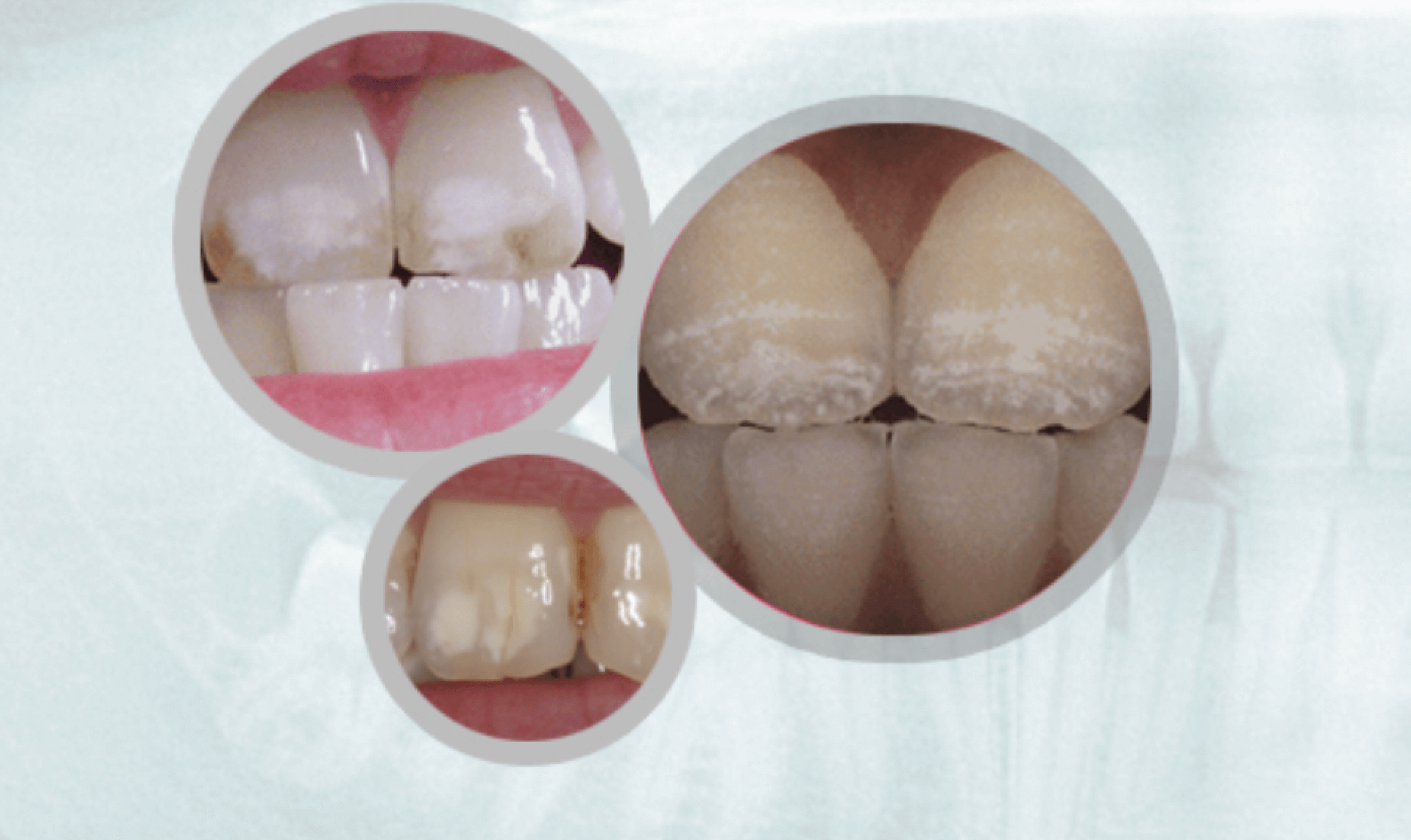
Evidence of Overexposure:Dental Fluorosis
Fluorosis is a defect of tooth enamel caused by too much fluoride intake during the first 8 years of life.

Thousands of Professionals Call for End to Fluoridation
A growing chorus of medical and scientific experts are warning about fluoridation. Over 4,800 have signed FAN’s Statement Against Fluoridation.
Take Action
Activist Toolkit
The toolkit provides various resources to help educate people in your community about fluoride.
Advocating for Change
What will you do to protect your community's drinking water? Anyone can make a difference, all you need to do is act.
Success Stories
Here’s a list of over 500 communities that rejected or stopped the addition of fluoridation chemicals to their water.


News Archive
The FAN News Archive serves as a historical repository for all news stories on fluoride.
Research Study Tracker
The most up-to-date and comprehensive source for studies on fluoride's systemic, multifaceted effects on human and animal health.












